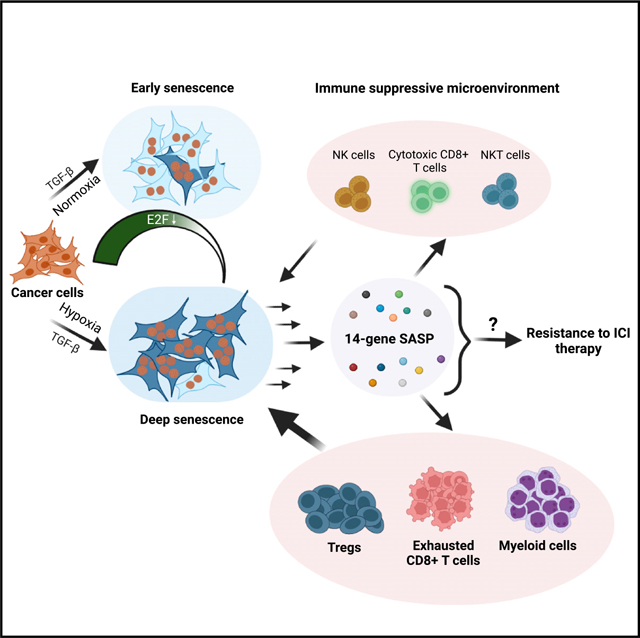
SUMMARY
TGF-β induces senescence in embryonic tissues. Whether TGF-β in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment (TME) induces senescence in cancer and how the ensuing senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) remodels the cellular TME to influence immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) responses are unknown. We show that TGF-β induces a deeper senescent state under hypoxia than under normoxia; deep senescence correlates with the degree of E2F suppression and is marked by multinucleation, reduced reentry into proliferation, and a distinct 14-gene SASP. Suppressing TGF-β signaling in tumors in an immunocompetent mouse lung cancer model abrogates endogenous senescent cells and suppresses the 14-gene SASP and immune infiltration. Untreated human lung cancers with a high 14-gene SASP display immunosuppressive immune infiltration. In a lung cancer clinical trial of ICIs, elevated 14-gene SASP is associated with increased senescence, TGF-β and hypoxia signaling, and poor progression-free survival. Thus, TME-induced senescence may represent a naturally occurring state in cancer, contributing to an immune-suppressive phenotype associated with immune therapy resistance.
In brief
Using cell culture and mouse tumor models, Matsuda et al. show that the TGF-β-hypoxic tumor microenvironment induces a physiological deep senescent state with a 14-gene immune-suppressive SASP. Non-small-cell lung cancer patients with high TGF-β and hypoxia signaling and the 14-gene SASP exhibit poor clinical outcome after ICI therapy.
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Senescence is associated with prolonged or irreversible growth arrest and is an integral feature of embryonic development, aging, and age-related degenerative diseases.1,2 Rather than a fixed cellular state, senescence is considered to be a continuous process with multiple intermediate states ranging from early to late or deep senescence,3–5 the underlying biology of which is not understood. In cancer, senescence is documented under three settings: in premalignant states,6 upon forced oncogene expression,7 and in response to therapies.8,9 Whether senescence also represents a naturally occurring cell state in cancers contributing to the heterogeneity of malignant tumors is unclear.
Senescent cells secrete bioactive proteins, and this is known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP),10 which is variable and context dependent.11–13 SASP induces pro-tumorigenic phenotypes, including angiogenesis14 and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).15 It also promotes immune cell infiltration that can either eliminate senescent cells16,17 or protect neighboring cancer cells from cytotoxic immune cells.18–20 SASP can also induce paracrine senescence through secretion of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β).21–23 Tissue-derived TGF-β itself induces senescence in developing embryos24 and it partially contributes to oncogene-induced senescence.21 Together, these facts suggest that TGF-β in the microenvironment is a key inducer of senescence in multiple contexts. In cancer, it is unclear whether TGF-β prevalent in the tumor microenvironment (TME)25 induces senescence in a subset of tumor cells as part of a naturally occurring cell-state transition.
TGF-β in the TME is secreted by the tumor cells,26 stromal cells,27 and immune cells.28 TGF-β signaling is relayed through Smad2/3-dependent29 and independent pathways.30 The majority of in vitro studies with TGF-β, the activity of which is context dependent, have been performed using experimental models maintained under supraphysiological oxygen levels (21%, which we will refer to as normoxia), and they do not accurately mimic the complexity of the oxygen gradient within the TME. The median oxygen concentration in normal and diseased human tissues ranges from 0.2% to 7.5% depending on tissue type, with physiological hypoxia in tumors ranging from 1% to <5%, creating an inherently heterogeneous microenvironment.31,32
TGF-β and hypoxia induce overlapping tumorigenic phenotypes, including vascularization, immune evasion, fibrosis, and EMT.33,34 They also induce diametrically opposite phenotypes; TGF-β induces senescence,35 whereas hypoxia inhibits senescence and maintains a stem cell niche.36 While these observations rely on individually testing either TGF-β or hypoxia, these two factors are critical physiological components of the TME, making it imperative to interrogate their combined influence on cell states such as senescence.
Here, we show that TGF-β, in the physiologically hypoxic TME, induces a deep state of senescence and that senescence is a physiological state in a fraction of cells within lung cancers. Cancer cells undergoing deep senescence secrete an immunosuppressive 14-gene SASP associated with adverse clinical outcome in lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Thus, cancers may be exploiting naturally occurring senescence to modulate their immune microenvironment as a mechanism to evade effective anti-tumor immunity.
RESULTS
TGF-β induces different levels of senescence depending on environmental oxygen concentration
To determine how oxygen concentration influences TGF-β-induced senescence, A549 lung cancer cells (wild-type p53; INK4A deleted) were propagated under normoxia (21% O2) or hypoxia (4% O2). Multiple hypoxia markers (SLC2A1, PGK1, ALDOA, ALDOC, PKM) were significantly induced upon switching cells from 21% O2 to 4% O2 (Figure S1A; ). TGF-β treatment (5 ng/mL, 15 days) under both conditions led to the appearance of large, flattened cells reminiscent of senescence. Cells positive for β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity, a senescence marker, increased under hypoxia and normoxia, showing that TGF-β induces senescence (Figure 1A), which increases over time (Figure S1B). Hypoxia alone did not increase β-gal positive cells (Figures 1A and S1B). Similar results were observed in human hepatoma and esophageal cancer lines, HEPG2 (wild-type INK4A; wild-type p53) and TE4 (mutant p53), respectively (Figure S1C).
Figure 1. TGF-β induces different degrees of senescence depending on oxygen concentration.
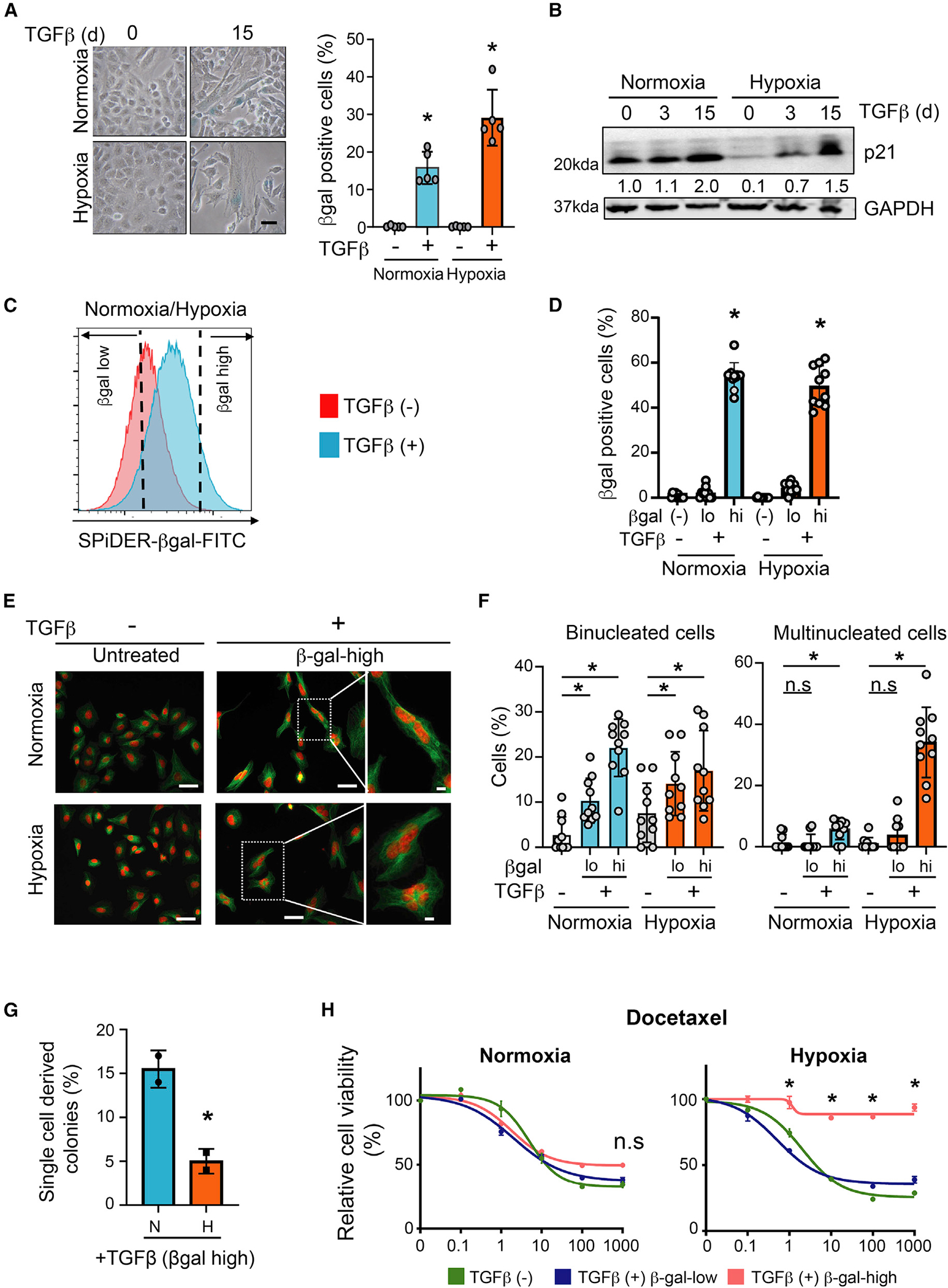
(A) TGF-β induces senescence in normoxic and hypoxic cells. A549 cells were treated with 5 ng/mL TGF-β for 15 days and stained for β-gal activity. Left: photomicrographs of β-gal-stained untreated and TGF-β-treated cells. Scale bar: 20 μm. Right: quantification of percentage of β-gal-positive cells. Mean ± SD was calculated from imaging 10 random fields. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test; biological replicates.
(B) TGF-β induces p21 in normoxic and hypoxic cells. Western blot showing p21 protein in A549 cells treated with 5 ng/mL TGF-β for 0, 3, and 15 days. p21 band intensity quantification is provided below. p21 expression in untreated normoxic cells was set at 1. GAPDH was used as loading control; biological replicates.
(C) Schematic showing β-gal-high senescent population enrichment. TGF-β-treated hypoxic and normoxic A549 cells (5 ng/mL for 15 days) were sorted after SPiDER-βGal staining. β-gal-low and β-gal-high populations, defined as the bottom and top 20% of the observed distribution, respectively, were collected for downstream analysis. Representative data from three biological replicates are shown.
(D) The β-gal-low and β-gal-high populations collected as described in (C) were cultured for 24 h and stained for β-gal. Bar graph shows percentage of β-gal-positive cells in each condition. Untreated A549 cells were used as control. Mean ± SD was calculated from imaging 10 random fields. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test; biological replicates.
(E) Multinucleated cells are prevalent in TGF-β-treated hypoxic cultures. The β-gal-high cells collected from TGF-β-treated (5 ng/mL, 15 days) hypoxic and normoxic cultures were stained with DAPI (red) and tubulin (green). Untreated cells were used as control. Photomicrographs of cells under each condition are shown. Scale bar: 50 μm. Far right images: higher-magnification images of binucleated (upper, normoxia) and multinucleated (lower, hypoxia) cells in highlighted images. Scale bar: 10 μm. Representative data from two biological replicates are shown.
(F) Quantification of binucleated and multinucleated cells in β-gal-low and β-gal-high populations sorted from TGF-β-treated (5 ng/mL, 15 days) hypoxic and normoxic A549 cells. Untreated cells are shown as controls. Mean ± SD was calculated from imaging 10 random fields. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test; biological replicates.
(G) β-gal-high TGF-β-treated hypoxic cells exhibit reduced ability to resume proliferation. TGF-β-treated (5 ng/mL, 15 days) hypoxic and normoxic A549 cells were sorted for β-gal activity and seeded as single cells into 96-well plates. Colony formation of single cells in medium without TGF-β was monitored after 7 days. Bar graph shows fraction of wells with colonies for each condition; biological replicates; mean ± SD; *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
(H) TGF-β-treated β-gal-high hypoxic cells are resistant to drug treatment. The β-gal-low and β-gal-high populations from TGF-β-treated hypoxic and normoxic A549 cells were cultured for a day without TGF-β and treated with increasing concentrations of docetaxel for 72 h. Graph shows relative viability of cells for each condition (y axis) under different drug concentrations (x axis). Untreated cells (TGF-β [−]) are shown as controls; biological replicates. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. See also Figures S1 and S2.
p21 protein, contributing to cellular senescence by inhibiting the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) such as CDK2 and CDK4,37,38 was suppressed by 10-fold in hypoxic cells compared with normoxic cells (Figure 1B). This is consistent with hypoxia suppressing senescence.39–42 The kinetics of TGF-β-induced p21 under normoxia and hypoxia, however, were different. TGF-β increased p21 protein by 2-fold in normoxic A549 cells after 15 days. In hypoxic cells, TGF-β induced p21 much earlier, by 7-fold at day 3 and by 15-fold at day 15 (Figure 1B). TGF-β also induced comparable levels of H3K9Me3 foci, another marker of senescence,43 in hypoxic and normoxic cells (Figure S1D). Very little apoptosis was observed under either condition (Figure S1E).
To further investigate differential oxygen concentration effects on senescence, we enriched cells with high β-gal activity. TGF-β-treated normoxic and hypoxic cells stained with SPiDER-βGal were sorted based on β-gal activity. The β-gal-low and β-gal-high populations were defined as the bottom and top 20%, respectively, of the observed distribution (Figure 1C). β-gal activity of sorted populations was confirmed by β-gal staining (Figure 1D). In western blots, β-gal-high populations expressed high p21 levels compared with untreated controls and β-gal-low populations (Figure S1F). DAPI and anti-tubulin staining of β-gal-high cell populations to visualize DNA and microtubules, respectively, identified mono-, bi-, and multinucleated cells (Figure 1E). Binucleated and multinucleated cells did not increase under hypoxia compared with normoxia. TGF-β increased the binucleated cell fraction by ~7-fold in β-gal-high normoxic cells (untreated, 3% ± 3.8%; treated β-gal high, 22% ± 6.0%; ) and by ~2-fold in β-gal-high hypoxic populations (untreated, 8% ± 6.2%; treated β-gal high, 17% ± 8.4%; ) (Figure 1F). However, there was >30-fold increase in cells with multiple nuclei in the TGF-β-treated β-gal-high hypoxic population (untreated, 1% ± 1.8%; treated β-gal-high, 34% ± 10.9%; ) (Figure 1F) compared with ~3-fold increase in TGF-β-treated β-gal-high normoxic cells (untreated, 1.4% ± 2.4%; treated β-gal-high, 5.7% ± 3.2%; ) (Figure 1F). TGF-β-treated hypoxic HepG2 and TE4 cells also showed significant increases in multinucleated cells (Figures S2A–S2D).
To determine whether the senescence phenotype can be recapitulated with physiological TGF-β levels produced by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), we co-cultured A549 cells with CAFs derived from two different lung cancer patients.44 The TGF-β1 concentration in supernatants of the two patient-derived CAFs ranged from 1.3 to 2.2 ng/mL (CAF#1, 2.17–2.33 ng/mL, mean 2.2 ng/mL; CAF#2, 1.25–1.5 ng/mL, mean 1.3 ng/mL). This concentration, although lower by ~2- to 3-fold, is comparable to the 5 ng/mL recombinant TGF-β used in our in vitro experiments (Figure S2E).
mCherry-labeled A549 cells were co-cultured under hypoxia with unlabeled lung CAFs at a 1:1 ratio for 15 days. β-gal-positive A549 cells were sorted based on mCherry positivity and quantified. TGF-β-treated hypoxic tumor cells were used as positive control. TGF-β increased the senescent tumor cell fraction, as did co-culturing with the two lung CAFs. The TGF-β inhibitor SB431542 suppressed TGF-β-induced and CAF-induced senescence (Figure S2F). The degree of senescence induction by lung CAFs was commensurate with the lower concentrations of TGF-β secreted by these cells compared with the 5 ng/mL TGF-β used in vitro (Figures S2E and S2F). Further, DAPI and tubulin staining of β-gal-high A549 cells co-cultured with CAFs showed increased multinucleated cell fraction (Figure S2G; untreated, 8.7% ± 3.2%; TGF-β-treated, 40.7% ± 9.9%; ; without CAF, 8.7% ± 3.2%; with CAF, 35.6% ± 10.0%; ). Thus, exposure to physiological levels of TGF-β produced by lung CAFs in a hypoxic microenvironment induces multinucleated senescent cells.
To evaluate whether these β-gal-high senescent cells resume proliferation, we sorted β-gal-high single cells from TGF-β-treated normoxic and hypoxic cultures into medium without TGF-β and monitored their ability to form colonies after 7 days. The ability of β-gal-high hypoxic cells to resume proliferation was significantly reduced compared with β-gal-high normoxic cells (Figure 1G). Upon TGF-β withdrawal, β-gal-high normoxic cells were just as sensitive as untreated control cells to docetaxel and cisplatin; similarly cultured TGF-β-β-gal-high hypoxic cells were resistant to drug treatment (Figures 1H and S2H).
These findings show that TGF-β, depending on environmental O2 concentration, induces different degrees of senescence. Since β-gal-high hypoxic cells exhibit a more severe senescence phenotype marked by multinucleated cells, reduced ability to resume proliferation, and continued drug resistance, we will refer to this condition as deep senescence (D-senescence) and the senescence in TGF-β-treated normoxic cells as early senescence (E-senescence).
Dosage of activator E2Fs and E2F targets gradually declines during progression into deep senescence
To define the mechanism responsible for promoting E- and D-senescence, we performed RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) of β-gal-high E- and D-senescent populations. Given the increased multinucleated phenotype in D-senescence, we interrogated whether paracrine senescence signatures,21,23 and cell-cycle, DNA-replication, and DNA-damage gene signatures (Figure S3A; Table S1), typically associated with senescence,45 are different across these populations. While paracrine senescence signatures were elevated in D-senescent cells, cell-cycle, DNA-replication, and DNA-damage signatures, defined by differential expression of >800 leading-edge genes, were suppressed in these cells compared with E-senescent cells (Figures 2A and S3A). Hypergeometric gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of motif enrichment of these >800 gene promoters showed E2F DNA binding motif enrichment (). RNA-seq analysis showed that E2F targets are suppressed as cells progress from E- to D-senescence (; Figures 2B and 2C).
Figure 2. Gradual decline in the dosage of E2F-mediated gene expression as cells progress into deep senescence.
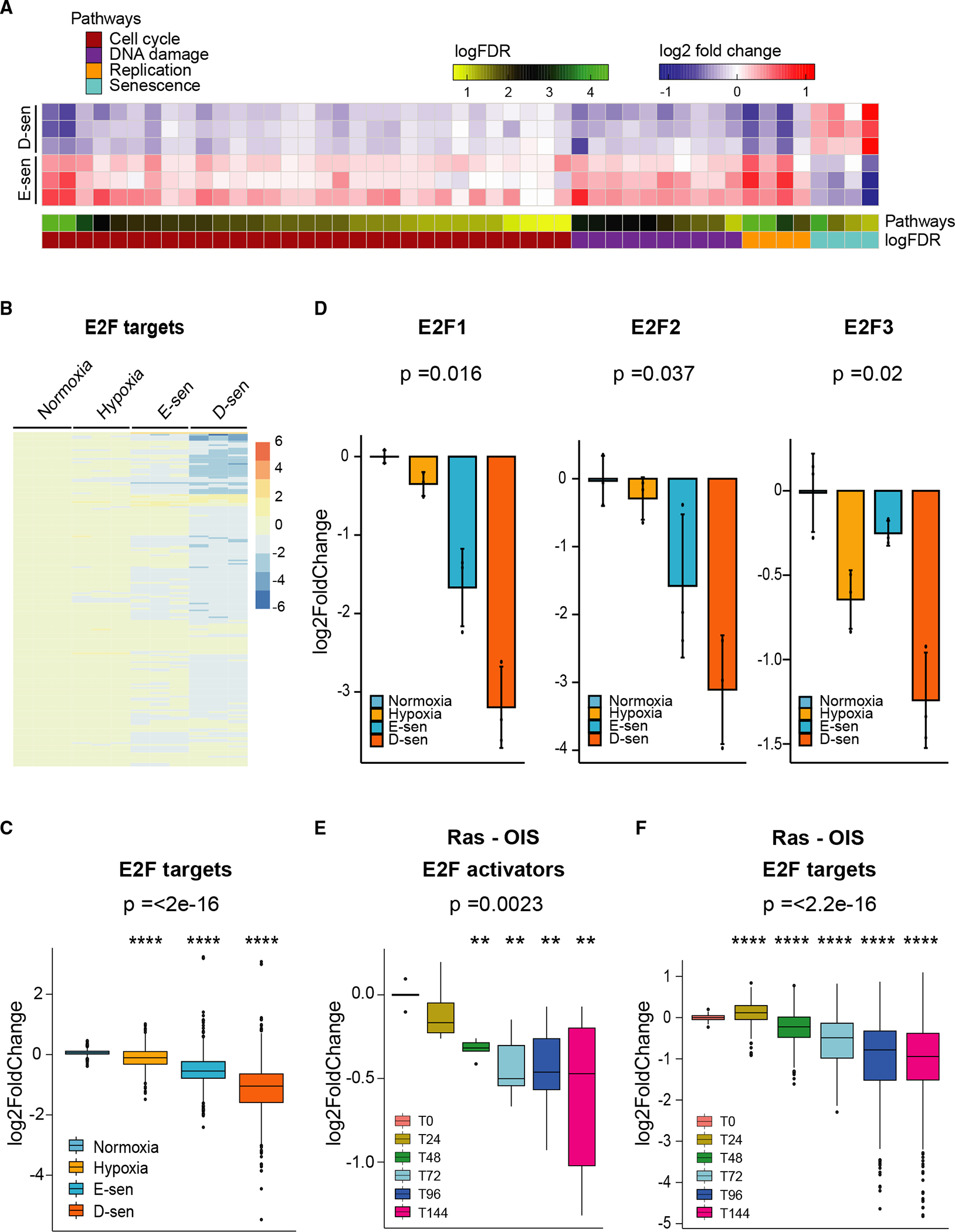
(A) RNA-sequencing data from β-gal-high cells from TGF-β-treated (5 ng/mL, 15 days) hypoxic and normoxic A549 cultures were evaluated for differential expression of 4 paracrine senescence signatures,21,23 45 cell-cycle (), DNA-replication (), and DNA-damage response () signatures (see Figure S3A). Heatmaps of gene set scores show significant differences in these pathways in deep-senescent cells (D-sen; β-gal-high-TGF-β-treated hypoxic cells) compared with early-senescent cells (E-sen; β-gal-high-TGF-β-treated normoxic cells). The scales for log2 fold change and log false discovery rate (FDR) are provided.
(B) E2F target gene expression is reduced in D-senescent cells. Heatmap shows gradual decline in E2F-target genes in E-sen and D-sen A549 cells compared with untreated normoxic and hypoxic cells; biological replicates.
(C) The bar graph (mean ± SD) provides the log2 fold change in E2F target genes quantified from samples shown in (B); biological replicates; ****p < 2.5e−16 was calculated using ANOVA.
(D) Activator E2Fs, E2F1, E2F2, and E2F3 are suppressed in D-senescent cells. Activator E2F expression in untreated normoxic, hypoxic, E-sen, and D-sen A549 cells is shown; biological replicates; p values were calculated using ANOVA.
(E) The dosage of activator E2Fs gradually decreases during Ras oncogene-induced senescence (Ras-OIS). Analysis of a time-series RNA-sequencing dataset {0, 24, 48, 72, 96, and 144 h] from human lung fibroblasts (WI-38) undergoing OIS with RasV12 (GEO: GSE112084) is shown; biological replicates; **p = 0.0023 was calculated using Kruskal-Wallis test.
(F) The bar graph (mean ± SD) shows gradual decline in E2F target genes during Ras-OIS in the samples described in (E). The y axis shows log2 fold change in expression; biological replicates; ****p < 2.2e−16 was calculated using ANOVA. See also Figure S3 and Table S1.
The prototypical cell-cycle regulator E2F1 is suppressed by TGF-β.46 It is significantly repressed in E-senescent cells but further suppressed in D-senescent cells, as were other activator E2Fs (E2F2 and E2F3) (; Figure 2D). Repressor E2F expression (E2F4, E2F5, E2F6, and E2F7) remained unaltered across these samples (Figure S3B). Activator E2Fs were also suppressed by TGF-β in hypoxic HepG2 and TE4 cells (; Figure S3C).
The gradual decline in the dosage of activator E2Fs and their targets was also observed during Ras oncogene-induced senescence (Ras-OIS), which is partially dependent on TGF-β signaling.21 Analysis of published transcriptomic data following oncogenic Ras-OIS of human lung fibroblasts47 showed a gradual decline in activator E2Fs (E2F1 and E2F3) (; Figure 2E) and E2F targets (; Figure 2F) as cells progress toward senescence.
These findings suggest that a gradual decline in the dosage of activator E2Fs and E2F targets driving critical cellular pathways may contribute to the intermediate senescence states as cells progress from a proliferative state into E- and subsequently D-senescence.
Depletion of E2F phenocopies deep senescence
We then determined whether TGF-β-mediated E2F suppression contributes to the strong senescence phenotype observed in D-senescence. Small hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) against E2F1 suppressed E2F1 by 87.0% ± 0.004% and 97.1% ± 0.001% compared with controls (Figure 3A). E2F1 knockdown (KD) led to the acquisition of a large flattened morphology and increased β-gal positivity (Figure 3B). E2F KD did not reliably increase binucleated cells. However, it significantly increased the multinucleated cell fraction irrespective of oxygen concentration (Figures 3C–3E). Thus, E2F suppression alone phenocopies the multinucleation observed in TGF-β and hypoxia-induced D-senescence, supporting a critical role for E2F in this phenomenon.
Figure 3. Suppression of E2F phenocopies in deep senescence.
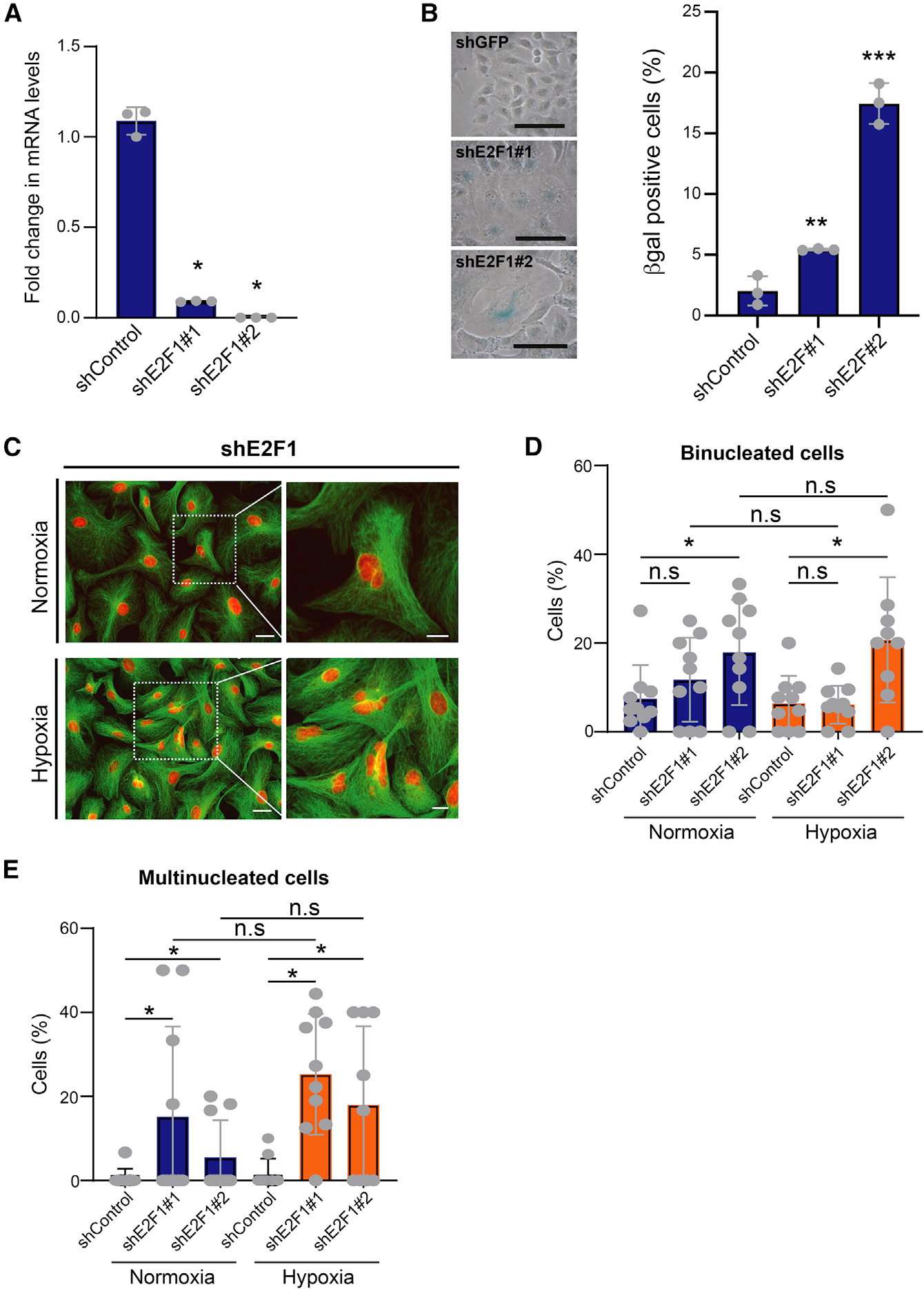
(A) qPCR of relative E2F1 mRNAs in cells infected with two different E2F1 shRNAs. shGFP was used as control; biological replicates. Data are represented as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05 by Student’s t test.
(B) E2F1 suppression induces senescence. E2F1-KD A549 cells were stained for β-gal activity. Left: photomicrographs of β-gal-stained control and E2F1-KD cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. Right: percentage of β-gal-positive cells for each condition; biological replicates. Data are shown as mean ± SD; **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
(C) E2F1 knockdown increases multinucleated cells irrespective of oxygen concentration. Control and E2F1-KD A549 cells were stained with DAPI (red) and tubulin (green). Left: photomicrographs of cells cultured under hypoxia and normoxia. Higher magnification of highlighted multinucleated cells is shown on the right. Scale bars: 50 μm (low magnification) and 20 μm (high magnification). Representative data from two biological replicates are shown.
(D and E) Bar graphs show percentage of binucleated (D) and multinucleated (E) E2F-KD A549 cells grown under hypoxia and normoxia. shGFP is shown as control; biological replicates. Mean ± SD was calculated from imaging 10 random fields. *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test; n.s, not significant. See also Table S3.
A 14-gene SASP is elevated in D-senescent cells
SASP is a key feature of senescence. Genes contributing to SASP activity are highly dependent on senescence-inducing stimuli.10 To determine whether SASPs associated with E- and D-senescence differ, we compared RNA-seq data from these two populations ( biological replicates). The expression of 14 targets, including the inflammatory cytokines CCL2, CCL5, CCL7, IL1A, IL1B, and IL32 (and SCG2, INHBA, INHA, WNT7A, CSF2, TNFRSF11B, GREM1, and CMTM3), was increased by >2-fold in D-senescent cells (Benjamini-Hochberg corrected ; Figures 4A, S4A, and S4B).
Figure 4. Lung cancers with high 14-gene SASP exhibit an immune-suppressive microenvironment.
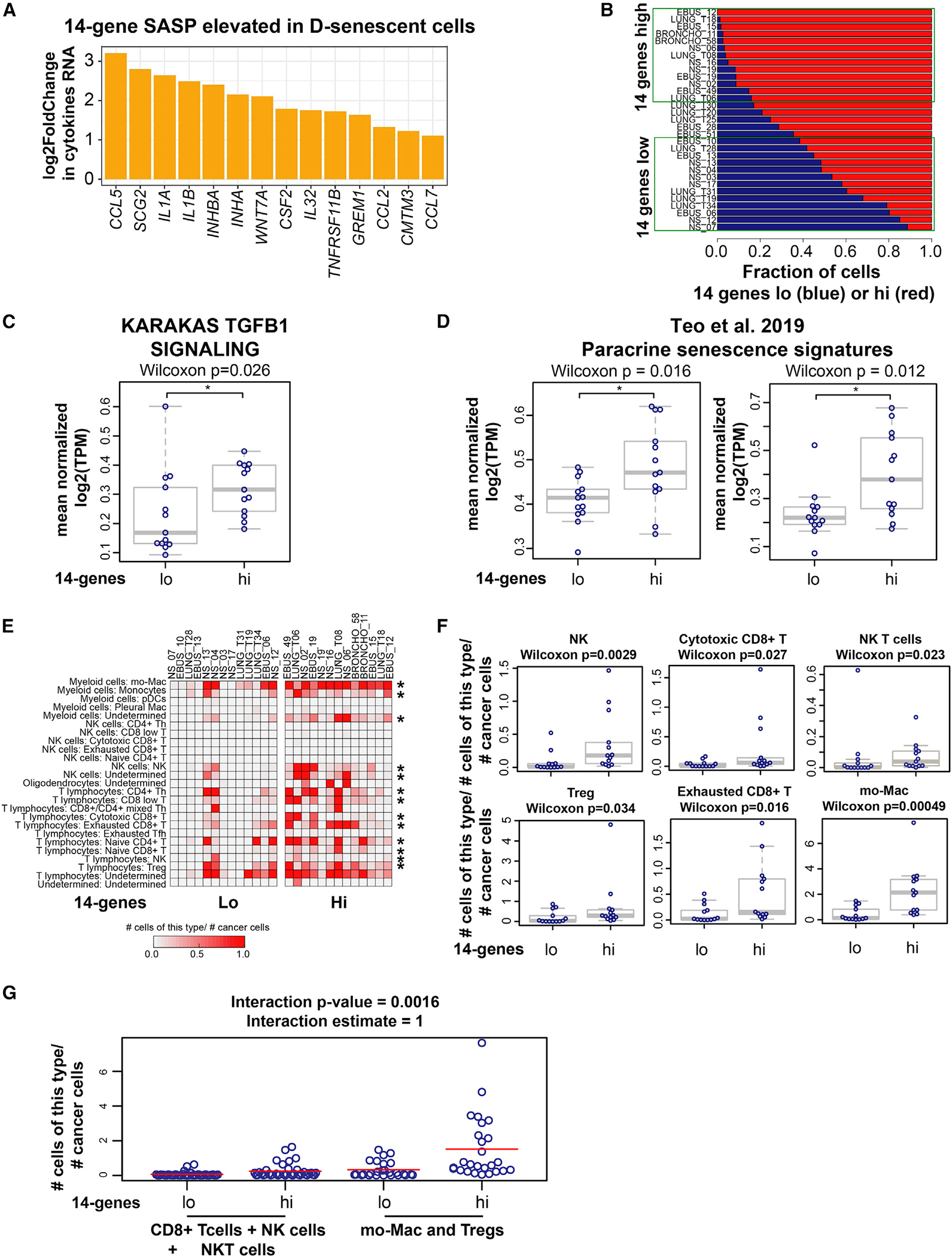
(A) A 14-cytokine SASP is elevated in deep-senescent cells. Bar graph shows log2 fold change in cytokines/growth factors constituting the 14-gene SASP elevated in D-senescent cells compared with E-senescent cells; biological replicates for each condition (see Figures S4A–S4C). Significantly different cytokines were selected based on Benjamini-Hochberg corrected and >2-fold differences in gene expression.
(B) Stratification of 31 treatment-naive metastatic lung cancers based on the fraction of tumor cells with high and low 14-gene metagene signature in each patient. Fractions of 14-gene low (blue) and 14-gene high (red) cancer cells in each patient are shown. We defined the top 13 tumors harboring >80% of tumor cells expressing a high 14-gene signature as “14 genes high” and the bottom 13 tumors with <60% of tumor cells expressing the 14-gene signature as “14 genes low” (marked within the green boxes).
(C) TGF-β signaling is significantly elevated in the tumor cell compartment of the 14-gene-high NSCLCs compared with 14-gene-low samples (*Wilcoxon ).
(D) Paracrine senescence signatures23 (paracrine/OIS48 and secondary senescence from time course/top overlap only [*Wilcoxon ]; secondary senescence from co-culture/OIS from co-culture and secondary senescence from time course/OIS from time course overlap only [*Wilcoxon ]) are elevated in 14-gene-high treatment-naive NSCLCs compared with 14-gene-low NSCLCs.
(E) Increased immune cell infiltration in lung cancers with higher fraction of tumor cells with high-14-gene expression. Quantification of each class of tumor-infiltrating immune cells (normalized to the number of cancer cells in each sample) across 14-gene-high and 14-gene-low lung cancers is shown. Asterisks mark the immune cell subtype significantly elevated in 14-gene-high lung cancers. *p < 0.05 was calculated using two-sample two-sided Wilcoxon test.
(F) Boxplots showing the fraction of indicated immune cell type residing within each lung cancer sample in 14-gene-high and -low groups. p < 0.05 was calculated using two-sample two-sided Wilcoxon test.
(G) Plot showing that the net increase in immune cells in the 14-gene-high NSCLCs is biased toward increased infiltration of immune-suppressive cell types (Mo-Macs and Tregs) compared with cytotoxic cells (cytotoxic CD8+ T cells + NK cells + NK-T cells). The linear model used to analyze these data are described in the STAR Methods. The interaction estimate shows a positive value of 1, indicating that the mean for 14-gene-high patients minus the mean for 14-gene-low patients is significantly greater for immune-suppressive cells than for cytolytic cells with an interactive p value of 0.0016. See also Figures S4 and S5.
Physiological hypoxia was shown to suppress SASP in cell culture and in normal tissues through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which suppresses mTOR-NF-κB signaling.49 We also observed mTOR activity being suppressed by hypoxia; however, it was further reduced in TGF-β/hypoxia-induced D-senescent cells (Figure S4C). Despite the robust suppression of mTOR, the 14-gene SASP is elevated in D-senescent cells, suggesting a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-independent SASP induction. The discrepancy between our observation and the results reported by van Vliet et al.49 could be reflective of differences in cell systems as well as the inducers used: hypoxia alone (in normal tissues)49 vs. hypoxia and TGF-β (in cancer) used in our experiments.
Lung cancers with high expression of 14-gene SASP exhibit an immune-suppressive microenvironment
To extend these findings to human cancer, we analyzed published single-cell RNA-seq data derived from treatment-naive metastatic lung adenocarcinomas.50 This study profiled changes in the cellular components of the TME (immune, endothelial, and stromal cells) during lung cancer progression.50 It included RNA-seq of 208,506 single cells from normal lung and metastatic lung cancer; 31,136 cells within this dataset were identified as malignant based on copy number variation.50 They were derived from 32 patient-derived lung cancers. Using canonical marker gene expression, cell lineages within tumors were annotated as stromal (fibroblasts and endothelial cells) and immune cells (T, natural killer [NK], B, myeloid, and mast cells).50
We stratified these lung tumors based on the cancer cell fraction expressing the 14-gene metagene signature: a lung cancer cell was defined to be 14-gene-low or 14-gene-high if the value of the 14-gene signature for that cell was below the 25th or above the 75th percentile, respectively, of the values of the 14-gene signature for all 31,136 malignant cells. For each patient, fractions of 14-gene-low (blue) and 14-gene-high (red) cancer cells were quantified (Figure 4B). We then classified the top 13 tumors harboring >80% of tumor cells expressing a high 14-gene signature as “14-gene-high” (stage IV, nine patients; stage IIIA, two patients; stage I, two patients) and the bottom 13 tumors (<60% of tumor cells expressing the 14-gene signature) as “14-gene-low” (stage IV, nine patients; stage IIIA, two patients; stage I, two patients) (Figure 4B). TGF-β signaling was significantly higher in tumor cells in the 14-gene-high tumors compared with the 14-gene-low tumors (Figure 4C). Consistent with Ras-OIS being partially dependent on TGF-β signaling,21 the 14-gene-high lung cancers showed significant overlap with lung cancers with high REACTOME Oncogene Induced Senescence signature (). Consistent with TGF-β being the most important SASP factor for paracrine senescence,21 paracrine senescence signatures23 were significantly elevated in the 14-gene-high tumors (Figure 4D).
Quantification of tumor-infiltrating cells across the 14-gene-high and 14-gene-low lung cancers showed no significant difference in myofibroblast- (Figure S4D) or tumor-derived endothelial cell (EC) infiltration (Figure S4D) between the two groups. However, there was extensive remodeling of the immune microenvironment (IME) in 14-gene-high lung cancers. There was increased infiltration of multiple immune cell types. This included those with cytolytic function (NK cells [], cytotoxic CD8+ T cells [], NK-T cells []; Figures 4E and 4F) and immune cells with immune-suppressive and tumor-promoting functions (T regulatory cells [Tregs] [], monocyte-derived macrophages [Mo-Macs] with immune-suppressive properties [],50 exhausted CD8+ T cells []; Figures 4E and 4F). We also observed increases in other immune cells, CD4+ Th (), naive CD4+ (), CD8+ low (), naive CD8+ (), monocytes (), and follicular B lymphocytes (), in the 14-gene-high lung tumors (Figure S4E). These findings show that elevated tumor cell-specific expression of D-senescence-associated 14-gene SASP correlates with highly complex remodeling of the IME in lung cancers with infiltration of immune cells of opposing activities (Figures 4E, 4F, and S4E).
We then determined whether the IME of 14-gene-high lung cancers is biased toward being immune suppressive or tumor suppressive by analyzing the ratios between NK and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and Tregs or Mo-Macs. We observed that the ratios of Tregs to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells () and exhausted CD8+ T cells to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (), as well as the ratios of Mo-Macs to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells () and Mo-Macs to NK cells (), were significantly higher in 14-gene-high lung cancers (Figure S5A), suggesting remodeling of the IME toward immune suppression in this subset of lung cancers.
We then investigated whether the net increase in immune-suppressive cell types (Mo-Macs + Tregs) is greater than the net increase in cytolytic immune cells (CD8+ T cells + NK cells + NK-T cells), thus skewing the increased immune infiltration observed in 14-gene-high non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) toward immune suppression. The mean for 14-gene-high patients minus the mean for 14-gene-low patients is significantly greater for immune-suppressive cells than for cytolytic cells with an interactive p value of 0.0016 (interaction estimate = 1). Thus, the net increase in immune cells in the 14-gene-high NSCLCs is biased toward increased infiltration of immune-suppressive cell types (Mo-Macs and Tregs) compared with cytotoxic cells (cytotoxic CD8+ T cells + NK cells + NK-T cells) (Figure 4G).
As a control, we also analyzed for differences in microenvironmental changes after stratifying these lung cancers based on high and low expression of the REACTOME SASP signature and other published SASP signatures and observed no significant differences in immune infiltrates between the two groups, suggesting the specificity of the 14-gene SASP elevated in D-senescent cells.
Kim et al., using a CellPhoneDB cell-cell interaction map, inferred significant interactions between Mo-Macs and tumor cells through interactions between TGF-β1 and TGF-β type II receptor (TGF-βR2), and TGF-β1 and the aVb6 complex, in these lung cancers.50 Consistently, we observed that Mo-Macs in the 14-gene-high lung cancers had elevated TGF-β1 expression compared with 14-gene-low samples (; Figure S5B); there was no difference in TGF-β expression in myofibroblasts across the groups (; Figure S5B).
These findings show that high tumoral expression of the distinct 14-gene SASP (elevated in the TGF-β/hypoxia-induced D-senescence) may represent an inherent program within a subset of lung cancers to promote an immune-suppressive microenvironment.
14-gene SASP-high non-small-cell lung cancers treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors exhibit poor clinical outcomes
To determine whether the SASP induced by a TGF-β-rich hypoxic TME would influence clinical outcomes, we analyzed the TCGA dataset from lung adenocarcinoma patients (TCGA_LUAD). Cox proportional hazards modeling showed that patients with a high 14-gene metagene signature exhibited poor overall survival (log rank ; Figure 5A); relapse-free survival in these patients was also poor, trending toward significance (log rank ; Figure S6A). TGF-β and hypoxia signaling pathways, as well as senescence signatures, were significantly elevated in the 14-gene-high group compared with the 14-gene-low group (Figures 5B and 5C, TGF-β signaling, Wilcoxon ; hypoxia signaling, Wilcoxon ; paracrine senescence, Acosta et al.,21 Wilcoxon ; Teo et al.,23 Wilcoxon ).
Figure 5. Lung cancers with high 14-gene SASP exhibit poor clinical outcome after ICI therapy.
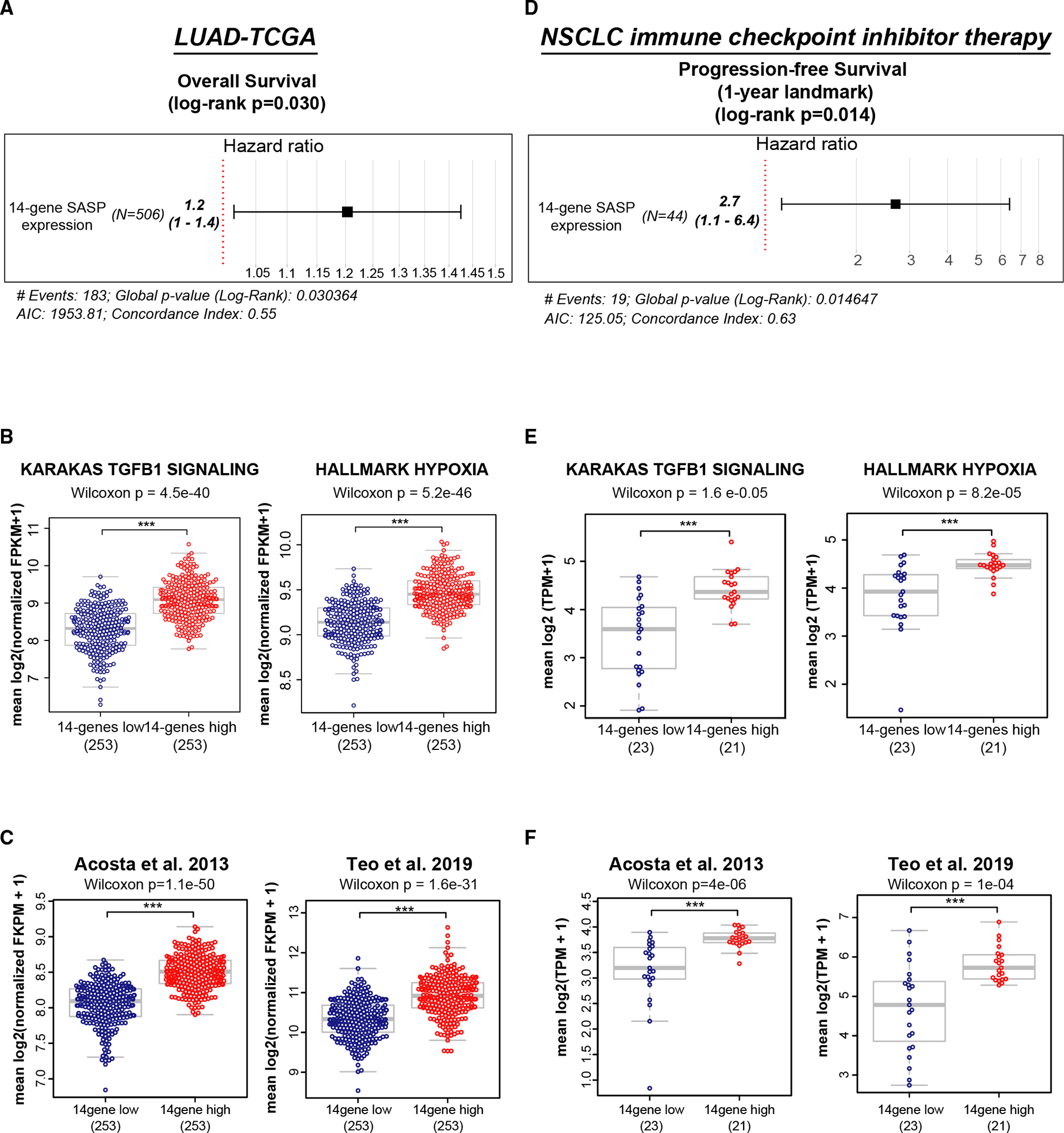
(A) Lung cancers from the TCGA dataset were stratified based on expression of the 14-gene SASP. High 14-gene SASP expression correlates with adverse clinical outcome by the Cox proportional hazards model applied to overall survival ().
(B and C) High (i.e., greater than median) 14-gene SASP correlates with (B) high TGF-β signaling (Wilcoxon ) and high hypoxia signaling (Wilcoxon ) and (C) high paracrine senescence signatures (Acosta et al.,21 Wilcoxon ; Teo et al.,23 Wilcoxon ).
(D) RNA-sequencing data from tumor samples collected from metastatic NSLC patients prior to initiation of ICI therapy. Cox proportional hazards model shows that high 14-gene SASP expression in pre-treatment samples correlates with poor PFS at the 1-year landmark (log rank ).
(E and F) High (i.e., greater than median) 14-gene SASP correlates with (E) high TGF-β signaling (Wilcoxon ) and high hypoxia signaling (Wilcoxon ) and (F) high paracrine senescence signatures (Acosta et al.,21 Wilcoxon ; Teo et al.,23 Wilcoxon ). See also Figure S6.
To address whether the 14-gene SASP, which induces an immune-suppressive TME, would adversely influence response to ICI therapy, we analyzed a cohort of NSCLC patients () receiving ICI therapy (Table S2). Samples in this study correspond to patients treated with anti-PD(L)1 (programmed death-ligand 1) therapy either as a single agent or in combination with other therapies. Progression-free survival (PFS) was as defined from the time of initiation of treatment with a PD(L)1 agent until the first evidence of clinical/radiographic progression. RNA-seq data from tumors collected prior to initiating ICI show that NSCLC patients expressing higher 14-gene SASP in their tumors exhibited poor PFS at the 1-year landmark (log rank ; Figure 5D). PFS was also poor across the entire follow-up period (mean, 316 days; range, 4 to 1,039 days) and trended toward significance (log rank ; Figure S6B). Further, TGF-β and hypoxia signaling and paracrine senescence signatures were significantly elevated in 14-gene SASP-high tumors (Figures 5E and 5F; TGF-β signaling, Wilcoxon ; hypoxia signaling, Wilcoxon ; paracrine senescence signatures, Acosta et al.,21 Wilcoxon ; Teo et al.,23 Wilcoxon ). Together, the 14-gene SASP expressed during TGFβ/hypoxia-induced D-senescence creates an immune-suppressive microenvironment that contributes to poor response to ICI therapy in NSCLC patients.
TGF-β induces a naturally occurring senescent cell state in an immune-competent mouse lung cancer model
To determine whether TGF-β/hypoxia-induced senescence and SASP in vitro represent a naturally occurring cell state in lung cancers and might be directly responsible for changing the IME, we turned to the Lewis lung carcinoma cell (LLC) immune-competent mouse tumor model.51 TGF-β-treated LLC cells undergo senescence in vitro (Figure S7A). TGF-βR2-KD in LLC cells (Figure 6A) reduces TGF-β-induced Smad3 phosphorylation (Figure S7B) but does not impair LLC proliferation in vitro (Figure S7C). β-gal staining of tumors identified senescence in 0.14% ± 0.12% (mean ± SD; range, 0.03%–0.38%) of tumor cells in the control tumors ( mice; 2 tumors/mouse). Senescent cells were present as either single cells or small clusters. This senescence phenotype was severely reduced in TGF-βR2-KD tumors (mean ± SD; 0.027% ± 0.02%; range, 0.003%–0.066%; Figure 6B; ). A raw intensity histogram of β-gal stain counts shifted from strong to weak from control to TGF-βR2-KD tumors (Figure S7D). p21 staining of the tumors showed a significant decline in the percentage of p21 positivity in shTGF-βR2 tumors compared with controls (Figure S7E). Quantification of western blot showed that the ratio of the senescence marker H3K9Me3 to the epithelial tumor cell marker E-cadherin (Figure 6C; H3K9Me3:E-cadherin ratio) was also reduced in the TGF-βR2-KD tumors compared with control tumors ().
Figure 6. TGF-βR2-KD in tumor cells suppresses senescence and immune cell infiltration in an immune-competent mouse lung cancer model.
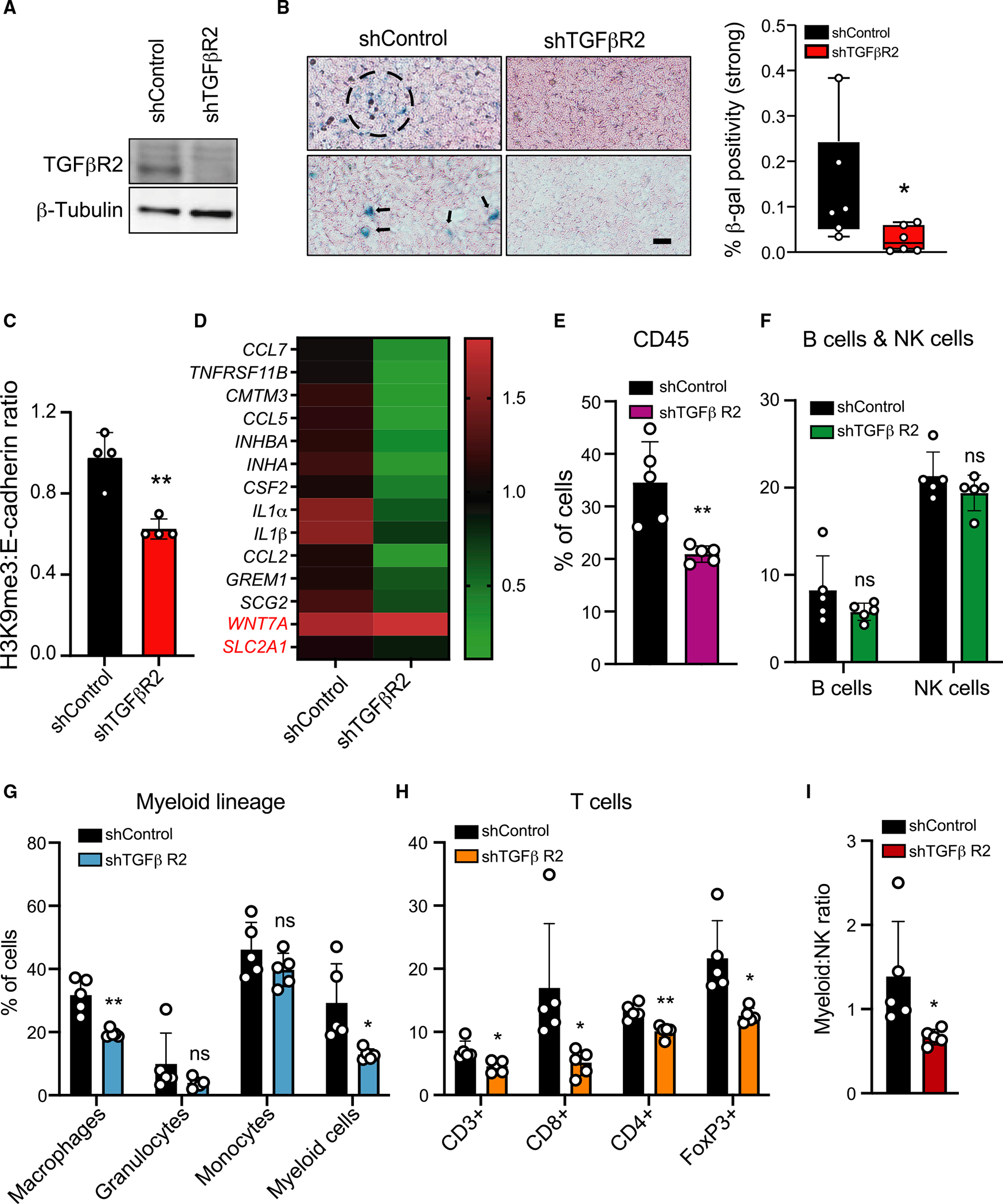
(A) Western blot showing knockdown of TGF-βR2 in LLC1. β-tubulin is shown as control.
(B) TGF-βR2-KD suppresses senescence in LLC tumors. shControl and TGF-βR2-KD LLC1 cells were inoculated into both flanks of C57BL/6 mice ( mice per group). Tumors resected after 14 days were stained for β-gal. Photomicrographs show β-gal-positive senescent cells present as single cells (arrows) or clusters (dashed circle) in two representative shControl tumors. Scale bar: 100 μm. Right: quantification of β-gal positivity in shControl and TGF-βR2-KD tumors; percentage of strong β-gal stain to total tissue area was computed and a Wilcoxon test was applied across the two conditions (*p = 0.026); tumors for each condition.
(C) The senescence marker H3K9Me3 is reduced in TGF-βR2-KD tumors. Quantification of western blot of proteins from shControl and TGF-βR2-KD tumors with antibodies against H3K9Me3 and E-cadherin. Bar graph shows the ratio of H3K9Me3:E-cadherin (H3K9Me3 expression in the epithelial tumor compartment) in tumors; tumors/condition. Bar graph shows mean ± SD. **p = 0.0021 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.
(D) SASP activity is reduced in TGF-βR2-KD tumors. RNA from shControl and TGF-βR2-KD tumors was analyzed for 14-gene SASP expression. Heatmap shows fold change in expression; shControl was set at 1; tumors/condition. IL-32 is not expressed in mouse cells.
(E–H) TGF-βR2-KD in tumor cells suppresses immune cell infiltration. Immune cells in shControl and TGF-βR2-KD tumors were quantified by FACS after staining for immune cell subtypes shown. The percentage of each immune cell type in shControl and TGF-βR2-KD tumors is shown. Significant decreases were observed in CD45+ cells (), CD3+ T cells (), CD8+ T cells (), CD4+ Tregs (), FoxP3+ Tregs (), macrophages (), and myeloid cells () in shTGF-βR2-KD tumors. Granulocytes, monocytes, B cells, and NK cells were not significantly altered (ns); tumors/condition. Bar graphs shows mean ± SD. The p values *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 were calculated by multiple unpaired Student’s t test.
(I) TGF-βR2-KD in tumors significantly reduced the ratio of myeloid:NK cells compared with shControl tumors; tumors/condition; *p = 0.04 calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. Also see Figure S7.
Of the 14 genes of the SASP, 12 were suppressed in TGF-βR2-KD tumors compared with controls (Figure 6D). WNT7A did not change and IL32 is not expressed in mice. We then quantified immune cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) to determine whether impairing TGF-β signaling in tumors would alter the IME. The TGF-βR2-KD tumors compared with controls exhibited significantly reduced immune infiltration of CD45+ cells (; Figure 6E).
Consistent with the extensive immune infiltration observed in 14-gene-high human lung cancers, the TGF-βR2-KD tumors, compared with controls, showed declines in multiple immune cell types: CD3+ T cells ), CD8+ T cells (), CD4+ Tregs (), FoxP3+Tregs (), macrophages (), and myeloid cells (). B cells, NK cells, granulocytes, and monocytes remained unchanged between the two groups (Figures 6F–6H). The ratios of myeloid:NK decreased from 1.39 to 0.67 (; Figure 6I) and Treg:NK decreased from 1.03 to 0.65 (; Figure S7F) in the control to TGF-βR2-KD tumors, respectively. Staining for granzyme B, a marker of cytotoxic lymphocytes,52 showed a decline in TGF-βR2-KD tumors compared with controls Figure S7G). Together, the results show that TGF-β signaling in the tumor cells themselves is responsible for inducing a senescence phenotype in LLC tumors and an ensuing immune-suppressive microenvironment.
DISCUSSION
Here, we identify a D-senescent state induced by TGF-β in a hypoxic microenvironment and a distinct 14-gene immune-suppressive secretory signature associated with this phenotype. This was confirmed in an immune-competent mouse lung tumor model, in which the prevalence of senescent cells, the 14-gene SASP, and an immune-suppressive phenotype were all dependent on tumor cell-specific TGF-β signaling. Indeed, patients with lung cancers harboring elevated expression of the 14-gene immune-suppressive SASP exhibit poor PFS on ICI therapy. Thus, senescence and the ensuing SASP induced by naturally occurring microenvironmental signals (TGF-β and hypoxia) may be exploited by tumors to promote anti-tumor immunity with clinical implications for patients receiving immune therapies.
The continuum of senescence
Senescence is a continuum of heterogeneous states with variable SASP, highly dependent on the inducer. We show that TGF-β-induced senescence states are dependent on ambient oxygen concentrations and range from E-senescence to D-senescence, which is associated with irreversibly arrested multinucleated cells. β-gal, p21, and H3K9Me3 levels were not able to differentiate between E- and D-senescence. Additional evaluation of nuclear/cytoplasmic architecture, cell-cycle reentry, and drug sensitivity identified the different degrees of senescence induced by TGF-β under varying oxygen concentrations.
We previously reported that TGF-β-treated normoxic cells exhibit cytokinesis failure resulting in binucleated cells that eventually divide, giving rise to daughter cells, which experience chromosome segregation defects resulting in genomic instability.53 In contrast, D-senescence induced by TGF-β under hypoxia is truly irreversible. While E-senescence may contribute to tumorigenesis through resumed proliferation of cells with genomic instability, we hypothesize that D-senescence mediates its effect primarily through a potent SASP. From a mechanistic standpoint, declining dosage of activator E2Fs and E2F-dependent processes may contribute to the dynamic continuum of senescence, suggesting the need for tight regulation of its levels for maintenance of cellular homeostasis.
TGF-β in TME induces senescence in cancer
TGF-β contributes to senescence during development35 and to Ras-OIS,22 suggesting that the TGF-β-rich TME may induce senescence in at least a subset of cancer cells. We show that senescence/SASP observed in LLC tumors at baseline is indeed mediated through TGF-β in the TME. Although all tumor cells harbor TGF-βR2, senescence is likely to occur only in tumor cells residing within hypoxic pockets, which possibly safeguards/preserves the proliferating fractions within the tumors. Further, patient-derived lung cancers with high 14-gene SASP also harbor elevated TGF-β and hypoxic signaling and senescence signatures. These findings suggest that TGF-β in the hypoxic TME induces senescence, which may represent a physiologically occurring cancer cell state, which is advantageous for remodeling the microenvironment to evade immune surveillance and immune therapies.
Remodeling of the IME by the 14-gene SASP elevated in D-senescent cells
Many immune cells—macrophages, NK cells, CD8+ T cells, and CD4+ T cells—are attracted by the SASP to eliminate senescent cells in tumors expressing exogenous oncogenes.54 The SASP can also support an immune-suppressive environment to promote tumor progression through recruitment of myeloid cells, which suppress NK cells,18 or myeloid-derived suppressor cells that prevent CD4+, CD8+, and NK cell expansion.55 A publicly available well-annotated single-cell transcriptomic dataset50 enabled us to simultaneously interrogate the infiltration of >50 immune cell, fibroblast, and EC subtypes in patient-derived lung cancers expressing higher levels of the hypoxia/TGF-β-induced 14-gene SASP. It did not affect EC and fibroblast infiltration in these cancers but led to an IME biased toward an immune-suppressive phenotype.
SASP and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors
Senescence induction and SASP by drug treatment, manipulating oncogene addiction, or adoptive transfer of SASP-activated cells remodel the immune or vascular microenvironment and sensitize tumors to ICIs in mouse tumor models.56–59 Our analysis of patient-derived lung cancers suggests that elevated senescence and 14-gene SASP induced by the physiological microenvironmental factors TGF-β and hypoxia in a subset of tumors may contribute to remodeling of their IME, enabling them to mount resistance to ICIs. Collectively, this provides clinical evidence linking TME-induced senescence and SASP interfering with response to ICI therapy and identifies possible biomarkers for patient selection.
TGF-β secretion by stromal fibroblasts and immune cells contributes to immune exclusion in tumors,60–62 and TGF-β inhibitors, which suppress TGF-β signaling in the TME, promote immune infiltration and improve PD1/PDL1 therapy responses in mouse models.60,62 We show that, in addition to causing immune exclusion through its effect on non-tumor cells,60–62 TGF-β also creates an immune-suppressive environment through induction of a senescent tumor cell-driven SASP. Thus, TGF-β may function at multiple levels to create a tumor-permissive immune cell milieu.
In conclusion, TGF-β-rich hypoxic TME-induced senescence in a small fraction of tumor cells may represent an inherent cell state in cancers. The SASP associated with this cell-state transition is likely a major contributor to the composition of the tumor IME and response to ICIs. These observations are of significant interest, given the anticipated testing of TGF-β inhibitors in diverse human cancers.
Limitations of the study
Using cell culture and mouse and human studies, we show that senescence represents a naturally occurring cell state in cancers. This phenomenon needs to be validated with a larger cohort of mouse and human tumors using multiple markers that detect senescence in situ. Our findings raise the possibility that SASP might contribute to the heterogeneity in the IME within tumors. Spatial profiling of the IME around senescent cells in tumors is required to further evaluate the role of senescence in cancers. Finally, in human NSLCs, the 14-gene signature elevated in D-senescent cells is associated with increased senescence and TGF-β and hypoxic signaling; additional studies testing responses to ICI therapy in appropriate mouse tumor models in which TGF-β and hypoxia signaling is manipulated will provide direct evidence that the physiological senescence state in cancers indeed plays a role in ICI responses.
STAR★METHODS
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to Shyamala Maheswaran (maheswaran@helix.mgh.harvard.edu).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new reagents.
Data and code availability
RNA-seq data used for Figure 2 has been deposited at GEO and will be made publicly available as of the date of publication. The accession number is GEO: GSE223037 and listed in the key resources table.
This paper does not report original code.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE.
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Antibodies | ||
|
| ||
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-p21 | Santa Cruz | Cat#sc-397; RRID:AB_632126 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Histone H3 (tri methyl K9) | abcam | Cat#ab8898; RRID:AB_306848 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-E-cadherin | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#3195; RRID:AB_2291471 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-TGF-β Receptor II | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#79424; RRID:AB_2799933 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-β-Tubulin | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2146; RRID:AB_2210545 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-GAPDH | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#SAB2108266 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP | BioRad | Cat#170-6515; RRID:AB_11125142 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP | BioRad | Cat#1706516; RRID:AB_2921252 |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#7074; RRID:AB_2099233 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-tubulin | NOVUS | Cat#NB100-690; RRID:AB_521686 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p21 | abcam | Cat#ab188224; RRID:AB_2734729 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-granzyme B | ThermoFischer | Cat#14-8822-80; RRID:AB_468529 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD45 | Invitrogen | Cat#MCD4501; RRID:AB_10371770 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-Ly-6G | StemCell Technologies Inc | Cat#60031 PB.1 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-Ly6C | Life Technologies | Cat#17-5932-82; RRID:AB_1724153 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD11b | Life Technologies | Cat#53-0112-82; RRID:AB_469901 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-F4/80 | Life Technologies | Cat#17-4801-80; RRID:AB_2784647 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-B220 | Life Technologies | Cat#17-0452-82; RRID:AB_469395 |
| Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-CD3 | Life Technologies | Cat#11-0031-82; RRID:AB_464882 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD8 | BioLegend | Cat#100712; RRID:AB_312751 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD4 | Life Technologies | Cat#48-0041-82; RRID:AB_10718983 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-NK1.1 | BioLegend | Cat#108706; RRID:AB_313393 |
| Phospho-S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ser240/244) Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2215; RRID:AB_331682 |
| Phospho-S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ser235/236) Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#4858; RRID:AB_916156 |
| Phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) (236B4) Rabbit mAb | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2855; RRID:AB_560835 |
| Phospho-Akt (Ser473) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#4051; RRID:AB_331158 |
| Phospho-Smad3 (Ser423/425) (C25A9) Rabbit mAb | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#9520; RRID:AB_2193207 |
| Smad3 Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#9513; RRID:AB_2286450 |
|
| ||
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
|
| ||
| One Shot™ Stbl3™ Chemically Competent E. coli | Invitrogen | C737303 |
|
| ||
| Biological samples | ||
|
| ||
| Immunotherapy Clinical Cohort Collection | Patients treated with anti-PD(L)1 therapy either as single agent or in combination with other therapies between 2013 and 2019 at Massachusetts General Hospital | Umbrella sequencing protocol Massachusetts General Hospital #13-416 |
|
| ||
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
|
| ||
| Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1 | R&D | 240-B |
| SB431542 | Sigma Aldrich | S4317 |
|
| ||
| Critical commercial assays | ||
|
| ||
| Cellular Senescence Detection Kit-SPiDER-βGal | Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan | SG03 |
| Senescence Cells Histochemical Staining Kit | Sigma Aldrich | CS0030 |
| RNeasy Mini kit | Qiagen | 74106 |
| Quantikine ELISA Human/Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Canine TGFβ1 | R&D Systems | DB100C |
| SMARTer Ultra Ultra-Low-input RNA kit, version 4 | Clontech Laboratory | 012516 |
| Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit | Illumina | FC-131-1024 |
| ERCC RNA Spike-In Mix | ThermoFisher Scientific | 4456740 |
| KAPA SYBR® FAST Universal qPCR Kit | Kapa Biosystems | N/A |
| X-tremeGENE HP DNA transfection reagent | Roche Applied Science | 6366236001 |
| Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix | Applied Biosystem | 4367659 |
| CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay | Promega | G9243 |
| SuperScript™ III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix for qRT-PCR | Invitrogen | 11752-050 |
| HiSpeed Plasmid Midi Kit (25) | Qiagen | 12643 |
| Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit | Thermo Scientific | 23227 |
|
| ||
| Deposited data | ||
|
| ||
| RNA-seq data | This paper | GEO: GSE223037 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
|
| ||
| A549 | ATCC | CCL-185 |
| HepG2 | ATCC | HB-8065 |
| TE4 | ATCC | HB-207 |
| Patient derived lung cancer associated fibroblasts | Dr. Cyril Benes, Massachusetts General Hospital, MA 02129 | Hu et al.44 |
| LLC-1 | ATCC | CRL-1642 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
|
| ||
| Mice (C57/BL6) | Charles River Laboratories | CCM21211956 |
|
| ||
| Oligonucleotides | ||
|
| ||
| Primers used for Real-time PCR reactions | See Table S3 | N/A |
|
| ||
| Software and algorithms | ||
|
| ||
| FlowJo software | FlowJo | FlowJo-Win64-10. |
| Halo software | Indica Labs | https://indicalab.com/halo/ |
| R software | R core team, R foundation | https://www.r-project.org/ |
| Illustrator software (26.5) | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html |
| Photoshop software (22.3.0) | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html |
| Fiji software | ImageJ | https://imagej.net/software/fiji |
| TrimGalore | https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ | 0.43 |
| TopHat | https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/index.shtml | 2.1.1 |
| HTSeq | See Ref.63. | 0.6.1 |
| GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 software | GraphPad Software | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
| Bio Render | Bio Render software | CI24XNA2XR |
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
LLC tumor growth in mice
All animal experiments were performed according to the animal protocol (2010N000006) reviewed and approved by MGH Subcommittee on Research Animal Care. Mice were maintained under a 12 h light and 12 h dark cycle in the animal facility at MGH. One million LLC cells (LLC-shControl and LLC-shTGFßR2) were transplanted subcutaneously into the right and left flanks of six-week-old C57BL/6 (male) mice. Tumors were harvested at day 14. Tumor tissues were collected immediately, immediately weighed and processed to prepare a single-cell suspension for immune characterization. For immunohistochemistry and tissue-specific SA-ß-gal assay, tumor tissue sections were processed using formalin solution and OCT to snap freeze, respectively.
METHOD DETAILS
Cell culture
Human lung cancer cell line, A549 (p53 wildtype; p16 deleted), was grown in Dulbeccco’s modified medium (DMEM). Human liver cancer cell line, HepG2 (p53 wildtype; p16 wildtype), was grown in DMEM: F12 medium. Human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line, TE4 (p53 mutant), was grown in RPMI 1640 medium. Lewis lung carcinoma cells (LLC; mutant KRAS) were grown in ATCC-formulated DMEM. All the above cell lines were purchased from ATCC. Patient derived lung cancer associated fibroblasts (gift from Dr. Cyril Benes, Massachusetts General Hospital, MA 0212944) were grown in RPMI 1640 medium. All cell culture media described above were supplemented with 10% female fetal bovine serum and penicillin/streptomycin. To induce senescence, A549 and LLC cells were treated with 5 ng/mL TGFß (R&D Systems) for the time periods indicated in the figure legends. All cell lines were authenticated and tested for mycoplasma contamination.
Flow cytometry analysis and cell sorting
SA-β-galactosidase staining was performed using a Cellular Senescence Detection Kit-SPiDER-βGal (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, cells were incubated with Bafilomycin for 1 hour followed by SPiDER-βGal solution for 30 min. Cells were trypsinized and analyzed by flow cytometry (BD LSRFortessa Cell analyzer) and Flowjo software (FLOWJO, LLC). For cell sorting, samples were processed by BD FACSAria Fusion with 100 micron nozzle at 4°C.
Viral infection
Lentiviral short hairpin RNA constructs against E2F1 and the TGFß type II receptor (TGFßR2) were obtained from the RNAi Consortium shRNA Library at the Broad Institute and Sigma Aldrich, respectively. Conditioned medium containing infective lentiviral particles was generated by co-transfecting 3 μg of lentiviral vector, 3 μg of pCMV ∂8.91 and 1 μg pHCMV-VSV-G into 2 × 106 293T human embryonic kidney cells using X-tremeGENE HP DNA transfection reagent (Roche Applied Science). Supernatants were collected 48 hours after transfection and filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane (Millipore). The cells were directly infected using 8 μg/mL of polybrene.
Target sequences against each gene within the lentiviral short hairpin RNA constructs are shown below:
TGFßR2 KD:
shControl: CCTAAGGTTAAGTCGCCCTCG (Addgene: 136035)
shTGFßR2: GCTCGCTGAACACTACCAAAT (Sigma Aldrich: TRC0000022626 NM_009371.2–20091c1)
E2F1 KD (RNAi Consortium shRNA Library at the Broad Institute)
shE2F#1: TAACTGCACTTTCGGCCCTTT
shE2F#2: CATCCAGCTCATTGCCAAGAA
qPCR
RNA was isolated using RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen) and mRNA quantitation was performed using SYBR Green in an ABI PRISM 7500 sequence detection system with 96-block module and automation accessory (Applied Bio-system). GAPDH was used as an internal control. All samples were analyzed in triplicate. The primer sequences are listed in the Table S3.
Western blot
Antibodies used were against the following proteins: p21 (Cat #: sc-397; Santa Cruz), H3K9Me3 (Cat #: 8898, Abcam), E-cadherin [Cat #: 3195s, Cell Signaling Technology (CST)], TGFß type II receptor (TGFßR2) (Cat #: 79424s, CST), β-Tubulin (Cat#2146, CST) and GAPDH (SAB2108266, Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were lysed in Laemmli buffer [150 mM Tris, pH6.8/3.75% SDS/15% glycerol/5% 2-Mercaptoethanol/0.01% brilliant blue], or RIPA lysis buffer [20 mM Tris, pH8.0 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM NaF, 0.1% SDS, 1% Nonidet P-40, 1X protease inhibitor mixture (Roche)]. Lysates were run on SDS-4–15% polyacrylamide gels (Bio-Rad) and transferred onto Nitrocellulose membrane (Invitrogen). Secondary antibodies used were goat anti-rabbit IgG (Cat #: 170–6515, BioRad) and goat anti-mouse IgG (Cat #: 1706516, BioRad). Immunoblots were visualized with a Western Lightning Plus chemiluminescence kit (PerkinElmer).
LLC tumors harvested from mice were lysed in RIPA Buffer (Cat #: BP-115X, Boston BioProducts) supplemented with Halt™ Protease inhibitor cocktail (Cat #: 78425, Thermo Scientific). Protein concentration was determined using Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (Cat#: 23227, Thermo Scientific). Protein lysates (10 μg per sample) were separated on SDS/4–15% polyacrylamide gels (Bio-Rad) and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Invitrogen). After blocking with 5% BSA buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, membranes were incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C, followed by the relevant HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (Cat#: 7074; CST) and visualized using Clarity Western ECL Substrate (BIORAD) and G box (Syngene).
Proliferation and drug resistance assays
For drug resistance assays, cells (5 × 103) were plated in individual wells of a 96-well plate (n = 96) and incubated overnight. The next day, drugs were added to each well and cell viability was evaluated on day 3. Briefly, 80 μL CellTiter Glo solution (CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay; Promega) was added into each well. Plates were then incubated for an additional 15 min at room temperature and luminescence was determined. The cell counts for 3 wells/time-point were averaged for each group and the data was used to derive growth curves.
For evaluating cell proliferation following TGFßR2 knockdown, shControl and shTGFßR2 knockdown cells (1,000 cells/well) were seeded in a 96-well plate in quadruplicates in 100 μL of media. Viability was measured using CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay was performed as described above at days 0, 3 and 5.
Staining procedures
a). Senescence associated (SA)-beta-galactosidase staining:
SA ß-galactosidase staining was performed using the Senescence Cells Histochemical Staining Kit (Cat # CS0030; Sigma-Aldrich). Briefly, cells were fixed and incubated with freshly prepared staining solution overnight according to manufacturer instructions. The percentage of positively stained cells was determined by counting ten random fields. Images of representative fields were captured under 200X magnification.
For SA-beta-galactosidase staining of tumors, samples were immediately frozen in OCT solution at −80°C and sections of 4 μm were prepared. Slides were either frozen or immediately proceeded for senescence-associated SA-β-gal staining, which was performed according to manufacturer’s instructions. Counter staining was performed using Eosin Y (Alcohol-based, Cat #: HT110116, Sigma Aldrich). Slides were mounted with DPX mounting media (Cat # 06522, Sigma Aldrich). The percentage of positivity was determined by counting ten random fields. Images of representative fields were captured under 10x magnification.
We also acquired raw intensity histogram of ß-gal stain counts of the control and shTGFßR2 LLC tumors by taking all pixels in the color deconvolved ß-gal images. We then removed the masked regions (debris) and white pixels (glass) and normalized them by the total number of pixels within each image (to remove image size bias).
b). Immunofluorescence staining:
Cells were plated overnight in a 4-well chamber slide (Millipore) coated with poly-L-lysine (Sigma), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and washed with PBS. Fixed cells were then permeabilized with 0.5% TritonX100 in PBS, blocked with 5% BSA, and stained with an anti-H3K9Me3 antibody (Cat #: 8898, Abcam), anti-tubulin antibody (Cat #: NB100–690, NOVUS) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Coverslips were mounted with anti-fade agent, Prolong with DAPI (Invitrogen). Photomicrographs were taken with the NIKON 90i microscope or with the confocal Zeiss LSM170. Analysis and quantification of the mitotic events of interest were performed with ImageJ software (NIH).
c). Immunohistochemistry:
Paraffin-embedded tissue sections from shControl and shTGFßR2 tumors were placed in a dry incubator at 65°C for 1 hour and dehydrated by the following treatments: xylene (3 min × 2), 100% Ethanol (2 mins ×2; 70% Ethanol (2 mins), 50% Ethanol (2 mins), 30% Ethanol (2 mins), dH2O (3 mins), TBST (3 mins). For antigen retrieval, slides were semi-dried and placed in 1x citrate buffer (AP-9003–500, thermo scientific) and placed inside a pressure cooker for 20 mins at a low-pressure program (Cuisinart electric cooker). Slides/sections were then cooled at room temperature and washed once with dH2O. Sections were marked with a hydrophobic pen and blocked with BLOXALL solution (SP-6000, Vector labs) for 15 mins. Sections were then washed once with TBST for 1–2 mins and incubated with the following primary antibodies at the given concentration in antibody diluent solution (S0809, Dako) for 1 hour: anti-p21 (1:250, ab188224, Abcam); anti-granzyme B (1:200, 14-8822-80, ThermoFischer). Sections were washed with TBST (2 mins ×2) and incubated with respective secondary antibodies (anti-rabbit RTU, K4003, DAKO, for p21, and anti-rat for Granzyme B) for 30 mins. Sections were then washed with TBST (2 mins × 2) and incubated with DAB solution (NovaRED substrate kit, SK-4800, Vector labs) for 8–10 mins. Counterstaining was performed using Hematoxylin for 15 secs, followed by tap water washes until clear. Finally, the sections were dehydrated with increasing ethanol conc in reverse order of dehydration provided above and mounted with mounting media (ProLong Diamond antifade mountant, P36965, Invitrogen).
ELISA for TGFß1
Supernatants from CAF1 and CAF2 cultured in RPMI 1640 with 10% FBS and 1%Pen-Strep was harvested and determined for the levels of TGFß1 using Quantikine ELISA Human/Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Canine TGFß1 (Cat No. DB100C, R&D Systems) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. RPMI 1640 1640 with 10% FBS and 1%Pen-Strep was used to determine the basal levels of TGFß1 in the media.
Quantification of SA ß-galactosidase stains
Images were acquired at 10x on an inverted Nikon Ti-S microscope. White balancing was applied to all images using the ImageJ plugin by Vytas Bindokas and Patrice Mascalchi. Images were then quantified using Halo software (Indica Labs) Area Quantification module. Color deconvolution was performed to isolate blue beta-gal signal from pink eosin. Pixels with strong blue staining were identified using a global intensity threshold. The output data table was analyzed using R. The percentage of strong beta-gal stain to total tissue area was computed and a Wilcoxon test was applied across the two conditions, shcontrol and shTGFβR2.
Quantification of immune infiltration into LLC tumors
Tumor pieces were washed with PBS to remove excessive blood and were minced with a scalpel. Tissue digestion was performed with collagenase/hyaluronidase cocktail (Cat #07912: Stemcell Technologies) in DMEM medium at 37°C on a rocker for 1 h. The tissue solution was then passed through a 70 μm filter to obtain a single-cell suspension. Single-cell suspensions were stained with specific monoclonal antibodies (primary antibodies directly conjugated) to assess the phenotype and diluted 1:200. The antibodies used were: CD45 (Cat #: MCD4501, Invitrogen); Ly-6G (Cat #: 60031PB.1, StemCell Technologies Inc); Ly6C (Cat #: 17-5932-82, Life Technologies), CD11b (Cat #: 53-0112-82, Life Technologies); F4/80 (Cat #: 17-4801-80, Life Technologies), B220 (Cat #: 17-0452-82, Life Technologies), CD3 (Cat #: 11-0031-82, Life Technologies), CD8 (Cat #: 100712, BioLegend), CD4 (Cat #: 48-0041-82, Life Technologies), NK1.1 (Cat #: 108706, BioLegend), FoxP3 (Cat #: 17-4801-80, Life Technologies). For flow gating, we used isotype controls of fluorescence (Cat #s: 17-4321-81, 12-4714-42 and 12-4888-81, Life Technologies). Samples were acquired on a BD Fortessa. Data were analyzed using FlowJo software.
The quantification of each immune cell type was done by FACS sorting of a total of 10, 000 cells following enzymatic digestion of control and shTGFßR2 tumors and staining of dissociated cells with antibodies described above. The program then removed cell doublets from the analysis and the number of positives were obtained as a percentage of each immune cell type present in the tumor.
RNA sequence and gene set enrichment analysis
A549 cells were incubated under either normoxia or hypoxia in the presence of TGFß for 15 days.
Cells were stained with SPiDER-βGal and sorted into βGal-high and ß-gal-low groups.
We had 3 biological replicates for each condition shown below:
| Condition | β-Gal | TGFβ treatment (days) |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Hypoxia | 0 | |
| Hypoxia | High | 15 |
| Normoxia | 0 | |
| Normoxia | High | 15 |
According to the manufacturer’s protocol, amplified cDNA was then generated using the SMARTer Ultra Ultra-Low-input RNA kit, version 4 (Clontech Laboratory) followed by Nextera® XT DNA Library Preparation kit (Illumina) for sample barcoding and fragmentation. Briefly, 1 μL of a 1:50,000 dilution of ERCC RNA Spike-In Mix (Thermo Fisher) was added to each sample. First-strand synthesis of RNA molecules was performed using the poly-dT-based 3′-SMART CDS primer II A (Clontech) followed by extension and template switching by the reverse transcriptase. The second strand synthesis and amplification polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was run for 18 cycles, and the amplified cDNA was purified with a 1× Agencourt AMPure XP bead cleanup (Beckman Coulter). The Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation kit (Illumina) was used for sample barcoding and fragmentation according to the manufacturer’s protocol. One nanogram of amplified cDNA was used for the enzymatic tagmentation, followed by 12 cycles of amplification and dual-index barcoding of individual libraries. PCR product was purified with a 1.8× Agencourt AMPure XP bead cleanup (Beckman Coulter). To validate and quantitate the Libraries, a quantitative PCR using the KAPA SYBR® FAST Universal qPCR Kit (Kapa Biosystems) was performed. The individual libraries were pooled at equal concentrations, and the pool concentration was determined using the KAPA SYBR FAST Universal qPCR Kit. The pool of libraries was subsequently sequenced on a NextSeq (Illumina).
We compared the RNA-seq expression of Hypoxic B-Gal High vs Normal B-Gal High samples using the differential analysis tool DESeq2 (9). Low expression genes (i.e. those with a sum total read count <10 across samples) were removed from all downstream analysis. Benjamini-Hochberg correction was used to correct for multiple hypothesis testing. Gene read counts were regularized log-transformed for further downstream visualization and analysis. Broad GSEA functional enrichment of the GO biological process gene sets collection from MSigDB v6.2 based on log2 fold change pre-ranked gene lists were determined using the standalone gsea2–2.2.2.jar tool (parameters: 10,000 permutations, minimum gene set size = 15) (1,2). Enriched gene sets with a multiple hypothesis test corrected p-value of less than 0.25 were considered significant.
Identification of gene patterns
Broad GSEA functional enrichment of the hypoxia vs normal (ß-gal high) RNA-seq log2 fold changes was performed. We focused on the enrichment of 45 selected GO biological process gene sets associated with cell cycle, DNA replication and DNA repair. The leading-edge genes across the selected 45 gene sets were collected yielding a list of 840 genes. The leading-edge gene sets were visualized in heatmap format colored by the appropriate gene specific hypoxia vs normal t-statistic.
Motif enrichment
Lists of predicted transcription factor motif associated gene sets were collected from regulatory target collection 3 found in MSigDB (v5.2). Using a hypergeometric overlap calculation, we were able to identify the sets of motifs significantly enriched in the 3 expression gene patterns defined previously. Each enrichment was calculated relative to all expressed genes as the background and the p-values were corrected for multiple hypothesis testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Significant motif enrichments were defined using an FDR<0.1 threshold. All statistical analyses and plots were done in R [13].
Differential cytokine expression analysis
A full list of genes associated with GO Cytokine activity was downloaded from MSigDB (v6.2). We calculated fold changes across replicates between ß-Gal high and untreated for hypoxia and normal conditions using the DESeq2 r-log transformed expression data. Differential expression between fold changes in early and deep senescent cells was performed using a Student’s T-test. Multiple hypothesis corrected p-values (FDR) were obtained using the Benjamini-Hochberg correction. Significant genes were identified with an absolute fold change ≥1 and an FDR<0.1. Differential expression results were visualized using a volcano plot and fold changes of up-regulated cytokine activity genes are visualized as a bar plot.
Activator E2F- and E2F target gene expression analysis
Reads from RNA-seq data described above were first cleaned using Trim Galore (v0.4.3) (https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore), and the trimmed reads were then aligned to human reference genome (hg19) using TopHat2 (v2.1.1).64 Gene counts was determined using HTSeq (v0.6.1).63 Quantile normalization and batch effect correction were performed using package RUVSeq (v1.24.0).65
For RAS oncogene induced senescence (RAS-OIS) time series data (6 time points (0, 24, 48, 72, 96 and 144 h) for 2 biological replicates), raw Affymetrix HTA 2.0 array intensity data were download from the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) accession GEO: GSE112084.47 Data were imported into R (v4.0.3) and processed as described in.47 Briefly, data were normalized using the robust multi-array average normalization approach implemented in package oligo (v1.54.1), and internal control probe sets and lowly expressed probe sets (lower than the 4th expression decile) were removed, and finally batch effects were corrected using the sva (v3.38.0) package.
E2F target genes were collect from the Hallmark_E2F_Targets gene set in Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) v7.5.1.66,67 Statistical analyses were performed to compare E2F genes and E2F targets expression across different time points/conditions (detailed methods were described in Figures), and plots were generated using the ggplot2 (v3.3.5) package.
Analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data from patient-derived lung cancers
Lung scRNA-seq data was downloaded from GEO GSE131907. To determine cell type, we used the “Cell_subtype” column of the file “GSE131907_Lung_Cancer_cell_annotation.txt”. We considered cells with “Cell_subtype” equal to “Malignant cells”, “t1”, “t2”, or “t3” to be cancer cells. Expression of the 14-gene SASP signature in the TCGA LUAD dataset was defined as the mean over the 14 genes of the log2 (normalized FPKM + 1).
The Cox proportional hazards model was fit and plotted using the ggforest function of version 0.4.6 of the survminer R package. Other plotting and statistical tests were implemented using base R version 3.1.2 or 3.6.1. We normalized the log2 expression data downloaded from GEO GSE131907 as follows: For each cell, we calculated the average log2 expression level over all genes. We called the average of all those averages the global average. For each cell, we then subtracted the average log2 expression level for that cell from the log2 expression levels for that cell and added the global average to the log2 expression levels for that cell.
To investigate whether the increased presence/infiltration of immune cells in the 14-gene high NSCLC samples compared with the 14-gene low samples is skewed towards a greater increase in immune suppressive cells than cytolytic immune cells creating a net balance towards immune suppression, we fit the following linear model to the data:
in which is (number of cells of a given immune cell type)/(number of cancer cells), is 1 if the datum measures the immune suppressive cells, 0 if it measures cytolytic immune cells, and is 1 if the datum is from a 14-gene high patient, 0 if it’s from a 14-gene low patient. The terms are determined by the model fitting algorithm so that the model best fits the data. This analysis shows that the increased presence of immune cells in the 14-gene-high NSCLC samples is biased towards increased infiltration of the immune suppressive mo-Macs compared with the cytotoxic CD8+ cells.
Immunotherapy clinical cohort collection
All patients in the clinical cohort were consented through the IRB-approved umbrella sequencing protocol Massachusetts General Hospital #13–416. Samples in this study correspond to patients treated with anti-PD(L)1 therapy either as single agent or in combination with other therapies between 2013 and 2019. Best overall response was assessed by RECIST v1.168 using standard of care clinical imaging (or in a subset of cases, imaging obtained as part of a clinical trial protocol). Progression free and overall survival were defined from the time of treatment start with a PD(L)1 agent until the first evidence of clinical/radiographic progression or death, respectively, and censoring was based on the date of last follow-up.
Immunotherapy cohort RNA-seq
RNA-Seq was performed at the Genomics Platform of the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT as described previously.69,70 In brief, RNA was extracted from FFPE specimens using the Qiagen AllPrep DNA/RNA Mini Kit (cat# 80204), followed by library preparation and sequencing using the TCap (Transcriptome Capture) protocol (genomics.broadinstitute.org/products/whole-transcriptome-sequencing). RNA-Seq data was processed using the GTEx RNA-Seq pipeline (GTEx Consortium, 2020) with use of the GENCODE v19 reference transcriptome, followed by quality control evaluation using the RNA-SeQC2 pipeline {Graubert, 2021 #111} GTEx Consortium, 2020). Sample QC was assessed via the associated quality metrics in the pipeline, median exon coefficient of variation (CV) and number of genes detected, with outliers being excluded from further analysis.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
All statistical analyses were performed using R or GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 (GraphPad Software). Detailed information about statistical analysis, including statistical tests performed to determine p values and Mean ± SD is provided in figure legends. Sample size (the number of animals or cells), the number of technical replicates, definitions of center and dispersion, and statistical methods for individual experiments were given in the respective figure legend, methods, and results.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
TGF-β under hypoxia induces irreversible deep senescence with a 14-gene SASP
Deep senescence is a naturally occurring immune-suppressive cell state in cancer
NSCLC patients with high 14-gene SASP exhibit poor clinical outcome after ICI therapy
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank L. Libby for technical support. We thank Drs. Demehri, Dyson, Zou, Motamedi, Sen, and Mostolovsky for critical comments. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (2RO1CA129933 to D.A.H., 2U01EB012493 to D.A.H. and S. Maheswaran, R01CA240924 to D.T.T., U01CA228963 to D.T.T.), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (to D.A.H.), the NCI K99 Award for Outstanding Early-Stage Postdoctoral Investigators (K99CA245897 to A. Ravi), the ESSCO Breast Cancer Research Fund (to S. Maheswaran), and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (to D.A.H. and S. Maheswaran). Funding for the clinical data in this study was provided by a Stand Up to Cancer-American Cancer Society Lung Cancer Dream Team Translational Research grant (grant SU2C-AACR-DT17-15). Stand Up to Cancer is a program of the Entertainment Industry Foundation. Research grants are administered by the American Association for Cancer Research, the scientific partner of SU2C. This work was additionally supported by the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research (grant 19-029-MIA) Expanding Therapeutic Options for Lung Cancer (EXTOL) project.
INCLUSION AND DIVERSITY
We support inclusive, diverse, and equitable conduct of research.
Footnotes
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
A. Ravi has served as a consultant to Halo Solutions and Tyra Biosciences. J.F.G. has served as a compensated consultant or received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Takeda, Loxo/Lilly, Blueprint, Oncorus, Regeneron, Gilead, Moderna, Mirati, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Novartis, iTeos, Nuvalent, Karyopharm, Beigene, Silverback Therapeutics, Merck, and GlydeBio; received research support from Novartis, Genentech/Roche, and Ariad/Takeda; received institutional research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Tesaro, Moderna, Blueprint, Jounce, Array Biopharma, Merck, Adaptimmune, Novartis, and Alexo; and has an immediate family member who is an employee with equity at Ironwood Pharmaceuticals. D.T.T. has received consulting fees from ROME Therapeutics, Tekla Capital, Ikena Oncology, Foundation Medicine, Inc., NanoString Technologies, and Pfizer that are not related to this work. D.T.T. is a founder of and has equity in ROME Therapeutics, PanTher Therapeutics, and TellBio, Inc., which are not related to this work. D.T.T. receives research support from ACD-Biotechne, PureTech Health LLC, and Ribon Therapeutics, which was not used in this work. D.T.T.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. S. Maheswaran and D.A.H. are co-founders and have equity in Tell-Bio, which is not related to this work.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112129.
REFERENCES
- 1.Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, Campisi J, Collado M, Evangelou K, Ferbeyre G, et al. (2019). Cellular senescence: defining a path forward. Cell 179, 813–827. 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ, and Peeper DS (2010). The essence of senescence. Genes Dev. 24, 2463–2479. 10.1101/gad.1971610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J, and Demaria M (2018). Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 28, 436–453. 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee S, and Schmitt CA (2019). The dynamic nature of senescence in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 94–101. 10.1038/s41556-018-0249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Deursen JM (2014). The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature 509, 439–446. 10.1038/nature13193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Collado M, Gil J, Efeyan A, Guerra C, Schuhmacher AJ, Barradas M, Benguría A, Zaballos A, Flores JM, Barbacid M, et al. (2005). Tumour biology: senescence in premalignant tumours. Nature 436, 642. 10.1038/436642a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang B, Kohli J, and Demaria M (2020). Senescent cells in cancer therapy: friends or foes? Trends Cancer 6, 838–857. 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ewald JA, Desotelle JA, Wilding G, and Jarrard DF (2010). Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 102, 1536–1546. 10.1093/jnci/djq364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Prasanna PG, Citrin DE, Hildesheim J, Ahmed MM, Venkatachalam S, Riscuta G, Xi D, Zheng G, Deursen JV, Goronzy J, et al. (2021). Therapy-induced senescence: opportunities to improve anticancer therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 113, 1285–1298. 10.1093/jnci/djab064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Coppé JP, Desprez PY, Krtolica A, and Campisi J (2010). The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 5, 99–118. 10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Basisty N, Kale A, Jeon OH, Kuehnemann C, Payne T, Rao C, Holtz A, Shah S, Sharma V, Ferrucci L, et al. (2020). A proteomic atlas of senescence-associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. PLoS Biol. 18, e3000599. 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Faget DV, Ren Q, and Stewart SA (2019). Unmasking senescence: context-dependent effects of SASP in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 19, 439–453. 10.1038/s41568-019-0156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lecot P, Alimirah F, Desprez PY, Campisi J, and Wiley C (2016). Context-dependent effects of cellular senescence in cancer development. Br. J. Cancer 114, 1180–1184. 10.1038/bjc.2016.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gonzalez-Meljem JM, Apps JR, Fraser HC, and Martinez-Barbera JP (2018). Paracrine roles of cellular senescence in promoting tumourigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 118, 1283–1288. 10.1038/s41416-018-0066-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Laberge RM, Awad P, Campisi J, and Desprez PY (2012). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by senescent fibroblasts. Cancer Microenviron. 5, 39–44. 10.1007/s12307-011-0069-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kale A, Sharma A, Stolzing A, Desprez PY, and Campisi J (2020). Role of immune cells in the removal of deleterious senescent cells. Immun. Ageing 17, 16. 10.1186/s12979-020-00187-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Prata LGPL, Ovsyannikova IG, Tchkonia T, and Kirkland JL (2018). Senescent cell clearance by the immune system: emerging therapeutic opportunities. Semin. Immunol. 40, 101275. 10.1016/j.smim.2019.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Eggert T, Wolter K, Ji J, Ma C, Yevsa T, Klotz S, Medina-Echeverz J, Longerich T, Forgues M, Reisinger F, et al. (2016). Distinct functions of senescence-associated immune responses in liver tumor surveillance and tumor progression. Cancer Cell 30, 533–547. 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Prieto LI, and Baker DJ (2019). Cellular senescence and the immune system in cancer. Gerontology 65, 505–512. 10.1159/000500683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ruhland MK, Loza AJ, Capietto AH, Luo X, Knolhoff BL, Flanagan KC, Belt BA, Alspach E, Leahy K, Luo J, et al. (2016). Stromal senescence establishes an immunosuppressive microenvironment that drives tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 7, 11762. 10.1038/ncomms11762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Acosta JC, Banito A, Wuestefeld T, Georgilis A, Janich P, Morton JP, Athineos D, Kang TW, Lasitschka F, Andrulis M, et al. (2013). A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 978–990. 10.1038/ncb2784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kuilman T, and Peeper DS (2009). Senescence-messaging secretome: SMS-ing cellular stress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 81–94. 10.1038/nrc2560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Teo YV, Rattanavirotkul N, Olova N, Salzano A, Quintanilla A, Tarrats N, Kiourtis C, Müller M, Green AR, Adams PD, et al. (2019). Notch signaling mediates secondary senescence. Cell Rep. 27, 997–1007.e5. 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Muñoz-Espín D, and Serrano M (2014). Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 482–496. 10.1038/nrm3823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Batlle E, and Massagué J (2019). Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in immunity and cancer. Immunity 50, 924–940. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Massagué J (2012). TGFbeta signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 616–630. 10.1038/nrm3434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, Tauriello DVF, Iglesias M, Céspedes MV, Sevillano M, Nadal C, Jung P, Zhang XHF, et al. (2012). Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-beta-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell 22, 571–584. 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Worthington JJ, Fenton TM, Czajkowska BI, Klementowicz JE, and Travis MA (2012). Regulation of TGFbeta in the immune system: an emerging role for integrins and dendritic cells. Immunobiology 217, 1259–1265. 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Massagué J, and Wotton D (2000). Transcriptional control by the TGFbeta/Smad signaling system. EMBO J. 19, 1745–1754. 10.1093/emboj/19.8.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang YE (2017). Non-smad signaling pathways of the TGF-beta family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9, a022129. 10.1101/cshperspect.a022129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Byrne MB, Leslie MT, Gaskins HR, and Kenis PJA (2014). Methods to study the tumor microenvironment under controlled oxygen conditions. Trends Biotechnol. 32, 556–563. 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McKeown SR (2014). Defining normoxia, physoxia and hypoxia in tumours-implications for treatment response. Br. J. Radiol. 87, 20130676. 10.1259/bjr.20130676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Harris AL (2002). Hypoxia–a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 38–47. 10.1038/nrc704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pickup M, Novitskiy S, and Moses HL (2013). The roles of TGFbeta in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 788–799. 10.1038/nrc3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Muñoz-Espín D, Cañamero M, Maraver A, Gómez-López G, Contreras J, Murillo-Cuesta S, Rodríguez-Baeza A, Varela-Nieto I, Ruberte J, Collado M, and Serrano M (2013). Programmed cell senescence during mammalian embryonic development. Cell 155, 1104–1118. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Welford SM, and Giaccia AJ (2011). Hypoxia and senescence: the impact of oxygenation on tumor suppression. Mol. Cancer Res. 9, 538–544. 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Campisi J, and d’Adda di Fagagna F (2007). Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 729–740. 10.1038/nrm2233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sturmlechner I, Zhang C, Sine CC, van Deursen EJ, Jeganathan KB, Hamada N, Grasic J, Friedman D, Stutchman JT, Can I, et al. (2021). p21 produces a bioactive secretome that places stressed cells under immunosurveillance. Science 374, eabb3420. 10.1126/science.abb3420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Packer L, and Fuehr K (1977). Low oxygen concentration extends the lifespan of cultured human diploid cells. Nature 267, 423–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Parrinello S, Samper E, Krtolica A, Goldstein J, Melov S, and Campisi J (2003). Oxygen sensitivity severely limits the replicative lifespan of murine fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 741–747. 10.1038/ncb1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee AC, Fenster BE, Ito H, Takeda K, Bae NS, Hirai T, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Howard BH, and Finkel T (1999). Ras proteins induce senescence by altering the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 7936–7940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tsai CC, Chen YJ, Yew TL, Chen LL, Wang JY, Chiu CH, and Hung SC (2011). Hypoxia inhibits senescence and maintains mesenchymal stem cell properties through down-regulation of E2A-p21 by HIF-TWIST. Blood 117, 459–469. 10.1182/blood-2010-05-287508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Narita M, Narita M, Krizhanovsky V, Nuñez S, Chicas A, Hearn SA, Myers MP, and Lowe SW (2006). A novel role for high-mobility group a proteins in cellular senescence and heterochromatin formation. Cell 126, 503–514. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hu H, Piotrowska Z, Hare PJ, Chen H, Mulvey HE, Mayfield A, Noeen S, Kattermann K, Greenberg M, Williams A, et al. (2021). Three subtypes of lung cancer fibroblasts define distinct therapeutic paradigms. Cancer Cell 39, 1531–1547.e10. 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pawlikowski JS, Adams PD, and Nelson DM (2013). Senescence at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 126, 4061–4067. 10.1242/jcs.109728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schwarz JK, Bassing CH, Kovesdi I, Datto MB, Blazing M, George S, Wang XF, and Nevins JR (1995). Expression of the E2F1 transcription factor overcomes type beta transforming growth factor-mediated growth suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 483–487. 10.1073/pnas.92.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Martínez-Zamudio RI, Roux PF, de Freitas JANLF, Robinson L, Doré G, Sun B, Belenki D, Milanovic M, Herbig U, Schmitt CA, et al. (2020). AP-1 imprints a reversible transcriptional programme of senescent cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 22, 842–855. 10.1038/s41556-020-0529-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hoare M, Ito Y, Kang TW, Weekes MP, Matheson NJ, Patten DA, Shetty S, Parry AJ, Menon S, Salama R, et al. (2016). NOTCH1 mediates a switch between two distinct secretomes during senescence. Nat Cell Biol 18, 979–992. 10.1038/ncb3397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.van Vliet T, Varela-Eirin M, Wang B, Borghesan M, Brandenburg SM, Franzin R, Evangelou K, Seelen M, Gorgoulis V, and Demaria M (2021). Physiological hypoxia restrains the senescence-associated secretory phenotype via AMPK-mediated mTOR suppression. Mol. Cell 81, 2041–2052.e6. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim N, Kim HK, Lee K, Hong Y, Cho JH, Choi JW, Lee JI, Suh YL, Ku BM, Eum HH, et al. (2020). Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 11, 2285. 10.1038/s41467-020-16164-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lechner MG, Karimi SS, Barry-Holson K, Angell TE, Murphy KA, Church CH, Ohlfest JR, Hu P, and Epstein AL (2013). Immunogenicity of murine solid tumor models as a defining feature of in vivo behavior and response to immunotherapy. J. Immunother. 36, 477–489. 10.1097/01.cji.0000436722.46675.4a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Afonina IS, Cullen SP, and Martin SJ (2010). Cytotoxic and non-cytotoxic roles of the CTL/NK protease granzyme B. Immunol. Rev. 235, 105–116. 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Comaills V, Kabeche L, Morris R, Buisson R, Yu M, Madden MW, LiCausi JA, Boukhali M, Tajima K, Pan S, et al. (2016). Genomic instability is induced by persistent proliferation of cells undergoing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Rep. 17, 2632–2647. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kang TW, Yevsa T, Woller N, Hoenicke L, Wuestefeld T, Dauch D, Hohmeyer A, Gereke M, Rudalska R, Potapova A, et al. (2011). Senescence surveillance of pre-malignant hepatocytes limits liver cancer development. Nature 479, 547–551. 10.1038/nature10599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Toso A, Revandkar A, Di Mitri D, Guccini I, Proietti M, Sarti M, Pinton S, Zhang J, Kalathur M, Civenni G, et al. (2014). Enhancing chemotherapy efficacy in Pten-deficient prostate tumors by activating the senescence-associated antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. 9, 75–89. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.De Martino M, Tkach M, Bruni S, Rocha D, Mercogliano MF, Cenciarini ME, Chervo MF, Proietti CJ, Dingli F, Loew D, et al. (2020). Blockade of Stat3 oncogene addiction induces cellular senescence and reveals a cell-nonautonomous activity suitable for cancer immunotherapy. OncoImmunology 9, 1715767. 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1715767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hao X, Zhao B, Zhou W, Liu H, Fukumoto T, Gabrilovich D, and Zhang R (2021). Sensitization of ovarian tumor to immune checkpoint blockade by boosting senescence-associated secretory phenotype. iScience 24, 102016. 10.1016/j.isci.2020.102016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Paffenholz SV, Salvagno C, Ho YJ, Limjoco M, Baslan T, Tian S, Kulick A, de Stanchina E, Wilkinson JE, Barriga FM, et al. (2022). Senescence induction dictates response to chemo- and immunotherapy in preclinical models of ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2117754119. 10.1073/pnas.2117754119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ruscetti M, Morris JP 4th, Mezzadra R, Russell J, Leibold J, Romesser PB, Simon J, Kulick A, Ho YJ, Fennell M, et al. (2020). Senescence-induced vascular remodeling creates therapeutic vulnerabilities in pancreas cancer. Cell 181, 424–441.e21. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mariathasan S, Turley SJ, Nickles D, Castiglioni A, Yuen K, Wang Y, Kadel EE III, Koeppen H, Astarita JL, Cubas R, et al. (2018). TGFbeta attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 554, 544–548. 10.1038/nature25501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Newsted D, Banerjee S, Watt K, Nersesian S, Truesdell P, Blazer LL, Cardarelli L, Adams JJ, Sidhu SS, and Craig AW (2019). Blockade of TGF-beta signaling with novel synthetic antibodies limits immune exclusion and improves chemotherapy response in metastatic ovarian cancer models. OncoImmunology 8, e1539613. 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1539613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tauriello DVF, Palomo-Ponce S, Stork D, Berenguer-Llergo A, Badia-Ramentol J, Iglesias M, Sevillano M, Ibiza S, Cañellas A, Hernando-Momblona X, et al. (2018). TGFbeta drives immune evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis. Nature 554, 538–543. 10.1038/nature25492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Anders S, Pyl PT, and Huber W (2015). HTSeq–a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31, 166–169. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, and Salzberg SL (2013). TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 14, R36. 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Risso D, Ngai J, Speed TP, and Dudoit S (2014). Normalization of RNA-seq data using factor analysis of control genes or samples. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 896–902. 10.1038/nbt.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Ghandi M, Mesirov JP, and Tamayo P (2015). The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 1, 417–425. 10.1016/j.cels.2015.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, and Mesirov JP (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550. 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, et al. (2009). New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 45, 228–247. 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Van Allen EM, Miao D, Schilling B, Shukla SA, Blank C, Zimmer L, Sucker A, Hillen U, Foppen MHG, Goldinger SM, et al. (2015). Genomic correlates of response to CTLA-4 blockade in metastatic melanoma. Science 350, 207–211. 10.1126/science.aad0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wagle N, Van Allen EM, Treacy DJ, Frederick DT, Cooper ZA, Taylor-Weiner A, Rosenberg M, Goetz EM, Sullivan RJ, Farlow DN, et al. (2014). MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 4, 61–68. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
RNA-seq data used for Figure 2 has been deposited at GEO and will be made publicly available as of the date of publication. The accession number is GEO: GSE223037 and listed in the key resources table.
This paper does not report original code.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE.
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
| Antibodies | ||
|
| ||
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-p21 | Santa Cruz | Cat#sc-397; RRID:AB_632126 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Histone H3 (tri methyl K9) | abcam | Cat#ab8898; RRID:AB_306848 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-E-cadherin | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#3195; RRID:AB_2291471 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-TGF-β Receptor II | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#79424; RRID:AB_2799933 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-β-Tubulin | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2146; RRID:AB_2210545 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-GAPDH | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#SAB2108266 |
| Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP | BioRad | Cat#170-6515; RRID:AB_11125142 |
| Goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP | BioRad | Cat#1706516; RRID:AB_2921252 |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#7074; RRID:AB_2099233 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-tubulin | NOVUS | Cat#NB100-690; RRID:AB_521686 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-p21 | abcam | Cat#ab188224; RRID:AB_2734729 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-granzyme B | ThermoFischer | Cat#14-8822-80; RRID:AB_468529 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD45 | Invitrogen | Cat#MCD4501; RRID:AB_10371770 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-Ly-6G | StemCell Technologies Inc | Cat#60031 PB.1 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-Ly6C | Life Technologies | Cat#17-5932-82; RRID:AB_1724153 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD11b | Life Technologies | Cat#53-0112-82; RRID:AB_469901 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-F4/80 | Life Technologies | Cat#17-4801-80; RRID:AB_2784647 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-B220 | Life Technologies | Cat#17-0452-82; RRID:AB_469395 |
| Armenian hamster monoclonal anti-CD3 | Life Technologies | Cat#11-0031-82; RRID:AB_464882 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD8 | BioLegend | Cat#100712; RRID:AB_312751 |
| Rat monoclonal anti-CD4 | Life Technologies | Cat#48-0041-82; RRID:AB_10718983 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-NK1.1 | BioLegend | Cat#108706; RRID:AB_313393 |
| Phospho-S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ser240/244) Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2215; RRID:AB_331682 |
| Phospho-S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ser235/236) Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#4858; RRID:AB_916156 |
| Phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) (236B4) Rabbit mAb | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#2855; RRID:AB_560835 |
| Phospho-Akt (Ser473) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#4051; RRID:AB_331158 |
| Phospho-Smad3 (Ser423/425) (C25A9) Rabbit mAb | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#9520; RRID:AB_2193207 |
| Smad3 Antibody | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat#9513; RRID:AB_2286450 |
|
| ||
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
|
| ||
| One Shot™ Stbl3™ Chemically Competent E. coli | Invitrogen | C737303 |
|
| ||
| Biological samples | ||
|
| ||
| Immunotherapy Clinical Cohort Collection | Patients treated with anti-PD(L)1 therapy either as single agent or in combination with other therapies between 2013 and 2019 at Massachusetts General Hospital | Umbrella sequencing protocol Massachusetts General Hospital #13-416 |
|
| ||
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
|
| ||
| Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1 | R&D | 240-B |
| SB431542 | Sigma Aldrich | S4317 |
|
| ||
| Critical commercial assays | ||
|
| ||
| Cellular Senescence Detection Kit-SPiDER-βGal | Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan | SG03 |
| Senescence Cells Histochemical Staining Kit | Sigma Aldrich | CS0030 |
| RNeasy Mini kit | Qiagen | 74106 |
| Quantikine ELISA Human/Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Canine TGFβ1 | R&D Systems | DB100C |
| SMARTer Ultra Ultra-Low-input RNA kit, version 4 | Clontech Laboratory | 012516 |
| Nextera XT DNA Library Preparation Kit | Illumina | FC-131-1024 |
| ERCC RNA Spike-In Mix | ThermoFisher Scientific | 4456740 |
| KAPA SYBR® FAST Universal qPCR Kit | Kapa Biosystems | N/A |
| X-tremeGENE HP DNA transfection reagent | Roche Applied Science | 6366236001 |
| Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix | Applied Biosystem | 4367659 |
| CellTiter-Glo® Cell Viability Assay | Promega | G9243 |
| SuperScript™ III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix for qRT-PCR | Invitrogen | 11752-050 |
| HiSpeed Plasmid Midi Kit (25) | Qiagen | 12643 |
| Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit | Thermo Scientific | 23227 |
|
| ||
| Deposited data | ||
|
| ||
| RNA-seq data | This paper | GEO: GSE223037 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
|
| ||
| A549 | ATCC | CCL-185 |
| HepG2 | ATCC | HB-8065 |
| TE4 | ATCC | HB-207 |
| Patient derived lung cancer associated fibroblasts | Dr. Cyril Benes, Massachusetts General Hospital, MA 02129 | Hu et al.44 |
| LLC-1 | ATCC | CRL-1642 |
|
| ||
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
|
| ||
| Mice (C57/BL6) | Charles River Laboratories | CCM21211956 |
|
| ||
| Oligonucleotides | ||
|
| ||
| Primers used for Real-time PCR reactions | See Table S3 | N/A |
|
| ||
| Software and algorithms | ||
|
| ||
| FlowJo software | FlowJo | FlowJo-Win64-10. |
| Halo software | Indica Labs | https://indicalab.com/halo/ |
| R software | R core team, R foundation | https://www.r-project.org/ |
| Illustrator software (26.5) | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html |
| Photoshop software (22.3.0) | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html |
| Fiji software | ImageJ | https://imagej.net/software/fiji |
| TrimGalore | https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ | 0.43 |
| TopHat | https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/index.shtml | 2.1.1 |
| HTSeq | See Ref.63. | 0.6.1 |
| GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 software | GraphPad Software | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ |
| Bio Render | Bio Render software | CI24XNA2XR |


