Abstract
It is over 25 years since Scadding first defined the term fibrosing alveolitis. It has since been established that complex mechanisms underlie its pathogenesis, including epithelial and endothelial injury, vascular leakage, production of inflammatory cells and their mediators, and fibroblast activation. Only through a detailed knowledge of how these cellular and molecular events are interlinked will we learn how to combat this disease, which is notoriously resistant to present treatments. So far the only therapeutic advances have been refinements in immunosuppression, and even these treatments are frequently disappointing. We believe that future advances in treatment will come from the development of agents that protect endothelial and epithelial cells from further injury and agents that can inhibit release of inflammatory mediators. A better knowledge of the mechanisms of collagen gene activation and the biochemical pathways of collagen production may also allow the identification of vulnerable sites at which new treatments may be directed. A combined approach to modifying appropriate parts of both the inflammatory component and the fibroblast/collagen component should provide a new stimulus to research. Further epidemiological studies are also needed to identify the environmental causes of lung injury that initiate the cascade of events leading to interstitial fibrosis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Bravo M. A., Avila R. E., Galanopoulos T., Neville-Golden J., Maxwell M., Selman M. Platelet-derived growth factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1055–1064. doi: 10.1172/JCI114808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes M. J., Constable B. J., Morton L. F., Kodicek E. Studies in vivo on the biosynthesis of collagen and elastin in ascorbic acid-deficient guinea pigs. Evidence for the formation and degradation of a partially hydroxylated collagen. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):575–585. doi: 10.1042/bj1190575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum B. J., Moss J., Breul S. D., Berg R. A., Crystal R. G. Effect of cyclic AMP on the intracellular degradation of newly synthesized collagen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2843–2847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S., Baum B. J., Crystal R. G. Fibroblasts degrade newly synthesised collagen within the cell before secretion. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):413–416. doi: 10.1038/276413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S. Intracellular degradation of newly synthesized collagen. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Oct;4(5):399–411. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage growth factor for fibroblasts. Regulation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):806–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI110677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. C., Osornio-Vargas A. R., Badgett A., Brody A. R. Differential proliferation of rat lung fibroblasts induced by the platelet-derived growth factor-AA, -AB, and -BB isoforms secreted by rat alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):539–547. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borok Z., Buhl R., Grimes G. J., Bokser A. D., Hubbard R. C., Holroyd K. J., Roum J. H., Czerski D. B., Cantin A. M., Crystal R. G. Effect of glutathione aerosol on oxidant-antioxidant imbalance in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 1991 Jul 27;338(8761):215–216. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. F., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F. Leaky vessels, fibrin deposition, and fibrosis: a sequence of events common to solid tumors and to many other types of disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A., Cottier H. Cellular events in alveolitis and the evolution of pulmonary fibrosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02890055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Poulter L. W., Du Bois R. M. Phenotypic analysis of alveolar macrophages in normal subjects and in patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1986 Jun;41(6):429–434. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.6.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Poulter L. W., Janossy G., du Bois R. M. Immunohistological analysis of lung tissue from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis suggesting local expression of immune hypersensitivity. Thorax. 1985 Jun;40(6):405–411. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.6.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Poulter L. W., du Bois R. M. Immunocompetent cells in bronchoalveolar lavage reflect the cell populations in transbronchial biopsies in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Dec;132(6):1300–1306. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.6.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., Boileau R., Bégin R. Increased procollagen III aminoterminal peptide-related antigens and fibroblast growth signals in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):572–578. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., Hubbard R. C., Crystal R. G. Glutathione deficiency in the epithelial lining fluid of the lower respiratory tract in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):370–372. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart M. K., Emdur L. I., Ahtiala-Stewart K., Ahmad M. Excessive helper T-cell function in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: correlation with disease activity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Jun;43(3):382–394. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N. On scleroderma. Mast cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. JAMA. 1989 Sep 1;262(9):1206–1209. doi: 10.1001/jama.262.9.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrin B., Dewar A., Rodriguez-Roisin R., Turner-Warwick M. Fine structural changes in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and asbestosis. J Pathol. 1985 Oct;147(2):107–119. doi: 10.1002/path.1711470206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dall'Aglio P. P., Pesci A., Bertorelli G., Brianti E., Scarpa S. Study of immune complexes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids. Respiration. 1988;54 (Suppl 1):36–41. doi: 10.1159/000195495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Regulation of the growth rate of mouse fibroblasts by IL-3-activated mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4307–4313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaton J. L., Gibson M., Blackmer K. M., Nakajima S. T., Badger G. J., Brumsted J. R. A randomized, controlled trial of clomiphene citrate and intrauterine insemination in couples with unexplained infertility or surgically corrected endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1990 Dec;54(6):1083–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djukanović R., Roche W. R., Wilson J. W., Beasley C. R., Twentyman O. P., Howarth R. H., Holgate S. T. Mucosal inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):434–457. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty A. J., Lyons A., Smith B. J., Wright E. M., Stephens P. E., Harris T. J., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Sequence of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and its identity to erythroid-potentiating activity. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):66–69. doi: 10.1038/318066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisin R. B., Schwarz M. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Stanford R. E. Circulating immune complexes in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 16;298(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802162980701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Reynolds M. M., Kotloff R. M., Kern J. A. Fibroblast interleukin 1 beta: synergistic stimulation by recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor and posttranscriptional regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6171–6175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emura M., Nagai S., Takeuchi M., Kitaichi M., Izumi T. In vitro production of B cell growth factor and B cell differentiation factor by peripheral blood mononuclear cells and bronchoalveolar lavage T lymphocytes from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Oct;82(1):133–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., McClure D. B. Fibronectin-associated transforming growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1987 May;131(2):184–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine A., Goldstein R. H. The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3897–3902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Kelman J. A., Fells G., Weinberger S. E., Horwitz A. L., Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 4;301(14):737–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910043011401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Carney D. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Cunningham D. D. Thrombin active site regions required for fibroblast receptor binding and initiation of cell division. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6609–6616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Krane S. M. Modulation by recombinant interleukin 1 of synthesis of types I and III collagens and associated procollagen mRNA levels in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16724–16729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Polgar P. The effect and interaction of bradykinin and prostaglandins on protein and collagen production by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8630–8633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Poliks C. F., Pilch P. F., Smith B. D., Fine A. Stimulation of collagen formation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in cultures of human lung fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):964–970. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosset P., Perez T., Lassalle P., Duquesnoy B., Farre J. M., Tonnel A. B., Capron A. Increased TNF-alpha secretion by alveolar macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3):593–597. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A. J., Reeves J. T., Harrison N. K., Winlove P., Laurent G. J. Growth factors for human fibroblasts in the solute remaining after clot formation. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):271–274. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths J. B. Serum and growth factors in cell culture media--an introductory review. Dev Biol Stand. 1987;66:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruschwitz M., Müller P. U., Sepp N., Hofer E., Fontana A., Wick G. Transcription and expression of transforming growth factor type beta in the skin of progressive systemic sclerosis: a mediator of fibrosis? J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Feb;94(2):197–203. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler V., Hanauske-Abel H. M., Myllylä R., Kaska D. D., Hanauske A., Kivirikko K. I. Syncatalytic inactivation of prolyl 4-hydroxylase by anthracyclines. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):365–372. doi: 10.1042/bj2510365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Welgus H. G., Krane S. M. Regulation of the mammalian collagenases. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Dec;4(6):493–512. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. K., Glanville A. R., Strickland B., Haslam P. L., Corrin B., Addis B. J., Lawrence R., Millar A. B., Black C. M., Turner-Warwick M. Pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis: the detection of early changes by thin section CT scan, bronchoalveolar lavage and 99mTc-DTPA clearance. Respir Med. 1989 Sep;83(5):403–414. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(89)80072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. K., Myers A. R., Corrin B., Soosay G., Dewar A., Black C. M., Du Bois R. M., Turner-Warwick M. Structural features of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):706–713. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschek W. M., Witschi H. Pulmonary fibrosis--a possible mechanism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;51(3):475–487. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Cromwell O., Dewar A., Turner-Warwick M. Evidence of increased histamine levels of lung lavage fluids from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jun;44(3):587–593. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L. Evaluation of alveolitis by studies of lung biopsies. Lung. 1990;168 (Suppl):984–992. doi: 10.1007/BF02718236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Heard B., Lukoszek A., Collins J. V., Salsbury A. J., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary fibrosis: comparison of cells obtained with lung biopsy and clinical features. Thorax. 1980 Jan;35(1):9–18. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Lukoszek A., Salsbury A. J., Dewar A., Collins J. V., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cell counts in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and their relation to therapy. Thorax. 1980 May;35(5):328–339. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.5.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty K. A., Jeffrey J. J., Hibbs M. S., Welgus H. G. The collagen substrate specificity of human neutrophil collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard B. E., Dewar A., Corrin B. Apposition of fibroblasts to mast cells and lymphocytes in normal human lung and in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Ultrastructure and cell perimeter measurements. J Pathol. 1992 Mar;166(3):303–310. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Turner-Warwick M. Assay of circulating immunoglobulins in patients with fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Nov;2(6):645–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R. The eosinophil and acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1245–1246. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON D. S., BENTLEY J. P. On the significance of the extractable collagens. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7:37–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I., Britton J., Kinnear W., Logan R. Rising mortality from cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. BMJ. 1990 Nov 3;301(6759):1017–1021. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6759.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordana M., Befus A. D., Newhouse M. T., Bienenstock J., Gauldie J. Effect of histamine on proliferation of normal human adult lung fibroblasts. Thorax. 1988 Jul;43(7):552–558. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.7.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordana M., Schulman J., McSharry C., Irving L. B., Newhouse M. T., Jordana G., Gauldie J. Heterogeneous proliferative characteristics of human adult lung fibroblast lines and clonally derived fibroblasts from control and fibrotic tissue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):579–584. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B. Vascular disease in scleroderma. Endothelial T lymphocyte-fibroblast interactions. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):53–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil N., O'Connor R. N., Unruh H. W., Warren P. W., Flanders K. C., Kemp A., Bereznay O. H., Greenberg A. H. Increased production and immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-beta in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;5(2):155–162. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kradin R. L., Divertie M. B., Colvin R. B., Ramirez J., Ryu J., Carpenter H. A., Bhan A. K. Usual interstitial pneumonitis is a T-cell alveolitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Aug;40(2):224–235. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., McAnulty R. J. Protein metabolism during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rabbits. In vivo evidence for collagen accumulation because of increased synthesis and decreased degradation of the newly synthesized collagen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):82–88. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. T., Norton J. A., Harvey A. K., Gorschboth C. M., Talbot T. L., Grotendorst G. R. Doxorubicin-induced impairment of wound healing in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Jan;76(1):119–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Cutroneo K. R., Davis G. S., Giancola M. S. Lavage type III procollagen N-terminal peptides in human pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis. Lab Invest. 1983 Jun;48(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., McKeown-Longo P. J., Millis A. J. Binding of soluble fibronectin and its subsequent incorporation into the extracellular matrix by early and late passage human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2756–2760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinelli W. A., Polunovsky V. A., Harmon K. R., Bitterman P. B. Role of platelet-derived growth factor in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):503–504. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet Y., Rom W. N., Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Exaggerated spontaneous release of platelet-derived growth factor by alveolar macrophages from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):202–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAnulty R. J., Campa J. S., Cambrey A. D., Laurent G. J. The effect of transforming growth factor beta on rates of procollagen synthesis and degradation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 31;1091(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
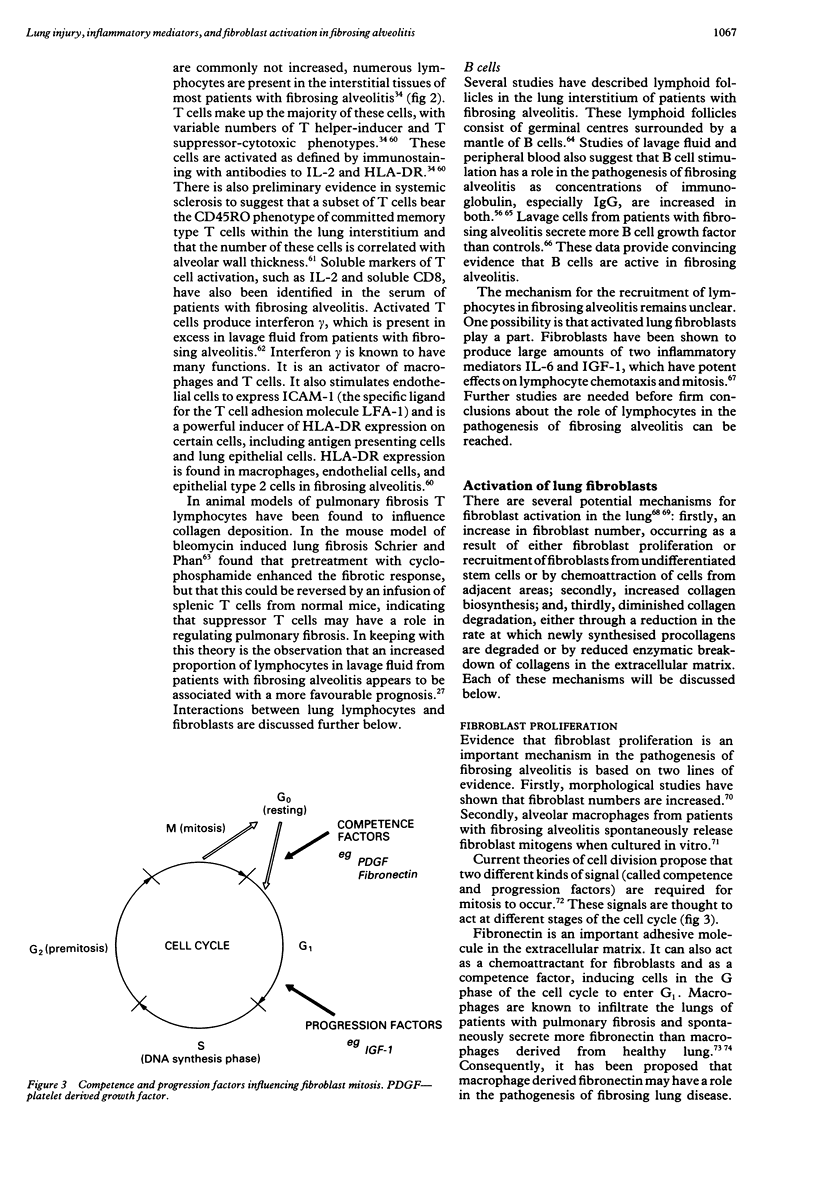
- McCullough B., Collins J. F., Johanson W. G., Jr, Grover F. L. Bleomycin-induced diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in baboons. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):79–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI108928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Koonce M. P. Mitosis. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2683078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara M., Njieha F. K., Prockop D. J. Formation of collagen fibrils in vitro by cleavage of procollagen with procollagen proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8442–8448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kawada K., Zhang P., Uesugi Y., Sakamoto O., Koda A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in genetically mast cell-deficient WBB6F1-W/Wv mice and mechanism of the suppressive effect of tranilast, an antiallergic drug inhibiting mediator release from mast cells, on fibrosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1991;95(2-3):195–201. doi: 10.1159/000235429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Bretz U., Baggiolini M., Reynolds J. J. The latent collagenase and gelatinase of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):517–525. doi: 10.1042/bj1920517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai S., Aung H., Takeuchi M., Kusume K., Izumi T. IL-1 and IL-1 inhibitory activity in the culture supernatants of alveolar macrophages from patients with interstitial lung diseases. Chest. 1991 Mar;99(3):674–680. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.3.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettelbladt O., Bergh J., Schenholm M., Tengblad A., Hällgren R. Accumulation of hyaluronic acid in the alveolar interstitial tissue in bleomycin-induced alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):759–762. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimni M. E., De Guia E., Bavetta L. A. Synthesis and turnover of collagen precursors in rabbit skin. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):143–147. doi: 10.1042/bj1020143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Zachariae C. O., Mukaida N., Matsushima K. Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:617–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M., Wrana J. L., Sodek J. Independent regulation of collagenase, 72-kDa progelatinase, and metalloendoproteinase inhibitor expression in human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1860–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine R., 3rd, Mody C. H., Chavis A., Spahr M. A., Turka L. A., Toews G. B. Alveolar epithelial cells block lymphocyte proliferation in vitro without inhibiting activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;5(3):221–229. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation. 1990 Oct;50(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Chen Y. Y., Rusch V., Rabinovitch P. S. Differential proliferation of fibroblasts cultured from normal and fibrotic human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):703–708. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu G., Masta S., Meyers D., Narayanan A. S. Collagen synthesis by normal and fibrotic human lung fibroblasts and the effect of transforming growth factor-beta. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):95–100. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Production of fibronectin by the human alveolar macrophage: mechanism for the recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury in interstitial lung diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. E., Rogers R. M. Adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):578–580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., Rose A. H. Pulmonary gamma interferon production in patients with fibrosing alveolitis. Thorax. 1990 Feb;45(2):105–108. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.2.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche W. R., Beasley R., Williams J. H., Holgate S. T. Subepithelial fibrosis in the bronchi of asthmatics. Lancet. 1989 Mar 11;1(8637):520–524. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche W. R. Mast cells and tumors. The specific enhancement of tumor proliferation in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1985 Apr;119(1):57–64. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Basset P., Fells G. A., Nukiwa T., Trapnell B. C., Crysal R. G. Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1685–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI113781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
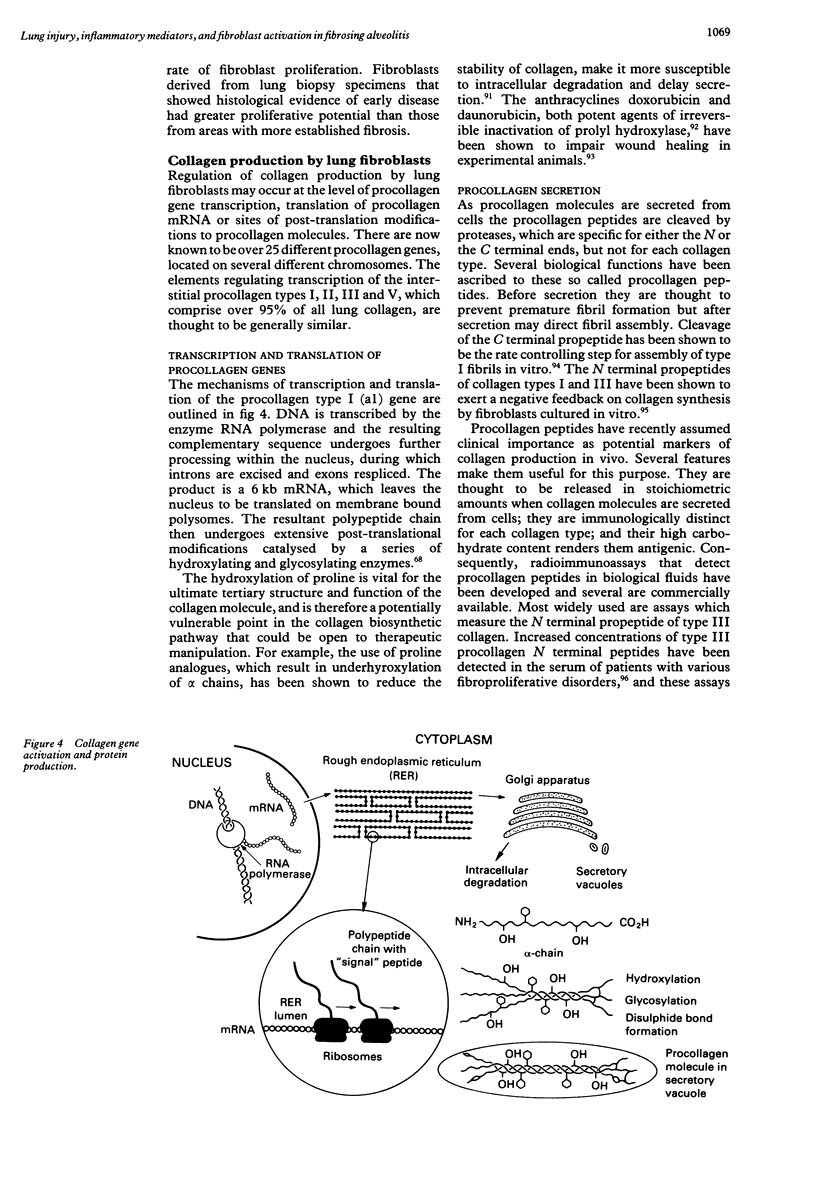
- Rosenbloom J., Feldman G., Freundlich B., Jimenez S. A. Transcriptional control of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by gamma-interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Evidence for chronic inflammation as a component of the interstitial lung disease associated with progressive systemic sclerosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):612–617. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCADDING J. G. FIBROSING ALVEOLITIS. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 12;2(5410):686–686. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5410.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto S., Sakamoto M. Degradative processes of connective tissue proteins with special emphasis on collagenolysis and bone resorption. Mol Aspects Med. 1988;10(4):299–428. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(88)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schollmeier K. Immunologic and pathophysiologic role of tumor necrosis factor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;3(1):11–12. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/3.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Phan S. H. Modulation of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the BALB/c mouse by cyclophosphamide-sensitive T cells. Am J Pathol. 1984 Aug;116(2):270–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Sticherling M., Henneicke H. H., Preissner W. C., Christophers E. IL-1 alpha or tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate release of three NAP-1/IL-8-related neutrophil chemotactic proteins in human dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2223–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein by adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1094–1101. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Johnston I., Britton J. What causes cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis? A case-control study of environmental exposure to dust. BMJ. 1990 Nov 3;301(6759):1015–1017. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6759.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selman M., Gonzalez G., Bravo M., Sullivan-Lopez J., Ramos C., Montano M., Barquin N., Vadillo F. Effect of lung T lymphocytes on fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Thorax. 1990 Jun;45(6):451–455. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.6.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Skogen W. F., Griffin G. L., Wilner G. D. Effects of fibrinogen derivatives upon the inflammatory response. Studies with human fibrinopeptide B. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1172/JCI112353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles A. D., Moats-Staats B. M. Production and action of insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin C in primary cultures of fetal lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;1(1):21–26. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER-WARWICK M., DONIACH D. AUTO-ANTIBODY STUDIES IN INTERSTITIAL PULMONARY FIBROSIS. Br Med J. 1965 Apr 3;1(5439):886–891. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5439.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Yasuoka S., Ogushi F., Asada K., Fujisawa K., Ozaki T., Sano N., Ogura T. Thrombin enhances lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):34–40. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi M., Nettesheim P., Williams M. L. Repopulation of denuded tracheal grafts with normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic epithelial cell populations. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4546–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P. L., Lukoszek A., Townsend P., Allan F., Du Bois R. M., Turton C. W., Collins J. V. Cells, enzymes and interstitial lung disease. The Philip Ellman Lecture. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1981 Jan;15(1):5–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P. L. The value of serial bronchoalveolar lavages in assessing the clinical progress of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):26–34. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vancheri C., Gauldie J., Bienenstock J., Cox G., Scicchitano R., Stanisz A., Jordana M. Human lung fibroblast-derived granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) mediates eosinophil survival in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Oct;1(4):289–295. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
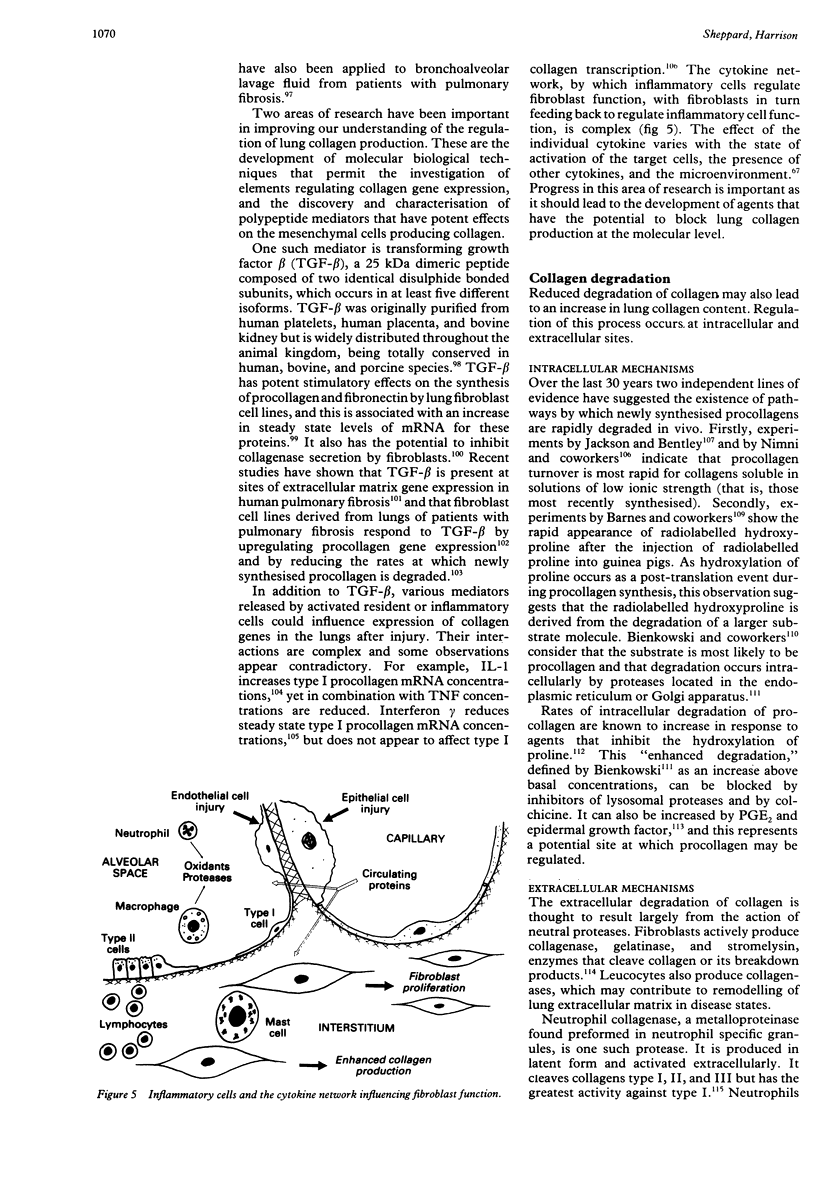
- Vergnon J. M., Vincent M., de Thé G., Mornex J. F., Weynants P., Brune J. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and Epstein-Barr virus: an association? Lancet. 1984 Oct 6;2(8406):768–771. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90702-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaud J. M., Allam M., Martinet N., Pech M., Plenat F., Martinet Y. Presence of platelet-derived growth factor in normal and fibrotic lung is specifically associated with interstitial macrophages, while both interstitial macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells express the c-sis proto-oncogene. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;5(6):531–538. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.6.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls A. F., Bennett A. R., Godfrey R. C., Holgate S. T., Church M. K. Mast cell tryptase and histamine concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with interstitial lung disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Aug;81(2):183–188. doi: 10.1042/cs0810183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangensteen D., Yankovich R., Hoidal J., Niewoehner D. Bleomycin-induced changes in pulmonary microvascular albumin permeability and extravascular albumin space. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;127(2):204–208. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. Overview of the process of cellular injury in interstitial lung disease. Chest. 1991 Jul;100(1):230–232. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.1.230-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Krieg T., Hörlein D., Glanville R. W., Fietzek P., Müller P. K. Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7016–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]