Abstract
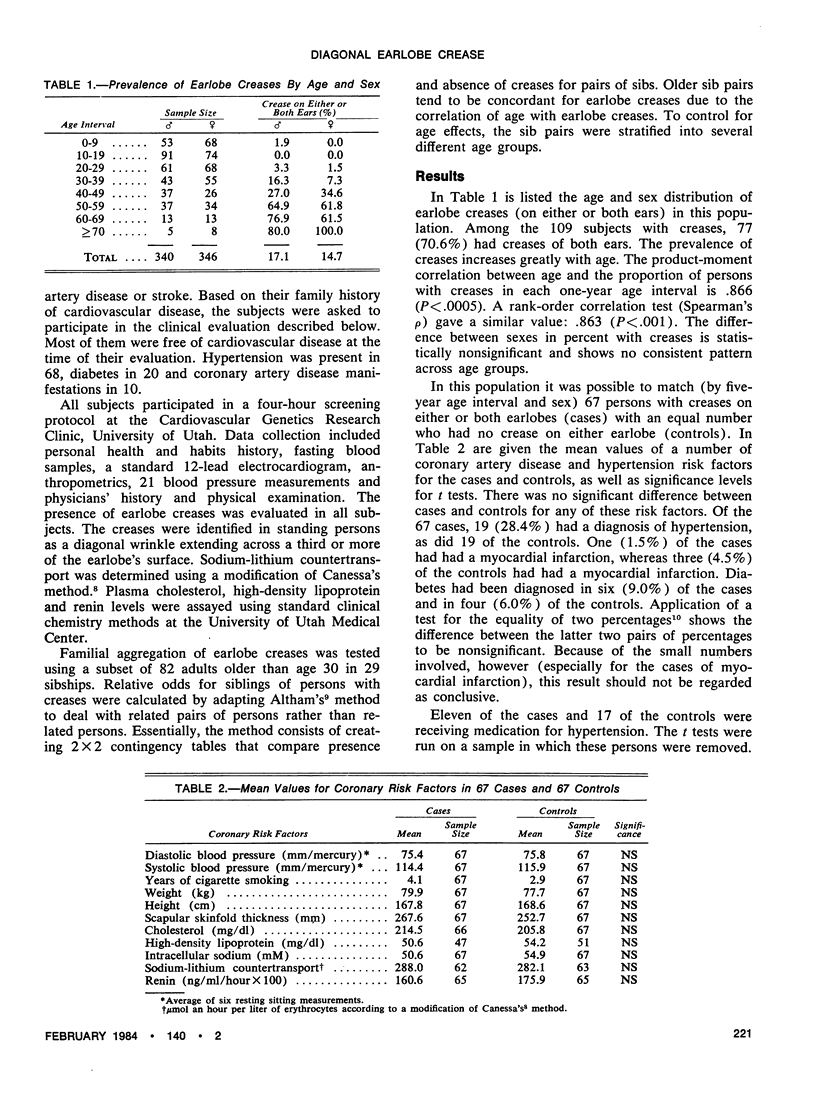
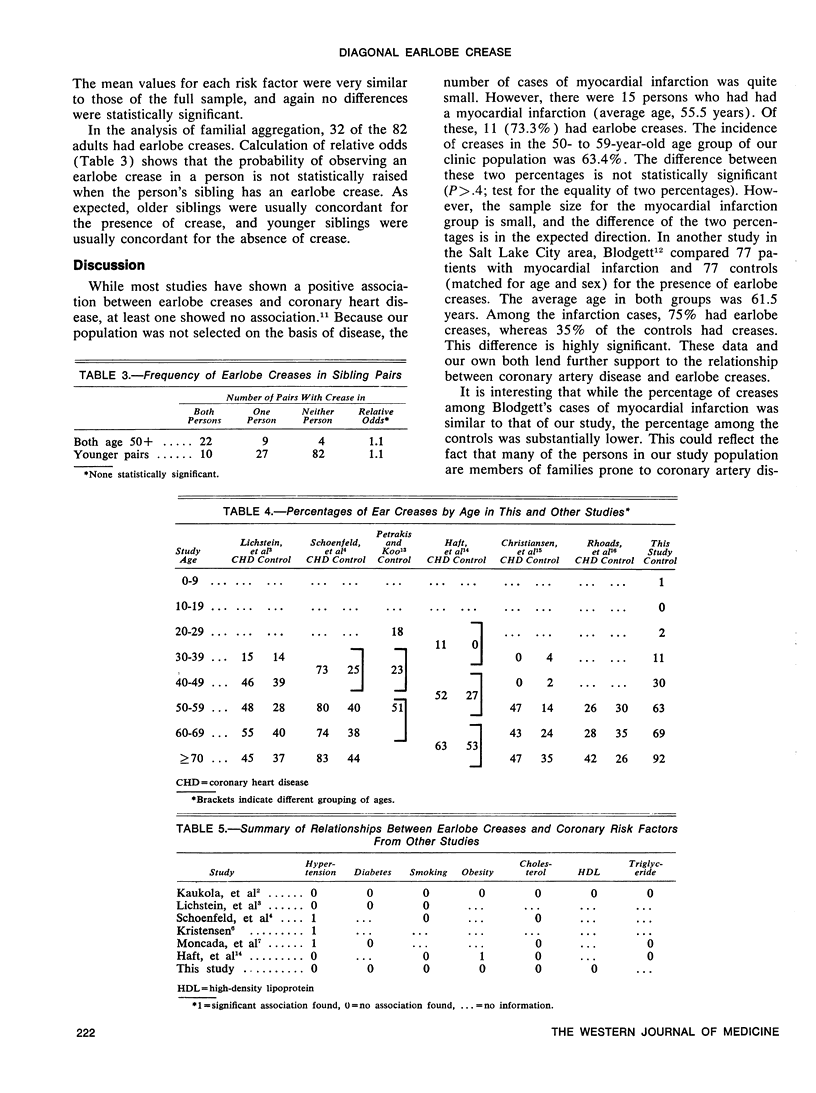
The relationship between diagonal earlobe crease and coronary risk factors, controlling for age and sex effects, was tested in 686 persons. A positive correlation (ρ=.86, P<.001) is obtained between age and percentage of persons with earlobe creases in each one-year age interval; no sex difference is seen. To test for associations between cardiovascular risk factors and earlobe creases, 67 persons with creases are compared with 67 controls (matched by age and sex) without creases, using the following variables: diastolic and systolic blood pressures, cigarette smoking, weight, height, scapular skinfold thickness, serum cholesterol level, high-density lipoprotein level, intracellular sodium, sodium-lithium countertransport, plasma renin level and the presence of diabetes and hypertension. None of these variables differs significantly between cases and controls, indicating that the previously documented association between earlobe crease and coronary heart disease may be independent of these risk factors. Although coronary heart disease has often been shown to aggregate in families, no familial aggregation is found for earlobe creases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christiansen J. S., Mathiesen B., Andersen A. R., Calberg H. Letter: Diagonal ear-lobe crease in coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 7;293(6):308–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508072930626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering C., Ruhsenberger C., Phillips D. S. Ear lobe creases and heart disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1977 Apr;25(4):183–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1977.tb00290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. T. Aural sign of coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 9;289(6):327–328. doi: 10.1056/nejm197308092890622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaukola S., Manninen V., Valle M., Halonen P. I. Ear-lobe crease and coronary atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1979 Dec 22;2(8156-8157):1377–1377. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen B. O. Ear-lobe crease and vascular complications in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1980 Feb 2;1(8162):265–265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90761-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichstein E., Chadda K. D., Naik D., Gupta P. K. Diagonal ear-lobe crease: prevalence and implications as a coronary risk factor. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):615–616. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtstein E., Chapman I., Gupta P. K., Chadda K. D., Smith H., Jr, Schwartz I., Naik D. Letter: Diagonal ear-lobe crease and coronary artery sclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Sep;85(3):337–338. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-3-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J., Hamby R. I. Letter: Diagonal ear-lobe crease as a coronary risk factor. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 1;291(5):260–260. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408012910519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada B., Ruíz J. M., Rodríguez E., Leiva J. L. Ear-lobe crease. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):220–221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90629-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrakis N. L., Koo L. Earlobe crease. Lancet. 1980 Feb 16;1(8164):376–376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90930-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Klein K., Yano K., Preston H. The earlobe crease--sign of obesity in middle-aged Japanese men. Hawaii Med J. 1977 Mar;36(3):74–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Mor R., Weinberger A., Avidor I., Pinkhas J. Diagonal ear lobe crease and coronary risk factors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1980 Apr;28(4):184–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1980.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


