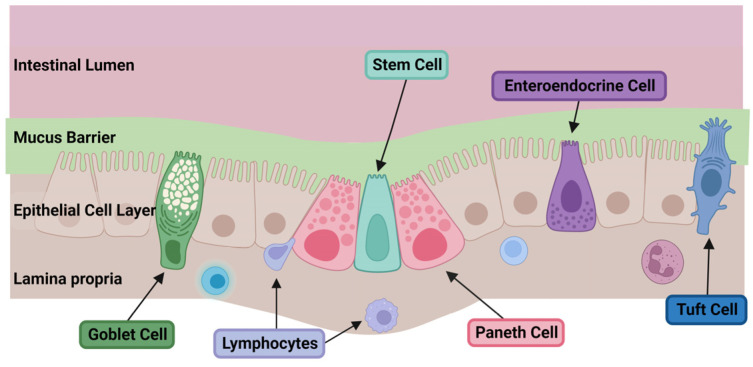
Figure 2.
Simplified depiction of the layers and cells of the intestinal barrier. The intestinal barrier is composed of chemical, physical, and immune defense layers. From the apical side facing the intestinal lumen, the first is a chemical barrier of mucus which covers the underlying well-appositioned epithelial cells which create the physical barrier of the intestine. The epithelial monolayer is composed of the following main cell types: absorptive enterocytes, mucin-secreting goblet cells, Paneth cells, stem cells, tuft cells, and enteroendocrine cells. The most basal layer underlying the epithelial cells is the lamina propria, which is the immune barrier composed of gut-associated lymphocytes. Created with BioRender.com.