Abstract
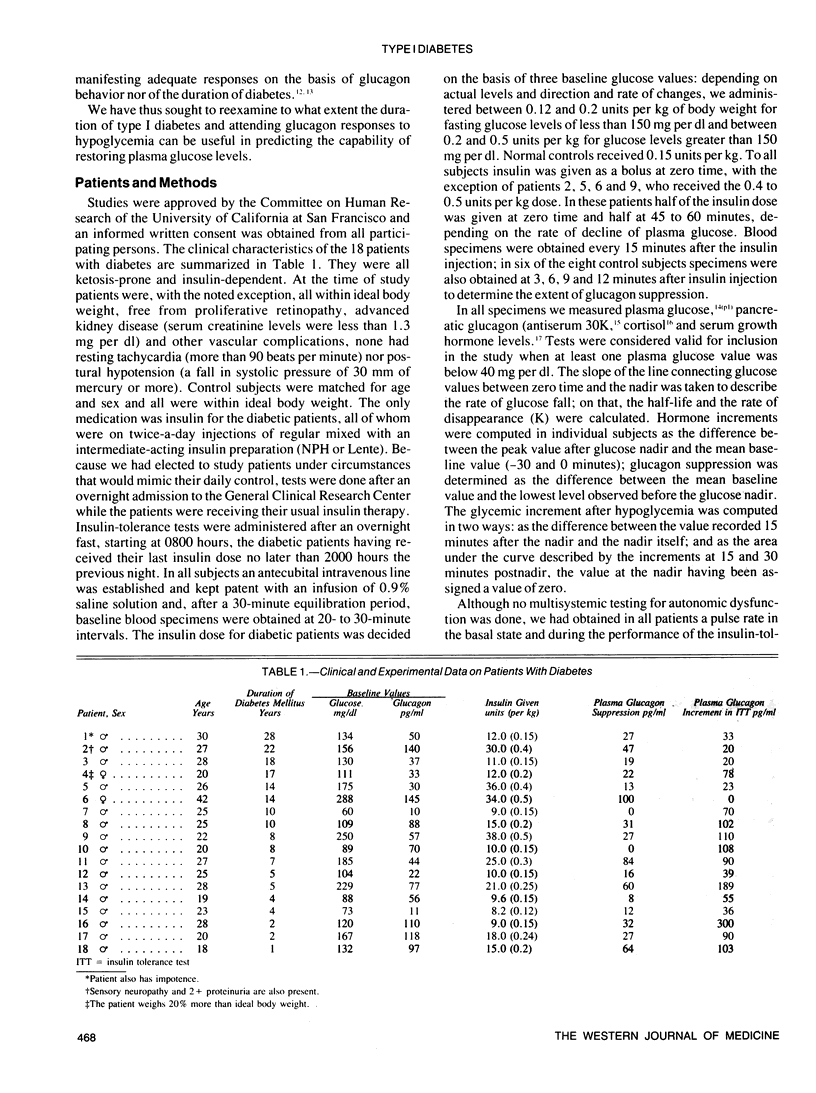
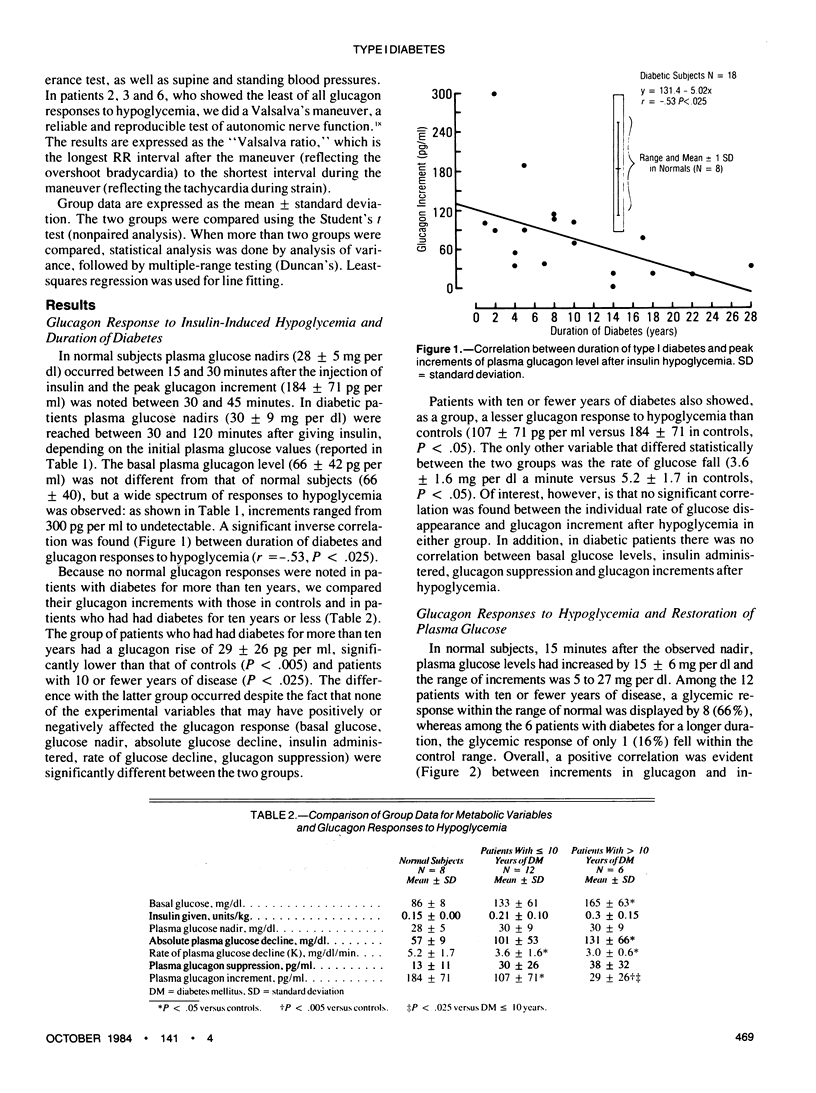
The glucagon response to hypoglycemia, which fulfills a primary role toward restoring the plasma glucose level, is blunted or absent in most patients with type I diabetes. To identify predictive factors for this abnormality and for the capability of glycemic counterregulation, we investigated the relationship between the duration of diabetes and glucagon and glucose responses to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. In 18 type I diabetic patients with 1 through 28 years of disease who had no detectable autonomic neuropathy, individual glucagon increments after insulin hypoglycemia were inversely correlated with the duration of disease (r = -.53, P < .025). Patients with disease for ten or fewer years showed a glucagon rise that was lower than in controls but significantly higher than in patients with a duration of more than ten years. The plasma glucose rise after the nadir correlated with peak glucagon increments (r = .60, P < .01); eight of the nine patients with glycemic increments comparable to normals had had diabetes for ten years or less. Thus, having diabetes for more than ten years implied that not only were glucagon responses to insulin hypoglycemia severely compromised but also that the abrupt restoration of plasma glucose levels was impaired. These findings should be taken into account when establishing goals and modalities for tight metabolic control.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson J. W., Jr, Johnson D. G., Palmer J. P., Werner P. L., Ensinck J. W. Glucagon and catecholamine secretion during hypoglycemia in normal and diabetic man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Mar;44(3):459–464. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., Calabrese G., De Feo P., Compagnucci P., Zega G., Angeletti G., Cartechini M. G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Lack of glucagon response in glucose counter-regulation in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetics: absence of recovery after prolonged optimal insulin therapy. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):100–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00254837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P., Gerich J. E. Abnormal glucose counterregulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Interaction of anti-insulin antibodies and impaired glucagon and epinephrine secretion. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):134–141. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., de Feo P., Compagnucci P., Cartechini M. G., Angeletti G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Important role of adrenergic mechanisms in acute glucose counterregulation following insulin-induced hypoglycemia in type I diabetes. Evidence for an effect mediated by beta-adrenoreceptors. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):641–647. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, McDevitt H. O. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the initial lesion. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1454–1465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. F., Ewing D. J., Campbell I. W. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetologia. 1979 Oct;17(4):195–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01235856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earll J. M., Sparks L. L., Forsham P. H. Glucose suppression of serum growth hormone in the diagnosis of acromegaly. JAMA. 1967 Aug 21;201(8):628–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by epinephrine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Sep;37(3):479–481. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Schneider V., Dippe S. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Characterization of the glucagon response to hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jan;38(1):77–82. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J., Davis J., Lorenzi M., Rizza R., Bohannon N., Karam J., Lewis S., Kaplan R., Schultz T., Cryer P. Hormonal mechanisms of recovery from insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):E380–E385. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.4.E380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilsted J., Madsbad S., Krarup T., Sestoft L., Christensen N. J., Tronier B., Galbo H. Hormonal, metabolic, and cardiovascular responses to hypoglycemia in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1981 Aug;30(8):626–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.8.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lager I., Blohmé G., von Schenck H., Smith U. Importance of glucose control for the recovery from hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):771–775. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTINGLY D. A simple fluorimetric method for the estimation of free 11-hydroxycorticoids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:374–379. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S., Faber O. K., Binder C., McNair P., Christiansen C., Transbøl I. Prevalence of residual beta-cell function in insulin-dependent diabetics in relation to age at onset and duration of diabetes. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):262–264. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietri A., Ehle A. L., Raskin P. Changes in nerve conduction velocity after six weeks of glucoregulation with portable insulin infusion pumps. Diabetes. 1980 Aug;29(8):668–671. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.8.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Bergenstal R., Pons G., Schneider M., Jaspan J., Rubenstein A. Relation of counterregulatory responses to hypoglycemia in type I diabetics. N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1106–1112. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp D. A., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Role of epinephrine-mediated beta-adrenergic mechanisms in hypoglycemic glucose counterregulation and posthypoglycemic hyperglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):315–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI110455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C., Molnar G. D., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H., Taylor W. F., Jiang N. S. Abnormalities of endogenous glucagon and insulin in unstable diabetes. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):36–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Gerich J. E. Role of glucagon, catecholamines, and growth hormone in human glucose counterregulation. Effects of somatostatin and combined alpha- and beta-adrenergic blockade on plasma glucose recovery and glucose flux rates after insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):62–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI109464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Meticulous control of diabetes: benefits, risks, and precautions. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):479–483. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G., Pickup J. C., Bilous R. W., Keen H., Mackintosh D. Correction of exercise-induced microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetics after 3 weeks of subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):818–823. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. H., Skor D. A., Cryer P. E., Levandoski L. A., Bier D. M., Santiago J. V. Identification of type I diabetic patients at increased risk for hypoglycemia during intensive therapy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 3;308(9):485–491. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303033080903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. H., Waltman S. R., Krupin T., Santiago J. V. Reversal of abnormalities in ocular fluorophotometry in insulin-dependent diabetes after five to nine months of improved metabolic control. Diabetes. 1982 Jan;31(1):80–85. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. H., Waltman S. R., Krupin T., Santiago J. V. Reversal of neuropathic and gastrointestinal complications related to diabetes mellitus in adolescents with improved metabolic control. J Pediatr. 1981 Jul;99(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80954-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


