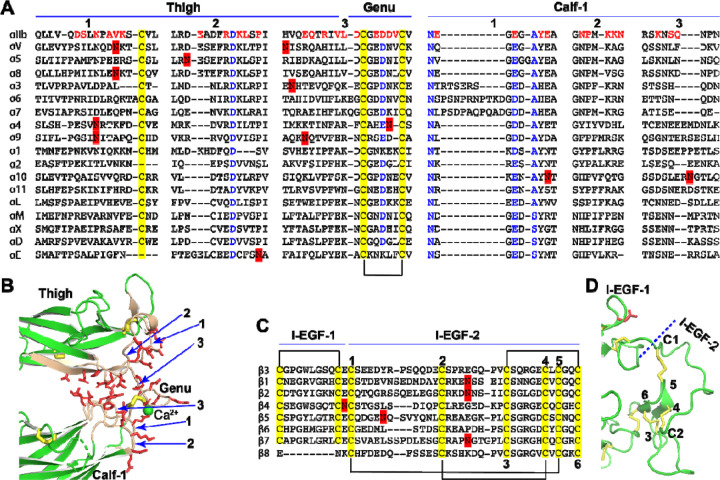
Figure 4. Sequence and structure of the domain interface where integrin becomes extended.
(A) Sequence alignment of the human α integrin thigh and calf-1 domain junction interface. Interfacial residues of αIIb are highlighted in red, while highly conserved residues are in blue. Disulfide bonds are indicated in yellow, and putative N-glycan sites are marked in red. (B) The interface between the thigh and calf-1 domains of the bent αIIb structure. The loops at the interface are numbered in panels A and B. Interfacial residues are shown as red sticks. Disulfide bonds are represented by yellow sticks. (C) Sequence alignment of the human β integrin I-EGF-1 and I-EGF-2 domain junction. Disulfide bonds are highlighted in yellow and putative N-glycan sites are marked in red. The six cysteines of I-EGF-2 domain are numbered. (D) Structure of β3 I-EGF-1 and I-EGF-2 domain junction. Disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks, and one N-glycan site on I-EGF-1 is depicted as a red stick.