Figure 7. Lead ternary si-NPs display minimal acute toxicity and improved in vivo pharmacokinetics following intravenous si-NP treatment.
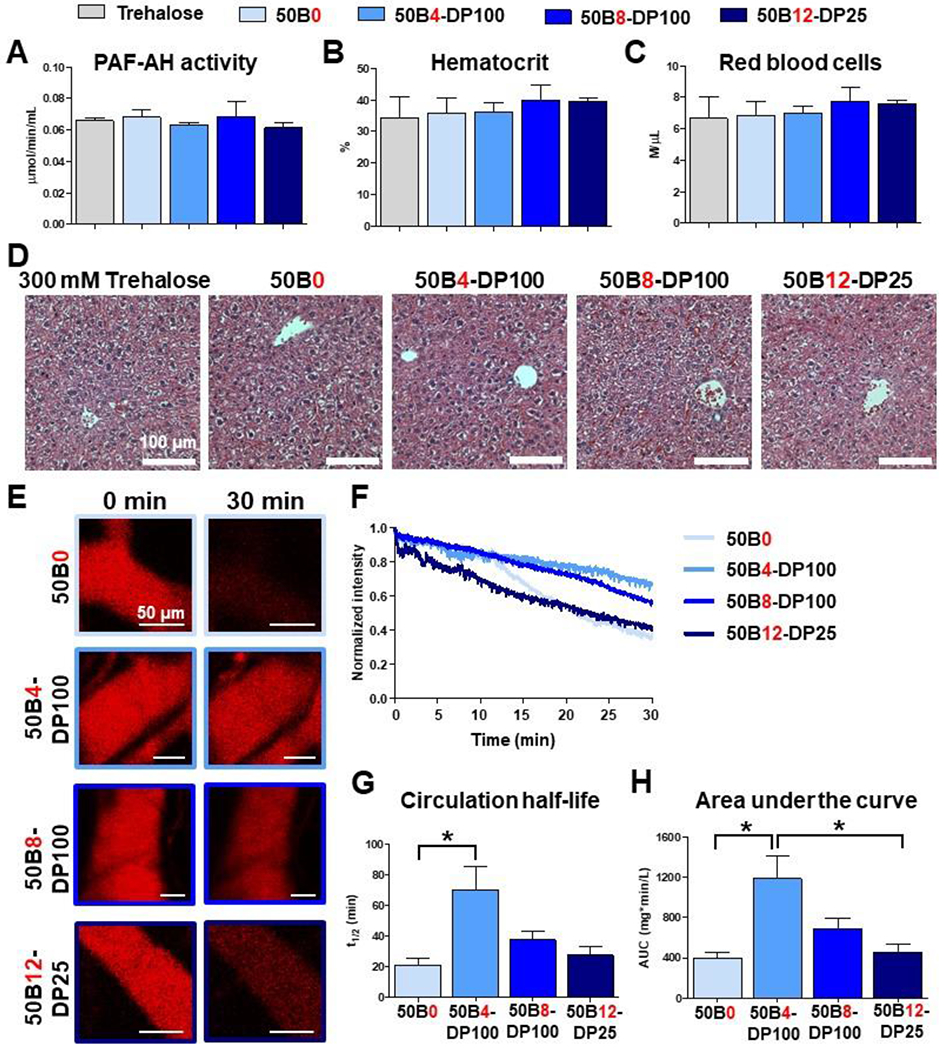
(A-D) Mice were i.v. treated with either trehalose vehicle or si-NPs and assessed after 30 min. Plasma PAF-AH activity was measured (A) as an indirect measure of plasma PAF levels, a biomarker for acute liver Kupffer cell toxicity (N = 4-5). Mouse blood was assessed for signs of PAF-induced hemoconcentration by measuring % hematocrit (B) and red blood cell level (C, N = 7-9). Mouse livers were evaluated for histological signs of toxicity, in particular vascular congestion, by H&E staining (D). (E) Representative intravital microscopy images of fluorescent Cy5 si-NPs in mouse ear vasculature (N = 3-4). (F) Average pharmacokinetic curves of each si-NP formulation. (G) Plasma half-life and (H) area under curve was calculated for each si-NP from intravital microscopy data. One-way ANOVA analysis with Tukey’s multiple comparison test was used to compare differences in pharmacokinetic parameters (*, p < 0.05).
