Dear Editor,
Parvimonas micra is a gram-positive obligate anaerobic bacterial species and known flora of the human oral cavity, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, and the female genitourinary tract.[1,2] It was originally identified in 1933 as Peptostreptococcus micros, underwent a reclassification in 1999 to Micromonas micros and ultimately was reclassified as P. micra in 2006.[1,3] Parvimonas micra has been implemented as an infectious organism in case reports of spondylodiscitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, iliopsoas abscess, hepatic abscess, endocarditis, empyema, meningitis, brain abscess and septic arthritis.[1-3] Although multiple areas of infection by P. micra have been described, tensor fascia lata infection has not been described.[4]
A patient with no significant past medical history presented to our outpatient multidisciplinary pain center complaining of left hip pain. He was seen in the emergency department the day prior. X-ray of the hip was performed which did not reveal any acute pathology. His pain had been present for one week and had been worsening in intensity. He did not describe any radiation of the pain to the lower legs and denied any recent trauma to the area. He described swelling and fullness of the hip worsened with movement and relieved by rest. His physical examination was only positive for tenderness of palpation over the left greater trochanter. Due to a presumed diagnosis of greater trochanteric bursitis, conservative measures were pursued. He was prescribed naproxen 500 mg twice a day as needed, tizanidine 2 mg three times per day as needed, topical EMLA to the painful area. He was also instructed to start physical therapy and was provided a referral for the same. He was discharged from the emergency department after this visit.
Nearly two weeks later, the patient presented to the emergency department with left thigh erythema and swelling. His laboratory work was significant for ESR of 115 and CRP of 16, white counts were 8.2. On exam, in the ED, he was afebrile and physical exam was positive for erythema, tenderness to palpation over the left thigh. Several pustules overlying the area along with areas of induration and fluctuance were noted. A CT with contrast of the left hip was performed which demonstrated a 20 × 10 × 6.5 cm rim enhancing fluid collection in the proximal lateral left thigh/gluteal region abutting and extending along the fascia lata of the thigh, dissecting into the substance of the tensor fasciae lata muscle and extending into the deep subcutaneous tissues [Figure 1]. The patient was started on broad-spectrum IV antibiotics and scheduled for incision and drainage in the operating room by general surgery. Drains were placed and the wound closed by secondary intention. Cultures from the operating room (anaerobic- tissue and abscess) yielded P. micra. Repeat blood cultures were negative at 5 days. The patient was kept on vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam for 3 days and transitioned to oral trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole at discharge.
Figure 1.
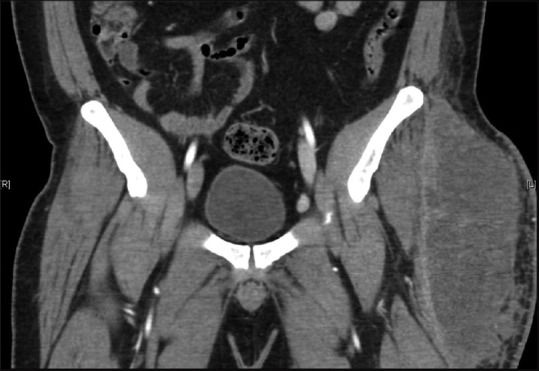
Coronal view of left thigh CT demonstrating abscess
This case represents an unusual occurrence of P. micra abscess requiring prompt recognition of the abscess and prudent microbial identification.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Shaparin reports the following disclosures outside the submitted manuscript; he was a consultant for Averitas Pharma and AcelRx Pharmaceuticals and has received research grant funding from Grunenthal and Heron Therapeutics. Dr. Koushik has served as a consultant for AcelRx Pharmaceuticals.
References
- 1.Chaucer B, Smith N, Beatty D, Yadav M. Multiple hepatic abscess from Parvimonas micra:An emerging gastrointestinal microbe. ACG Case Rep J. 2018;5:e70. doi: 10.14309/crj.2018.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.van Duijvenbode DC, Kuiper JWP, Holewijn RM, Stadhouder A. Parvimonas micra spondylodiscitis:A case report and systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Case Rep. 2018;8:67–71. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Uemura H, Hayakawa K, Shimada K, Tojo M, Nagamatsu M, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, et al. Parvimonas micra as a causative organism of spondylodiscitis:A report of two cases and a literature review. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;23:53–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sawai T, Koga S, Ide S, Yoshioka S, Matsuo N, Mukae H. An iliopsoas abscess caused by Parvimonas micra:A case report. J Med Case Rep. 2019;13:47. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2004-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


