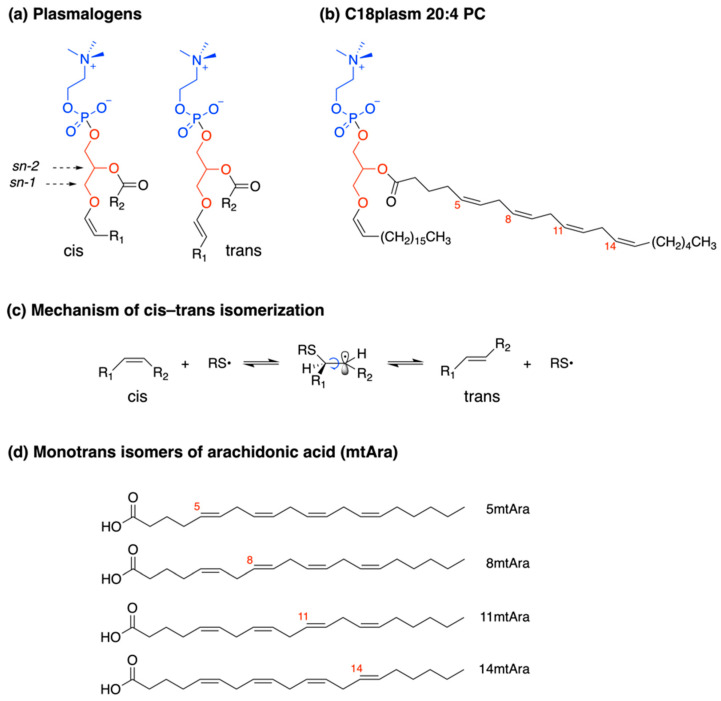
Figure 1.
(a) General structure of plasmalogens with a fatty acid in position sn-2 and a vinyl ether-containing hydrocarbon chain in position sn-1. The natural structure has a cis-vinyl ether function. The trans-vinyl ether containing plasmalogen is a synthetically modified lipid. (b) 1-(1Z-octadecenyl)-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (acronym: C18 plasm 20:4-PC) with all cis double bonds. (c) Mechanism of thiyl radical catalyzed cis-trans double bond isomerization of unsaturated fatty acid moieties in lipids depicted as consecutive addition-elimination process. (d) The four monotrans isomers of arachidonic acid (mtAra) structures, as product mix obtained from the thiyl radical-catalyzed isomerization of Ara.