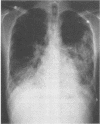
Abstract
The frequency of fulminant pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae is relatively rare despite the high prevalence of Mycoplasma species infection in the general population. We recently encountered such a case and have reviewed the English-language literature on cases of M pneumoniae pneumonia that have resulted in respiratory failure or death. Due to host factors or on epidemiologic grounds, fulminant cases seem to be more common in young healthy adults, in males, and possibly in smokers among the 46 patients we found. An enhanced host cellular immune response may be responsible for the development of severe cases. A spectrum of small airways disease is characteristic, including cellular bronchiolitis and bronchiolitis obliterans with and without organizing pneumonia. Based largely on anecdotal experience, corticosteroid use may be salutary in patients with respiratory failure. For reasons that are not well known, the incidence of pulmonary thromboembolism is increased in fatal cases.
Full text
PDF

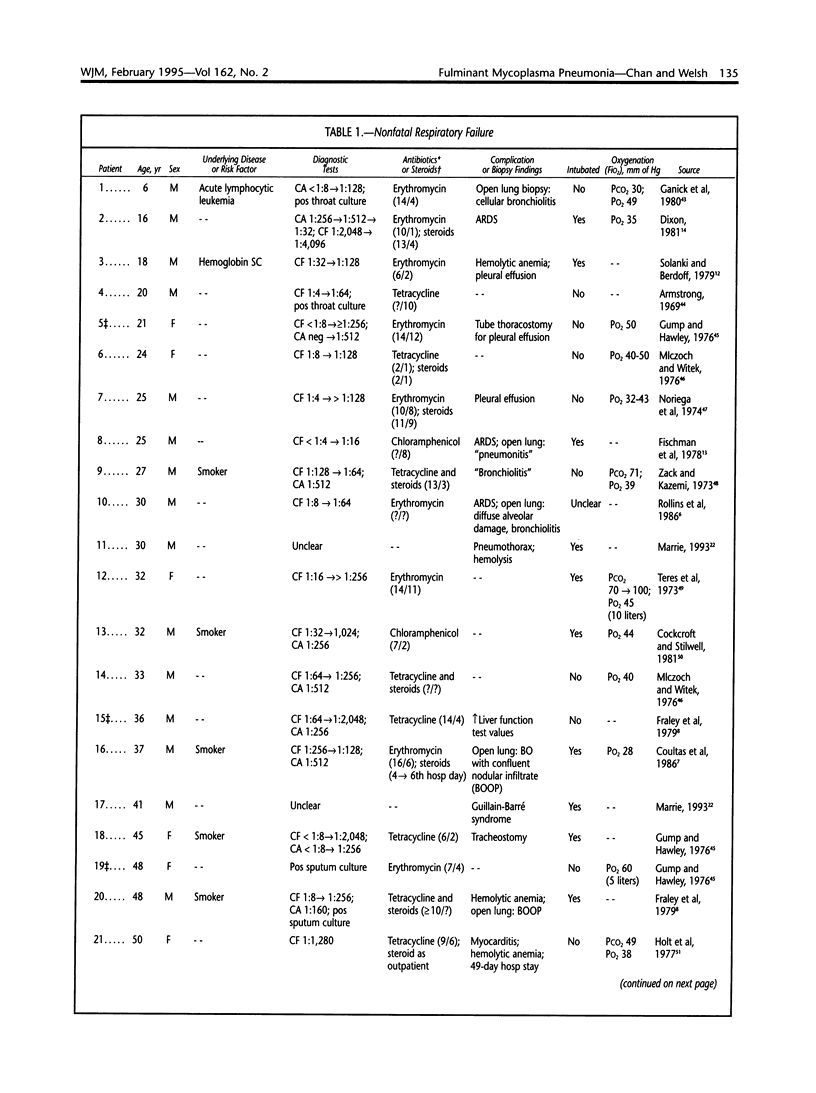
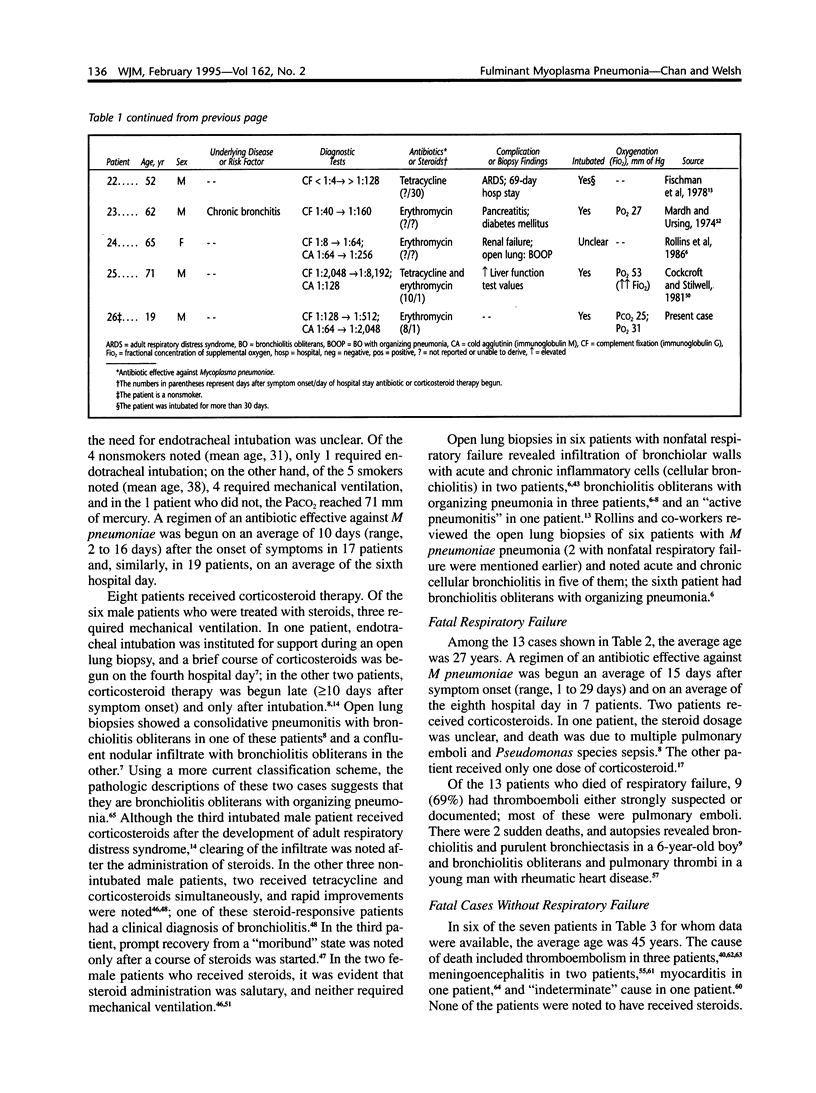
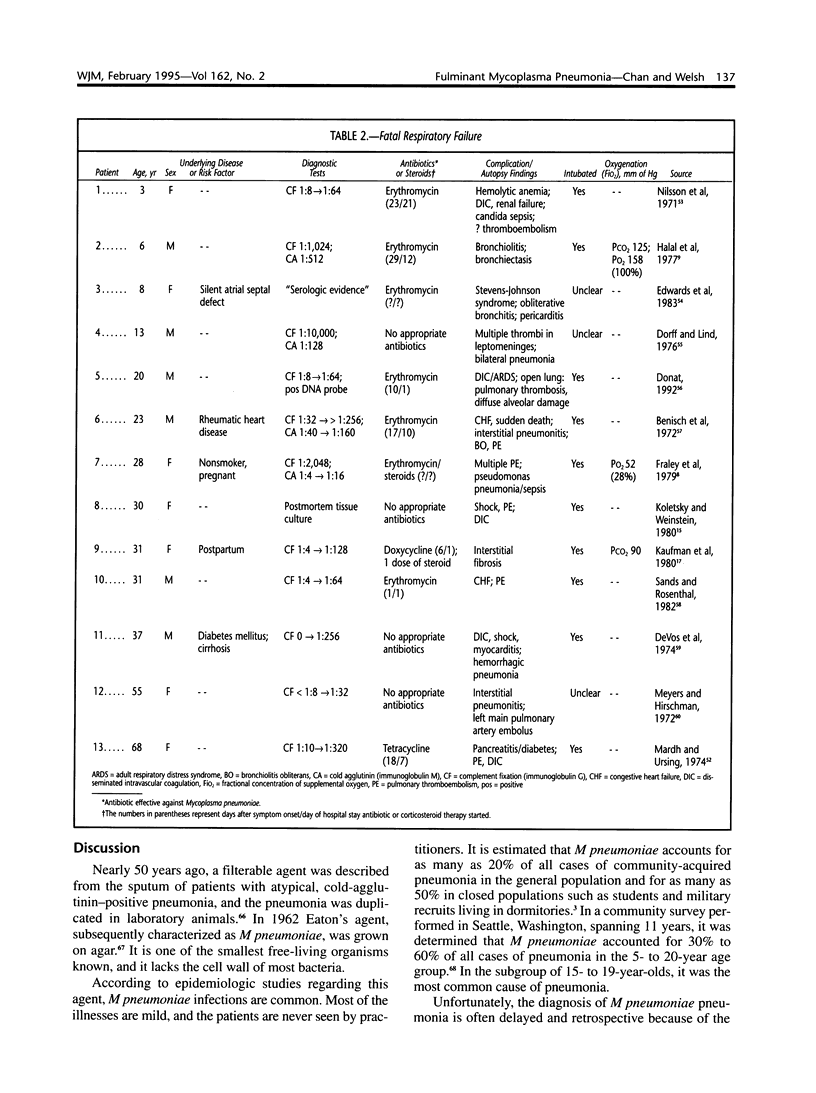




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali N. J., Sillis M., Andrews B. E., Jenkins P. F., Harrison B. D. The clinical spectrum and diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Q J Med. 1986 Mar;58(227):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alshafi K. M., Ironton R. Unusual presentation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Lancet. 1991 Dec 14;338(8781):1519–1520. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92331-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. Virus and Mycoplasma respiratory infections. Adv Cardiopulm Dis. 1969;4:175–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubertin J., Dabis F., Fleurette J., Bornstein N., Salamon R., Brottier E., Brune J., Vincent P., Migueres J., Jover A. Prevalence of legionellosis among adults: a study of community-acquired pneumonia in France. Infection. 1987;15(5):328–331. doi: 10.1007/BF01647732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benisch B. M., Fayemi A., Gerber M. A., Axelrod J. Mycoplasmal pneumonia in a patient with rheumatic heart disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Sep;58(3):343–348. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berntsson E., Blomberg J., Lagergård T., Trollfors B. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in patients requiring hospitalization. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF02013650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Sterner G. Effect of Mycoplasma pheumoniae infection on cell-mediated immunity. Infection. 1976;4(1 Suppl):17–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01638416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 5-1992. A 20-year-old man with diffuse pulmonary infiltrates and disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 30;326(5):324–336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201303260508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell G. H., Cole B. C. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):80–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. K., Hyland R. H., Hutcheon M. A. Pulmonary complications following bone marrow transplantation. Clin Chest Med. 1990 Jun;11(2):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chusid M. J., Lachman B. S., Lazerson J. Severe Mycoplasma pneumonia and vesicular eruption in SC hemoglobinopathy. J Pediatr. 1978 Sep;93(3):449–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Stilwell G. A. Lobar pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Jun 1;124(11):1463–1468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coultas D. B., Samet J. M., Butler C. Bronchiolitis obliterans due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. West J Med. 1986 Apr;144(4):471–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos M., Van Nimmen L., Baele G. Disseminated intravascular coagulation during a fatal Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Acta Haematol. 1974;52(2):120–125. doi: 10.1159/000208229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. Mycoplasmal pneumonia and adult respiratory distress syndrome: a complication to be recognized. J Natl Med Assoc. 1981 Jun;73(6):549–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorff B., Lind K. Two fatal cases of meningoencephalitis associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1976;8(1):49–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorff G. J., Rytel M. W., Farmer S. G., Scanlon G. Etiologies and characteristic features of pneumonias in a municipal hospital. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Nov;266(5):349–358. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197311000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Penny M., Newman J. Mycoplasma pneumonia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and chronic obliterative bronchitis. Thorax. 1983 Nov;38(11):867–869. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.11.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G. D., Fine M., Orloff J., Arisumi D., Yu V. L., Kapoor W., Grayston J. T., Wang S. P., Kohler R., Muder R. R. New and emerging etiologies for community-acquired pneumonia with implications for therapy. A prospective multicenter study of 359 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990 Sep;69(5):307–316. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199009000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekety F. R., Jr, Caldwell J., Gump D., Johnson J. E., Maxson W., Mulholland J., Thoburn R. Bacteria, viruses, and mycoplasmas in acute pneumonia in adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):499–507. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W. Immunologic mechanisms suggested in the association of M. pneumoniae infection and extrapulmonary disease: a review. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):475–479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine M. J., Singer D. E., Hanusa B. H., Lave J. R., Kapoor W. N. Validation of a pneumonia prognostic index using the MedisGroups Comparative Hospital Database. Am J Med. 1993 Feb;94(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90177-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischman R. A., Marschall K. E., Kislak J. W., Greenbaum D. M. Adult respiratory distress syndrome caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Chest. 1978 Oct;74(4):471–473. doi: 10.1378/chest.74.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Cooney M. K., Allan I. D. Long-term epidemiology of infections with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):681–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Sefi R., Ochs H. D., Allan I. D. Second attacks of pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):673–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Nolan C. M., Allan I. D. Epidemiologic aspects of M. pneumoniae disease complications: a review. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):469–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Ochs H., Davis S. D., Kenny G. E., Luce R. R. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in patients with immunodeficiency syndromes: report of four cases. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):388–393. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraley D. S., Ruben F. L., Donnelly E. J. Respiratory failure secondary to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. South Med J. 1979 Apr;72(4):437–440. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197904000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganick D. J., Wolfson J., Gilbert E. F., Joo P. Mycoplasma infection in the immunosuppressed leukemic patient. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Oct;104(10):535–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gump D. W., Hawley H. B. Severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Respiration. 1976;33(6):475–486. doi: 10.1159/000193765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halal F., Brochu P., Delage G., Lamarre A., Rivard G. Severe disseminated lung disease and bronchiectasis probably due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Can Med Assoc J. 1977 Nov 5;117(9):1055–1056. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg H. Aetiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospital treated patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(5):491–501. doi: 10.3109/00365548709032413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S., Ryan W. F., Epstein E. J. Severe mycoplasma pneumonia. Thorax. 1977 Feb;32(1):112–115. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Cigarette smoking and lung destruction. Accumulation of neutrophils in the lungs of cigarette smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Nov;128(5):833–838. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.5.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jastremski M. S. Adult respiratory distress syndrome due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Chest. 1979 Apr;75(4):529–529. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.4.529a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. M., Cuvelier C. A., Van der Straeten M. Mycoplasma pneumonia with fulminant evolution into diffuse interstitial fibrosis. Thorax. 1980 Feb;35(2):140–144. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletsky R. J., Weinstein A. J. Fulminant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Report of a fatal case, and a review of the literature. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Sep;122(3):491–496. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Lerner A. M. The clinical spectrum of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Med Clin North Am. 1978 Sep;62(5):961–978. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31749-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim I., Shaw D. R., Stanley D. P., Lumb R., McLennan G. A prospective hospital study of the aetiology of community-acquired pneumonia. Med J Aust. 1989 Jul 17;151(2):87–91. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb101168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S. Human mycoplasmal infections: serologic observations. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):216–231. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linz D. H., Tolle S. W., Elliot D. L. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Experience at a referral center. West J Med. 1984 Jun;140(6):895–900. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby J. P. Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Chest Med. 1991 Jun;12(2):237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy M., Dromer F., Brion N., Leturdu F., Carbon C. Community-acquired pneumonia. Importance of initial noninvasive bacteriologic and radiographic investigations. Chest. 1988 Jan;93(1):43–48. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. T., Finch R. G., Ward M. J., Macrae A. D. Hospital study of adult community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet. 1982 Jul 31;2(8292):255–258. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansel J. K., Rosenow E. C., 3rd, Smith T. F., Martin J. W., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Chest. 1989 Mar;95(3):639–646. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.3.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Durant H., Yates L. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: 5-year prospective study. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11(4):586–599. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia requiring hospitalization, with emphasis on infection in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Feb 22;153(4):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Fatal infections associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae: discussion of three cases with necropsy findings. Mt Sinai J Med. 1972 May-Jun;39(3):258–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H., Mizutani H. Circulating immune complexes in patients with mycoplasmal pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):627–629. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlczoch F., Witek F. Miliary mycoplasmal pneumonia: a report of six cases. Infection. 1976;4(1 Suppl):64–67. doi: 10.1007/BF01638428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Senterfit L. B., Roberts R. B. The protean manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in adults. Am J Med. 1975 Feb;58(2):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Ursing B. The occurrence of acute pancreatitis in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(2):167–171. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-2.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftalin J. M., Wellisch G., Kahana Z., Diengott D. Letter: Mycoplasma pneumoniae septicemia. JAMA. 1974 Apr 29;228(5):565–565. doi: 10.1001/jama.228.5.565d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Rausing A., Denneberg T., Christensson P. Intravascular coagulation and acute renal failure in a child with mycoplasma infection. Acta Med Scand. 1971 May;189(5):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1971.tb04390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noriega E. R., Simberkoff M. S., Gilroy F. J., Rahal J. J., Jr Life-threatening Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. JAMA. 1974 Sep 9;229(11):1471–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburger D., Carson J. P., Gundlach W. J., Ghaly F. I., Wright W. H. Legionnaires' disease. Association with mycoplasma pneumonia and disseminated intravascular coagulation. JAMA. 1979 Mar 23;241(12):1269–1270. doi: 10.1001/jama.241.12.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez C. R., Leigh M. W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae as the causative agent for pneumonia in the immunocompromised host. Chest. 1991 Sep;100(3):860–861. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.3.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins S., Colby T., Clayton F. Open lung biopsy in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Jan;110(1):34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands M. J., Jr, Rosenthal R. Progressive heart failure and death associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Chest. 1982 Jun;81(6):763–765. doi: 10.1378/chest.81.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman S. T., Bartlett J., Clyde W. A., Jr, Ayoub E. M. The unusual severity of Mycoplasmal pneumonia in children with sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 27;287(4):164–167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207272870403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegler D. I. Lung abscess associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Br J Dis Chest. 1973 Apr;67(2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(73)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. I., DeVoe W. M. Severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in otherwise healthy siblings. J Pediatr. 1979 Dec;95(6):999–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solanki D. L., Berdoff R. L. Severe mycoplasma pneumonia with pleural effusions in a patient with sickle cell-hemoglobin C(SC) disease. Case report and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1979 Apr;66(4):707–710. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner G., Biberfeld G. Central nervous system complications of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1969;1(3):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D., Sigler A., Khouri N. F., Talamo R. C. Unilateral hyperlucent lung (Swyer-James syndrome) after severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):145–152. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R. J., Jr, Dowdle W. R., Marine W. M., Hierholzer J. C. Adult pneumonia in a general hospital. Etiology and host risk factors. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jun;129(6):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. E., Schlichtig R. Acute respiratory failure due to atypical pneumonia. Case report. Mo Med. 1983 Mar;80(3):144–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Reyes M. P. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis following Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Am J Med. 1985 Aug;79(2):268–270. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. Immunity to mycoplasma infections of the respiratory tract: a review. J R Soc Med. 1979 Jul;72(7):520–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Taylor-Robinson D., Fernald G. W. Reduction in the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced pneumonia in hamsters by immunosuppressive treatment with antithymocyte sera. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Aug;7(3):343–348. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teres D., Roizen M. F., Bushnell L. S. Successful weaning from controlled ventilation despite high deadspace-to-tidal volume ratio. Anesthesiology. 1973 Dec;39(6):656–659. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197312000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Caplan E. S. Fatal Mycoplasma pneumoniae encephalitis in an adult. Arch Neurol. 1980 May;37(5):321–321. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500540099024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Blainey A. D., Harrison K. J., Clarke S. K. Causes of pneumonia presenting to a district general hospital. Thorax. 1981 Aug;36(8):566–570. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.8.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack M. B., Kazemi H. Carbon dioxide retention in Mycoplasma pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jun;107(6):1052–1054. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.6.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]