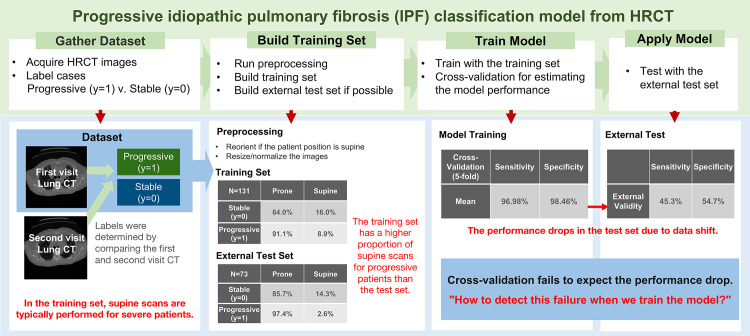
Figure 1.
Diagram of the binary classification model for predicting progressive versus stable (nonprogressive) IPF from three-dimensional lung high-resolution CT (HRCT) images. Patients were imaged at total lung capacity (TLC) in the prone position using standard diffuse lung disease CT protocols, and a few patients were imaged in the supine position owing to their severe symptoms. A notable data shift in this example is the change in the proportion of supine images for patients with progressive IPF. The model shows performance drop due to data shift.