Abstract
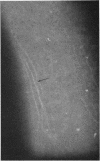
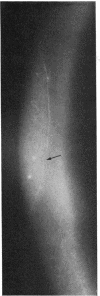
Fibrillary lines, whether in the normal cornea or in keratoconus, are faint structures which must be searched for diligently with the appropriate biomicroscopical settings, using a high magnification and oblique focal illumination of high intensity. They are unlikely to be confused with other superficial linear changes in the cornea, such as mare's tail epithelial lines, fingerprint lines and their variants, ring lines, and so on. A detailed description of these and other entities is given elsewhere (Brown and Bron, in preparation).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bron A. J. Vortex patterns of the corneal epithelium. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1973;93(0):455–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASS J. D. THE IRON LINES OF THE SUPERFICIAL CORNEA. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964 Mar;71:348–358. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1964.00970010364010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELE P. P., WEDDELL G. The relationship between neurohistology and corneal sensibility. Brain. 1956 Mar;79(1):119–154. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., King N. Turnover of basic protein of rat brain. Nature. 1971 Jan 1;229(5279):56–58. doi: 10.1038/229056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZANDER E., WEDDELL G. Observations on the innervation of the cornea. J Anat. 1951 Jan;85(1):68–99. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]