Abstract
Background:
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology (JOMFP) is a periodical publication and is one of the most prestigious dental specialty journals in India.
Aim:
To perform bibliometric analysis and network visualisation of articles published in the JOMFP.
Methodology:
Scopus online bibliometric search of articles published in JOMFP from 2011 (Issue 2, May–August) to 2022 (Issue 2, April–June) was performed. A total of 1385 articles out of 1453 were included for analysis. VOSviewer software was used for science mapping and network analysis of extracted data from JOMFP. Basic steps of bibliometric analysis including performance analysis, science mapping, and network analysis were performed to draw conclusions and recommendations.
Results:
The annual frequency of articles was maximum in the year 2019 with 150 articles. The most frequently appearing keywords were “oral squamous cell carcinoma” and “immunohistochemistry”. The mean count of the top 10 cited articles and authors was 144.6 and 293.2, respectively.
Conclusion:
More efforts are warranted not only for increasing the volume of quality papers in JOMFP but also to enhance the collaborations between the various authors and research groups. Large volumes of laboratory and clinical-based research have been published in JOMFP from every part of India; thus, this journal truly represents the global face of Indian oral and maxillofacial pathologists.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis, COVID-19, JOMFP, VOSviewer
INTRODUCTION
Bibliometric analysis is a precise mathematical and statistical evaluation of books, journals, or other publications for exploring and analysing large volumes of scientific data. This process unpacks nuances of the studied field while shedding light on current status, development, and future research directions.[1,2] Bibliometric audit of journal articles can enable scientists to recognise the thrust topics yet to be studied and also explore the updated insights into specific research fields.[1]
There are many journals targeting dental research and academics, which have direct implications on the global oral health care burden. At the national level, many journals focus on this arena, and the Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology (JOMFP) has emerged to be one of the most important and well-read in the scientific community. JOMFP was started in the year 1993 and is a tri-annual publication of the “The Indian Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathologists”. The topics covered in JOMFP are of a wide spectrum but within the scope of oral pathology.[3]
A bibliometric analysis of JOMFP is of special interest since it is one of the most prestigious dental speciality journals from India, having the advantage of being open access to readers. JOMFP is included in PubMed since 2009[4] and covered by Scopus since 2011.[5] It has a CiteScore 2021 of 2.1, an SCImago Journal Rank of 0.391, and a Source Normalized Impact per Paper of 1.048.[5]
Bibliometric analysis of various health care journals has been carried out globally,[1,6,7,8,9,10,11] including the recently analysed Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry.[12] After careful appraisal of the literature, we found that little is known about the bibliometric evaluation of JOMFP. Therefore, in the current article, the published literature by JOMFP, which is included in Scopus online database, was analysed for bibliometric analysis. Scopus was the obvious choice of database to be scanned because of the following:
It is considered to be one of the most comprehensive databases of peer-reviewed journals.[13]
It has combined characteristics of both PubMed and Web of Science.[14]
JOMFP is included in the Scopus database for more than a decade (i.e., 2011 to 2022).
It is compatible with software like Visualization of similarities (VOS) viewer.
VOSviewer is a freely available computer program, developed by van Eck N. J., Waltman L 2010 in the Netherlands,[15] and was used for science mapping and network analysis of extracted data of JOMFP published articles in the current study. The entire bibliometric analysis and visualisation were performed in the current article with an aim to provide readers with a better understanding of how JOMFP articles are performing and are interrelated. The result of this audit of JOMFP articles will trail in identifying current thrust research topics in dentistry, especially in the discipline of oral pathology, which will subsequently lead to appealing pathways for future research.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Previously followed primary steps for conducting bibliometric analysis of journals were incorporated in the current study.[16,17] These steps included data extraction, performance analysis (i.e., descriptive method), science mapping (co-occurrence weight and total link strength), network analysis (metrics, clustering, and visualisation), and conclusions. In studies like the current bibliometric analysis, ethical review is not required.
Scopus online bibliometric search of articles published in JOMFP from 2011 (Issue 2, May–August) to 2022(Issue 2, April–June) on 11th August 2022 was performed. The articles along with information were downloaded in CSV (comma-separated values) format and then exported to VOSviewer (version 1.6.17) for data mining, mapping, and grouping.
RESULTS
Bibliometric analysis of publication output
Extracted publications from the Scopus database were examined for performance analysis; that is, we descriptively examined and described the performance of published articles. All the publications of JOMFP were in English with open access through the website of the journal. Out of all 1453 articles published in JOMFP, 1385 were considered for analysis. A total of 68 excluded articles were editorials, erratum, and a single conference paper [Table 1].
Table 1.
Articles included from JOMFP in Scopus from 2011 (Issue 2, May–August) to 2022 (Issue 2, April–June) on 11 August, 2022
| Articles Included | Articles Excluded | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Article | 1,135 | Editorial | 59 |
| Review | 211 | Erratum | 8 |
| Short Survey | 18 | Conference Paper | 1 |
| Note | 13 | ||
| Letter | 8 | ||
| Total | 1385 | Total | 68 |
The volume of articles published and document citations by the time of JOMFP from 2011 (Issue 2, May–August) to 2022(Issue 2, April–June) is depicted in Figure 1. The annual frequency of the publication of scholarly articles in JOMFP was maximum in the year 2019 with 150 articles published in that year. The 2022 year had already completed the publication of 100 articles, with more issues to come. The annual frequency of citations of articles in JOMFP was maximum in the year 2012 with 1723 citations. Although more articles are supposed to be published in 2022, a sudden drop in citations was seen from 2020 onwards. This decrease in citations might be because of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic disrupting research nationally and internationally.
Figure 1.

Volume of articles published and document citation per year of JOMFP from 2011 (Issue 2, May–August) to 2022(Issue 2, April–June)
Bibliometric analysis of the keywords
Keywords provided by authors in articles that had occurred more than 10 times in the Scopus online database were included for this analysis. Out of 3200 keywords found by VOSviewer, 48 met the threshold. Total link strength for keywords is the number of publications in which two keywords are present simultaneously, or it can simply be termed as “co-occurrence connection between two keywords”.[18] The keywords that appeared most were “oral squamous cell carcinoma” (total link strength 95) and “immunohistochemistry” (total link strength 63) [Figure 2].
Figure 2.

Map of co-occurrence of keywords: Node size is indicative of the frequency of keyword and connecting curves between the nodes are for the co-occurrence connection between two keywords. The shorter distance between the two nodes corresponds to a large number of co-occurrence between keywords
Bibliometric analysis of the citations and publications
The top ten most cited articles and authors' compilation had interesting observations for JOMFP readers [Table 2]. The mean count of the top ten cited articles and authors was 144.6 and 293.2, respectively. Maximum papers of the top ten citations were from the years 2012 and 2014 with three articles from each year. Most of the articles were on histopathological techniques which made it to top of the citation count. It was noted that most of the articles were having multiple authors, which highlight research planning and collaborative writing amongst JOMP authors.
Table 2.
Top 10 cited articles and authors of JOMFP
| Top 10 cited articles of JOMFP | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| Title | Authors | Year | Citations |
| Chemical and physical basics of routine formaldehyde fixation | Thavarajah R, Mudimbaimannar V.K. Elizabeth J, Rao UK, Ranganathan K. | 2012 | 257 |
| Toluidine blue: A review of its chemistry and clinical utility | Sridharan G, Shankar AA. | 2012 | 231 |
| Oral lichen planus: An update on pathogenesis and treatment | Lavanya N, Jayanthi P, Rao UK, Ranganathan K. | 2011 | 161 |
| Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals | Deo P.N, Deshmukh R. | 2019 | 160 |
| Recurrent aphthous stomatitis | Preeti L, Magesh K, Rajkumar K, Karthik R. | 2011 | 145 |
| Oral candidiasis: An overview | Singh A, Verma R, Murari A, Agrawal A. | 2014 | 136 |
| Artefacts in histopathology | Chatterjee S. | 2014 | 101 |
| Oral pyogenic granuloma: Various concepts of etiopathogenesis | Kamal R, Dahiya P, Puri A. | 2012 | 95 |
| MicroRNAs - Biology and clinical applications | Ranganathan K, Sivasankar V. | 2014 | 81 |
| Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in oral potentially malignant disorders: A systematic review | Venugopal A, Uma Maheswari TN. | 2016 | 79 |
|
| |||
| Top 10 cited authors of JOMFP | |||
|
| |||
| Author | Number of articles | Citations | Total Link Strength |
|
| |||
| Ranganathan K. | 24 | 689 | 16 |
| Rao U.K. | 6 | 319 | 10 |
| Thavarajah R. | 6 | 267 | 10 |
| Elizabeth J. | 2 | 259 | 5 |
| Mudimbaimannar V.K. | 1 | 257 | 4 |
| Deshmukh R. | 8 | 253 | 3 |
| Sridharan G. | 2 | 245 | 1 |
| Shankar A.A. | 1 | 231 | 1 |
| Jayanthi P. | 8 | 220 | 3 |
| Deo P.N. | 4 | 192 | 3 |
The range of total link strength of the top ten cited authors was between 1 and 16. Keeping a minimum number of citations 192 for authors, 10 out of 3358 met the threshold. For each of the ten authors, the total strength of co-authorship links with other authors was calculated. The largest network working together consisted of six authors [Figure 3].
Figure 3.

Map of largest co-authorship links consisting of six authors
Top ten authors with a maximum number of published articles in JOMFP was found to be in the range of 13–33 [Table 3]. The tenth position of the author producing a maximum number of articles was taken by three authors with 13 articles produced by each author. Four Asian countries including India, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and Iran were among the top ten most active countries producing the maximum research volume of JOMFP [Figure 4]. India topped the list of these countries with the highest number of included articles in JOMFP (n = 1275). Three countries (France, Italy and Mexico) made it to tenth position with four publications made by each country in JOMFP.
Table 3.
Top ten authors in research volume for JOMFP
| Name | Number of Articles | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Smitha T. | 33 |
| 2 | Ranganathan K. | 24 |
| 3 | Singh S. | 19 |
| 4 | Wadhwan V. | 19 |
| 5 | Bavle R.M. | 18 |
| 6 | Gupta S. | 17 |
| 7 | Kumar S. | 16 |
| 8 | Paremala K. | 15 |
| 9 | Saxena S. | 15 |
| 10 | Kale A.D. | 13 |
| Sivapathasundharam B. | 13 | |
| Sudhakara M. | 13 |
Figure 4.
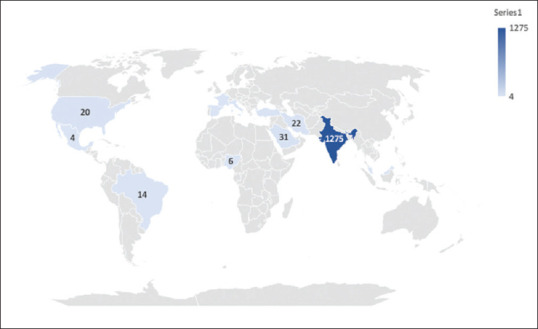
Top ten countries in research volume for JOMFP
We attempted to compile top organisations with maximum research included in JOMFP, but it was impossible because the data provided in the article were confusing and did not match with details of the same department in different articles. This made VOSviewer pick the same department as a separate entry. For example, for the same department, Bengaluru was submitted as Bangalore by the same department in different publications, and hence, VOSviewr counted it as a separate different article in bibliometric analysis.
Authors' bibliographic coupling and co-citation analysis
VOSviewer can be used for visualisation of patterns of influence in bibliometric coupling[19] and co-citation.[20] Both these are like a mirror image of each other; that is, they are opposite of each other. Two articles or authors are considered to be “bibliographically coupled” when they both cite single or more articles/authors simultaneously. Keeping a limit of a minimum of 13 articles by an author, out of 3358 authors, 12 met the threshold of being bibliographically coupled. The total strength of bibliographic coupling links with other authors was calculated for network visualisation using VOSviewer [Figure 5]. This author bibliographic coupling can help us in discovering the intellectual structure of various common topics of oral pathology the active authors are working on and can subsequently reflect the research thrust areas of the discipline.
Figure 5.

Map of authors' bibliographic coupling
Author co-citation analysis is a significant branch of scientometrics, and the main purpose of this analysis is to map scientific domains by pointing out the relationship of co-cited authors.[21] With a minimum of 88 articles by an author, 10 out of 48545 met the threshold. The total strength of co-citation links with various other authors was calculated for network visualisation using VOSviewer software. [Figure 6] shows top 10 authors (items) having highest link strength, 2 clusters and 45 links with a total link strength of 1980.
Figure 6.

Map of authors' co-citation analysis
CONCLUSIONS
The popularity of JOMFP has increased many folds in past years, but our mapping and network visualisation of JOMFP using VOSviewer points that more efforts are warranted not only for increasing the volume of quality papers but also to enhance the collaborations between the various authors and research groups.
A sudden drop in the citation count of JOMFP seen from 2020 onwards might be because of the COVID-19 pandemic disrupting research all over the world. With laboratories, research institutes, and colleges opening and going for “non-virtual mode”, this citation count might swell up soon.
Authors with leading publications and articles with the highest citations in JOMFP were from various parts of India. It was noteworthy that slightly more number of these authors and articles were from the southern part of India. This may be because there are more teaching as well as postgraduation institutes in the south zone, as highlighted by an earlier bibliometric study.[12] International collaborations and multi-centric studies can not only enhance JOMFP's global presence but also lead to an increase in legitimate citations.
Our bibliometric analysis and cluster visualisations using VOSviewer may help to simulate more research collaborations between authors, organisations, and countries. It may also help in reinforcing the existing collaborations for continuing productivity. An increase in linkage within the research setup will increase the quality of articles. These good quality articles will surely be cited and increase the impact of JOMFP. Furthermore, with an increase in the volume of publications in JOMFP, a diversity of topics can be achieved by the inclusion of unexplored fields of oral pathology.
Our bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive description of JOMFP but poses some limitations too. We used the Scopus database, which has many advantages and a few disadvantages like the limited period of 1996+ covered by citation tracking in Scopus. Although our research audit of JOMFP used a wide range of parameters to provide readers with a comprehensive overview from various perspectives, we do admit that our analysis is not perfect and missing indicators can be worked upon in future research.
Comparative trends can be generated by bibliometric analysis of JOMFP every 5 or 10 years. The comparative bibliometric information will make it possible for the editorial board to gauge the growth and other characteristic changes in JOMFP.
With newer and innovative sections like: “Living legends” “Forensic Corner” “Online only articles” “Case report volume” we are sure that JOMFP will generate interest in authors to contribute even more to the journal.Both laboratory and clinical-based research studies from every part of India have been important contributions of JOMFP in the past decade. Thus, JOMFP truly represents the global face of Indian Oral Pathologists.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Liu FH, Yu CH, Chang YC. Bibliometric analysis of articles published in journal of dental sciences from 2009 to 2020. J Dent Sci. 2022;17:642–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133:285–96. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology (JOMFP): About us. [Last accessed on 2022 Aug 10]. Available from: https://www.jomfp.in/aboutus.asp .
- 4.Journal of oral and maxillofacial pathology: JOMFP.-NLM Catalog-NCBI. [Last accessed on 2022 Aug 10]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nlmcatalog/?term=jomfp .
- 5.Scopus preview-Scopus-Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. [Last accessed on 2022 Aug 10]. Available from: https://www.scopus.com/sourceid/20000195014 .
- 6.Moraes RR de, Morel LL, Correa MB, Lima G da S. A Bibliometric Analysis of Articles Published in Brazilian Dental Journal over 30 years. Braz Dent J. 2020;31:10–8. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440202004550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rogers JL, Barpujari A, Reddy VP. Letter to the editor regarding “Bibliometric analysis of publications from 2011-2020 in 6 major neurosurgical journals (part 1): Geographic, demographic, and article type trends”. World Neurosurg. 2022;158:341–2. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.11.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Erdag TK, Kurtoglu G. The 100 most cited Turkish papers in the otorhinolaryngology journals of web of science. Turk Otolarengoloji ArsiviTurkish Arch Otolaryngol. 2015;53:112–9. doi: 10.5152/tao.2015.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blažun Vošner H, Železnik D, Kokol P. Bibliometric analysis of the International Medical Informatics Association official journals. Inform Health Soc Care. 2019;44:405–21. doi: 10.1080/17538157.2018.1525734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vishwanathan K, Kambhampati SBS, Patralekh MK, Vaish A, Vaishya R. Bibliometric analysis of the top 50 most cited publications of the Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;22:101590. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101590. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot. 2021.101590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Luxenburg D, Constantinescu D, St. Louis G, Bondar KJ, Sudah SY, D'Apuzzo M. Characteristics and trends of the most cited publications in The Journal of Arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2022;16:211–8. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2022.05.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Karishma J, Patti B, Parlapalli V, Pydi S, Prathyusha C, Pallekonda AP. Bibliometric analysis of the Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry from 2014 to 2020. J Indian Assoc Public Health Dent. 2021;19:180. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Effendi DN, Irwandani, Anggraini W, Jatmiko A, Rahmayanti H, Ichsan IZ, et al. Bibliometric analysis of scientific literacy using VOS viewer: Analysis of science education. J Phys Conf Ser. 2021;1796:012096. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saad RK, Abu Khudair S, El Rabbat M, Omar M, Al Nsour M, Khader Y, et al. Published research on COVID-19 in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: Bibliometric analysis. Interact J Med Res. 2022;11:e38935. doi: 10.2196/38935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84:523–38. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tamala JK, Maramag EI, Simeon KA, Ignacio JJ. A bibliometric analysis of sustainable oil and gas production research using VOSviewer? Clean Eng Technol. 2022;7:100437. doi: 10.1016/j.clet. 2022.100437. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xiao Z, Qin Y, Xu Z, Antucheviciene J, Zavadskas EK. The journal buildings: A bibliometric analysis (2011–2021) Buildings. 2022;12:37. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guo YM, Huang ZL, Guo J, Li H, Guo XR, Nkeli MJ. Bibliometric analysis on smart cities research. Sustainability. 2019;11:3606. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kessler MM. Bibliographic coupling between scientific papers. Am Doc. 1963;14:10–25. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Small H. Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J Am Soc Inf Sci. 1973;24:265–9. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang B, Bu Y, Huang WB. Document- and keyword-based author co-citation analysis. Data Inf Manag. 2018;Sep; 2:70–82. [Google Scholar]


