Abstract
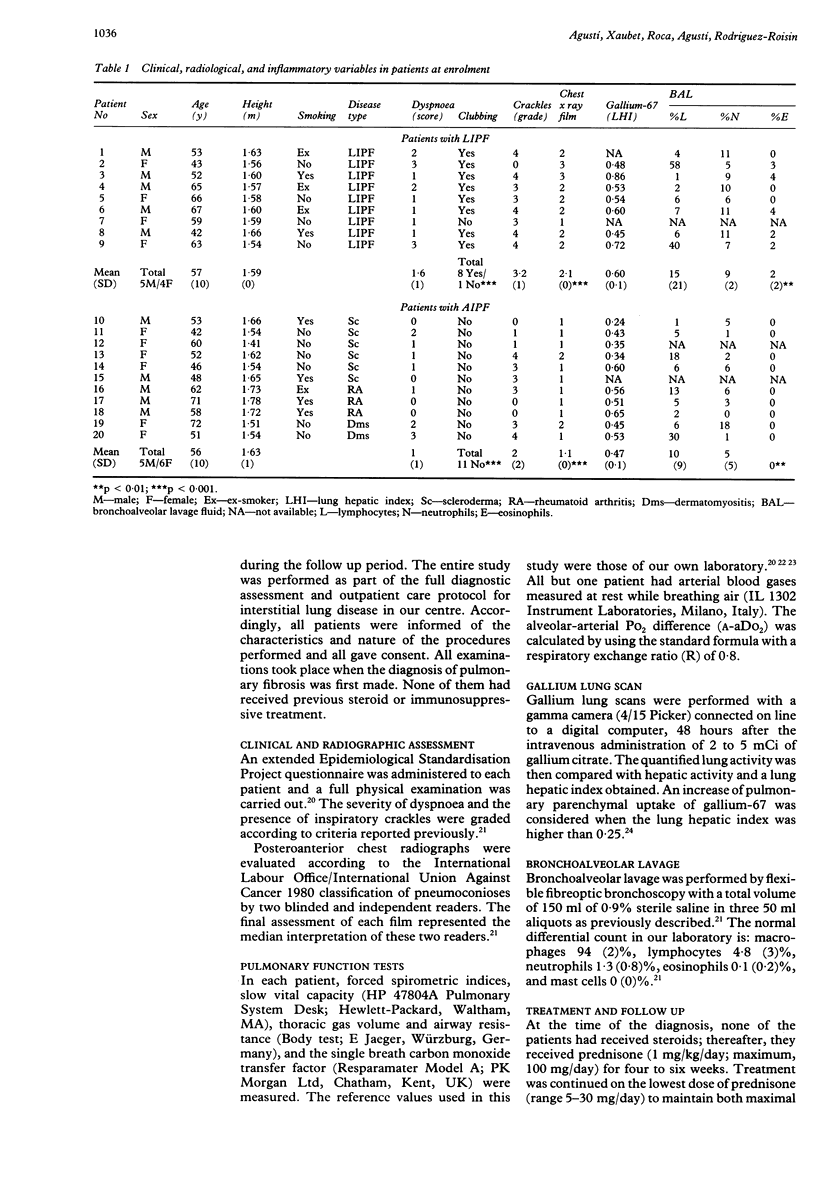
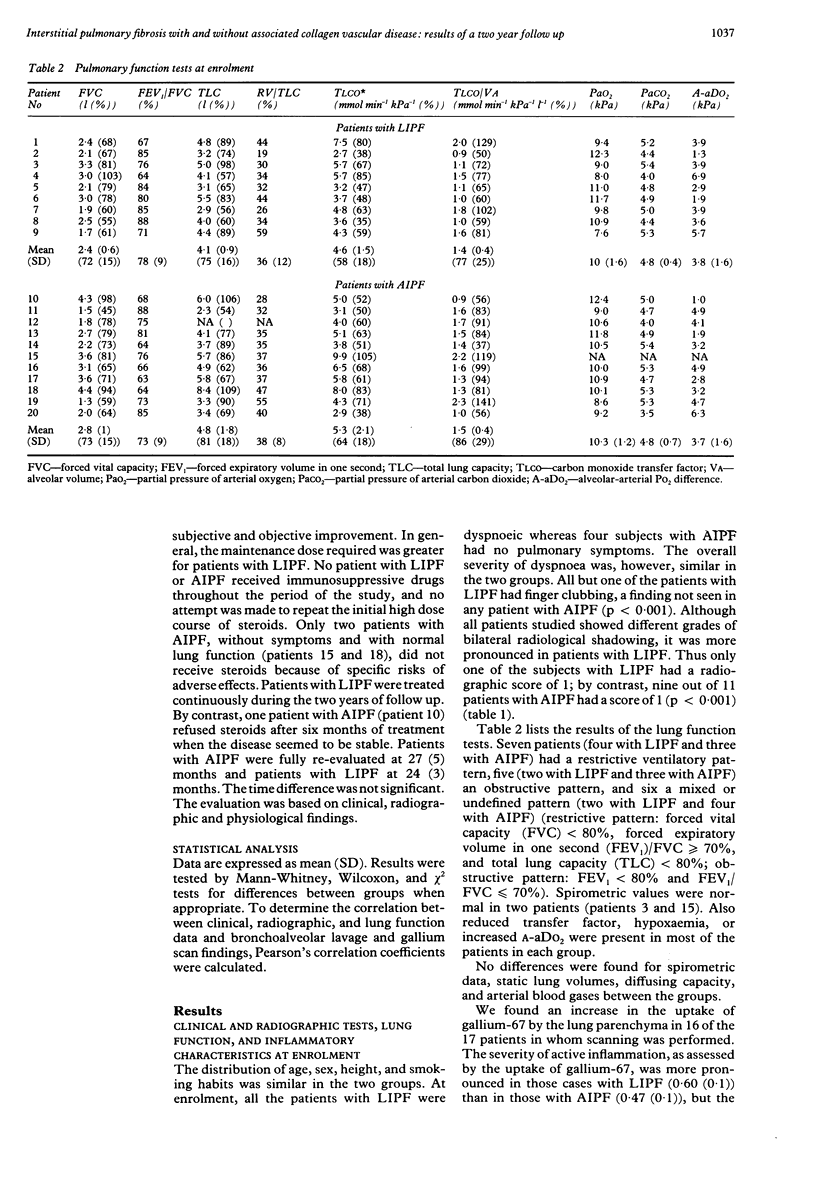
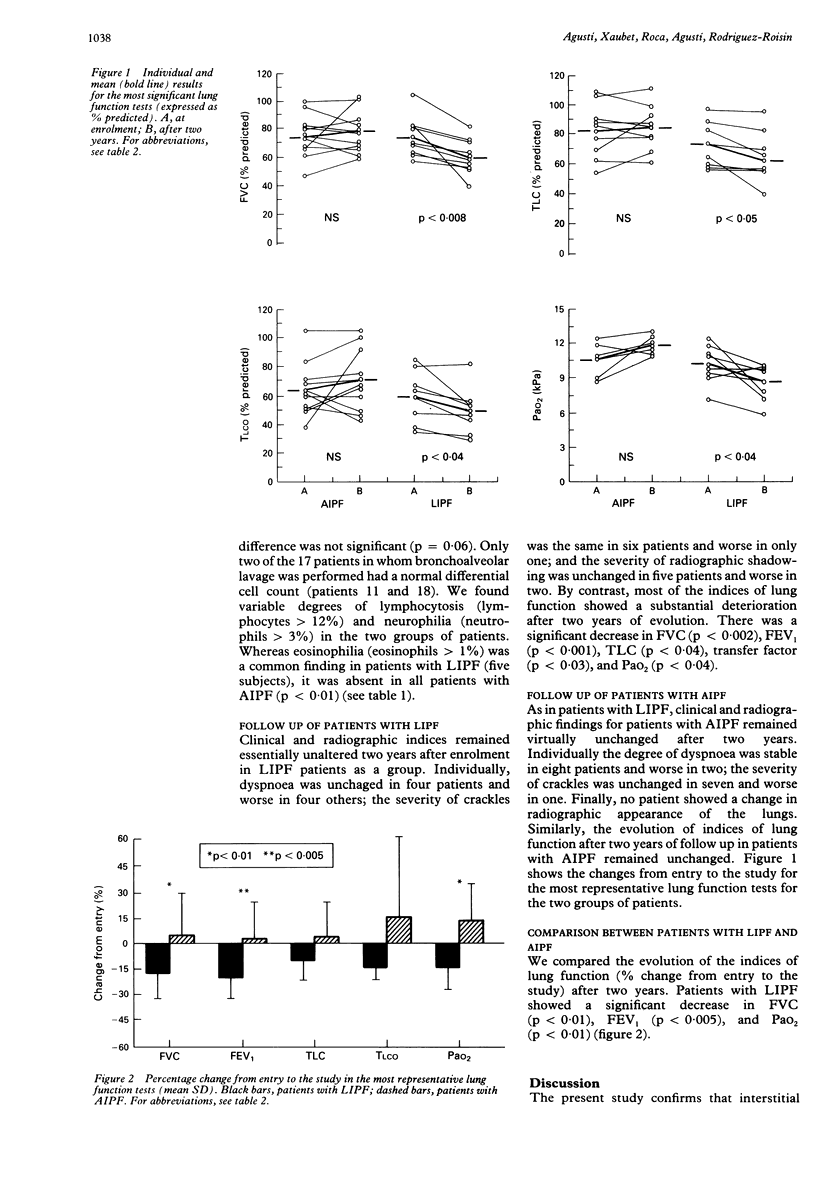
BACKGROUND: Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis is a disease with a highly variable clinical course. To ascertain if an inadequate selection of patients might explain part of this variability, two different groups of patients with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, those with the "lone" form of the disease (LIPF) and those with associated collagen vascular disorders (AIPF), were studied separately. METHODS: Twenty consecutive patients (nine with LIPF and 11 with AIPF) were included. Their clinical and radiographic findings and results of pulmonary function tests, gallium-67 lung scanning, and cellular analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were compared at diagnosis. Moreover, the evolution of LIPF and AIPF was contrasted after a follow up of two years, both groups having received a similar treatment regimen of corticosteroids. RESULTS: At enrollment, patients with LIPF and AIPF were of similar age, and had similar symptoms and derangement of lung function, but patients with LIPF presented with finger clubbing, more obvious radiographic abnormalities, and a greater percentage of eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Two years later, patients with LIPF had significantly decreased FVC, FEV1, TLC, TLCO, and PaO2. By contrast, lung function remained unaltered in patients with AIPF. Similarly, when the percentage change from entry to the study was compared, patients with LIPF showed a significant decrease in FVC, FEV1, and PaO2. CONCLUSIONS: Unlike the patients with AIPF, those with LIPF showed a deterioration in lung function and developed further restrictive impairment and poorer gas exchange. This has implications in their clinical management.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agustí A. G., Roca J., Gea J., Wagner P. D., Xaubet A., Rodriguez-Roisin R. Mechanisms of gas-exchange impairment in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Feb;143(2):219–225. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A., Coutu R. E., FitzGerald M. X., Gupta R. G. Natural history and treated course of usual and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 13;298(15):801–809. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804132981501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colp C. R., Riker J., Williams M. H., Jr Serial changes in scleroderma and idiopathic interstitial lung disease. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Oct;132(4):506–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W. Interstitial lung disease: current concepts of pathogenesis, staging and therapy. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):542–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. T., Weg J. G., Harkleroad L. E., Fitch R. F. Pulmonary dysfunction in rheumatoid disease. Chest. 1973 Jan;63(1):27–34. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene N. B., Solinger A. M., Baughman R. P. Patients with collagen vascular disease and dyspnea. The value of gallium scanning and bronchoalveolar lavage in predicting response to steroid therapy and clinical outcome. Chest. 1987 May;91(5):698–703. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.5.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Lukoszek A., Salsbury A. J., Dewar A., Collins J. V., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cell counts in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and their relation to therapy. Thorax. 1980 May;35(5):328–339. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.5.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Bjermer L., Lundgren R., Venge P. The eosinophil component of the alveolitis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Signs of eosinophil activation in the lung are related to impaired lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):373–377. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Clinical significance of pulmonary function tests. Pulmonary function testing in interstitial pulmonary disease. What does it tell us? Chest. 1980 Dec;78(6):856–865. doi: 10.1378/chest.78.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König G., Luderschmidt C., Hammer C., Adelmann-Grill B. C., Braun-Falco O., Fruhmann G. Lung involvement in scleroderma. Chest. 1984 Mar;85(3):318–324. doi: 10.1378/chest.85.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Line B. R., Fulmer J. D., Reynolds H. Y., Roberts W. C., Jones A. E., Harris E. K., Crystal R. G. Gallium-67 citrate scanning in the staging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Correlation and physiologic and morphologic features and bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Aug;118(2):355–365. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.2.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Fujimura N., Hirata T., Izumi T. Differentiation between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial pneumonia associated with collagen vascular diseases by comparison of the ratio of OKT4+ cells and OKT8+ cells in BALF T lymphocytes. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;67(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. R., Paradis I. L., Gryzan S., Medsger T. A., Jr, Follansbee W. P., Klein H. A., Dauber J. H. Role of inflammation in the lung disease of systemic sclerosis: comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Mar;107(3):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panos R. J., Mortenson R. L., Niccoli S. A., King T. E., Jr Clinical deterioration in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: causes and assessment. Am J Med. 1990 Apr;88(4):396–404. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90495-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters-Golden M., Wise R. A., Schneider P., Hochberg M., Stevens M. B., Wigley F. Clinical and demographic predictors of loss of pulmonary function in systemic sclerosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Jul;63(4):221–231. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198407000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. W., Monick M., Hunninghake G. W. Prognostic role of eosinophils in pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1):51–56. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A rational clinical approach. Chest. 1987 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Cobo E., Burgos F., Perez J., Clausen J. L. Single-breath carbon monoxide diffusing capacity prediction equations from a Mediterranean population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):1026–1032. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Sanchis J., Agusti-Vidal A., Segarra F., Navajas D., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Casan P., Sans S. Spirometric reference values from a Mediterranean population. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 May-Jun;22(3):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Evidence for chronic inflammation as a component of the interstitial lung disease associated with progressive systemic sclerosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):612–617. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P. D., Wise R. A., Hochberg M. C., Wigley F. M. Serial pulmonary function in systemic sclerosis. Am J Med. 1982 Sep;73(3):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90732-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz M. I., Matthay R. A., Sahn S. A., Stanford R. E., Marmorstein B. L., Scheinhorn D. J. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: analysis of six cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1976 Jan;55(1):89–104. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197601000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. M., Miller K. S., Kinsella M. B., Smith E. A., Schabel S. I. Evaluation and management of scleroderma lung disease using bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Med. 1990 May;88(5):470–476. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90425-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen V. D., Owens G. R., Fino G. J., Rodnan G. P., Medsger T. A., Jr Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jul;28(7):759–767. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen V. D., Owens G. R., Redmond C., Rodnan G. P., Medsger T. A., Jr The effect of D-penicillamine on pulmonary findings in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):882–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER-WARWICK M. SYSTEMIC ARTERIAL PATTERNS IN THE LUNG AND CLUBBING OF THE FINGERS. Thorax. 1963 Sep;18:238–250. doi: 10.1136/thx.18.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Viggiano R. W., Pickersgill J., Colby T. V. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clinical features and prognosis as correlated with histologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):727–733. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukiainen P., Taskinen E., Holsti P., Korhola O., Valle M. Prognosis of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Thorax. 1983 May;38(5):349–355. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.5.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Burrows B., Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax. 1980 Mar;35(3):171–180. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P. L. The value of serial bronchoalveolar lavages in assessing the clinical progress of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):26–34. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallaert B., Hatron P. Y., Grosbois J. M., Tonnel A. B., Devulder B., Voisin C. Subclinical pulmonary involvement in collagen-vascular diseases assessed by bronchoalveolar lavage. Relationship between alveolitis and subsequent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;133(4):574–580. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H. P., Matthay R. A. Pulmonary manifestations of the collagen vascular diseases. Clin Chest Med. 1989 Dec;10(4):677–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xaubet A., Roca J., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Herranz J., Marin A., Lomeña F., Montserrat J. M., Agustí-Vidal A. Bronchoalveolar lavage cellular analysis and gallium lung scan in the assessment of patients with amiodarone-induced pneumonitis. Respiration. 1987;52(4):272–280. doi: 10.1159/000195336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xaubet A., Rodriguez-Roisín R., Bombí J. A., Marín A., Roca J., Agustí-Vidal A. Correlation of bronchoalveolar lavage and clinical and functional findings in asbestosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):848–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Colby T. V., Carrington C. B. Lung biopsy in rheumatoid arthritis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):770–777. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


