Abstract
The epidemiological data suggest that endurance athletes are at increased risk for upper respiratory tract infections during periods of heavy training and the 1-2 week period following a marathon or similar event. At present there is no clear indication that chronic alterations in immune function explain this increased risk. Following acute bouts of prolonged heavy endurance exercise, several components of the immune system are suppressed for several hours. This has led to the concept of the "open window" theory described as the 1-9 hour period following prolonged endurance exercise when host defense is decreased and the risk of upper respiratory tract infection is increased.
Full text
PDF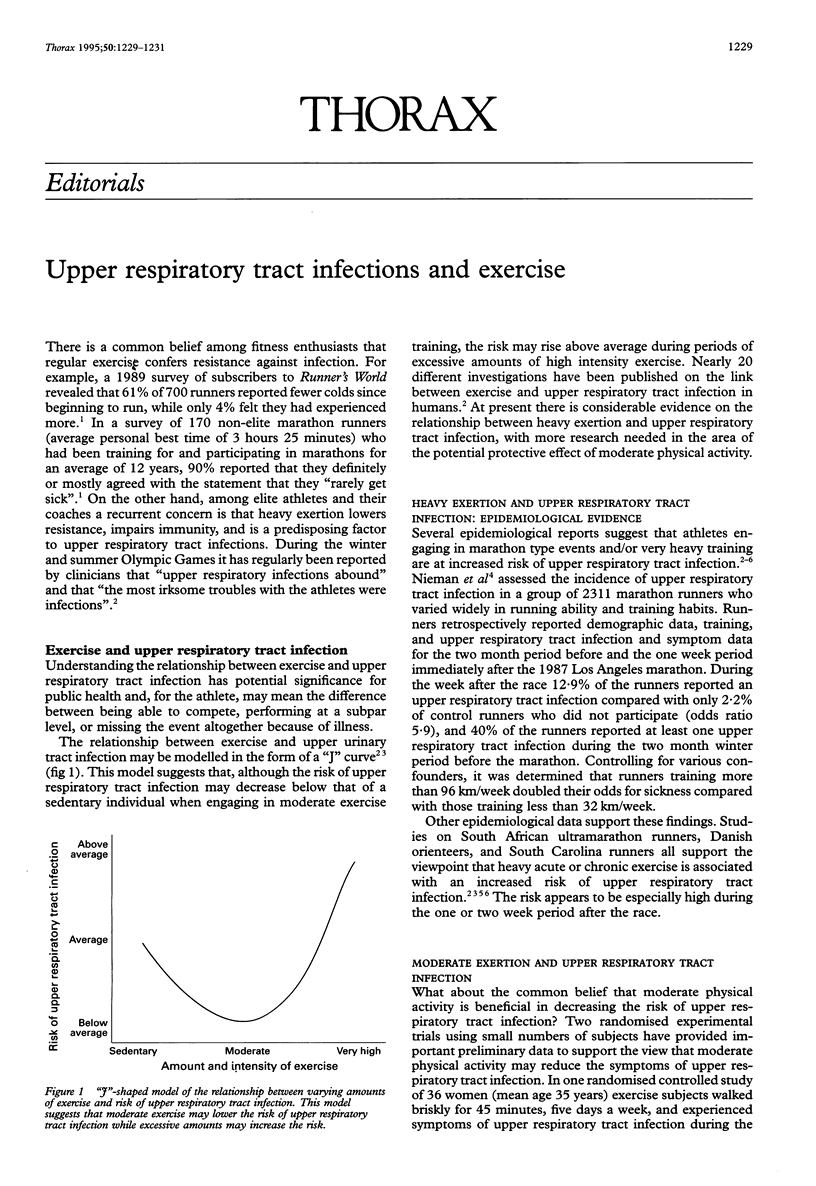

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandra R. K. 1990 McCollum Award lecture. Nutrition and immunity: lessons from the past and new insights into the future. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 May;53(5):1087–1101. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.5.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskola J., Ruuskanen O., Soppi E., Viljanen M. K., Järvinen M., Toivonen H., Kouvalainen K. Effect of sport stress on lymphocyte transformation and antibody formation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 May;32(2):339–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmünder F. K., Lorenzi G., Bechler B., Joller P., Müller J., Ziegler W. H., Cogoli A. Effect of long-term physical exercise on lymphocyte reactivity: similarity to spaceflight reactions. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1988 Feb;59(2):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khansari D. N., Murgo A. J., Faith R. E. Effects of stress on the immune system. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):170–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90069-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackinnon L. T., Hooper S. Mucosal (secretory) immune system responses to exercise of varying intensity and during overtraining. Int J Sports Med. 1994 Oct;15 (Suppl 3):S179–S183. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müns G. Effect of long-distance running on polymorphonuclear neutrophil phagocytic function of the upper airways. Int J Sports Med. 1994 Feb;15(2):96–99. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Ahle J. C., Henson D. A., Warren B. J., Suttles J., Davis J. M., Buckley K. S., Simandle S., Butterworth D. E., Fagoaga O. R. Indomethacin does not alter natural killer cell response to 2.5 h of running. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1995 Sep;79(3):748–755. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1995.79.3.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Buckley K. S., Henson D. A., Warren B. J., Suttles J., Ahle J. C., Simandle S., Fagoaga O. R., Nehlsen-Cannarella S. L. Immune function in marathon runners versus sedentary controls. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995 Jul;27(7):986–992. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199507000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C. Exercise, upper respiratory tract infection, and the immune system. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994 Feb;26(2):128–139. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199402000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Henson D. A., Gusewitch G., Warren B. J., Dotson R. C., Butterworth D. E., Nehlsen-Cannarella S. L. Physical activity and immune function in elderly women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993 Jul;25(7):823–831. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199307000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Johanssen L. M., Lee J. W., Arabatzis K. Infectious episodes in runners before and after the Los Angeles Marathon. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 1990 Sep;30(3):316–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Miller A. R., Henson D. A., Warren B. J., Gusewitch G., Johnson R. L., Davis J. M., Butterworth D. E., Herring J. L., Nehlsen-Cannarella S. L. Effect of high- versus moderate-intensity exercise on lymphocyte subpopulations and proliferative response. Int J Sports Med. 1994 May;15(4):199–206. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Miller A. R., Henson D. A., Warren B. J., Gusewitch G., Johnson R. L., Davis J. M., Butterworth D. E., Nehlsen-Cannarella S. L. Effects of high- vs moderate-intensity exercise on natural killer cell activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993 Oct;25(10):1126–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C., Nehlsen-Cannarella S. L., Markoff P. A., Balk-Lamberton A. J., Yang H., Chritton D. B., Lee J. W., Arabatzis K. The effects of moderate exercise training on natural killer cells and acute upper respiratory tract infections. Int J Sports Med. 1990 Dec;11(6):467–473. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieman D. C. The effect of exercise on immune function. Bull Rheum Dis. 1994 Dec;43(8):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K., Tvede N., Christensen L. D., Klarlund K., Kragbak S., Halkjr-Kristensen J. Natural killer cell activity in peripheral blood of highly trained and untrained persons. Int J Sports Med. 1989 Apr;10(2):129–131. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K., Tvede N., Christensen L. D., Klarlund K., Kragbak S., Halkjr-Kristensen J. Natural killer cell activity in peripheral blood of highly trained and untrained persons. Int J Sports Med. 1989 Apr;10(2):129–131. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1024888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K., Ullum H. NK cell response to physical activity: possible mechanisms of action. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994 Feb;26(2):140–146. doi: 10.1249/00005768-199402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters E. M., Bateman E. D. Ultramarathon running and upper respiratory tract infections. An epidemiological survey. S Afr Med J. 1983 Oct 1;64(15):582–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne D. B. Regulation of neutrophil function during exercise. Sports Med. 1994 Apr;17(4):245–258. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199417040-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Trudeau F. B., Czerwinski D., Erredge S. Immune parameters in athletes before and after strenuous exercise. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Jul;2(3):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00915219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


