Abstract
The role of endoscope has been changing from that being an adjuvant during microear surgery to the exclusive endoscopic middle ear surgery. However the only disadvantage of endoscopic ear surgery is its single handed technique as the non-dominant hand is used to hold the endoscope. We propose the concept and design of our portable endoscope holder for two handed endoscopic ear surgery. It is based on the gas spring action and rack and pinion system which act as a third arm to hold the endoscope. The novel portable endoscope holder bears the potential to provide benefits for various two handed endoscopic ear nose and throat surgeries.
Level of evidence: Level V.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s12070-022-03246-3.
Keywords: Endoscope holder, Portable, Two handed endoscopic technique, Endoscopic ear nose throat surgery, Cartilage tympanoplasty
Introduction
For surgeries of middle ear, microscope has played a major role and still is being used by most of the ENT surgeons. As the techniques of ear surgeries are getting evolved so are the needs to visualise the hidden areas of middle ear (facial recess, sinus tympani, posterior sinus etc.) for improvising the surgical outcome and success. Endoscopic ear surgery is gaining popularity and there has been s a gradual shift from the conventional Wulstein’s microscopic ear surgery to endoscopic ear surgery. With the introduction of the concept of endoscope in ear surgery by Thomassin et al. [1] the hidden areas were visualised very easily and clearly by endoscopes (either 0 degree or angled) and hence the cholesteatoma in these areas can be removed easily [2] without much bone removal. Previously endoscopes were used for second look procedures but now the use of endoscopes has been extended for the entire operative procedure [3–5]. Endoscope provides minimal invasive approach to the middle ear. The endoscope provides a panoramic view of the entire tympanic membrane and external ear canal without either moving the head of the patient or the microscope [6]. The traditional otology training is with the operating microscope with the two handed technique. One handed endoscopic approach is manageable in sinus surgeries. However, one handed technique is difficult in ear surgeries where the conventional teaching is two handed microscopic technique. The use of two hands in any surgery is of immense importance. The suction held in the left hand helps in defogging and also helpful to remove the irrigating fluid during drilling, and also for manipulating the prosthesis. So introduction of endoscope in ear surgery will be beneficial and complete only in the presence of complimentary action of two hands. This necessitated the need for development of the endoscope holder which would allow the panoramic advantage of endoscope to be incorporated without any effective reduction in the working hands. Shifting from two handed microscopic ear surgery to single handed endoscopic ear surgery is cumbersome especially when both hands are required in certain steps of surgery like drilling, fogging, haemorrhage and ossiculoplasty. To overcome this disadvantage, we have developed endoscope holders, one of which is a floor model [7], Endohold™ (Patent Application No. 2313-Mum-2013) and the other endoscope holder, Justtach™ (Patent Application No. 3300-Mum-2013 and Patent Number 401115) is the attachment to the existing microscope [8, 9] to convert it into an endoscope holding unit. The disadvantage of the floor model being bulky and difficult for out station ear surgeries. The other endoscope holder, Justtach™ may not fit onto all microscopes. This posed the need to develop an exclusive endoscope holder which could be attached to the operating table and user friendly too. The portable endoscope holder is based on gas spring and rachet and pinion action and is trademarked as Endohold™ GS 201B (Fig. 1) and is applied for patent (Patent Application no. 201921021758).
Fig. 1.

Endohold™ GS 201B
Concept of the Portable Endoscope Holder, Endohold™ GS 201B
The basic idea behind the portable endoscope holder is to utilise the Gas Spring and Rack and Pinion mechanism along with the multiple joints for 360 degree freedom of rotation in space (rotated forwards, rotated backwards, upwards, downwards and sidewise angular rotation) to drive the endoscope into any biological cavity. In simply words, applying all the possible actions of operating microscope in space to hold the endoscope to simulate the action of the arm. The gas spring (GS) action which allows smooth upward and downward motion in 180 degree and also tilts the endoscope in any direction. The peculiarity of the endoscope holder is that it is provided with ratchet and pinion mechanism which allows the additional few centimetres closer motion of the endoscope into the biological cavity.
Technical Description of Endohold™ GS 201 B (Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5 and Supplementary videos 1 to 8)
Fig. 2.

Parts of Endohold™ GS 201B
Fig. 3.

Gas Spring part of the Endohold™ GS 201B
Fig. 4.

Rack and pinion part of Endohold™ GS 201B
Fig. 5.

Slot to hold endoscope
Technical description of Endohold™ GS 201 B (Patent Application no. 201921021758)
O.T. table gripping attachment (Fig. 1)
Horizontal metallic rod (Fig. 2)
Gas Spring arm (Fig. 3)
Metallic connecting rod
Rack and Pinion system attached (Fig. 4)
Attachment with slot for holding the endoscope (Fig. 5)
A gas spring is a type of spring that, unlike a typical mechanical spring uses compressed gas contained within an enclosed cylinder sealed by a sliding piston to pneumatically store potential energy and withstand external force applied parallel to the direction of the piston shaft [10]. Gas springs are usually implemented in two different suspension frameworks. The first one is the pneumatic suspension, where the spring is implemented by an air chamber surrounding the shock absorber. The second is hydro-pneumatic suspension where an accumulator is linked to the shock absorber and the gas included is compressed by the movements of the fluid [11].
The flexibility of inclination and rotation offers an extreme customization of the positioning of the endoscope. The gas spring perfectly counterbalances the weight of the endoscope and the endoscopic camera system. Different weight can be counterbalanced depending on the hydraulic action of the gas spring. Because of the high pressure of the gas inside it, a gas spring can be much more compact than a metal spring that would provide the same amount of force. Gas springs expand and contract more smoothly than metal springs and can be designed to open and close at an exact and constant speed (unlike metal springs, which contract faster when they are extended further and can be very unpredictable). Mechanically, gas springs are simple and have few moving parts, so they are relatively cheap, extremely reliable, and often last many years without any maintenance at all. Metal springs are more likely to break through repeated stretching and releasing (loading and unloading) because of fatigue [12].
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the pinion) engaging a linear gear (the rack), which operate to translate rotational motion into linear motion [13]. The endoscope holder is dynamic, allowing the endoscope to be tilted in any direction (rotated forwards, rotated backwards, upwards, downwards and sidewise angular rotation). The peculiarity of the endoscope holder is that it is provided with rack and pinion mechanism which allows the additional few centimetres closer motion of the endoscope into the ear canal and middle ear cavity. The Rack and Pinion is an adjustment mechanism that allows the user to move one part, close to another part, in a controlled fashion. The most common use is for the coarse focus mechanism of a microscope. It has also been used to focus the substage, and occasionally is found with a circular rack to rotate a circular stage, and sometimes for other uses. In use, the pinion is turned by a knob attached to its axle. The pinion teeth mesh with the rack teeth, and, usually, as the pinion is turned, the rack moves. The pinion is usually enclosed in a pinion box which holds the pinion with the proper tension against the rack [14].
Position of Endoscope Holder
The endoscope is mounted onto the endoscope holder with the camera using all sterile aseptic precautions.
For Ear Surgery: The endoscope holder is fixed to the operation table on the opposite side of the ear to be operated. The operating surgeon sits on the same side as the ear with the monitor facing the surgeon.
For Septal Surgery: The endoscope holder is attached on the left side of the operating table with the surgeon standing on the right side.
For Throat Surgery (Tonsillectomy or Laryngeal Surgery): The endoscope holder is attached on the left side of the operating table with the surgeon at the head end of the patient.
The endoscope is directed into the cavity (Ear canal, septum, oral cavity) to be operated. The surgeon operates by seeing onto the monitor thus requiring hand-eye-monitor coordination.
Applications of Endohold™ 201B [15–20]:
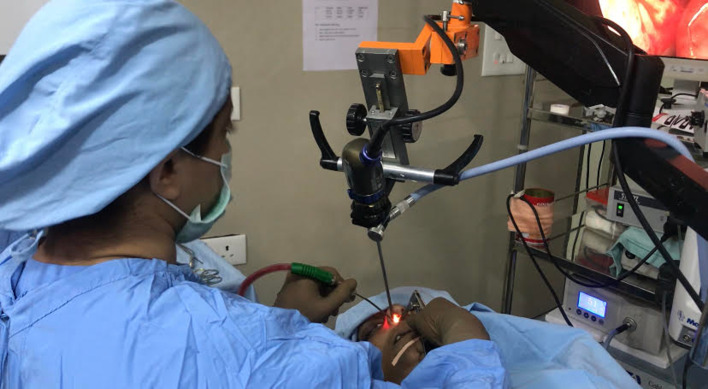
Two handed endoscopic ear surgery (tympanoplasty, stapedotomy, canalplasty, ossiculoplasty, atticotomy, atticoantrostomy, mastoidectomy) (Fig. 6)
Two handed endoscopic coblation tonsillectomy (Fig. 7)
Two handed endoscopic nasal surgeries (septoplasty, dacryocystorhinostomy) (Fig. 8)
Two handed endoscopic ENT surgeries
Fig. 6.

Endohold™ GS 201B for two handed endoscopic ear surgery
Fig. 7.

Endohold™ GS 201B for two handed endoscopic cobation tonsillectomy
Fig. 8.
Endohold™ GS 201B for two handed endoscopic Septal surgery
Advantages of Our Endohold™ GS 201B
Both the hands of the surgeon are free for operative intervention which is of paramount importance both for diagnostic and operative procedure.
It can be used effectively without compromising the surgical field.
It is a useful teaching aid.
The stability of the endoscope, camera and image on the monitor is ensured throughout.
Minimizes the need for assistance.
No surgeon fatigue in holding the endoscope as the endoscope is fixed on the endoscope holder (as compared with single handed EES).
The rack and pinion action allows additional manipulation/advancing into the biological cavity to be operated.
With the angled endoscope mounted on the endoscope holder, there is better visualisation of sinus tympani, facial recess, anterior tympanic cavity and hypotympanum with just rotation of the endoscope within the Holder.
With the two handed technique, the elevation of the tympanomeatal flap (ear surgery) and mucoperichondrial flap (septal surgery) is much better.
Continuous use of suction cannula in the left hand prevents the fogging of the endoscope. Drilling for canalplasty, atticotomy, atticoantrostomy or inside out mastoidectomy can be done with the drill in the right hand and suction in the left hand (ear surgery).
Sterilisation:
Autoclave
Cidex sterilization
UV- C sterilization
With slight modification, Endohold™ GS 201 B can be used during.
Laparoscopic Surgeries
Urosurgeries
Laparoscopic gynaecologic surgeries
Arthroscopies
Neurosurgical procedures
Lateral and anterior skull bases surgeries
Vision for use of Endohold™:
Automated Endoholder like robot
3D endoscopy with automated Endoholder
Automated cleaning of fogging
Voice controlled Endoholder
Motorised rack pinion action
Conclusion
Endohold™ GS 201B is a good option for two handed endoscopic ear surgeries in cases with or without drilling due to its stable dynamic properties and can be used for two handed endoscopic nasal and throat surgeries. Use of the endoscope holder requires the training to acquire the skills.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We wish to express our gratitude to Dr. Mrs Shirin M. Khan and Master Asim Khan for all the technical help provided during the design and development of the Endohold GS 201B and for manuscript editing. This study was not financially supported from external sources. EndoHold GS 201 B is the trademark registered under the name of Dr. Mubarak M. Khan and the design has been applied under Patent Act, (India and International; Patent Application number 201921021758) under the name of Dr. Mubarak M. Khan.
Author Contributions
Dr. Mubarak M. Khan: Instrument design and development, manuscript drafting, editing. Dr. Sapna R Parab: Instrument development, manuscript drafting, editing. Dr Amit Kumar Rana and Dr Shivesh Kumar: Drafting and editing of manuscript.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 helsinski declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Institutional Ethics Committee has approved the study.
Financial Support and Funding
None.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Mubarak Muhamed Khan, Email: ent.khan@gmail.com.
Sapna Ramkrishna Parab, Email: drsapnaparab@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Thomassin JM, Korchia D, Doris JM. Endoscopic guided otosurgery in the prevention of residual cholesteatomas. Laryngoscope. 1993;103:939–943. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199308000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Badr-El-Dine M. Value of ear endoscopy in cholesteatoma surgery. Otol Neurotol. 2002;23:631–635. doi: 10.1097/00129492-200209000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Khan MM, Parab SR. Endoscopic cartilage tympanoplasty: a two-handed technique using an endoscope holder. Laryngoscope. 2016;126:1893–1898. doi: 10.1002/lary.25760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Parab SR, Khan MM. Endoscopic management of tympanic membrane retraction pockets: a two handed technique with endoscope holder. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;71(4):504–511. doi: 10.1007/s12070-019-01682-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parab SR, Khan MM. Minimal invasive endoscopic ear surgery: a two handed technique. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;71(2):1334–1342. doi: 10.1007/s12070-018-1411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tarabichi M. Endoscopic middle ear surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999;108(1):39–46. doi: 10.1177/000348949910800106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Khan MM, Parab SR. Concept, design and development of innovative endoscope holder system for endoscopic otolaryngological surgeries. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;67(2):113–119. doi: 10.1007/s12070-014-0738-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Khan MM, Parab SR. Novel concept of attaching endoscope holder to microscope for two handed endoscopic tympanoplasty. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;68(2):230–240. doi: 10.1007/s12070-015-0916-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Parab SR, Khan MM. Modified endoscope holder for two handed endoscopic ear surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-01841-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_spring
- 11.Sergio M. Savaresi, et al, in Semi-active suspension control design for vehicles, 2010. Semi-active suspension technologies and models.
- 12.https://www.explainthatstuff.com/gassprings.html
- 13.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rack_and_pinion
- 14.https://www.microscope-antiques.com/randp.html
- 15.Parab SR, Khan MM. Pinna stay suture in two handed endoscopic ear surgery: Our experience. Am J Otolaryngol. 2020;41(5):102582. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Khan MM, Parab SR. Exclusive two handed endoscopic cartilage type 3 tympanoplasty with endoscope holders. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02484-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Khan MM, Parab SR. Endoscopic cartilage umberlla ossiculoplasty: as total ossicular replacement using endoscope holder. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02518-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Parab SR, Khan MM. Endoscope holder-assisted endoscopic coblation tonsillectomy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;277(11):3223–3226. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Khan MM, Parab SR. Endoscopic septoplasty: two handed technique with endoscope holder: a novel approach. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;68(4):475–480. doi: 10.1007/s12070-016-0997-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Khan MM, Parab SR. Endoscopic cartilage boomerang ossiculoplasty: as total ossicular replacement using endoscope holder. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02854-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.