Abstract
The C-terminal domain of the A subunit of DNA gyrase, which we term Gac, is naturally synthesized in Borrelia burgdorferi as an abundant DNA-binding protein. Full-length GyrA, which includes the C-terminal domain, is also synthesized by the spirochete and functions as a subunit of DNA gyrase. We have disrupted synthesis of Gac as an independent protein and demonstrated that it is not essential for growth in a coumarin-resistant background. We detected no alterations in DNA maintenance, condensation, or topology in B. burgdorferi lacking this small DNA-binding protein.
Borrelia burgdorferi, a spirochete that causes Lyme disease, naturally synthesizes the C-terminal domain of the A subunit of DNA gyrase as an abundant 34-kDa DNA-binding protein (5). A full-length GyrA protein that includes the GyrA C-terminal domain is also synthesized in the organism. GyrA and GyrB comprise DNA gyrase, an A2B2 heterotetramer, which is the only topoisomerase capable of introducing negative supercoiling into closed-circular DNA molecules (2, 3, 9, 20). The B. burgdorferi GyrA C-terminal domain is encoded on a transcript that initiates within gyrA and is translated in the identical reading frame as full-length GyrA (5). We term the protein Gac (GyrA C-terminal domain) because it is a separate product of a distinct genetic unit. The gac gene encodes Gac and consists of the 3′ 939 nucleotides of the gyrA gene. Gac, which has not yet been found in any organism outside of the Borrelia genus, functions similarly to the Escherichia coli protein HU (5).
To begin to understand the role of Gac in B. burgdorferi, we disrupted synthesis of the protein by mutating nucleotides critical for its translation while maintaining the gyrA open reading frame. These mutations were introduced along with a coumermycin A1 resistance (Cour) gyrB allele (gyrBr), which was the only selectable marker available for genetic studies in B. burgdorferi (10, 13, 14). The gyrBr allele has been used for genetic disruption by allelic exchange on the B. burgdorferi 26-kb circular plasmid (1, 16, 18). Insertional inactivation of gac was not feasible because such a mutation would also disrupt gyrA and the synthesis of full-length GyrA, which is presumably essential in B. burgdorferi (12).
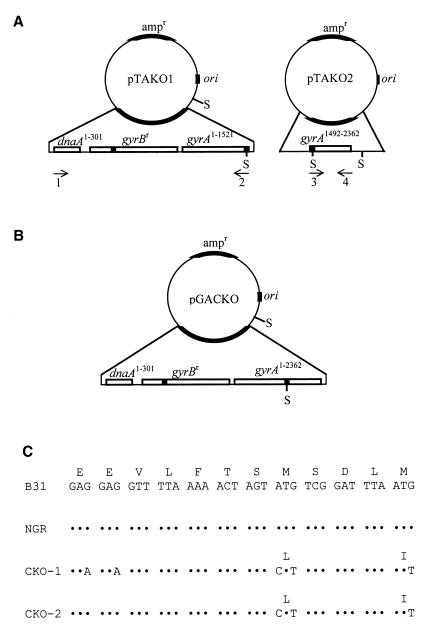
For introducing mutations in gac, plasmid pGACKO was created by first subcloning partially overlapping PCR products containing the mutations into pTAKO1 and pTAKO2 (Fig. 1A and B). pTAKO1 was constructed by PCR amplifying an approximately 4-kb fragment encoding the 5′ 301 bp of dnaA, all of gyrBr, and the 5′ 1,521 bp of gyrA from B. burgdorferi strain B31-NGR, using primers dnaA 301R and gyrA 1521R/GACKO (Table 1). B31-NGR was created by site-directed mutagenesis of strain B31 and contains mutations in gyrB encoding Asn-102 to Asp, Gly-104 to Asp, and Arg-133 to Ile, which confer high-level resistance to coumermycin A1 (D. S. Samuels, B. J. Kimmel, D. C. Criswell, C. F. Garon, W. M. Huang, and C. H. Eggers, unpublished data). The amplification product was adenylated and cloned into plasmid PCR 2.1-TOPO (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions, creating plasmid pTAKO1 (Fig. 1A). Primer gyrA 1521R/GACKO was a mutagenic primer that introduced silent mutations into the Shine-Dalgarno sequence to decrease ribosome binding, mutated an ATG Met codon (position 499 of GyrA) (which is predicted to be the translational start codon) to a CTT Leu codon to prevent translation of Gac, and mutated an ATG Met codon (position 503 of GyrA) to an ATT Ile codon to prevent translation from initiating downstream (Fig. 1C). The introduced mutations correspond to residues found at the homologous sites in E. coli GyrA (15).
FIG. 1.
Strategy for gac gene disruption. (A) Plasmid maps of pTAKO1 and pTAKO2. Plasmid pTAKO1 contains the 5′ 301 bp of dnaA (dnaA1–301), all of gyrBr (dnaA and gyrB are divergently expressed), and the 5′ 1,521 bp of gyrA (gyrA1–1521). Plasmid pTAKO2 contains nucleotides 1492 to 2362 of gyrA (gyrA1492–2362). SpeI (S) restriction sites are shown. Arrows indicate oligonucleotide primers used in site-directed mutagenesis and PCR analysis; numbers below the arrows correspond to oligonucleotides listed in Table 1. Mutated sites in gyrB from B31-NGR and introduced mutations in gyrA are indicated by shaded boxes. (B) Plasmid map of pGACKO. The ∼800-bp SpeI fragment of plasmid pTAKO2 was cloned into the SpeI site of plasmid pTAKO1 to create plasmid pGACKO. (C) Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of gyrA from strains B31, B31-NGR, CKO-1, and CKO-2. Nucleotides 1474 to 1509 of gyrA, which encode amino acids 492 to 503 of GyrA (and amino acids 1 to 5 of Gac) are shown. Mutations are indicated with the corresponding amino acid change. Dots indicate nucleotide identity. Met 499 serves as the initiation codon for Gac, the naturally synthesized GyrA C-terminal domain.
TABLE 1.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| No. | Name | Sequence (5′-3′)a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | dnaA 301R | AAGTTTCGTTAAGAGCCG |
| 2 | gyrA 1521R/GACKO | ATTTTCTTTTTGAATTAAATCCGAAAGACTAGTTTTTAAAACTTCTTCATCATAAATTAT |
| 3 | gyrA 1462F/GACKO | ATAATTTATGATGAAGAAGTTTTAAAAACTAGTCTTTCGGATTTAATTCAAAAAGAAAAT |
| 4 | gyrA 2362R | CTTTGCCTTGTTCAGATAC |
| 5 | gyrA 1492F/GACKOSC | AGTCTTTCGGATTTAATT |
Mutagenic nucleotides are underlined.
Plasmid pTAKO2 was constructed by PCR amplifying a 900-bp fragment encoding gac from B31-NGR, using primers gyrA 1462F/GACKO and gyrA 2362R. Primer gyrA 1462F/GACKO was a mutagenic primer that introduced the complementary mutations as described above for primer gyrA 1521R/GACKO. The amplification product was purified, the 5′ ends were adenylated, and the product was cloned as described above, creating plasmid pTAKO2 (Fig. 1A). The mutagenic plasmid for disrupting synthesis of Gac (pGACKO) was constructed by ligating the approximately 800-bp SpeI fragment from plasmid pTAKO2 into the SpeI sites in plasmid pTAKO1 (Fig. 1B).
B. burgdorferi B31 was transformed with pGACKO and was plated in solid medium containing 0.5 μg of coumermycin A1 ml−1 as previously described (11). A successful recombination event resulted from a double crossover or a single crossover and branch migration spanning the mutations conferring coumarin resistance in the 5′ region of gyrB and the mutations in the gac gene (approximately 4 kb). Cour transformants were screened for gyrA mutations by PCR analysis with primers gyrA 1492F/GACKOSC and gyrA 2362R as previously described (10). Primer gyrA 1492F/GACKOSC is complementary to the mutated sequence, but only 15 of the 18 nucleotides in the primer are complementary to the wild-type sequence, including a noncomplementary nucleotide at the 3′ end. These two primers amplify a ∼900-bp fragment from the mutated sequence, but they fail to amplify the same product from wild-type gyrA with a 56°C annealing temperature (data not shown).
Three of 400 Cour colonies contained the introduced mutations. The frequency of recombination was comparable to or better than the directed insertion of gyrBr into cp26 (1, 10, 16, 18). An increase in recombination efficiency may be due to the need for only a single crossover, followed by branch migration, rather than a double crossover event. However, the efficiency remains low, possibly because of the large size of the fragment required to recombine. The presence of mutations in two clones, CKO-1 and CKO-2, was confirmed by DNA sequencing (Fig. 1C). Clone CKO-1 contained all of the introduced mutations. Clone CKO-2 contained the mutations that changed the two Met residues, but lacked the mutations in the Shine-Dalgarno sequence.
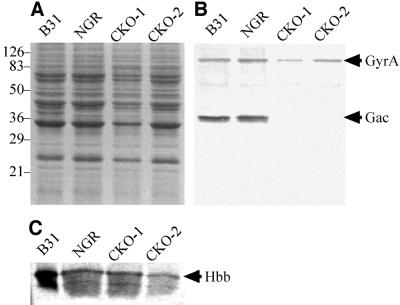
Western analysis confirmed that Gac synthesis was successfully disrupted in both clones (Fig. 2A and B). Whole-cell lysates from B. burgdorferi strains B31 (wild type), B31-NGR, CKO-1, and CKO-2 were analyzed by using an anti-Gac antiserum (5). The antiserum recognized the full-length 91-kDa GyrA protein in all the whole-cell lysates, but it failed to detect Gac in strains CKO-1 and CKO-2. B. burgdorferi B31-NGR is isogenic to CKO-1 and CKO-2 with respect to the mutations in gyrB. The successful disruption of Gac synthesis in CKO-2 indicates that the mutations in the Shine-Dalgarno sequence were not critical for preventing translation.
FIG. 2.
Analysis of Gac synthesis in mutants by Western blotting. Whole-cell B. burgdorferi lysates resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate–12.5% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (panel A). Fractionated lysates were electroblotted to polyvinylidene difluoride and were probed with an anti-Gac polyclonal antiserum (panel B) or an anti-Hbb polyclonal antiserum (panel C). Molecular mass standards are shown on the left in kilodaltons.
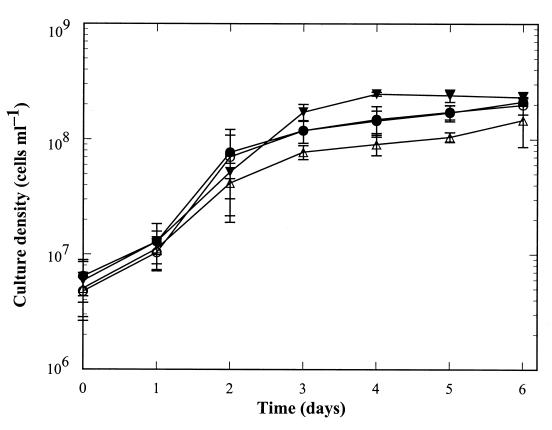
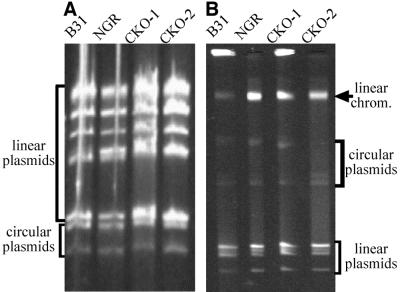
The Gac-deficient strains grow in both liquid culture and solid medium. They exhibit a growth rate and cellular morphology similar to B31 and B31-NGR (Fig. 3 and data not shown). We have hypothesized that Gac may function in the replication, compaction, and maintenance of linear replicons, or in other aspects of linear DNA metabolism, in B. burgdorferi (5). However, ethidium bromide staining of DNA extracts fractionated by agarose gel electrophoresis indicate that linear and circular DNA molecules are maintained in CKO-1 and CKO-2 (Fig. 4). Gross DNA structure and morphology in strains CKO-1 and CKO-2 is also unchanged, as examined by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining (data not shown). No differences in gene expression of the GyrA C-terminal domain-deficient strains compared to strain B31-NGR were detected by Coomassie brilliant blue-stained sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels of whole-cell lysates (Fig. 2A).
FIG. 3.
Effect of Gac on growth of B. burgdorferi. Growth was assayed essentially as described previously (12). Cultures of B. burgdorferi strains B31 (●), B31-NGR (○), CKO-1 (▵), and CKO-2 (▾) were inoculated with the same number of cells into BSK-H medium and were grown for 6 days. One milliliter of each culture was removed each day, cells were pelleted and resuspended in 1 ml of Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline, and the optical density at 600 nm was determined. Plotted are the means of five independent experiments (four for days 4 and 6); error bars represent standard deviations.
FIG. 4.
Effect of Gac on plasmid maintenance in B. burgdorferi. DNA isolated from B. burgdorferi strains B31, B31-NGR, CKO-1, and CKO-2 was analyzed by conventional 0.35% agarose gel electrophoresis (panel A) or field-inversion 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis (panel B) and was stained with ethidium bromide.
The absence of a distinguishable phenotype in the gac mutants suggested that the mutation may be suppressed by an increase in expression of genes encoding other small DNA-binding proteins. We examined strains CKO-1 and CKO-2 for an increase in expression of the hbb gene, which encodes Hbb, the B. burgdorferi HU/IHF homolog (17). Whole-cell lysates were examined by Western analysis using a polyclonal antiserum raised against a synthetic peptide (KRKGRLNARNPQTGEA) designed with predicted antigenicity (MacVector; Oxford Molecular). Hbb was present at low levels in all strains examined, and its synthesis was unchanged in the gac mutants (Fig. 2C), supporting previous biochemical evidence that Hbb may play a limited role in B. burgdorferi DNA metabolism (5, 17).
The ability to disrupt synthesis of Gac demonstrates that the protein is not essential. Based on the HU-like activity of the protein (5), this finding is perhaps not surprising. E. coli strains lacking both subunits of HU are viable (7). Major abnormalities of these E. coli strains include slow doubling times, poor plasmid maintenance, and the inability to support bacteriophage Mu growth (4, 8, 19). Some of the observed phenotypes of HU-deficient E. coli are unstable and are compensated by the accumulation of suppressor mutations (4, 6). In E. coli, mutations that map to gyrB (and confer resistance to the coumarin antibiotic novobiocin) suppress an HU deficiency (6). The data presented here indicate that B. burgdorferi strains lacking Gac do not exhibit any phenotypic differences in DNA metabolism compared to isogenic strains. However, based on the HU-like activity of this protein, the phenotype may be suppressed by the presence of gyrBr, which confers resistance to the coumarin antibiotic coumermycin A1.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kit Tilly, Karl Drlica, and Tasha Knight for thoughtful and critical reading of the manuscript; Stuart Hill, Joe Hinnebusch, and Tim Gsell for useful discussions; and the late Joan Strange for DNA sequencing and peptide synthesis.
Work in our laboratory is supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (MCB-9722408), the National Institutes of Health (AI41559 and AI39695), MONTS (NSF EPSCoR), the Arthritis Foundation, and The University of Montana University Grant Program. S.W.K. and C.H.E. are recipients of Predoctoral Honors Fellowships from The University of Montana.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bono J L, Tilly K, Stevenson B, Hogan D, Rosa P. Oligopeptide permease in Borrelia burgdorferi: putative peptide-binding components encoded by both chromosomal and plasmid loci. Microbiology. 1998;144:1033–1044. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-4-1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cozzarelli N R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980;207:953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gellert M, Mizuuchi K, O'Dea M H, Nash H A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73:3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huisman O, Faelen M, Girard D, Jaffe A, Toussaint A, Rouviere-Yaniv J. Multiple defects in Escherichia coli mutant lacking HU protein. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:3704–3712. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3704-3712.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Knight S W, Samuels D S. Natural synthesis of a DNA-binding protein from the C-terminal domain of DNA gyrase A in Borrelia burgdorferi. EMBO J. 1999;18:4875–4881. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.17.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Malik M, Bensaid A, Rouviere-Yaniv J, Drlica K. Histone-like protein HU and bacterial DNA topology: suppression of an HU deficiency by gyrase mutations. J Mol Biol. 1996;256:66–76. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nash H A. The HU and IHF proteins: accessory factors for complex protein-DNA assemblies. In: Lin E C C, Lynch A S, editors. Regulation of gene expression. R. G. Austin, Tex: Landes Company; 1996. pp. 149–179. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ogura T, Niki H, Kano Y, Imamoto F, Hiraga S. Maintenance of plasmids in HU and IHF mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1990;220:197–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00260482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reece R J, Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26:335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rosa P, Samuels D S, Hogan D, Stevenson B, Casjens S, Tilly K. Directed insertion of a selectable marker into a circular plasmid of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:5946–5953. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.20.5946-5953.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Samuels D S. Electrotransformation of the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Methods Mol Biol. 1995;47:253–259. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-310-4:253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Samuels D S, Garon C F. Coumermycin A1 inhibits growth and induces relaxation of supercoiled plasmids in Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:46–50. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Samuels D S, Mach K E, Garon C F. Genetic transformation of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi with a coumarin-resistant gyrB. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:6045–6049. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.19.6045-6049.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Samuels D S, Marconi R T, Huang W M, Garon C F. gyrB mutations in coumermycin A1-resistant Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:3072–3075. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.3072-3075.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Swanberg S L, Wang J C. Cloning and sequencing of the Escherichia coli gyrA gene coding for the A subunit of DNA gyrase. J Mol Biol. 1987;197:729–736. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tilly K, Casjens S, Stevenson B, Bono J L, Samuels D S, Hogan D, Rosa P. The Borrelia burgdorferi circular plasmid cp26: conservation of plasmid structure and targeted inactivation of the ospC gene. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:361–373. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4711838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tilly K, Fuhrman J, Campbell J, Samuels D S. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi genes encoding homologues of DNA-binding protein HU and ribosomal protein S20. Microbiology. 1996;142:2471–2479. doi: 10.1099/00221287-142-9-2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tilly K, Lubke L, Rosa P. Characterization of circular plasmid dimers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:5676–5681. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.21.5676-5681.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wada M, Kano Y, Ogawa T. Construction and characterization of the deletion mutant of hupA and hupB genes in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988;204:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang J C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:635–692. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.003223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]