Abstract
BACKGROUND
Fibroblast plays a major role in tendon-bone healing. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can activate fibroblasts and promote tendon-bone healing via the contained microRNAs (miRNAs). However, the underlying mechanism is not comprehensively understood. Herein, this study aimed to identify overlapped BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs in three GSE datasets, and to verify their effects as well as mechanisms on fibroblasts.
AIM
To identify overlapped BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs in three GSE datasets and verify their effects as well as mechanisms on fibroblasts.
METHODS
BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs data (GSE71241, GSE153752, and GSE85341) were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The candidate miRNAs were obtained by the intersection of three data sets. TargetScan was used to predict potential target genes for the candidate miRNAs. Functional and pathway analyses were conducted using the Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases, respectively, by processing data with the Metascape. Highly interconnected genes in the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were analyzed using Cytoscape software. Bromodeoxyuridine, wound healing assay, collagen contraction assay and the expression of COL I and α-smooth muscle actin positive were applied to investigate the cell proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction was applied to determine the cell fibroblastic, tenogenic, and chondrogenic potential.
RESULTS
Bioinformatics analyses found two BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs, has-miR-144-3p and has-miR-23b-3p, were overlapped in three GSE datasets. PPI network analysis and functional enrichment analyses in the GO and KEGG databases indicated that both miRNAs regulated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN). In vitro experiments confirmed that miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p stimulated proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis of NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Interfering with PTEN affected the phosphorylation of Akt and thus activated fibroblasts. Inhibition of PTEN also promoted the fibroblastic, tenogenic, and chondrogenic potential of NIH3T3 fibroblasts.
CONCLUSION
BMSC-derived exosomes promote fibroblast activation possibly through the PTEN and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which may serve as potential targets to further promote tendon-bone healing.
Keywords: Exosome, MicroRNA, Fibroblast, Mesenchymal stem cell, Tendon-bone healing
Core Tip: Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can activate fibroblasts and promote tendon-bone healing via the contained microRNAs (miRNAs). Supported by bioinformatics tools, this study identified two BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs, has-miR-144-3p and has-miR-23b-3p, were overlapped in three GSE datasets. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that both miRNAs regulated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN). Experiments in vitro confirmed that interfering with PTEN can affect the phosphorylation of Akt and thus the activation of fibroblasts. These results suggested a potential mechanism by which BMSC-derived exosomes promote tendon-bone healing.
INTRODUCTION
Tendon-bone insertion (TBI) injury, such as rotator cuff tears and anterior cruciate ligament injuries, is one of the common injuries in daily life and sports. Thus, how to promote tendon-bone healing becomes an important issue in research and clinical practice. The normal TBI has a transitional structure consisting of four gradated layers including bone, mineralized fibrocartilage layer, non-mineralized fibrocartilage layer and tendon[1,2]. This complex structure can disperse force from bone to tendon, preventing stress concentration[3]. However, current therapeutic strategies cannot restore this structure, hence raising the risk of re-injury.
Fibroblasts play a key role in tendon-bone healing. In the early stages of TBI injury, α-smooth muscle actin positive (α-SMA+) fibroblasts help form Sharpey-like fibers to withstand strength at TBI and participate in early ligament remodeling by producing collagen and restoring in situ tension[4,5]. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a kind of stem cells with strong proliferation capacity and multilineage differentiation potential, which can differentiate into myoblasts, osteoblasts, adipocytes and chondroblast[6]. MSCs can be extracted from bone, adipose tissue, blood, and amniotic membrane[7]. They have multiple functions including immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and angiogenesis promotion, making them ideal candidate cells for tissue engineering research[8]. Recent evidence indicates that conditioned medium, primarily containing exosomes of MSCs, can stimulate the activation of fibroblasts, thereby promoting tendon-bone healing[9-12]. However, the underlying mechanism is not comprehensively understood.
Bioinformatics has played an important role in exploring disease mechanisms by allowing parallel processing of large volumes of high-throughput sequencing data. To identify key bone marrow MSC (BMSC)-derived exosome microRNAs (miRNAs), three Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets were interrogated using bioinformatics tools in this study. TargetScan, a software designed to predict miRNA binding sites, is often used to analyze target genes of miRNAs[13]. Metascape, a powerful gene functional annotation analysis tool, enables pathway enrichment and biological process (BP) annotation[14]. STRING database allows for assessing the functional associations among target genes[15]. Cytoscape software enables visualization of miRNA-target gene pairs.
Therefore, using the above database tools, this study aimed to identify overlapped BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs in three GSE datasets and verify their effects as well as mechanisms on fibroblasts, so as to facilitate further studies to verify the role of exosomal miRNAs and their potential in promoting tendon-bone healing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
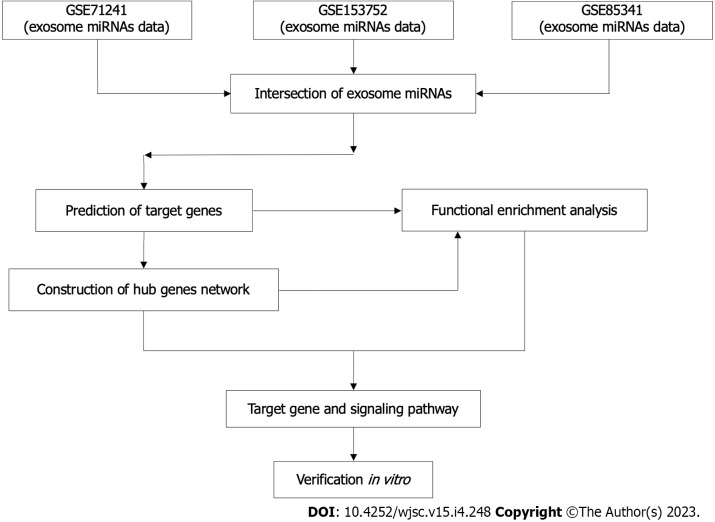
The workflow of this study was described (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The flowchart of this study. miRNAs: MicroRNAs.
Data collection
Three BMSC-derived exosomal miRNA expression microarray datasets (GSE71241, GSE153752, and GSE85341) were retrieved from the GEO repository on 20 April 2022. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo). GSE71241[16], GSE153752[17], and GSE85341[18] included nine, four and one BMSC-derived exosome samples respectively. The above datasets were produced independently using the GPL18743, GPL16791, and GPL22300 platforms, respectively.
Venn diagram analysis and prediction of target genes
After obtaining the top 100 BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs in each dataset, Venn diagram analysis was used to identify overlapped miRNAs in the three datasets through online tool Venny (version 2.1) (https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny). The overlapped miRNAs were considered as candidate miRNAs. Potential target genes for the candidate miRNAs were predicted by TargetScan, an experimentally validated database of miRNA-target interactions[13].
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analyses
Functional and pathway analyses of the predicted target genes were conducted using the Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases, respectively, by processing data with the Metascape[14].
Construction of target gene-protein-protein interaction and miRNA-gene networks
Target gene data was uploaded to the STRING database[15] to assess the functional associations among the target genes of candidate miRNAs. Highly interconnected (hub) genes in the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were analyzed using Cytoscape software (version 3.9.1). After candidate exosomal miRNAs and their hub target genes were identified, Cytoscape was used to visualize the resulting miRNA-gene network.
Cell culture and treatment
The NIH3T3 fibroblast (Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences) was used as a model in vitro to further determine the effect of SF1670 [a specific phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) inhibitor] on fibroblasts[19]. Cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 mg/mL streptomycin and maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. When the cells reached 80% confluence, they were digested with 0.25% trypsin and sub-cultured 1:3. To determine the effect of SF1670, NIH3T3 cells were starved for 24 h with DMEM containing 0.5% FBS and then treated with or without SF1670 2 μM for the indicated time. NIH3T3 fibroblast was seeded and cultured into six-well plate.
Western blot assay
Protein was extracted and analyzed using an established method[20]. Anti-phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) (CST, United States, 1:1000) and anti-Akt (CST, United States, 1:1000) were used as primary antibodies. Each group contains 3 protein samples for calculation.
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
RNA was extracted and analyzed using the previous method[21]. Total RNA was obtained by the Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and quantified by Nanodrop. RNA was then reversely transcribed by the PrimeScript RT reagent kit (Takara Bio). Specific primers used in the experiment are from PrimerBank (Table 1). The operation was performed on the ABI7900 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The expression of mRNAs relative to the expression of GAPDH was calculated and normalized to the control group.
Table 1.
Primers used in the experiment
|
Genes
|
Primers (5’ - 3’)
|
| PTEN | F: TCAGCCGTTACCTGTGTGTG |
| R: TCCTTGTCATTATCTGCACGC | |
| α-SMA | F: GACAATGGCTCTGGGCTCTGTAA |
| R: CTGTGCTTCGTCACCCACGTA | |
| Vimentin | F: GACGCCATCAACACCGAGTT |
| R: CTTTGTCGTTGGTTAGCTGGT | |
| Tenomodulin | F: CCATGCTGGATGAGAGAGGTT |
| R: CCGTCCTCCTTGGTAGCAGT | |
| Col I | F: CCCGGGTTTCAGAGACAACTTC |
| R: TCCACATGCTTTATTCCAGCAATC | |
| Sox 9 | F: GAGCCGGATCTGAAGAGGGA |
| R: GCTTGACGTGTGGCTTGTTC | |
| Col II | F: GGGAATGTCCTCTGCGATGAC |
| R: GAAGGGGATCTCGGGGTTG | |
| GAPDH | F: ACTCCACTCACGGCAAATTC |
| R: TCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGACA |
PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin positive.
Luciferase reporter assay
Validation of miR-144 and miR-23b binding to 3’-UTR was performed using Dual-Glo Luciferase assay system (Promega) as recommended by the manufacturer. The relative luciferase activities were determined by calculating the ratio of firefly luciferase activities over Renilla luciferase activities. All experiments were repeated three times in triplicate. Two constructs of pmirGLO luciferase reporter plasmid were generated: MUT-PTEN (with mutation of part of miRNA binding site sequence) and WT-PTEN [containing the wild-type (WT) miRNA binding site sequence]. 500 ng of the pmirGLO luciferase reporter plasmid and appropriate miRNA plasmid were co-transfected with lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen) into NIH3T3 cells. 48 h after transfection, the luciferase expression was determined using the Dual-Glo Luciferase Reporter Assay Kit (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The pRL-TK vector (Promega) containing Renilla luciferase was also co-transfected for normalization in all relevant experiments.
Bromodeoxyuridine assays
The Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay was performed using Cell Proliferation ELISA kits (1647229; Roche Applied Science, Mannheim, Germany). Briefly, NIH3T3 cells were plated at 5000 cells/well in 96-well culture plates in complete media. After attaining 70% confluence, cells were treated with media containing 10% FBS. BrdU solution (10 μM) was added after intervention. The cells were dried and fixed, and cellular DNA was denatured with FixDenat solution (Roche Applied Science) for 30 min at room temperature. A peroxidase-conjugated mouse anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody (Roche Applied Science) was added to the culture plates and cells were incubated for 90 min at room temperature. Tetramethyl-benzidine substrate was added and the plates were incubated for 15 min at room temperature. The absorbance of samples was measured using a microplate reader at 450-620 nm.
Wound healing assay
Cells at logarithmic growth stage were taken and placed in a six-well plate with a cell density of 5 × 105/well. Three multiple wells were set for each group. When the cells were adherent to the wall in a single layer, a pipetting tip was used to vertically scratch the six-well plate to avoid tilting. The suspension cells were cleaned and removed with PBS and cultured in an incubator with 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Photographs were taken at 0 and 24 h under the microscope. The wound healing area was measured using ImageJ[22].
Collagen gel contraction assay
Cell contraction was determined using a kit from Cell Biolabs (San Diego, CA). Briefly, cells were seeded in collagen solution according to the manufacturer’s instructions and release from the plates with a sterile spatula. Gel images were taken after release and the surface area of each gel was measured using ImageJ[22].
Immunofluorescence
NIH3T3 cells were cultured in a 24-well plate. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and incubated with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma) and then blocked with goat serum (Biyuntian Company, China) for 1 h. The cells were then incubated overnight at 4 °C with the primary antibody. The secondary antibody was applied, and the cells were incubated for 1 h in the dark. Finally, the nuclei were counterstained with DAPI for 15 min. The stained cells were photographed using a fluorescence microscope.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed at least three times. Data were analyzed with GraphPad Prism 7.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, United States) and were presented by mean ± SD. Significance was typically analyzed by student’s t-test, one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc LSD test, and two-way ANOVA followed by multiple t-tests. P < 0.05 was regarded as significant.
RESULTS
Identification of candidate exosomal miRNAs and target genes
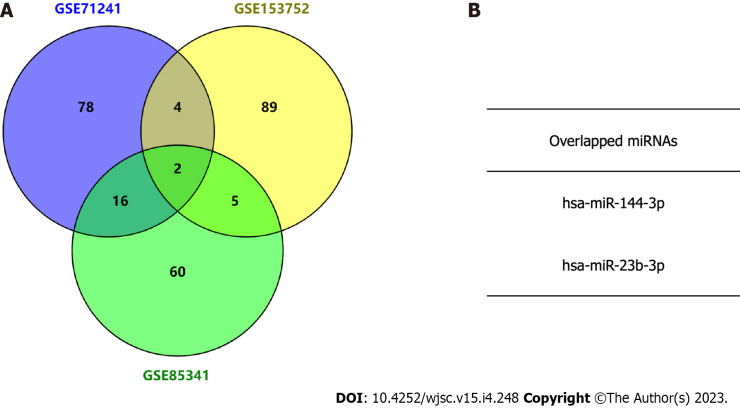
Three independent BMSC-derived exosomal miRNA expression microarray datasets (GSE71241, GSE153752, and GSE85341)[16-18] were downloaded from the GEO database. Subsequently, top 100 BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs in each dataset were obtained. The Venn diagram analysis demonstrated two miRNAs in the intersection of the three datasets (Figure 2). The target gene interactions of two candidate miRNAs, hsa-miR-144-3p and hsa-miR-23b-3p, were assessed by the TargetScan[13]. In total, 1048 and 105 potential target genes were identified for miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p, respectively.
Figure 2.
Identification of candidate microRNAs by intersecting three exosome microRNA expression microarray datasets. A: Venn diagram analysis showing the top 100 exosome microRNAs (miRNAs) in the three Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets; B: Identification of two miRNAs overlapping between the three GEO datasets. miRNAs: MicroRNAs.
Functional enrichment analysis of miRNAs’ target genes
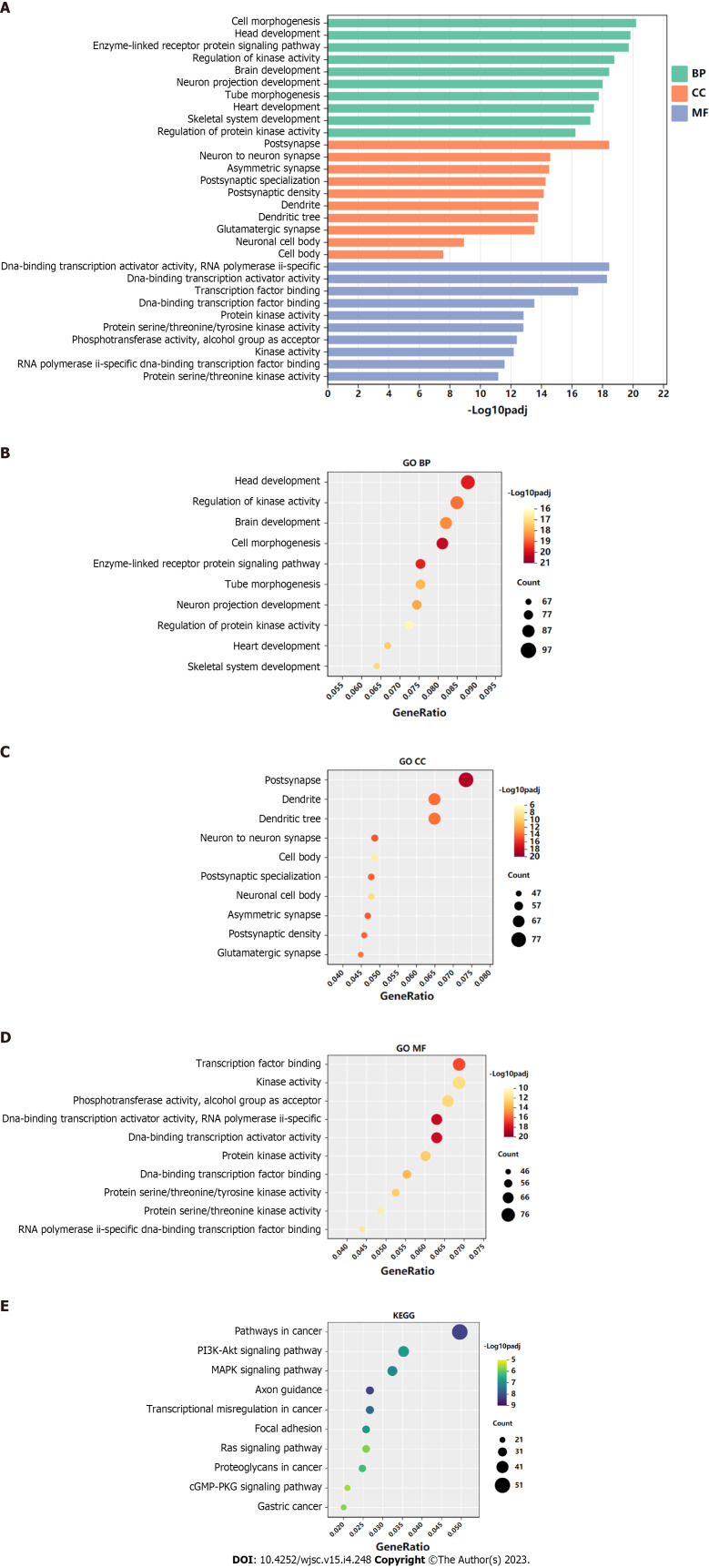
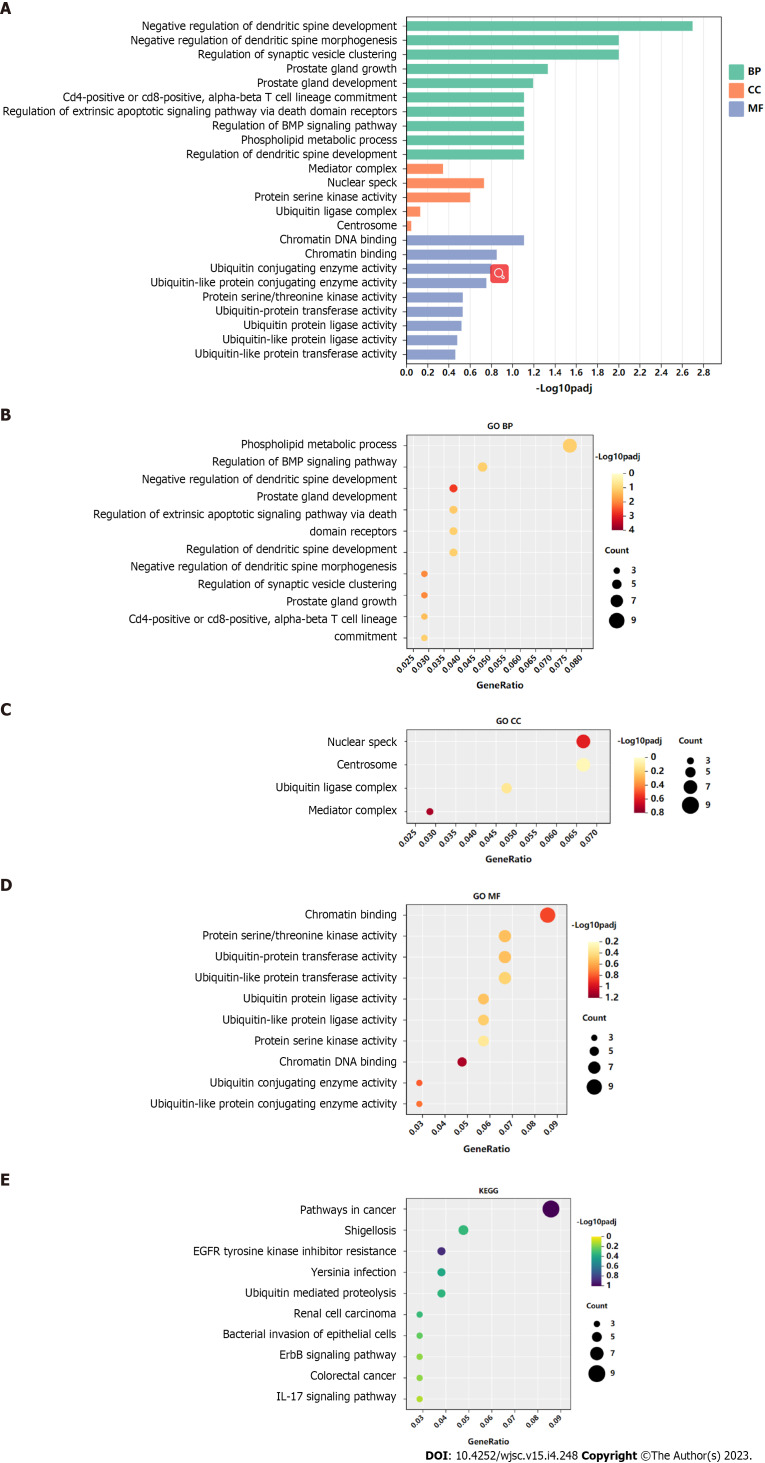
GO functional annotation analysis revealed that the most enriched terms for the target genes of miR-144-3p were ‘head development’ and ‘regulation of kinase activity’ in the BP, ‘postsynapse’ in the cellular component (CC), and ‘transcription factor binding’ and ‘kinase activity’ in the molecular function (MF) (Figures 3A-D). On the other hand, the target genes of miR-23b-3p were mostly enriched in ‘phospholipid metabolic process’ in the BP, ‘nuclear speck’ and ‘centrosome’ in the CC, and ‘chromatin binding’ in the MF (Figures 4A-D). KEGG pathway analysis revealed that most of target genes of miR-144-3p enriched in ‘pathways in cancer’ and ‘PI3K-AKT signaling pathway’ (Figure 3E); most of target genes of miR-23b-3p enriched in ‘pathways in cancer’ (Figure 4E).
Figure 3.
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of genes targeted by hsa-miR-144-3p. A-D: Top 10 Gene Ontology biological process, cellular component, and molecular function terms enriched in target genes of hsa-miR-144-3p; E: Top 10 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways enriched in target genes of hsa-miR-144-3p. BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function; GO: Gene Ontology; KEEG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Figure 4.
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of genes targeted by hsa-miR-23b-3p. A-D: Top 10 Gene Ontology biological process, cellular component, and molecular function terms enriched in target genes of hsa-miR-23b-3p; E: Top 10 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways enriched in target genes of hsa-miR-23b-3p. BP: Biological process; CC: Cellular component; MF: Molecular function; GO: Gene Ontology; KEEG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Construction of target gene-PPI and miRNA-hub gene networks
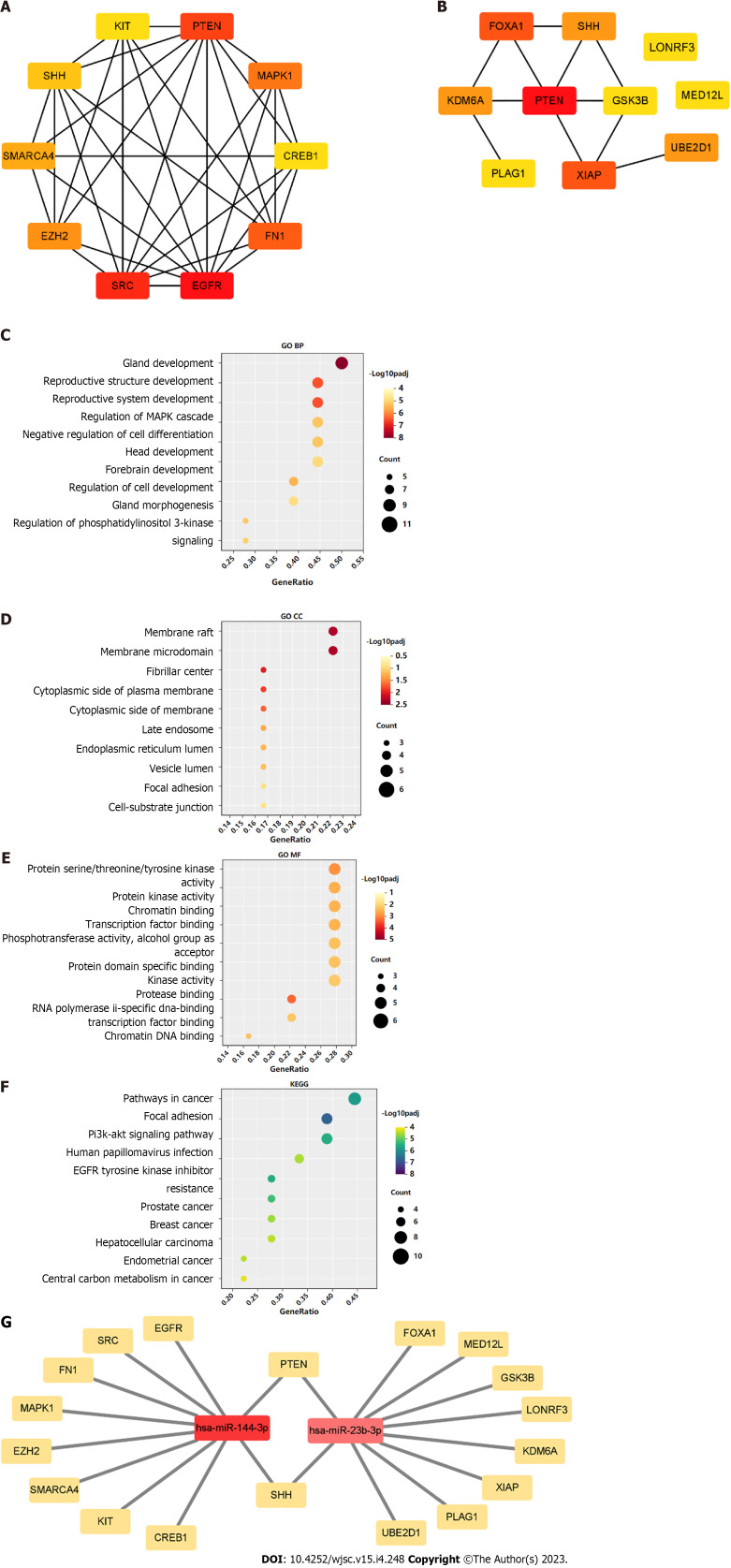
A PPI network was constructed through the STRING database[15]. Interactions with an overall score of more than 0.4 were considered significant. Further processing was carried out using Cytoscape software. Then, the cytoHubba plugin was used to determine the top 10 hub genes based on the Degree algorithm. The top 10 predicted hub genes of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p were presented (Figures 5A and B). GO and KEGG analysis revealed that these hub genes were mostly enriched in ‘regulation of MAPK cascade’, ‘regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling’ and ‘negative regulation of cell differentiation’ in the BP (Figure 5C, Table 2), ‘fibrillar center’ and ‘focal adhesion’ in the CC (Figure 5D, Table 3), and ‘protein kinase activity’ and ‘transcription factor binding’ in the MF (Figure 5E, Table 4). Most of these genes were mainly enriched in PI3K-Akt signaling pathway (Figure 5F, Table 5). Interactional analysis showed that PTEN and sonic hedgehog (SHH) are potentially co-regulated by miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p (Figure 5G).
Figure 5.
Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis of hub-gene targets. A: Top 10 hub-gene targets for hsa-miR-144-3p; B: Top 10 hub-gene targets for hsa-miR-23b-3p; C-E: Top 10 Gene Ontology biological process, cellular component, and molecular function terms enriched in the top 20 hub-gene targets; F: Top 10 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways enriched in the 20 hub-gene targets; G: Interaction network of the two microRNAs and their hub-gene targets.
Table 2.
Top 10 clusters with Gene Ontology Biological Processes analysis of hub-gene targets
|
Term
|
Description
|
LogP
|
Log(q-value)
|
Count
|
| GO:0048732 | Gland development | -12.279 | -7.927 | 9 |
| GO:0048608 | Reproductive structure development | -10.269 | -6.495 | 8 |
| GO:0061458 | Reproductive system development | -10.245 | -6.495 | 8 |
| GO:0030900 | Forebrain development | -8.922 | -5.472 | 7 |
| GO:0043408 | Regulation of MAPK cascade | -8.603 | -5.240 | 8 |
| GO:0045596 | Negative regulation of cell differentiation | -8.549 | -5.238 | 8 |
| GO:0022612 | Gland morphogenesis | -8.482 | -5.208 | 5 |
| GO:0014066 | Regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | -8.316 | -5.077 | 5 |
| GO:0060322 | Head development | -8.138 | -4.931 | 8 |
| GO:0060284 | Regulation of cell development | -8.045 | -4.868 | 7 |
Table 3.
Top 10 clusters with Gene Ontology Cellular Components analysis of hub-gene targets
|
Term
|
Description
|
LogP
|
Log(q-value)
|
Count
|
| GO:0045121 | Membrane raft | -4.441 | -2.311 | 4 |
| GO:0098857 | Membrane microdomain | -4.436 | -2.310 | 4 |
| GO:0001650 | Fibrillar center | -4.076 | -2.035 | 3 |
| GO:0009898 | Cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | -3.849 | -1.860 | 3 |
| GO:0098562 | Cytoplasmic side of membrane | -3.638 | -1.688 | 3 |
| GO:0005770 | Late endosome | -3.205 | -1.308 | 3 |
| GO:0005788 | Endoplasmic reticulum lumen | -3.103 | -1.227 | 3 |
| GO:0031983 | Vesicle lumen | -3.041 | -1.174 | 3 |
| GO:0005925 | Focal adhesion | -2.726 | -0.896 | 3 |
| GO:0030055 | Cell-substrate junction | -2.699 | -0.873 | 3 |
Table 4.
Top 10 clusters with Gene Ontology Molecular Functions analysis of hub-gene targets
|
Term
|
Description
|
LogP
|
Log(q-value)
|
Count
|
| GO:0002020 | Protease binding | -5.941 | -3.326 | 4 |
| GO:0004712 | Protein serine/threonine /tyrosine kinase activity | -5.299 | -2.910 | 5 |
| GO:0004672 | Protein kinase activity | -4.802 | -2.546 | 5 |
| GO:0003682 | Chromatin binding | -4.726 | -2.507 | 5 |
| GO:0008134 | Transcription factor binding | -4.694 | -2.487 | 5 |
| GO:0031490 | Chromatin DNA binding | -4.457 | -2.319 | 3 |
| GO:0016773 | Phosphotransferase activity, alcohol group as acceptor | -4.435 | -2.310 | 5 |
| GO:0019904 | Protein domain specific binding | -4.395 | -2.280 | 5 |
| GO:0061629 | RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | -4.331 | -2.228 | 4 |
| GO:0016301 | Kinase activity | -4.267 | -2.193 | 5 |
Table 5.
Top 10 clusters with Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Pathway analysis of hub-gene targets
|
Term
|
Description
|
LogP
|
Log(q-value)
|
Count
|
| hsa04510 | Focal adhesion | -10.807 | -6.755 | 7 |
| hsa05200 | Pathways in cancer | -9.488 | -5.834 | 8 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | -9.088 | -5.538 | 7 |
| hsa01521 | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance | -9.046 | -5.538 | 5 |
| hsa05215 | Prostate cancer | -8.593 | -5.240 | 5 |
| hsa05224 | Breast cancer | -7.682 | -4.608 | 5 |
| hsa05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | -7.560 | -4.511 | 6 |
| hsa05213 | Endometrial cancer | -7.435 | -4.444 | 4 |
| hsa05225 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | -7.392 | -4.437 | 5 |
| hsa05230 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | -7.102 | -4.181 | 4 |
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor.
PTEN is verified as the targets of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p
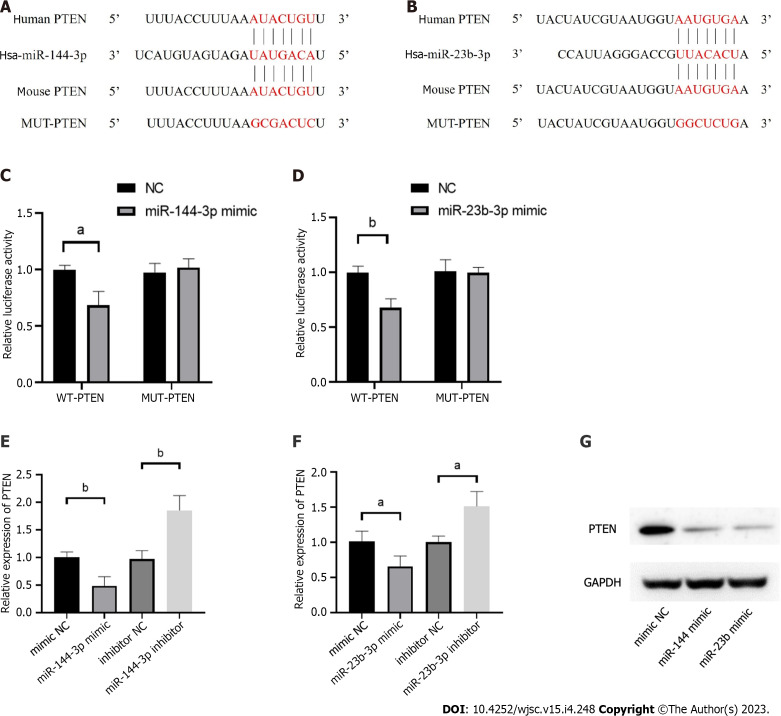
The phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN), was predicted as the hub gene of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p (Figures 6A and B). To further validate the putative binding sites, WT and mutated 3’-UTR of PTEN were cloned into the pmirGLO vector. The transcripts of the target gene were then evaluated by dual luciferase reporter assays. Compared with the control group, luciferase reporter assays showed that miR-144-3p mimics and miR-23b-3p mimics significantly decreased the luciferase activity of WT-PTEN but did not show a significant effect on the luciferase activity of MUT-PTEN (Figures 6C and D). In addition, miR-144-3p mimic significantly down-regulated the mRNA levels of PTEN, while miR-144-3p inhibitor up-regulated the mRNA levels of PTEN (Figure 6E). Similarly, miR-23b-3p mimic down-regulated the mRNA level of PTEN, while miR-23b-3p inhibitor up-regulated the mRNA level of PTEN (Figure 6F). These results indicated that miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p repressed the expression of PTEN by specifically binding with and subsequently inducing the degradation of mRNA.
Figure 6.
Phosphatase and tensin homolog is verified as the targets of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p. A: Human and mouse sequence of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) for miR-144-3p binding site; B: Human and mouse sequence of PTEN for miR-23b-3p binding site; C: The relative luciferase activity was tested after co-transfection of WT/MUT pmirGLO-PTEN-3’UTR and miR-144-3p mimics or their control groups in NIH3T3 cells; D: The relative luciferase activity was tested after co-transfection of WT/MUT pmirGLO-PTEN-3’UTR and miR-23b-3p mimics or their control groups in NIH3T3 cells; E: The mRNA levels of PTEN in NIH3T3 cells transfected with miR-144-3p mimics or miR-144-3p inhibitors; F: The mRNA levels of PTEN in NIH3T3 cells transfected with miR-23b-3p mimics or miR-23b-3p inhibitors; G: Western blot showing the PTEN expression levels after transfected with miR-144-3p mimics and miR-23b-3p mimics. n = 3 per groups. Data are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
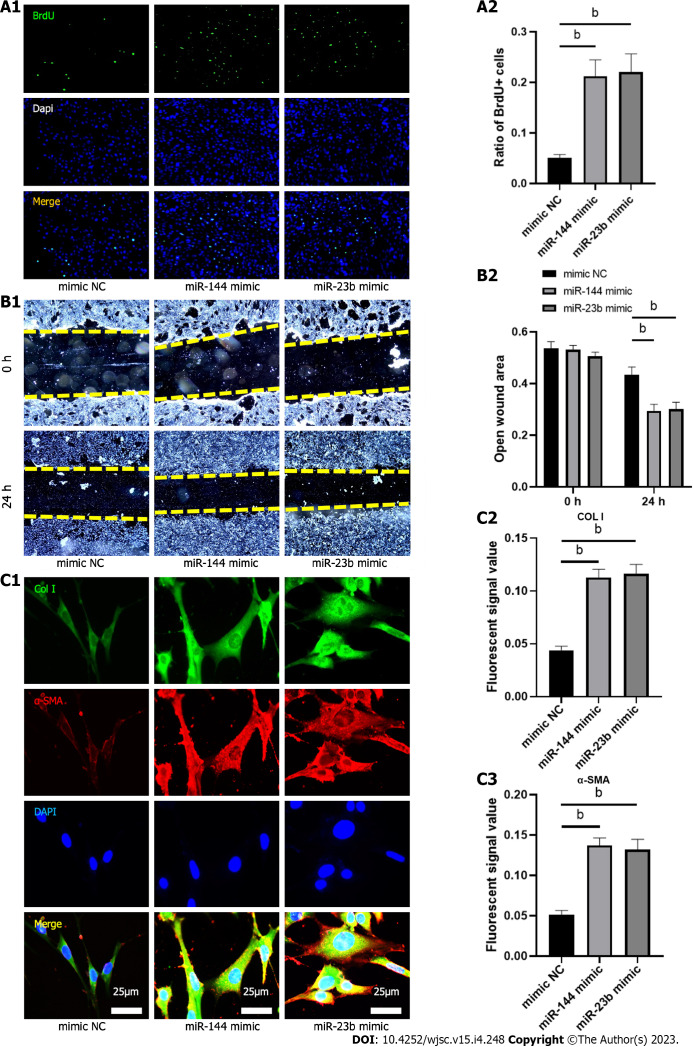
miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p regulate the proliferation, migration, and collagen synthesis of NIH3T3 fibroblasts
To evaluate the effect of the identified miRNAs on fibroblast biology and activation, analysis of proliferation and migration was then performed 24 h after transfection of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p respectively. Compared with the control group, proliferation and migration capacity of NIH3T3 cells in transfection groups were significantly increased (Figures 7A and B). Furthermore, overexpression of miR-144-3p or miR-23b-3p upregulated the expression of Col I and a-SMA in NIH3T3 cells (Figure 7C). These in vitro transfection data indicated that increment in intracellular miR-144-3p or miR-23b-3p stimulated NIH3T3 fibroblast proliferation and migration, and promoted fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation and collagen synthesis.
Figure 7.
MiR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p regulate the proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis of NIH3T3 fibroblasts. A: Bromodeoxyuridine assay was performed to measure the proliferation ability; B: Wound healing assay was performed to measure the migratory capability; C: Immunofluorescence was performed to determine the effects of miR-144-3p and miR-23b-3p on COL I and α-smooth muscle actin expression. n = 3 per groups. Data are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
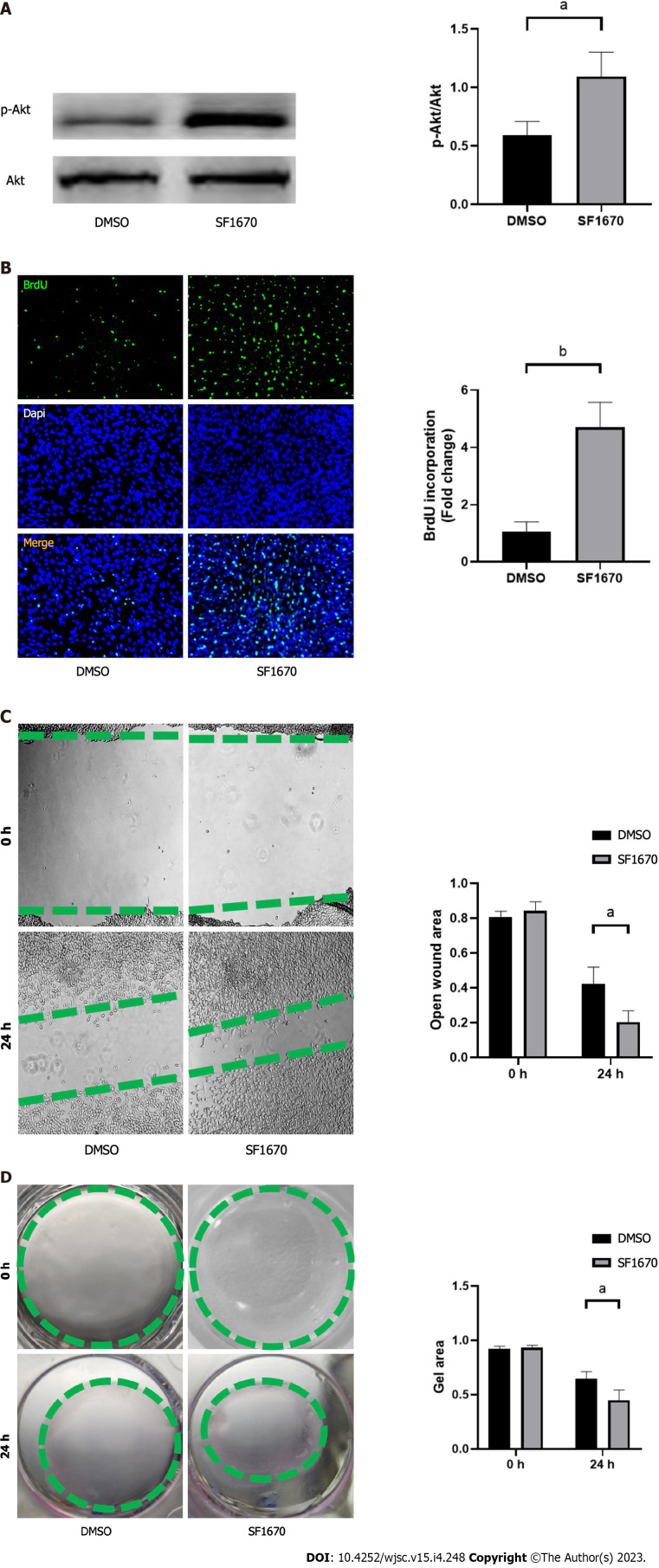
Inhibition of PTEN promote cell proliferation, migration, collagen synthesis and change the gene expression of fibroblastic-, tenogenic-, and chondrogenic-related factors in NIH3T3 cells
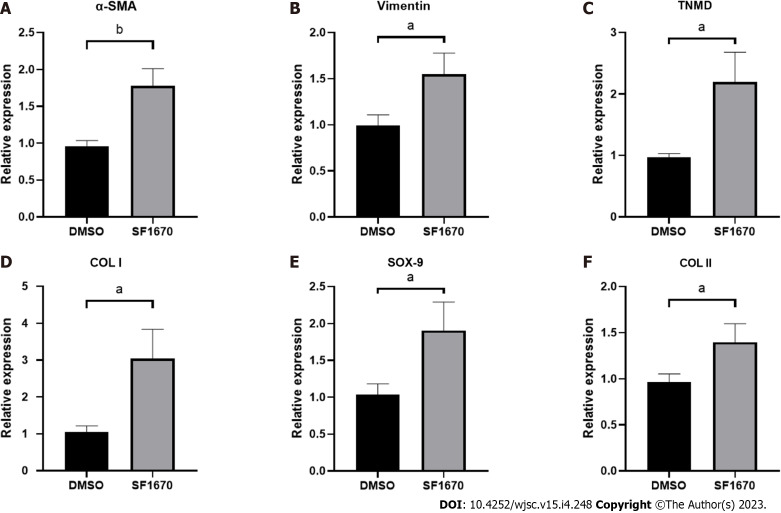
To explore whether BMSC-derived exosome promoted tendon bone healing by directly targeting PTEN in fibroblasts, SF1670, a specific PTEN inhibitor that binds to the active site of PTEN and increases cellular PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 levels and phosphorylation of Akt in vitro[19], was used to examine the effect of PTEN inhibition on NIH3T3 cells. The results showed that SF1670 significantly increased the phosphorylation level of Akt compared with DMSO group (Figure 8A). Moreover, BrdU and wound healing assays showed that SF1670 significantly increased proliferation (Figure 8B) and migration (Figure 8C) of NIH3T3 cells. Collagen contraction assays indicated that SF1670 significantly enhanced the contractility of NIH3T3 cells (Figure 8D). Finally, the properties necessary for tendon-bone healing was examined by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. The results showed that the mRNA level of fibroblast-related genes (α-SMA and vimentin), tenogenic-related genes (TNMD and Col I), and chondrogenic-related genes (SOX-9 and Col II) were significantly up-regulated by SF1670 (Figure 9).
Figure 8.
Inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homolog promoted cell proliferation, migration, and collagen synthesis. A: The protein levels of p-Akt and Akt in NIH3T3 cells were determined by western blot; B: Bromodeoxyuridine assay was performed to measure the proliferation ability; C: Wound healing assay was performed to measure the migratory capability; D: Collagen contraction assay was performed to evaluate the cell contractility. n = 3 per groups. Data are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
Figure 9.
Inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homolog change the gene expression of fibroblastic-, tenogenic-, and chondrogenic-related factors in NIH3T3 cells. The mRNA level of α-smooth muscle actin, vimentin, TNMD, Col I, Sox-9, and Col II in NIH3T3 cells treated with or without SF1670 was determined by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Data are shown as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.
DISCUSSION
Tendon-bone healing has always been an important challenge in orthopedics and sports medicine research and clinical practice. Fibroblasts play a key role in early ligament remodeling and a large number of studies have verified the effective role of MSC-derived exosomes in tendon-bone healing[9-12]. However, because the status of MSCs may be influenced by their generations or donors, the expression of exosomal miRNAs may be more or less different. This presents difficulties in identifying the roles associated with MSC-derived exosomal miRNAs. On ground of this, three GEO datasets were interrogated through bioinformatics tools to determine key BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs. Two candidate miRNAs (miRNA-144 and miRNA-23b) were obtained by intersecting the top 100 exosomal miRNAs in each dataset (Figure 2). Their target genes and hub genes were obtained subsequently. GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis suggested that these genes were involved in multiple cellular processes (e.g., regulation of kinase activity, transcription factor binding, and phospholipid metabolic process) and signaling cascades (e.g., focal adhesion, and PI3K-Akt pathways). A miRNA-target gene interaction network indicated that PTEN was co-regulated by miRNA-144 and miRNA-23b (Figure 5G).
PTEN functions primarily via dephosphorylation of PIP3 to PIP2, resulting in negative regulation of the PI3K/Akt activity[23]. The PTEN/PI3K/Akt nexus participates in various physiological and pathological conditions, and plays an important role in regulating cell growth, apoptosis, metabolism and other processes[24]. Being the direct target of PTEN, PI3K/Akt is also involved in activation of fibroblasts[25,26]. In this study, the effect of PTEN on fibroblasts was also demonstrated. The results showed that inhibition of PTEN increased the level of Akt phosphorylation and promoted the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts (Figure 8), which suggest that PTEN plays an important role in the activation of fibroblasts.
Normal TBI has a transitional structure consisting of four graduated layers including bone tissue, mineralized fibrocartilage layer, non-mineralized fibrocartilage layer and tendon tissue[27], which means that fibrogenesis, tenogenesis and chondrogenesis are key characteristics of tendon-bone healing. As the markers of fibrogenesis, α-SMA and vimentin are expressed in activated fibroblasts[28]. Similarly, tenomodulin (TNMD) and collagen I, collagen II and Sox-9 are well-acknowledged indicators for representing the activation of tenogenic and chondrogenic process[29,30]. By inhibiting PTEN, the results showed increased expression of fibroblastic, tenogenic and chondrogenic markers in fibroblasts (Figure 9), implying that PTEN and PI3K/Akt pathway may be targets for promoting tendon-bone healing.
In addition, this study found that SHH was also regulated by both miRNA-144 and miRNA-23b (Figure 5G). HH signaling pathway is a highly conserved pathway involved in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis and stem cell maintenance[31]. HH signaling is also involved in regulating proliferation of MSCs in adult tissues and plays critical roles in promoting tendon-bone healing[32-34]. SHH, one of three HH family members in mammals, acts in the early stages of development to regulate patterning and growth[35], and plays a crucial role in bone healing[36]. These evidences suggested that MSC-derived exosomal miRNAs may promote tendon-bone healing in more than one way.
The outcomes of the current study were guaranteed by several factors. In this study, three BMSC-derived exosomal miRNA expression microarray datasets were searched from the GEO repository to avoid batch differences. Moreover, due to the costs, technical challenges, and lack of biomarkers suitable for specific exosomes, it is difficult to isolate large number of pure and specific exosomes from mixtures of different vesicle types in a large volume of solution[37]. Therefore, this study identified the key pathway of exosomal miRNA through comprehensive analysis, providing a theoretical basis for developing methods to stably regulate the activation of fibroblasts and thus promote tendon-bone healing.
However, the outcomes should also be interpreted with caution. The biological functions of exosomal miRNAs are diverse, but this study only took the overlapped target gene, i.e., PTEN, for analysis. Thus, further exploration is needed to pinpoint the specific functions of each miRNA. In addition, this study only used murine NIH3T3 cells in vitro. Experiments in vivo is needed to verify the reconstruction of the natural gradient structure of TBI.
CONCLUSION
BMSC-derived exosomes promote fibroblast activation possibly through the PTEN and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which may serve as potential targets to further promote tendon-bone healing.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The normal tendon-bone insertion has a transitional structure consisting of four gradated layers including bone, mineralized fibrocartilage layer, non-mineralized fibrocartilage layer and tendon. This complex structure can disperse force from bone to tendon, preventing stress concentration. However, current therapeutic strategies cannot restore this structure, hence raising the risk of re-injury.
Research motivation
Recent evidence indicates that conditioned medium, primarily contains exosomes of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), can stimulate the activation of fibroblasts, thereby promoting tendon-bone healing. However, the underlying mechanism is not comprehensively understood. Moreover, the expression of exosome microRNA (miRNA) may vary depending on the status of MSCs, which presents difficulties in identifying the roles associated with MSC-derived exosomal miRNAs.
Research objectives
To identify overlapped bone marrow MSC (BMSC)-derived exosomal miRNAs in three GSE datasets and verify their effects as well as mechanisms on fibroblasts.
Research methods
BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. The candidate miRNAs were obtained by the intersection of different datasets. TargetScan was used to predict potential target genes. Functional and pathway analyses were conducted using the Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes databases. Hub genes in the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were analyzed using Cytoscape software. The transcripts of the target gene were assessed by dual luciferase reporter assays. BrdU, wound healing assay, collagen contraction assay and the expression of COL I and α-smooth muscle actin positive were applied to investigate the cell proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis.
Research results
Bioinformatics analyses showed two BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs, has-miR-144-3p and has-miR-23b-3p, were overlapped in three GSE datasets. PPI network analysis and functional enrichment analyses indicated that both miRNAs regulated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN). In vitro experiments confirmed that both miRNAs stimulated proliferation, migration and collagen synthesis of NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Interfering with PTEN affected the phosphorylation of Akt and thus activated fibroblasts.
Research conclusions
BMSC-derived exosomes promote fibroblast activation possibly through the PTEN and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, which may serve as potential targets to further promote tendon-bone healing.
Research perspectives
Further exploration is needed to pinpoint the specific functions of exosomal miRNAs. In vivo studies may better reveal the effect of exosomal miRNAs on tendon-bone healing.
Footnotes
Institutional review board statement: This study involves no human or animal subjects.
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Peer-review started: November 23, 2022
First decision: January 6, 2023
Article in press: March 23, 2023
Specialty type: Cell and tissue engineering
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Lei X, China; Tan W, China; Li SC, United States S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhang XD
Contributor Information
Fang-Qi Li, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
Wen-Bo Chen, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
Zhi-Wen Luo, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
Yi-Sheng Chen, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
Ya-Ying Sun, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China.
Xiao-Ping Su, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Rehabilitation and Reconstruction, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China.
Jun-Ming Sun, Laboratory Animal Center, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China.
Shi-Yi Chen, Department of Sports Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China. cshiyi@163.com.
Data sharing statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
- 1.Zelzer E, Blitz E, Killian ML, Thomopoulos S. Tendon-to-bone attachment: from development to maturity. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014;102:101–112. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.21056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Genin GM, Thomopoulos S. The tendon-to-bone attachment: Unification through disarray. Nat Mater. 2017;16:607–608. doi: 10.1038/nmat4906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thomopoulos S, Genin GM, Galatz LM. The development and morphogenesis of the tendon-to-bone insertion - what development can teach us about healing - J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2010;10:35–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kosaka M, Nakase J, Hayashi K, Tsuchiya H. Adipose-Derived Regenerative Cells Promote Tendon-Bone Healing in a Rabbit Model. Arthroscopy. 2016;32:851–859. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2015.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Weiler A, Unterhauser FN, Bail HJ, Hüning M, Haas NP. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is expressed by fibroblastic cells of the ovine anterior cruciate ligament and its free tendon graft during remodeling. J Orthop Res. 2002;20:310–317. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Polymeri A, Giannobile WV, Kaigler D. Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Horm Metab Res. 2016;48:700–713. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-118458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Robey P. "Mesenchymal stem cells": fact or fiction, and implications in their therapeutic use. F1000Res. 2017;6 doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10955.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Squillaro T, Peluso G, Galderisi U. Clinical Trials With Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An Update. Cell Transplant. 2016;25:829–848. doi: 10.3727/096368915X689622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen W, Sun Y, Gu X, Cai J, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen J, Hao Y, Chen S. Conditioned medium of human bone marrow-derived stem cells promotes tendon-bone healing of the rotator cuff in a rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120714. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sun Y, Chen W, Hao Y, Gu X, Liu X, Cai J, Liu S, Chen J, Chen S. Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Promotes Graft Remodeling of Midsubstance and Intratunnel Incorporation After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47:2327–2337. doi: 10.1177/0363546519859324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shi Y, Kang X, Wang Y, Bian X, He G, Zhou M, Tang K. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (BMSCs) Enhance Tendon-Bone Healing by Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e923328. doi: 10.12659/MSM.923328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhou Y, Xie S, Tang Y, Li X, Cao Y, Hu J, Lu H. Effect of book-shaped acellular tendon scaffold with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells sheets on bone-tendon interface healing. J Orthop Translat. 2021;26:162–170. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2020.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM, Bisaria N, Kelley GM, Bartel DP. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science. 2019;366 doi: 10.1126/science.aav1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1523. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D, Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:D605–D612. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J, Sala E, Shiva S, St Croix CM, Stolz DB, Watkins SC, Di YP, Leikauf GD, Kolls J, Riches DW, Deiuliis G, Kaminski N, Boregowda SV, McKenna DH, Ortiz LA. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8472. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bliss SA, Sinha G, Sandiford OA, Williams LM, Engelberth DJ, Guiro K, Isenalumhe LL, Greco SJ, Ayer S, Bryan M, Kumar R, Ponzio NM, Rameshwar P. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Stimulate Cycling Quiescence and Early Breast Cancer Dormancy in Bone Marrow. Cancer Res. 2016;76:5832–5844. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Soni N, Gupta S, Rawat S, Krishnakumar V, Mohanty S, Banerjee A. MicroRNA-Enriched Exosomes from Different Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can Differentially Modulate Functions of Immune Cells and Neurogenesis. Biomedicines. 2021;10 doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rosivatz E, Matthews JG, McDonald NQ, Mulet X, Ho KK, Lossi N, Schmid AC, Mirabelli M, Pomeranz KM, Erneux C, Lam EW, Vilar R, Woscholski R. A small molecule inhibitor for phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) ACS Chem Biol. 2006;1:780–790. doi: 10.1021/cb600352f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sun Y, Wang H, Li Y, Liu S, Chen J, Ying H. miR-24 and miR-122 Negatively Regulate the Transforming Growth Factor-β/Smad Signaling Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Fibrosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;11:528–537. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang N, Luo Z, Jin M, Sheng W, Wang HT, Long X, Wu Y, Hu P, Xu H, Zhang X. Exploration of age-related mitochondrial dysfunction and the anti-aging effects of resveratrol in zebrafish retina. Aging (Albany NY) 2019;11:3117–3137. doi: 10.18632/aging.101966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rueden CT, Schindelin J, Hiner MC, DeZonia BE, Walter AE, Arena ET, Eliceiri KW. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017;18:529. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1934-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pulido R. PTEN Inhibition in Human Disease Therapy. Molecules. 2018;23 doi: 10.3390/molecules23020285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Papa A, Pandolfi PP. The PTEN⁻PI3K Axis in Cancer. Biomolecules. 2019;9 doi: 10.3390/biom9040153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huang Z, Xing S, Liu M, Deng W, Wang Y, Huang Z, Huang Y, Huang X, Wu C, Guo X, Pan X, Jiang J, Feng F, Li T. MiR-26a-5p enhances cells proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis resistance of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39 doi: 10.1042/BSR20182192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cao C, Wu F, Niu X, Hu X, Cheng J, Zhang Y, Li C, Duan X, Fu X, Zhang J, Zhang X, Ao Y. Cadherin-11 cooperates with inflammatory factors to promote the migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in pigmented villonodular synovitis. Theranostics. 2020;10:10573–10588. doi: 10.7150/thno.48666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu Y, Dong Y, Jiang J, Li H, Zhu T, Chen S. Evaluation of the Bone-ligament and tendon insertions based on Raman spectrum and its PCA and CLS analysis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:38706. doi: 10.1038/srep38706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 2007;170:1807–1816. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chu Y, Huang L, Hao W, Zhao T, Zhao H, Yang W, Xie X, Qian L, Chen Y, Dai J. Long-term stability, high strength, and 3D printable alginate hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering application. Biomed Mater. 2021;16 doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac2595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Younesi Soltani F, Javanshir S, Dowlati G, Parham A, Naderi-Meshkin H. Differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward tenocyte by platelet-derived growth factor-BB and growth differentiation factor-6. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022;23:237–246. doi: 10.1007/s10561-021-09935-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Huang D, Wang Y, Tang J, Luo S. Molecular mechanisms of suppressor of fused in regulating the hedgehog signalling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:6077–6086. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mak KK, Bi Y, Wan C, Chuang PT, Clemens T, Young M, Yang Y. Hedgehog signaling in mature osteoblasts regulates bone formation and resorption by controlling PTHrP and RANKL expression. Dev Cell. 2008;14:674–688. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zong JC, Mosca MJ, Degen RM, Lebaschi A, Carballo C, Carbone A, Cong GT, Ying L, Deng XH, Rodeo SA. Involvement of Indian hedgehog signaling in mesenchymal stem cell-augmented rotator cuff tendon repair in an athymic rat model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26:580–588. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2016.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carbone A, Carballo C, Ma R, Wang H, Deng X, Dahia C, Rodeo S. Indian hedgehog signaling and the role of graft tension in tendon-to-bone healing: Evaluation in a rat ACL reconstruction model. J Orthop Res. 2016;34:641–649. doi: 10.1002/jor.23066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang J, Andre P, Ye L, Yang YZ. The Hedgehog signalling pathway in bone formation. Int J Oral Sci. 2015;7:73–79. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2015.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Horikiri Y, Shimo T, Kurio N, Okui T, Matsumoto K, Iwamoto M, Sasaki A. Sonic hedgehog regulates osteoblast function by focal adhesion kinase signaling in the process of fracture healing. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8:237–255. doi: 10.7150/thno.21945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.