Figure 1.
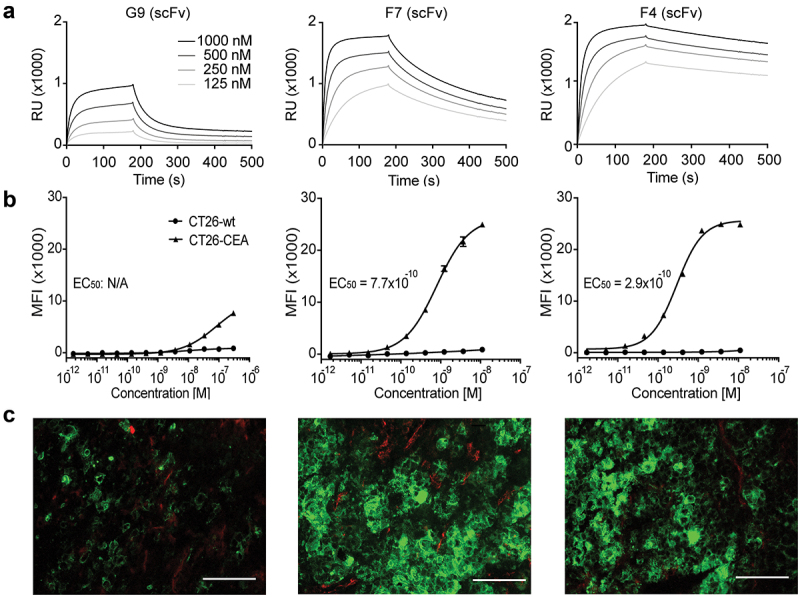
In vitro characterization of new anti-CEA antibodies. (a) SPR sensorgram of G9, F7, and F4 in a scFv format. KD values were calculated to be 640 nM, 50 nM, and 7.7 nM, respectively. (b) Flow cytometry analysis with the new antibodies in IgG format on CEA-expressing CT26 cells and on CEA-negative CT26 wild-type cells. (c) Immunofluorescence staining with IgG formats on the human colon adenocarcinoma xenograft LS174T. Anti-CEA antibodies were detected in green. Blood vessels were detected by CD31 staining (red). 20× magnification, scale bars = 100 μm.
