Abstract
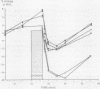
Ten patients with exercise induced asthma, in whom inhaled nedocromil sodium 4 mg by metered dose inhaler attenuated the exercise fall in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) by at least 40%, participated in a double blind dose response study to compare the protective effect of nedocromil sodium given 15 minutes before exercise challenge via a nebuliser (Wright) in concentrations of 0.5, 5, 10, and 20 mg/ml with that of placebo (saline). Response was assessed as the maximum fall in FEV1 after the patient had run on a treadmill for six to eight minutes. Plasma concentrations of nedocromil sodium were measured at the time of challenge. After exercise challenge the mean (SEM) maximum percentage falls in FEV1 were 30.3 (1.6) for the control run and 28.0 (4.1) after placebo. The percentage fall was attenuated by pretreatment with all concentrations of nedocromil sodium to 12.8 (2.8), 11.2 (2.1), 12.8 (2.1), and 14.1 (3.5) for the 0.5, 5, 10, and 20 mg/ml concentrations respectively (p less than 0.001). There were no significant differences between the different nedocromil concentrations. Mean plasma concentrations of nedocromil were proportional to dose. Thus concentrations of nebulised nedocromil sodium that ranged from 0.5 to 20 mg/ml gave a similar degree of protection (50-60%) against exercise induced asthma. This appears to be the maximum protection that can be achieved with nedocromil sodium and is similar to the protection obtained with 4 mg nedocromil administered by metered dose aerosol.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cairns H., Cox D., Gould K. J., Ingall A. H., Suschitzky J. L. New antiallergic pyrano [3,2-g]quinoline-2,8-dicarboxylic acids with potential for the topical treatment of asthma. J Med Chem. 1985 Dec;28(12):1832–1842. doi: 10.1021/jm00150a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns H., Orr T. S. The development of a new agent for the treatment of inflammatory/allergic conditions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):513–517. doi: 10.1159/000234267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. M., Fuller R. W., Barnes P. J. Effect of nedocromil sodium on sulphur dioxide induced bronchoconstriction. Thorax. 1987 Jun;42(6):462–465. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.6.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairfax A. J., Allbeson M. A double-blind group comparative trial of nedocromil sodium and placebo in the management of bronchial asthma. J Int Med Res. 1988 May-Jun;16(3):216–224. doi: 10.1177/030006058801600309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyans P. G., Chatterjee P. C., Chatterjee S. S. A trial comparing nedocromil sodium (Tilade) and placebo in the management of bronchial asthma. Clin Allergy. 1986 Nov;16(6):505–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1986.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. J., Preston J. R., Gilbert C. M., Wilkinson D. J., Lockley W. J., Brown K. A radioimmunoassay method for the determination of nedocromil sodium in plasma and urine. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1988;6(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0731-7085(88)80055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. P., Nogrady S. G. Effect of an inhaled antihistamine on exercise-induced asthma. Thorax. 1980 Sep;35(9):675–679. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.9.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper E. F., Kline P. A., Morris M. M., Hargreave F. E. Airway constriction by isocapnic hyperventilation of cold, dry air: comparison of magnitude and duration of protection by nedocromil sodium and sodium cromoglycate. Clin Allergy. 1987 Nov;17(6):523–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1987.tb02048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal S., Malhotra S., Gribben D., Hodder D. Nedocromil sodium: a new drug for the management of bronchial asthma. Thorax. 1984 Nov;39(11):809–812. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.11.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Brown M. J., Nagy L., Causon R., Walport M. J., Kay A. B. Exercise-induced release of histamine and neutrophil chemotactic factor in atopic asthmatics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Aug;70(2):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Nagy L., Nagakura T., Walport M. J., Kay A. B. Identification and partial characterization of an exercise-induced neutrophil chemotactic factor in bronchial asthma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):889–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI110528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. R., Berkin K. E., Kerr J. W. Dose-response study of sodium cromoglycate in exercise-induced asthma. Thorax. 1982 Sep;37(9):663–666. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.9.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Al-Laith M., Bosman L., Brostoff J., Cunniffe T. M., Flint K. C., Hudspith B. N., Jaffar Z. H., Johnson N. M., Kassessinoff T. A. Effects of sodium cromoglycate and nedocromil sodium on histamine secretion from mast cells from various locations. Drugs. 1989;37 (Suppl 1):37–77. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198900371-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Befus A. D., Bienenstock J. Mucosal mast cells. III. Effect of quercetin and other flavonoids on antigen-induced histamine secretion from rat intestinal mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jun;73(6):819–823. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R., Phillips G. D., Holgate S. T. Nedocromil sodium is more potent than sodium cromoglycate against AMP-induced bronchoconstriction in atopic asthmatic subjects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 May;19(3):285–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. A., Thomson N. C. Attenuation of exercise-induced asthma by pretreatment with nedocromil sodium and minocromil. Clin Allergy. 1985 Jul;15(4):377–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb03006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robuschi M., Vaghi A., Simone P., Bianco S. Prevention of fog-induced bronchospasm by nedocromil sodium. Clin Allergy. 1987 Jan;17(1):69–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1987.tb02321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchiccioli K. M., Riley P. A. Clinical pharmacology of nedocromil sodium. Drugs. 1989;37 (Suppl 1):123–136. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198900371-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Kay A. B. Nedocromil, a mucosal and connective tissue mast cell stabilizer, inhibits exercise-induced asthma. Br J Dis Chest. 1985 Oct;79(4):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(85)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullett W. M., Tan K. M., Wall R. T., Patel K. R. Dose-response effect of sodium cromoglycate pressurised aerosol in exercise induced asthma. Thorax. 1985 Jan;40(1):41–44. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells E., Jackson C. G., Harper S. T., Mann J., Eady R. P. Characterization of primate bronchoalveolar mast cells. II. Inhibition of histamine, LTC4, and PGD2 release from primate bronchoalveolar mast cells and a comparison with rat peritoneal mast cells. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3941–3945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van As A., Chick T. W., Bodman S. F., Storms W. W., Nathan R. A., Selner J. C., Koepke J. W., Townley R. G., Bewtra A. K., Nair N. A group comparative study of the safety and efficacy of nedocromil sodium (Tilade) in reversible airways disease: a preliminary report. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1986;147:143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]