Abstract
Portal hypertension is frequently complicated by upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding and ascites. Hemorrhage from esophageal varices is the most common cause of death from portal hypertension. Medical treatment, including resuscitation, vasoactive drugs, and endoscopic sclerosis, is the preferred initial therapy. Patients with refractory hemorrhage frequently are referred for immediate surgical intervention (usually emergency portacaval shunt). An additional cohort of patients with a history of at least 1 episode of variceal hemorrhage is likely to benefit from elective shunt operations. Shunt operations are classified as total, partial, or selective shunts based on their hemodynamic characteristics. Angiographically created shunts have been introduced recently as an alternative to operative shunts in certain circumstances. Devascularization of the esophagus or splenectomy is done for specific indications. Medically intractable ascites is a separate indication for surgical intervention. Liver transplantation has been advocated for patients whose portal hypertension is a consequence of end-stage liver disease. In the context of an increasingly complex set of treatment options, we present an overview of surgical therapy for complications of portal hypertension.
Full text
PDF


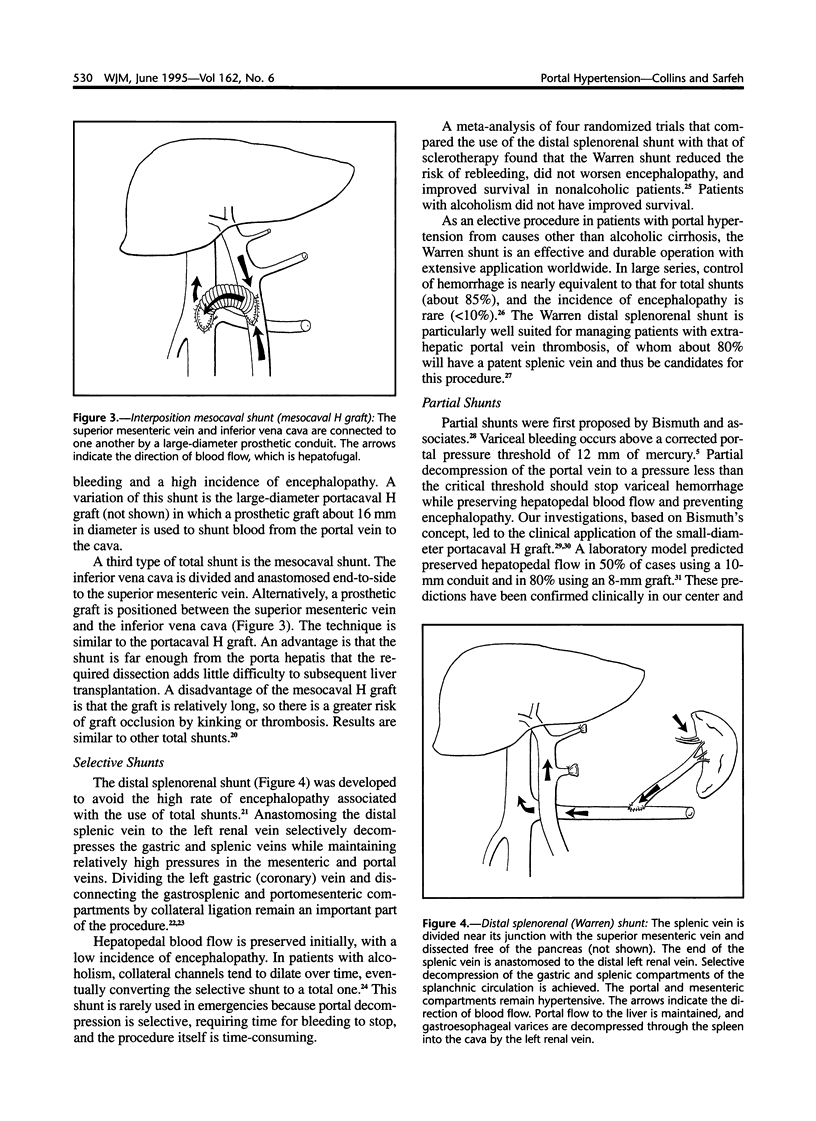


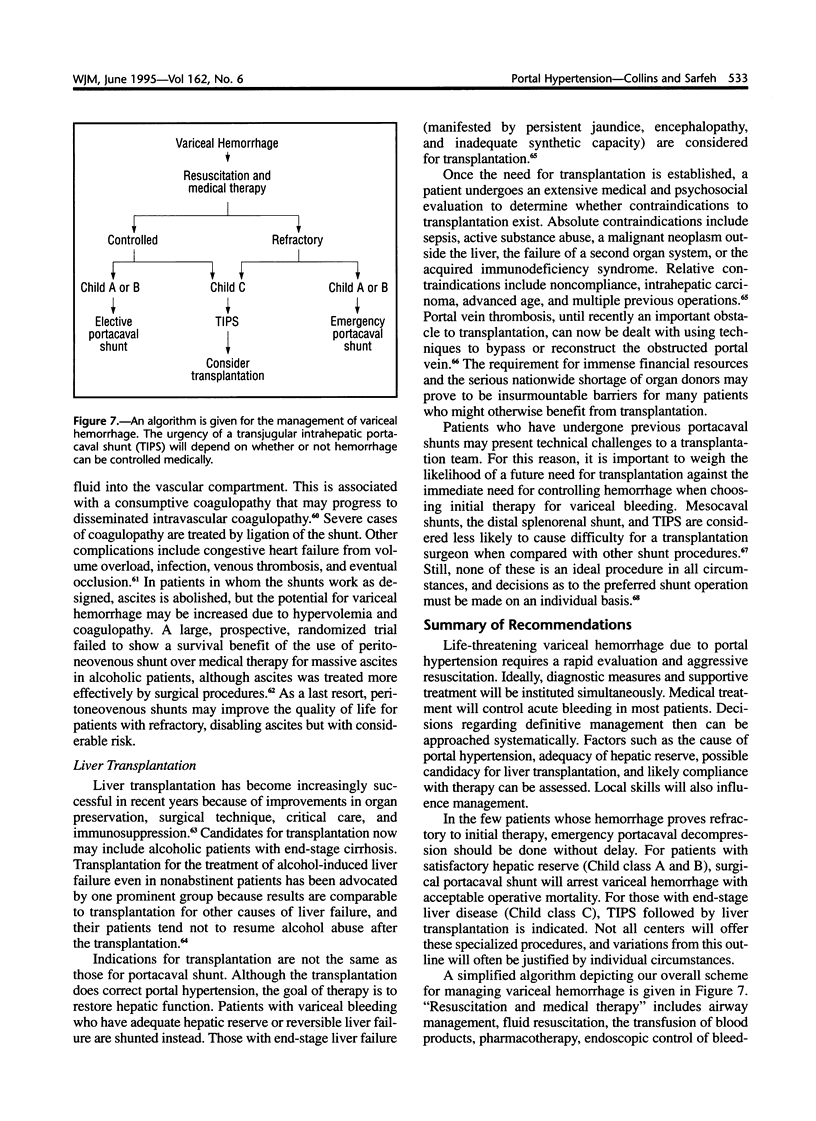
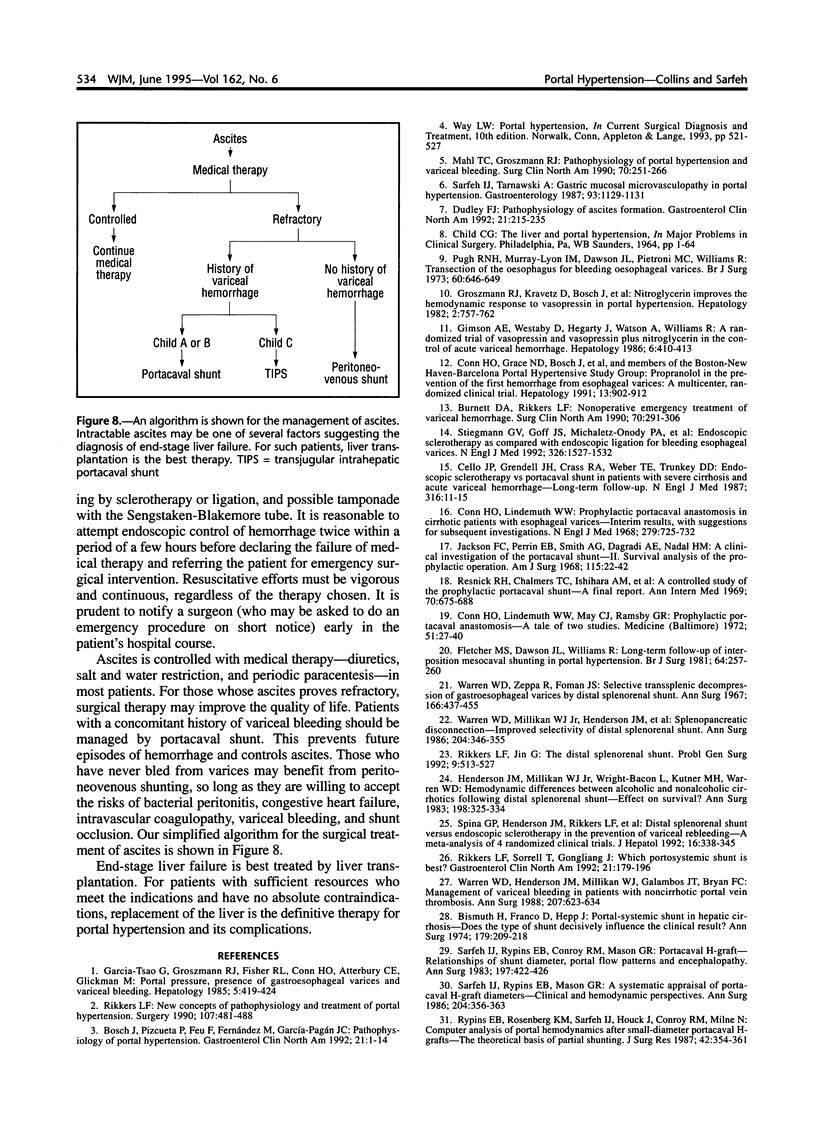

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R., Diamond T., Bismuth H. Partial portacaval shunt: renaissance of an old concept. Surgery. 1992 Jun;111(6):610–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo V., Ginès P., Planas R. Treatment of ascites in cirrhosis. Diuretics, peritoneovenous shunt, and large-volume paracentesis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;21(1):237–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth H., Adam R., Mathur S., Sherlock D. Options for elective treatment of portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients in the transplantation era. Am J Surg. 1990 Jul;160(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80878-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth H., Franco D., Hepp J. Portal-systemic shunt in hepatic cirrhosis: does the type of shunt decisively influence the clinical result? Ann Surg. 1974 Feb;179(2):209–218. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197402000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Pizcueta P., Feu F., Fernández M., García-Pagán J. C. Pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;21(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., 3rd The natural history of splenic vein thrombosis due to chronic pancreatitis: indications for surgery. Int J Pancreatol. 1987 Apr;2(2):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF03015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D. A., Rikkers L. F. Nonoperative emergency treatment of variceal hemorrhage. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;70(2):291–306. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs A. K., Hamilton G., Phillips A., Mezzanotte G., McIntyre N., Hobbs K. E. A comparison of sclerotherapy with staple transection of the esophagus for the emergency control of bleeding from esophageal varices. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):857–862. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cello J. P., Crass R., Trunkey D. D. Endoscopic sclerotherapy versus esophageal transection of Child's class C patients with variceal hemorrhage. Comparison with results of portacaval shunt: preliminary report. Surgery. 1982 Mar;91(3):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cello J. P., Grendell J. H., Crass R. A., Weber T. E., Trunkey D. D. Endoscopic sclerotherapy versus portacaval shunt in patient with severe cirrhosis and acute variceal hemorrhage. Long-term follow-up. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 1;316(1):11–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701013160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. C., Rypins E. B., Sarfeh I. J. Narrow-diameter portacaval shunts for management of variceal bleeding. World J Surg. 1994 Mar-Apr;18(2):211–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00294403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O., Grace N. D., Bosch J., Groszmann R. J., Rodés J., Wright S. C., Matloff D. S., Garcia-Tsao G., Fisher R. L., Navasa M. Propranolol in the prevention of the first hemorrhage from esophagogastric varices: A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. The Boston-New Haven-Barcelona Portal Hypertension Study Group. Hepatology. 1991 May;13(5):902–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O., Lindenmuth W. W., May C. J., Ramsby G. R. Prophylactic portacaval anastomosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Jan;51(1):27–40. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O. Transjugular intrahepatic portal-systemic shunts: the state of the art. Hepatology. 1993 Jan;17(1):148–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagenais M., Langer B., Taylor B. R., Greig P. D. Experience with radical esophagogastric devascularization procedures (Sugiura) for variceal bleeding outside Japan. World J Surg. 1994 Mar-Apr;18(2):222–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00294405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling R. C., 3rd, Shah D. M., Chang B. B., Thompson P. N., Leather R. P. Long-term follow-up of poor-risk patients undergoing small-diameter portacaval shunts. Am J Surg. 1992 Sep;164(3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)81075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J. Pathophysiology of ascites formation. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;21(1):215–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco D., Vons C., Traynor O., de Smadja C. Should portosystemic shunt be reconsidered in the treatment of intractable ascites in cirrhosis? Arch Surg. 1988 Aug;123(8):987–991. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400320073015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulenwider J. T., Galambos J. D., Smith R. B., 3rd, Henderson J. M., Warren W. D. LeVeen vs Denver peritoneovenous shunts for intractable ascites of cirrhosis. A randomized, prospective trial. Arch Surg. 1986 Mar;121(3):351–355. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1986.01400030113018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Tsao G., Groszmann R. J., Fisher R. L., Conn H. O., Atterbury C. E., Glickman M. Portal pressure, presence of gastroesophageal varices and variceal bleeding. Hepatology. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):419–424. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimson A. E., Westaby D., Hegarty J., Watson A., Williams R. A randomized trial of vasopressin and vasopressin plus nitroglycerin in the control of acute variceal hemorrhage. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):410–413. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace N. D. The side-to-side portacaval shunt revisited. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 20;330(3):208–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401203300312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig P. D., Langer B., Blendis L. M., Taylor B. R., Glynn M. F. Complications after peritoneovenous shunting for ascites. Am J Surg. 1980 Jan;139(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groszmann R. J., Kravetz D., Bosch J., Glickman M., Bruix J., Bredfeldt J., Conn H. O., Rodes J., Storer E. H. Nitroglycerin improves the hemodynamic response to vasopressin in portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):757–762. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helton W. S., Belshaw A., Althaus S., Park S., Coldwell D., Johansen K. Critical appraisal of the angiographic portacaval shunt (TIPS). Am J Surg. 1993 May;165(5):566–571. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. M. Liver transplantation for portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;21(1):197–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. M., Millikan W. J., Jr, Wright-Bacon L., Kutner M. H., Warren W. D. Hemodynamic differences between alcoholic and nonalcoholic cirrhotics following distal splenorenal shunt--effect on survival? Ann Surg. 1983 Sep;198(3):325–334. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198309000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga W. K., Angorn I. B., Baker L. W. Esophageal transection versus injection sclerotherapy in the management of bleeding esophageal varices in patients at high risk. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985 Jun;160(6):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idezuki Y., Kokudo N., Sanjo K., Bandai Y. Sugiura procedure for management of variceal bleeding in Japan. World J Surg. 1994 Mar-Apr;18(2):216–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00294404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. C., Perrin E. B., Smith A. G., Dagradi A. E., Nadal H. M. A clinical investigation of the portacaval shunt. II. Survival analysis of the prophylactic operation. Am J Surg. 1968 Jan;115(1):22–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(68)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBerge J. M., Ring E. J., Gordon R. L., Lake J. R., Doherty M. M., Somberg K. A., Roberts J. P., Ascher N. L. Creation of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts with the wallstent endoprosthesis: results in 100 patients. Radiology. 1993 May;187(2):413–420. doi: 10.1148/radiology.187.2.8475283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahl T. C., Groszmann R. J. Pathophysiology of portal hypertension and variceal bleeding. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;70(2):251–266. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaferro V., Todo S., Tzakis A. G., Stieber A. C., Makowka L., Starzl T. E. Liver transplantation in patients with previous portasystemic shunt. Am J Surg. 1990 Jul;160(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80879-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragni M. V., Lewis J. H., Spero J. A. Ascites-induced LeVeen shunt coagulopathy. Ann Surg. 1983 Jul;198(1):91–95. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198307000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. H., Chalmers T. C., Ishihara A. M., Garceau A. J., Callow A. D., Schimmel E. M., O'Hara E. T. A controlled study of the prophylactic portacaval shunt. A final report. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Apr;70(4):675–688. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-4-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikkers L. F. New concepts of pathophysiology and treatment of portal hypertension. Surgery. 1990 May;107(5):481–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikkers L. F., Sorrell W. T., Jin G. Which portosystemic shunt is best? Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992 Mar;21(1):179–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ring E. J., Lake J. R., Roberts J. P., Gordon R. L., LaBerge J. M., Read A. E., Sterneck M. R., Ascher N. L. Using transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts to control variceal bleeding before liver transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Feb 15;116(4):304–309. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-4-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemurgy A. S., McAllister E. W., Kearney R. E. Prospective study of a prosthetic H-graft portacaval shunt. Am J Surg. 1991 Jan;161(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(91)90378-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rypins E. B., Rosenberg K. M., Sarfeh I. J., Houck J., Conroy R. M., Milne N. Computer analysis of portal hemodynamics after small-diameter portacaval H-grafts: the theoretical basis for partial shunting. J Surg Res. 1987 Apr;42(4):354–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(87)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rypins E. B., Sarfeh I. J. Small-diameter portacaval H-graft for variceal hemorrhage. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;70(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rössle M., Haag K., Ochs A., Sellinger M., Nöldge G., Perarnau J. M., Berger E., Blum U., Gabelmann A., Hauenstein K. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 20;330(3):165–171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401203300303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfeh I. J., Rypins E. B., Conroy R. M., Mason G. R. Portacaval H-graft: relationships of shunt diameter, portal flow patterns and encephalopathy. Ann Surg. 1983 Apr;197(4):422–426. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198304000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfeh I. J., Rypins E. B., Mason G. R. A systematic appraisal of portacaval H-graft diameters. Clinical and hemodynamic perspectives. Ann Surg. 1986 Oct;204(4):356–363. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198610000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfeh I. J., Rypins E. B. Partial versus total portacaval shunt in alcoholic cirrhosis. Results of a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 1994 Apr;219(4):353–361. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199404000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfeh I. J., Tarnawski A. Gastric mucosal vasculopathy in portal hypertension. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):1129–1131. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spina G. P., Henderson J. M., Rikkers L. F., Teres J., Burroughs A. K., Conn H. O., Pagliaro L., Santambrogio R. Distal spleno-renal shunt versus endoscopic sclerotherapy in the prevention of variceal rebleeding. A meta-analysis of 4 randomized clinical trials. J Hepatol. 1992 Nov;16(3):338–345. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80666-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley M. M., Ochi S., Lee K. K., Nemchausky B. A., Greenlee H. B., Allen J. I., Allen M. J., Baum R. A., Gadacz T. R., Camara D. S. Peritoneovenous shunting as compared with medical treatment in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis and massive ascites. Veterans Administration Cooperative Study on Treatment of Alcoholic Cirrhosis with Ascites. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 14;321(24):1632–1638. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912143212403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D. Liver transplantation (2). N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1092–1099. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Van Thiel D., Tzakis A. G., Iwatsuki S., Todo S., Marsh J. W., Koneru B., Staschak S., Stieber A., Gordon R. D. Orthotopic liver transplantation for alcoholic cirrhosis. JAMA. 1988 Nov 4;260(17):2542–2544. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegmann G. V., Goff J. S., Michaletz-Onody P. A., Korula J., Lieberman D., Saeed Z. A., Reveille R. M., Sun J. H., Lowenstein S. R. Endoscopic sclerotherapy as compared with endoscopic ligation for bleeding esophageal varices. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1527–1532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Futagawa S. A new technique for treating esophageal varices. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Nov;66(5):677–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terés J., Baroni R., Bordas J. M., Visa J., Pera C., Rodés J. Randomized trial of portacaval shunt, stapling transection and endoscopic sclerotherapy in uncontrolled variceal bleeding. J Hepatol. 1987 Apr;4(2):159–167. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Henderson J. M., Millikan W. J., Galambos J. T., Bryan F. C. Management of variceal bleeding in patients with noncirrhotic portal vein thrombosis. Ann Surg. 1988 May;207(5):623–634. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198805000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Millikan W. J., Jr, Henderson J. M., Abu-Elmagd K. M., Galloway J. R., Shires G. T., 3rd, Richards W. O., Salam A. A., Kutner M. H. Splenopancreatic disconnection. Improved selectivity of distal splenorenal shunt. Ann Surg. 1986 Oct;204(4):346–355. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198610000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Millikan W. J., Jr, Henderson J. M., Wright L., Kutner M., Smith R. B., 3rd, Fulenwider J. T., Salam A. A., Galambos J. T. Ten years portal hypertensive surgery at Emory. Results and new perspectives. Ann Surg. 1982 May;195(5):530–542. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198205000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Zeppa R., Fomon J. J. Selective trans-splenic decompression of gastroesophageal varices by distal splenorenal shunt. Ann Surg. 1967 Sep;166(3):437–455. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196709000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler M. J., Stein B. L. Nonshunting operations for variceal hemorrhage. Surg Clin North Am. 1990 Apr;70(2):425–448. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler M. J. Treatment of bleeding esophageal varices by transabdominal esophageal transection with the EEA stapling instrument. Surgery. 1980 Sep;88(3):406–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Khishen M. A., Henderson J. M., Millikan W. J., Jr, Kutner M. H., Warren W. D. Splenectomy is contraindicated for thrombocytopenia secondary to portal hypertension. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985 Mar;160(3):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


