Abstract
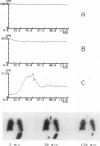
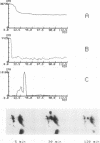
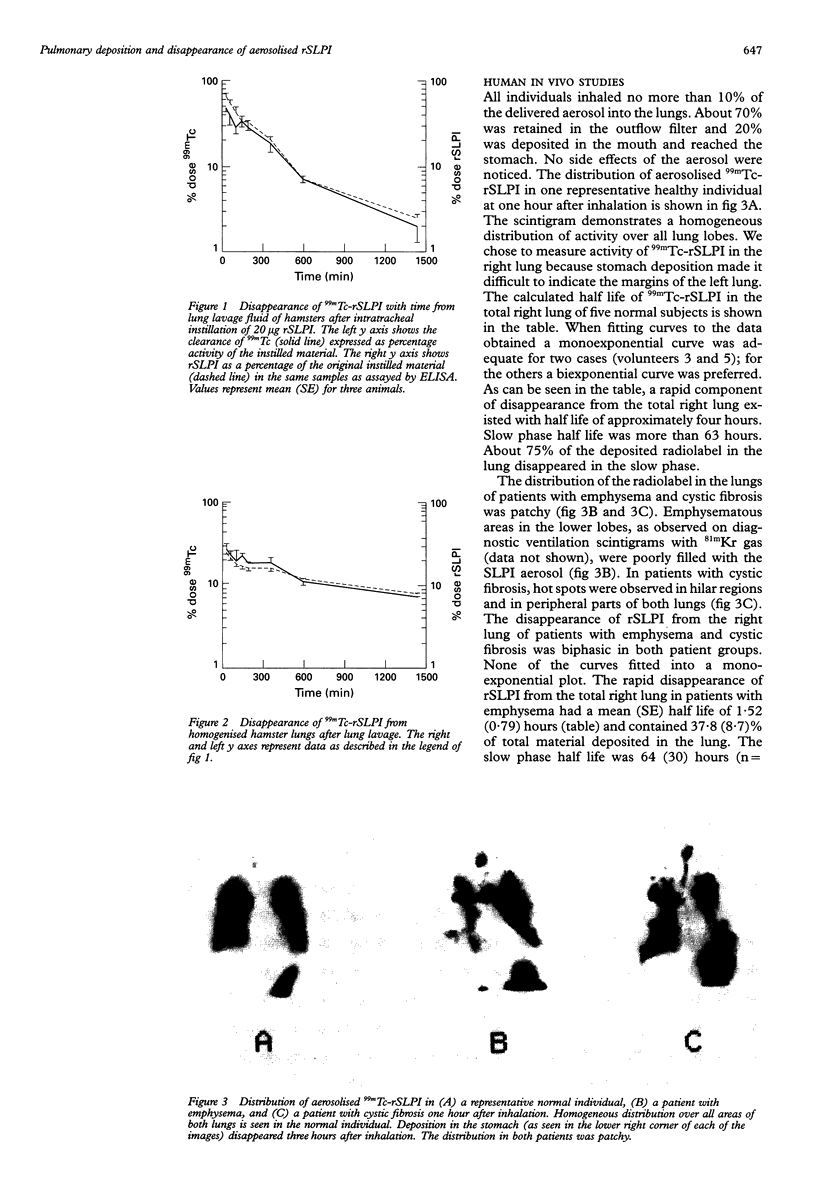
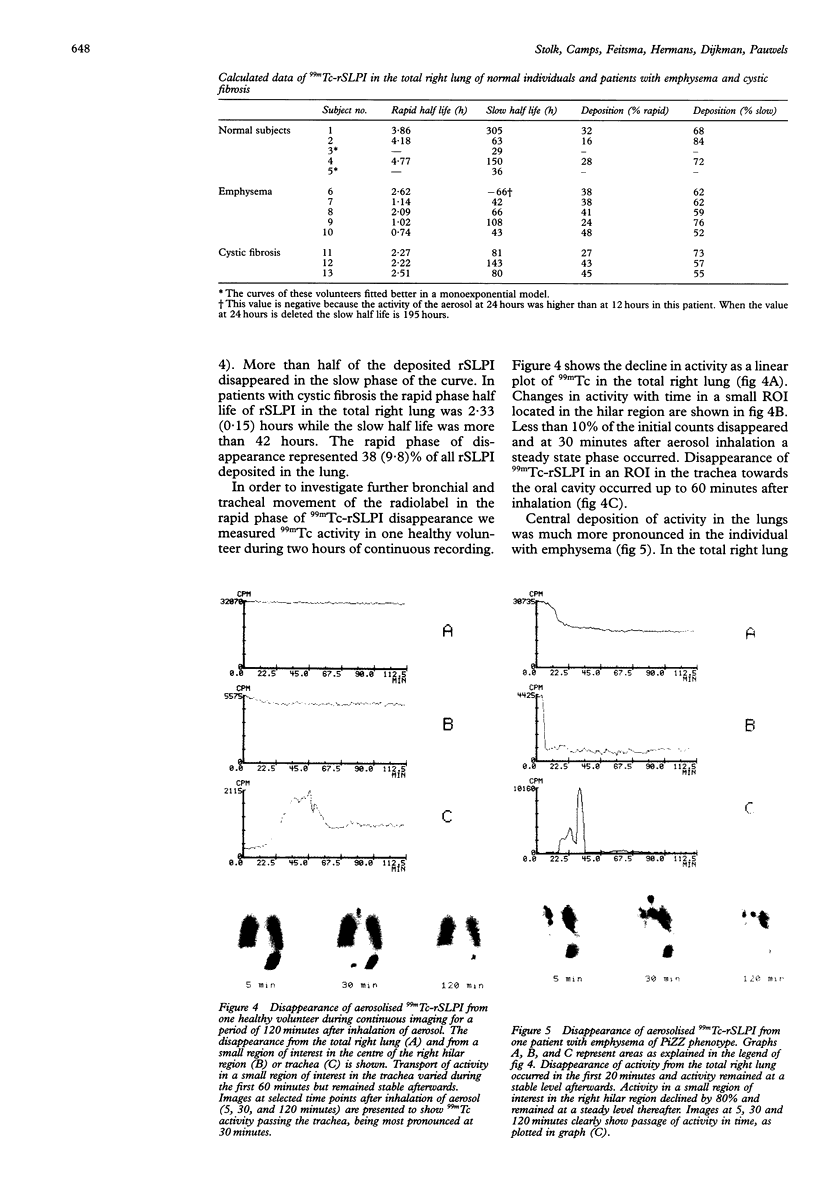
BACKGROUND--The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, secretory leucocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI), is a potential therapeutic tool in inflammatory lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis and pulmonary emphysema. The distribution and disappearance in the lung of aerosolised recombinant SLPI (rSLPI) was investigated in healthy humans and in patients with cystic fibrosis or alpha 1-antitrypsin-associated emphysema. METHODS--To distinguish aerosolised rSLPI from endogenous SLPI the recombinant inhibitor was radiolabelled with 99m-technetium (99mTc) pertechnetate. Distribution and disappearance of aerosolised 99mTc-rSLPI in the lungs were studied by gamma radiation imaging. RESULTS--The deposition of 99mTc-rSLPI in normal volunteers was homogeneous in all lung lobes, while in patients with cystic fibrosis or emphysema only well ventilated areas showed deposition of the aerosol. The disappearance rate of 99mTc-rSLPI was biexponential. The half life of the rapid phase was 0.2-2.8 hours, while that of the slow phase was more than 24 hours. CONCLUSIONS--Future aerosol therapy with rSLPI will be most beneficial for well ventilated lung tissue that needs protection against neutrophil derived elastase. It may be more difficult to neutralise the burden of elastase in poorly ventilated, highly inflamed areas as are seen in cystic fibrosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain J. D., Valberg P. A. Deposition of aerosol in the respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Dec;120(6):1325–1373. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Water R., Willems L. N., Van Muijen G. N., Franken C., Fransen J. A., Dijkman J. H., Kramps J. A. Ultrastructural localization of bronchial antileukoprotease in central and peripheral human airways by a gold-labeling technique using monoclonal antibodies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):882–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkman J. H., Kramps J. A., Franken C. Antileukoprotease in sputum during bronchial infections. Chest. 1986 May;89(5):731–736. doi: 10.1378/chest.89.5.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Hale K. K., Heimdal P., Thompson R. C. Location of the protease-inhibitory region of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7976–7981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast A., Anderson W., Probst A., Nick H., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P., Schnebli H. Pharmacokinetics and distribution of recombinant secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):889–894. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human D. G., Hill I. D., Fraser C. B. Critical congenital heart disease. S Afr Med J. 1984 Jun 16;65(24):958–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Franken C., Dijkman J. H. Quantity of anti-leucoprotease relative to alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor in peripheral airspaces of the human lung. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Oct;75(4):351–353. doi: 10.1042/cs0750351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Te Boekhorst A. H., Fransen J. A., Ginsel L. A., Dijkman J. H. Antileukoprotease is associated with elastin fibers in the extracellular matrix of the human lung. An immunoelectron microscopic study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):471–476. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., van Twisk C., Appelhans H., Meckelein B., Nikiforov T., Dijkman J. H. Proteinase inhibitory activities of antileukoprotease are represented by its second COOH-terminal domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 19;1038(2):178–185. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElvaney N. G., Doujaiji B., Moan M. J., Burnham M. R., Wu M. C., Crystal R. G. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant secretory leukoprotease inhibitor aerosolized to normals and individuals with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Oct;148(4 Pt 1):1056–1060. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.4_Pt_1.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels E. K., Welling M. M., Feitsma R. I., Atsma D. E., Nieuwenhuizen W. The labeling of proteins and LDL with 99mTc: a new direct method employing KBH4 and stannous chloride. Nucl Med Biol. 1993 Oct;20(7):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0969-8051(93)90148-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolphus A., Stolk J., van Twisk C., van Noorden C. J., Dijkman J. H., Kramps J. A. Detection of extracellular neutrophil elastase in hamster lungs after intratracheal instillation of E. coli lipopolysaccharide using a fluorogenic, elastase-specific, synthetic substrate. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):153–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Traber L. D., Traber D. L., Spragg R. G. Pulmonary deposition and clearance of aerosolized alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor administered to dogs and to sheep. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1145–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI114278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerhoff C. P., Nadel J. A., Basbaum C. B., Caughey G. H. Neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G stimulate secretion from cultured bovine airway gland serous cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):682–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI114492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlhofen W., Gebhart J., Heyder J., Scheuch G. Deposition pattern of droplets from medical nebulizers in the human respiratory tract. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Sep-Oct;19(5):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterk P. J., Plomp A., van de Vate J. F., Quanjer P. H. Physical properties of aerosols produced by several jet- and ultrasonic nebulizers. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1984 Jan-Feb;20(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley R. A., Morrison H. M., Kramps J. A., Dijkman J. H., Burnett D. Studies of proteinases and their inhibitors in lung secretions. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1987;153:86–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Ohlsson K. Isolation, properties, and complete amino acid sequence of human secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, a potent inhibitor of leukocyte elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6692–6696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. F., Berger M. Functional differences between the 40 kDa and 50 to 70 kDa IgG Fc receptors on human neutrophils revealed by elastase treatment and antireceptor antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2097–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. F., Zakem H., Berger M. Neutrophil elastase cleaves C3bi on opsonized pseudomonas as well as CR1 on neutrophils to create a functionally important opsonin receptor mismatch. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):300–308. doi: 10.1172/JCI114699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelmeier C., Buhl R., Hoyt R. F., Wilson E., Fells G. A., Hubbard R. C., Schnebli H. P., Thompson R. C., Crystal R. G. Aerosolization of recombinant SLPI to augment antineutrophil elastase protection of pulmonary epithelium. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Nov;69(5):1843–1848. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.5.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]