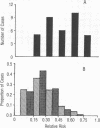
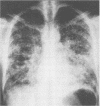
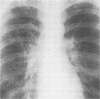
Abstract
Coccidioidomycosis is a systemic fungal infection endemic to the southwestern United States and other parts of the western hemisphere. Although producing a wide range of disorders in healthy persons, immunosuppression predisposes to especially severe disease. Thus, a knowledge of the pathogenesis of coccidioidal infections and its relation to the normal immune responses is useful to understand the diversity of problems that Coccidioides immitis may cause. Diagnosis usually requires laboratory studies such as fungal culture or specific serologic testing. Fortunately, many patients do not need to be treated for the infection to resolve. Therapy for the more severe forms of coccidioidal infection was once limited to amphotericin B but now includes azole antifungal agents. These expanded alternatives now require physicians to weigh many factors in determining the best management for specific patients.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams D. I., Robia M., Blumenfeld W., Simonson J., Cohen M. B., Hadley W. K. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis in AIDS. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 12;310(15):986–987. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404123101511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni R., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R., Puri J. Immunomodulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by antibodies to the antigen-Ia complex. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):147–150. doi: 10.1038/351147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Bejarano G. C., Galgiani J. N. Killing of Coccidioides immitis by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4200–4204. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4200-4204.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Bejarano G. C., Salas S. D., Galgiani J. N. In vitro assessment of cellular immunity in human coccidioidomycosis: relationship between dermal hypersensitivity, lymphocyte transformation, and lymphokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy adults. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):710–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Dols C. L., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioidomycosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection: results of a prospective study in a coccidioidal endemic area. Am J Med. 1993 Mar;94(3):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90054-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Galgiani J. N. Interaction of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with Coccidioides immitis arthroconidia. Cell Immunol. 1991 Mar;133(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90195-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Ryan K. J., Carry P. J., Wieden M. A., Schifman R. B. Fungemia due to Coccidioides immitis. An analysis of 16 episodes in 15 patients and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1986 Sep;65(5):312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., White J. D., Varanasi U. R., Larwood T. R., Van Wyck D. B., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioidal peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1988 Jun;11(6):512–514. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(88)80088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampel N. M., Wieden M. A., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioidomycosis: clinical update. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11(6):897–911. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniskis D., Larsen R. A., Akil B., Rarick M. U., Leedom J. M. Seronegative disseminated coccidioidomycosis in patients with HIV infection. AIDS. 1990 Jul;4(7):691–693. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199007000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRSNER J. W. The roentgen aspects of five hundred cases of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1954 Oct;72(4):556–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSS W. C., GIBSON T. E., GIFFORD M. A. Coccidioidomycosis of the meninges. Calif Med. 1950 Mar;72(3):167–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babycos P. B., Hoda S. A. A fatal case of disseminated coccidioidomycosis in Louisiana. J La State Med Soc. 1990 Aug;142(8):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. J., Hawkins J. A., Waskow E. A. Surgery for coccidioidomycosis in 52 diabetic patients with special reference to related immunologic factors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978 May;75(5):680–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbee R. A., Hicks M. J. Clinical usefulness of lymphocyte transformation in patients with coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1988 May;93(5):1003–1007. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.5.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbee R. A., Hicks M. J., Grosso D., Sandel C. The maternal immune response in coccidioidomycosis. Is pregnancy a risk factor for serious infection? Chest. 1991 Sep;100(3):709–715. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.3.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S. Fungal pneumonias; pulmonary coccidioidal syndromes (Part I). Primary and progressive primary coccidioidal pneumonias -- diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic considerations. Chest. 1981 May;79(5):575–583. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Guze L. B. Fungal arthritis. II. Coccidioidal synovitis: clinical, diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic considerations. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;8(3):200–211. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(79)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. V., Pappagianis D., Benjamini E. Mechanisms of resistance to infection with Coccidioides immitis in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):681–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Benjamini E., Pappagianis D. Activation of macrophages by lymphokines: enhancement of phagosome-lysosome fusion and killing of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1201–1207. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1201-1207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. Effects of recombinant gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor on in vitro interactions of human mononuclear phagocytes with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4227–4229. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4227-4229.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L. Fungicidal activation of murine macrophages by recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2951–2955. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2951-2955.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. J., Yost B. A. Coccidioidomycosis versus pollen. South Med J. 1989 Feb;82(2):277–277. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198902000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., Tipton J. R., Schott S. F., Cherry J. D. Coccidioidomycosis in a neonate; maternal-infant transmission. J Pediatr. 1981 Nov;99(5):752–754. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddicker J. H., Fong D., Walsh T. E., Schillaci R. F., Moniot A. L., Catanzaro A. Bone and gallium scanning in the evaluation of disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):279–287. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouza E., Dreyer J. S., Hewitt W. L., Meyer R. D. Coccidioidal meningitis. An analysis of thirty-one cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):139–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. H., Taylor J. W., Brownlee A. G., Lee J., Lu S. D., White T. J. Molecular evolution of the fungi: relationship of the Basidiomycetes, Ascomycetes, and Chytridiomycetes. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Mar;9(2):285–296. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. H., Taylor J. W., White T. J. Molecular evolution of the fungi: human pathogens. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Sep;9(5):893–904. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. O., Coulthard S. W., Mandel R. M. Laryngeal involvement in disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991 Apr;117(4):433–438. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1991.01870160087016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bried J. M., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioides immitis infections in bones and joints. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986 Oct;(211):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt R. H., Enzmann D. R., Remington J. S. Intracranial infection in cardiac transplant recipients. Ann Neurol. 1981 Feb;9(2):107–119. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronnimann D. A., Adam R. D., Galgiani J. N., Habib M. P., Petersen E. A., Porter B., Bloom J. W. Coccidioidomycosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Mar;106(3):372–379. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiuc D., Dobrescu A., Dobrescu G., Petrescu Z., Brănişteanu L. Incă o dată despre importanţa microscopiei în microbiologia clinică. Argumentum după diagnosticarea unor manifestări cutanate ale histoplasmozei şi coccidioidomicozei. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 1990 Apr-Jun;94(2):393–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch R. F. Coccidioidomycosis of the external ear. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992 Sep;107(3):491–492. doi: 10.1177/019459989210700331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. J., Nanfro J. J., Marsh W. L., Jr Coccidioidomycosis of the female genital tract. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Mar;110(3):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COBURN J. W. Scalene lymph node involvement in primary and disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Evidence of extrapulmonary spread in primary infection. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Jun;56:911–924. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-56-6-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONVERSE J. L. Growth of spherules of Coccidioides immitis in a chemically defined liquid medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):709–711. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. C., Winter J. A., Bjelland J. C., Wieden M., Sobonya R. E., Galgiani J. N. Clinical conference in pulmonary disease. Coccidioidomycosis. Clinical conference in pulmonary disease from the Tucson V.A. Medical Center and the University of Arizona. Chest. 1982 Apr;81(4):488–492. doi: 10.1378/chest.81.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrada-Bravo T. La coccidioidomicosis en los niños. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 1989 Jul;46(7):507–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll G. F., Haley L. D., Brown J. M. Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis: a review of the literature and a report of a new case. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Jul;113(7):933–936. doi: 10.1001/archderm.113.7.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino R. A., Blank N. Pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. The wide spectrum of roentgenographic manifestations. Calif Med. 1968 Jul;109(1):41–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro A., Fierer J., Friedman P. J. Fluconazole in the treatment of persistent coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1990 Mar;97(3):666–669. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.3.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro A., Spitler L. E., Moser K. M. Cellular immune response in coccidioidomycosis. Cell Immunol. 1975 Feb;15(2):360–371. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayce W. R. Cases from the aerospace medicine residents' teaching file. Case #47. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1991 Dec;62(12):1200–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. M., Galgiani J. N., Potter D., Ogden D. A. Coccidioidomycosis in renal replacement therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):489–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kirkland T. N., Franco M., Zhu S., Yuan L., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Immunoreactivity of a surface wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2695–2701. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2695-2701.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Seshan K. R. Antigen complex of Coccidioides immitis which elicits a precipitin antibody response in patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2434–2446. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2434-2446.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Kruse D., Zhu S. W., Seshan K. R., Wheat R. W. Composition, serologic reactivity, and immunolocalization of a 120-kilodalton tube precipitin antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.179-188.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Seshan K. R., Franco M., Bukownik E., Sun S. H., Hearn V. M. Isolation and morphology of an immunoreactive outer wall fraction produced by spherules of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2686–2694. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2686-2694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. T., Zhu S. W., Pan S. C., Yuan L., Kruse D., Sun S. H. Isolation of antigens with proteolytic activity from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1524–1534. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1524-1534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner W. T., Drach G. W., Bucher W. C., Jr Genitourinary aspects of disseminated coccidioidomycosis. J Urol. 1975 Jan;113(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse J. L., Besemer A. R. NUTRITION OF THE PARASITIC PHASE OF COCCIDIOIDES IMMITIS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED LIQUID MEDIUM. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78(2):231–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.231-239.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Baker B. S., Stevens D. A. Specificity of immunoglobulin E in coccidioidomycosis and correlation with disease involvement. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):609–616. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.609-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Immunosuppression by cell wall antigens of Coccidioides immitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S415–S418. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kennell W., Boncyk L., Murphy J. W. Induction and expression of cell-mediated immune responses in inbred mice infected with Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):13–17. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.13-17.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kennell W. Suppression of T-lymphocyte response by Coccidioides immitis antigen. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1424–1429. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1424-1429.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Sun S. H., Dolan M. J., Harrison J. L. Localization of the tube precipitin and complement fixation antigens of Coccidioides immitis by immunoelectron microscopy with murine monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3315–3324. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3315-3324.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Vivas J. R., Gross A., Lecara G., Miller E., Brummer E. In vivo and in vitro cell-mediated responses in coccidioidomycosis. I. Immumologic responses of persons with primary, asymptomatic infections. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Nov;114(5):937–943. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Vivas J. R. Spectrum of in vivo and in vitro cell-mediated immune responses in coccidioidomycosis. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jun 1;31(1):130–141. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. R., Hillberg R. H., Balchum O. J. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Diagnosis by needle biopsy of liver. West J Med. 1975 Feb;122(2):171–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. C., Graybill J. R., Jorgensen J. H., Dismukes W. E., Levine B. E. High-dose ketoconazole for treatment of fungal infections of the central nervous system. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Feb;98(2):160–167. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-2-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. T., Einstein H. Coccidioidal pulmonary cavities with rupture. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982 Aug;84(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelice R., Wieden M. A., Galgiani J. N. The incidence and implications of coccidioidouria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;125(1):49–52. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deresinski S. C., Levine H. B., Stevens D. A. Soluble antigens of mycelia and spherules in the in vitro detection of immunity to Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):700–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.700-704.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deresinski S. C., Pappagianis D., Stevens D. A. Association of ABO blood group and outcome of coccidioidal infection. Sabouraudia. 1979 Sep;17(3):261–264. doi: 10.1080/00362177985380381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deresinski S. C., Stevens D. A. Coccidioidomycosis in compromised hosts. Experience at Stanford University Hospital. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Sep;54(5):377–395. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M., Puente R., de Hoyos L. A., Cruz S. Itraconazole in the treatment of coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1991 Sep;100(3):682–684. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.3.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd L. G., Nelson S. D. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis detected by percutaneous liver biopsy in a liver transplant recipient. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jan;93(1):141–144. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge R. R., Lebowitz M. D., Barbee R., Burrows B. Estimates of C. immitis infection by skin test reactivity in an endemic community. Am J Public Health. 1985 Aug;75(8):863–865. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.8.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Catanzaro A. Coccidioidomycosis. Part II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):727–771. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J., Huppert M. Coccidioidomycosis: factors affecting the host-parasite interaction. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):372–390. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Ampel N. M., Sun S. H., Magee D. M., Harrison J., Law J. H. An immunoreactive apoglycoprotein purified from Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2245–2251. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2245-2251.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Ziebert A. P., Donahoe L. W., Standard P. Unexpected laboratory diagnosis of latent urogenital coccidioidomycosis in a nonendemic area. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Mar;110(3):236–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EINSTEIN H. E., HOLEMAN C. W., Jr, SANDIDGE L. L., HOLDEN D. H. Coccidioidal meningitis. The use of amphotericin B in treatment. Calif Med. 1961 Jun;94:339–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols R. M., Palmer D. L., Long G. W. Tissue eosinophilia in human coccidioidomycosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;4(3):656–664. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.3.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein H. E., Johnson R. H. Coccidioidomycosis: new aspects of epidemiology and therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;16(3):349–354. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIESE M. J. Treatment of disseminated coccidioidomycosis with amphotericin B; report of a case. Calif Med. 1957 Feb;86(2):119–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish D. G., Ampel N. M., Galgiani J. N., Dols C. L., Kelly P. C., Johnson C. H., Pappagianis D., Edwards J. E., Wasserman R. B., Clark R. J. Coccidioidomycosis during human immunodeficiency virus infection. A review of 77 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990 Nov;69(6):384–391. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199011000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forseth J., Rohwedder J. J., Levine B. E., Saubolle M. A. Experience with needle biopsy for coccidioidal lung nodules. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Feb;146(2):319–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. I., Ang E. P., Haley R. S. Identification of coccidioidomycosis of the lung by fine needle aspiration biopsy. Acta Cytol. 1986 Jul-Aug;30(4):420–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. L., Drutz D. J. Influence of fungal surface components on the interaction of Coccidioides immitis with polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):933–943. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gade W., Ledman D. W., Wethington R., Yi A. Serological responses to various Coccidioides antigen preparations in a new enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1907-1912.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Ampel N. M. Coccidioidomycosis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1165–1169. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Catanzaro A., Cloud G. A., Higgs J., Friedman B. A., Larsen R. A., Graybill J. R. Fluconazole therapy for coccidioidal meningitis. The NIAID-Mycoses Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Jul 1;119(1):28–35. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-1-199307010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Dugger K. O., Ito J. I., Wieden M. A. Antigenemia in primary coccidioidomycosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jul;33(4):645–649. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Grace G. M., Lundergan L. L. New serologic tests for early detection of coccidioidomycosis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):671–674. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Inhibition of different phases of Coccidioides immitis by human neutrophils or hydrogen peroxide. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):217–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Isenberg R. A., Stevens D. A. Chemotaxigenic activity of extracts from the mycelial and spherule phases of Coccidioides immitis for human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):862–865. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.862-865.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Killing of Coccidioides immitis by hypochlorous acid or monochloramine. J Med Vet Mycol. 1990;28(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Payne C. M., Jones J. F. Human polymorphonuclear-leukocyte inhibition of incorporation of chitin precursors into mycelia of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):404–412. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Stevens D. A., Graybill J. R., Dismukes W. E., Cloud G. A. Ketoconazole therapy of progressive coccidioidomycosis. Comparison of 400- and 800-mg doses and observations at higher doses. Am J Med. 1988 Mar;84(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Studies of the effects of spherulin from Coccidioides immitis on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Mycopathologia. 1985 May;90(2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00436860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Sun S. H., Dugger K. O., Ampel N. M., Grace G. G., Harrison J., Wieden M. A. An arthroconidial-spherule antigen of Coccidioides immitis: differential expression during in vitro fungal development and evidence for humoral response in humans after infection or vaccination. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2627–2635. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2627-2635.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Yam P., Petz L. D., Williams P. L., Stevens D. A. Complement activation by Coccidioides immitis: in vitro and clinical studies. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):944–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.944-949.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallis H. A., Drew R. H., Pickard W. W. Amphotericin B: 30 years of clinical experience. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12(2):308–329. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn K. P., Alazraki N. P., Waltz T. A. Coccidioidal meningitis. Intrathecal treatment with hyperbaric amphotericin B. Calif Med. 1973 Sep;119(3):6–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A. R. Fungal autofluorescence with ultraviolet illumination. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Feb;79(2):231–234. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A. R., Sobonya R. E., Bronnimann D. A., Galgiani J. N. Quantitative pathology of coccidioidomycosis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1988 Jul;19(7):800–806. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80263-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Stevens D. A., Galgiani J. N., Dismukes W. E., Cloud G. A. Itraconazole treatment of coccidioidomycosis. NAIAD Mycoses Study Group. Am J Med. 1990 Sep;89(3):282–290. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90339-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R. Treatment of coccidioidomycosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;544:481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb40445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajare S., Rakusan T. A., Kalia A., Gibson F. B., Strunk C. L. Laryngeal coccidioidomycosis causing airway obstruction. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Jan;8(1):54–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K. A., Copeland J. G., Zukoski C. F., Sethi G. K., Galgiani J. N. Markers of coccidioidomycosis before cardiac or renal transplantation and the risk of recurrent infection. Transplantation. 1993 Jun;55(6):1422–1424. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199306000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K. A., Sethi G. K., Rosado L. J., Martinez J. D., Huston C. L., Copeland J. G. Coccidioidomycosis and heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1993 May-Jun;12(3):525–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardenbrook M. H., Barriere S. L. Coccidioidomycosis: evaluation of parameters used to predict outcome with amphotericin B therapy. Mycopathologia. 1982 May 22;78(2):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00442628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison H. R., Galgiani J. N., Reynolds A. F., Jr, Sprunger L. W., Friedman A. D. Amphotericin B and imidazole therapy for coccidioidal meningitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 May-Jun;2(3):216–221. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198305000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison W. R., Merbs C. F., Leathers C. R. Evidence of coccidioidomycosis in the skeleton of an ancient Arizona Indian. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):436–437. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Pappagianis D., Cochran J., Stevens D. A. Otomycosis due to coccidioidomycosis. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Sep;138(9):1434–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hector R. F. Compounds active against cell walls of medically important fungi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jan;6(1):1–21. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hector R. F., Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Evaluation of nikkomycins X and Z in murine models of coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and blastomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):587–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- High K. P., Handschumacher R. E. Immunity, microbial pathogenesis, and immunophilins: finding the keys, now where are the locks? Infect Agents Dis. 1992 Jun;1(3):121–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs E. R. Coccidioidomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1989 Apr;7(2):227–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. F., Smith J. W. Diagnosis of disseminated coccidioidomycosis by liver biopsy. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jul;143(7):1335–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. W., Kvale P. A. Pleural effusion in Michigan caused by Coccidioides immitis after travel to an endemic area. Henry Ford Hosp Med J. 1989;37(1):47–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Peterson E. T., Sun S. H., Chitjian P. A., Derrevere W. J. Evaluation of a latex particle agglutination test for coccidioidomycosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):96–102. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M. Racism in coccidioidomycosis? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Oct;118(4):797–798. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Harrison J. L. Morphogenesis throughout saprobic and parasitic cycles of Coccidioides immitis. Mycopathologia. 1982 May 22;78(2):107–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00442634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Specificity of exoantigens for identifying cultures of Coccidioides immitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):346–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.346-348.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Itaoka T., Onuki T., Yokoyama M., Yamamoto N., Nitta S. [A case of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis]. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1991 Aug;39(8):1222–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamidar P. A., Campbell D. R., Fishback J. L., Klotz S. A. Peritoneal coccidioidomycosis associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J. G., Hesselink J. R., Wiley C., Mercer S., Robbins B., Higginbottom P. Coccidioidomycotic brain abscess in an HIV-infected man. West J Med. 1988 Jul;149(1):83–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. W., Jr Persistent adenopathy in coccidioidomycosis: an indication for therapy. South Med J. 1977 May;70(5):531–532. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197705000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Jeffery B., Huppert M. Evaluation of five commercially available immunodiffusion kits for detection of Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):530–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.530-532.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Pappagianis D. The coccidioidal complement fixation and immunodiffusion-complement fixation antigen is a chitinase. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2588–2592. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2588-2592.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M. Occupational factors in coccidioidomycosis. J Occup Med. 1981 May;23(5):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONG Y. C., LEVINE H. B., MADIN S. H., SMITH C. E. FUNGAL MULTIPLICATION AND HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES IN VACCINATED MICE INFECTED WITH COCCIDIOIDES IMMITIS. J Immunol. 1964 May;92:779–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONG Y. C., LEVINE H. B., MADIN S. H., SMITH C. E. FUNGAL MULTIPLICATION AND HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES IN VACCINATED MICE INFECTED WITH COCCIDIOIDES IMMITIS. J Immunol. 1964 May;92:779–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. Laboratory methods for the diagnosis and confirmation of systemic mycoses. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14 (Suppl 1):S23–S29. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.supplement_1.s23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. G., Huppert M., Pappagianis D. Comparison and diagnostic value of the coccidioidin heat-stable (HS and tube precipitin) antigens in immunodiffusion. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.515-518.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Standard P. Improved version of the exoantigen test for identification of Coccidioides immitis and Histoplasma capsulatum cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):42–45. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.42-45.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerrick S. S., Lundergan L. L., Galgiani J. N. Coccidioidomycosis at a university health service. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;131(1):100–102. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Fierer J. Cyclosporin A inhibits Coccidioides immitis in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):921–924. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Zhu S. W., Kruse D., Hsu L. L., Seshan K. R., Cole G. T. Coccidioides immitis fractions which are antigenic for immune T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3952–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3952-3961.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs A., Forthal D. N., Kovacs J. A., Overturf G. D. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. West J Med. 1984 Mar;140(3):447–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse D., Cole G. T. A seroreactive 120-kilodalton beta-1,3-glucanase of Coccidioides immitis which may participate in spherule morphogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4350–4363. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4350-4363.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse D., Cole G. T. Isolation of tube precipitin antibody-reactive fractions of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.169-178.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntze J. R., Herman M. H., Evans S. G. Genitourinary coccidioidomycosis. J Urol. 1988 Aug;140(2):370–374. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41611-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVAN N. E., HUNTINGTON R. W., Jr PRIMARY CUTANEOUS COCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS IN AGRICULTURAL WORKERS. Arch Dermatol. 1965 Sep;92:215–220. doi: 10.1001/archderm.92.3.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunogenicity of spherule-endospore vaccines of Coccidioides immitis for mice. J Immunol. 1961 Aug;87:218–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., KONG Y. C., SMITH C. IMMUNIZATION OF MICE TO COCCIDIOIDES IMMITIS: DOSE, REGIMEN AND SPHERULATION STAGE OF KILLED SPHERULE VACCINES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:132–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labadie E. L., Hamilton R. H. Survival improvement in coccidioidal meningitis by high-dose intrathecal amphotericin B. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Oct;146(10):2013–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc M., Giammona S. T. Coccidioidal meningitis the use of amphotericin B intravenously and intrathecally by repeated lumbar punctures. West J Med. 1975 Mar;122(3):251–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefler E., Weiler-Ravell D., Merzbach D., Ben-Izhak O., Best L. A. Traveller's coccidioidomycosis: case report of pulmonary infection diagnosed in Israel. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1304–1306. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1304-1306.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Bredesen D. E., Rosenblum M. L. Neurological manifestations of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): experience at UCSF and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1985 Apr;62(4):475–495. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.4.0475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. M., Livermore B. M., Wofsy D. Coccidioidomycosis of the thyroid. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):409–411. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonky S. A., Catanzaro A., Moser K. M., Einstein H. Acute coccidioidal pleural effusion. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Oct;114(4):681–688. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADDY K. T. The geographic distribution of coccidioides immitis and possible ecologic implications. Ariz Med. 1958 Mar;15(3):178–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffree M. A., Altshuler G., Benirschke K. Placental coccidioidomycosis without fetal disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Oct;102(10):512–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy M. J., Ellenberg J. F., Killam A. P. Coccidioidomycosis complicating pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Jul 15;137(6):739–740. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(15)33252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morwood D. T., Nichter L. S., Wong V. An unusual complication of an open-head injury: coccidioidal meningitis. Ann Plast Surg. 1989 Nov;23(5):437–441. doi: 10.1097/00000637-198911000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D. Coccidioides in the soil and the meninges. Calif Med. 1973 Sep;119(3):51–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Einstein H. Tempest from Tehachapi takes toll or Coccidioides conveyed aloft and afar. West J Med. 1978 Dec;129(6):527–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D. Epidemiology of coccidioidomycosis. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1988;2:199–238. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3730-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Krasnow R. I., Beall S. False-positive reactions of cerebrospinal fluid and diluted sera with the coccidioidal latex-agglutination test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Nov;66(5):916–921. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/66.5.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Lindsay S., Beall S., Williams P. Ethnic background and the clinical course of coccidioidomycosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):959–961. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappagianis D., Zimmer B. L. Serology of coccidioidomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):247–268. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. M., Johnson S. L., Kelly J. V., Kelly P. C. Coccidiodal meningitis and pregnancy: a case report. Obstet Gynecol. 1989 May;73(5 Pt 2):835–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. M., Schuppert K., Kelly P. C., Pappagianis D. Coccidioidomycosis and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1993 Mar;48(3):149–156. doi: 10.1097/00006254-199303000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkus A. F., Baum L. L., Ellis R. B., Stern M., Danley D. L. Pure spherules of Coccidioides immitis in continuous culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):165–167. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.165-167.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkus A. F., Baum L. L. Natural killer cell inhibition of young spherules and endospores of Coccidioides immitis. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3107–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam J. S., Harper W. K., Greene J. F., Jr, Nelson K. G., Zurek R. C. Coccidioides immitis. A rare cause of pulmonary mycetoma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Nov;112(5):733–738. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.5.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quimby S. R., Connolly S. M., Winkelmann R. K., Smilack J. D. Clinicopathologic spectrum of specific cutaneous lesions of disseminated coccidioidomycosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Jan;26(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. H., Johnson R., Einstein H., Levan N. E. Dinitrochlorobenzene responsivity: difference between patients with severe pulmonary coccidioidomycosis and patients with disseminated coccidioidomycosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):353–356. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. T. Coin lesion, pulmonary: in the Southwest. (Solitary pulmonary nodules). Ariz Med. 1972 Oct;29(10):775–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. B., Jr, Anderson J. A., McKay B. M. Acute pulmonary coccidioidomycosis in children. J Pediatr. 1967 Mar;70(3):376–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J. Coccidioidomycosis in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Depressed humoral as well as cellular immunity. Am J Med. 1984 Apr;76(4):734–736. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenbiker H. T., Ganley J. P., Galgiani J. N., Axline S. G. Prevalence of chorioretinal scars associated with coccidioidomycosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Jan;99(1):71–75. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010073005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenbiker H. T., Ganley J. P. Ocular coccidioidomycosis. Surv Ophthalmol. 1980 Mar-Apr;24(5):263–290. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(80)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Cintron W., Fraire A. E., Greenberg S. D., Stevens P. M., Stager C. E. Pulmonary coccidioidal pseudomycetoma. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Mar-Apr;15(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(92)90123-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohatgi P. K., Schmitt R. G. Pulmonary coccidioidal mycetoma. Am J Med Sci. 1984 May-Jun;287(3):27–30. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198405000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutala P. J., Smith J. W. Coccidioidomycosis in potentially compromised hosts: the effect of immunosuppressive therapy in dissemination. Am J Med Sci. 1978 May-Jun;275(3):283–295. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197805000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW J. B., WYNN-WILLIAMS N. Infectivity of pulmonary tuberculosis in relation to sputum status. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 May;69(5):724–732. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.5.724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., SIMONS S. A. Pattern of 39,500 serologic tests in coccidioidomycosis. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Feb 18;160(7):546–552. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960420026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarosi G. A., Parker J. D., Doto I. L., Tosh F. E. Chronic pulmonary coccidioidomycosis. N Engl J Med. 1970 Aug 13;283(7):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197008132830701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saw E. C., Smale L. E., Einstein H., Huntington R. W., Jr Female genital coccidioidomycosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Feb;45(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanarini M., Rotilio A., Rigobello L., Pomes A., Parenti A., Alessio L. Primary intrasellar coccidioidomycosis simulating a pituitary adenoma. Neurosurgery. 1991 May;28(5):748–751. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199105000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. N., Fihn S. D., Miller R. A. Infection of an arterial prosthesis as the presenting manifestation of disseminated coccidioidomycosis: control of disease with fluconazole. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;16(4):486–488. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.4.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. A., Lamberts R. J. Isolated nodular cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. The initial manifestation of disseminated disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Jan;4(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon A. S., Isaac-Renton J., Dixon J. M., Stein L., Sims H. V. Review of human and animal cases of coccidioidomycosis diagnosed in Canada. Mycopathologia. 1991 Jan;113(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00436377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafai T. Neonatal coccidioidomycosis in premature twins. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Jun;132(6):634–634. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120310098021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Ellis W. G., Nielsen S. L., Davis R. L. Central nervous system coccidioidomycosis: a clinicopathologic study of treatment with and without amphotericin B. Hum Pathol. 1984 Oct;15(10):980–995. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Barbee R. A. Isolation of Coccidioides immitis from bronchoalveolar lavage is diagnostic of infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Feb;143(2):451–451. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.2.451b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Barbee R. A., Wiens J., Trego D. Detection of fungi and other pathogens in immunocompromised patients by bronchoalveolar lavage in an area endemic for coccidioidomycosis. Chest. 1990 Jun;97(6):1349–1355. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.6.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadalnik R. C., Goldstein E., Hoeprich P. D., dos Santos P. A., Lee K. K. Diagnostic value of gallium and bone scans in evaluation of extrapulmonary coccidioidal lesions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Apr;121(4):673–676. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P., Kaufman L. Evaluation of Leathers-Awasthi medium for identifying Coccidioides immitis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2428–2429. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2428-2429.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockman L., Clark K. A., Hunt J. M., Roberts G. D. Evaluation of commercially available acridinium ester-labeled chemiluminescent DNA probes for culture identification of Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioides immitis, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Histoplasma capsulatum. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):845–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.845-850.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. H., Huppert M., Vukovich K. R. Rapid in vitro conversion and identification of Coccidioides immitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):186–190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.186-190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. H., Sekhon S. S., Huppert M. Electron microscopic studies of saprobic and parasitic forms of Coccidioides immitis. Sabouraudia. 1979 Sep;17(3):265–273. doi: 10.1080/00362177985380391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. D., Boettger D. W., Miedzinski L. J., Tyrrell D. L. Coccidioidal meningitis acquired during holidays in Arizona. CMAJ. 1990 Jun 15;142(12):1388–1390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thadepalli H., Salem F. A., Mandal A. K., Rambhatla K., Einstein H. E. Pulmonary mycetoma due to Coccidioides immitis. Chest. 1977 Mar;71(3):429–430. doi: 10.1378/chest.71.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. M., Denning D. W., Arathoon E. G., Rinaldi M. G., Stevens D. A. Itraconazole therapy for nonmeningeal coccidioidomycosis: clinical and laboratory observations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Sep;23(3 Pt 2):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70261-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. M., Denning D. W., Dupont B., Stevens D. A. Itraconazole therapy for chronic coccidioidal meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jan 15;112(2):108–112. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-2-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. M., Galgiani J. N., Denning D. W., Hanson L. H., Graybill J. R., Sharkey K., Eckman M. R., Salemi C., Libke R., Klein R. A. Treatment of coccidioidal meningitis with fluconazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Mar-Apr;12 (Suppl 3):S380–S389. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_3.s380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartivarian S. E., Coudron P. E., Markowitz S. M. Disseminated coccidioidomycosis. Unusual manifestations in a cardiac transplantation patient. Am J Med. 1987 Nov;83(5):949–952. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90657-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent T., Galgiani J. N., Huppert M., Salkin D. The natural history of coccidioidal meningitis: VA-Armed Forces cooperative studies, 1955-1958. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;16(2):247–254. doi: 10.1093/clind/16.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINN W. A. THE TREATMENT OF COCCIDIOIDAL MENINGITIS. THE USE OF AMPHOTERICIN B IN A GROUP OF 25 PATIENTS. Calif Med. 1964 Aug;101:78–89. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wack E. E., Ampel N. M., Galgiani J. N., Bronnimann D. A. Coccidioidomycosis during pregnancy. An analysis of ten cases among 47,120 pregnancies. Chest. 1988 Aug;94(2):376–379. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. P., Brody C. Z., Resnik R. Reactivation of coccidioidomycosis in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 May;79(5 ):815–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. H., Berci G., Morledge D., Schwartz H. Coccidioidomycosis of the larynx in infants and adults. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977 Sep-Oct;86(5 Pt 1):655–660. doi: 10.1177/000348947708600521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. C., Chandler F. W., Mihalov M. L., Kammeyer P. L., Armin A. R. Giant forms of Blastomyces dermatitidis in the pulmonary lesions of blastomycosis. Potential confusion with Coccidioides immitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;93(4):575–578. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. H. Antigenemia detected in human coccidioidomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):136–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.136-142.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman I. M., Moreno A. J., Parker A. L., Sippo W. C., Liles W. J. Gastrointestinal dissemination of coccidioidomycosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986 Jul;81(7):589–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S. B., Pappagianis D., Heindl I., Mickel A. An epidemic of coccidioidomycosis among archeology students in northern California. N Engl J Med. 1972 Mar 9;286(10):507–512. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197203092861003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Connolly-Stringfield P., Blair R., Connolly K., Garringer T., Katz B. P. Histoplasmosis relapse in patients with AIDS: detection using Histoplasma capsulatum variety capsulatum antigen levels. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Dec 15;115(12):936–941. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-12-936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Connolly-Stringfield P., Kohler R. B., Frame P. T., Gupta M. R. Histoplasma capsulatum polysaccharide antigen detection in diagnosis and management of disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1989 Oct;87(4):396–400. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80820-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieden M. A., Galgiani J. N., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunodiffusion techniques with standard complement fixation assay for quantitation of coccidioidal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):529–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.529-534.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Johnson R., Pappagianis D., Einstein H., Slager U., Koster F. T., Eron J. J., Morrison J., Aguet J., River M. E. Vasculitic and encephalitic complications associated with Coccidioides immitis infection of the central nervous system in humans: report of 10 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):673–682. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Sable D. L., Mendez P., Smyth L. T. Symptomatic coccidioidomycosis following a severe natural dust storm. An outbreak at the Naval Air Station, Lemoore, Calif. Chest. 1979 Nov;76(5):566–570. doi: 10.1378/chest.76.5.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. A. Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Reevaluation of its potentiality based on study of three new cases. Arch Dermatol. 1965 Sep;92(3):221–228. doi: 10.1001/archderm.92.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson D., Lee S. Coccidioidomycosis diagnosed from bone marrow smear. JAMA. 1991 Aug 7;266(5):707–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel C. J., Alksne J. F. Retromastoid cisternal Ommaya reservoir for intrathecal therapy of coccidioidomycosis meningitis. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1992 Sep;77(3):476–477. doi: 10.3171/jns.1992.77.3.0476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel C. J., Meyer S., Johnson R. H., Hesselink J. R. MR findings in acute and chronic coccidioidomycosis meningitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;13(4):1241–1245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel C. J., Rothrock J. Coccidioidomycosis meningitis presenting as anterior spinal artery syndrome. Neurology. 1992 Sep;42(9):1840–1840. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.9.1840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinoya S., Cox R. A., Pope R. M. Circulating immune complexes in coccidioidomycosis. Detection and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):655–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI109901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yozwiak M. L., Lundergan L. L., Kerrick S. S., Galgiani J. N. Symptoms and routine laboratory abnormalities associated with coccidioidomycosis. West J Med. 1988 Oct;149(4):419–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yturraspe D. J. Clinical evaluation of a latex particle agglutination test and a gel diffusion precipitin test in the diagnosis of canine coccidioidomycosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1971 Apr 1;158(7):1249–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Characterization of a soluble protein of Coccidiodes immitis with activity as an immunodiffusion-complement fixation antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2250–2256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2250-2256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Immunoaffinity isolation and partial characterization of the Coccidioides immitis antigen detected by the tube precipitin and immunodiffusion-tube precipitin tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1759–1766. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1759-1766.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]