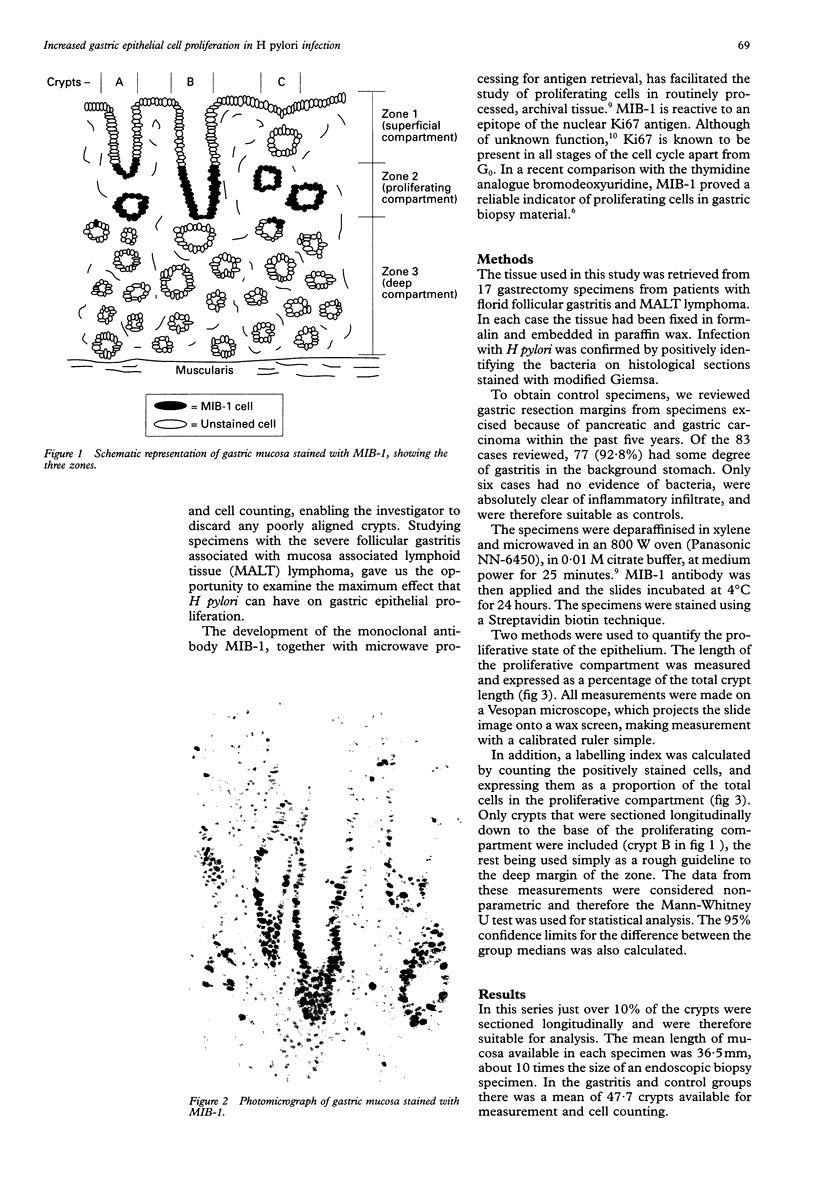
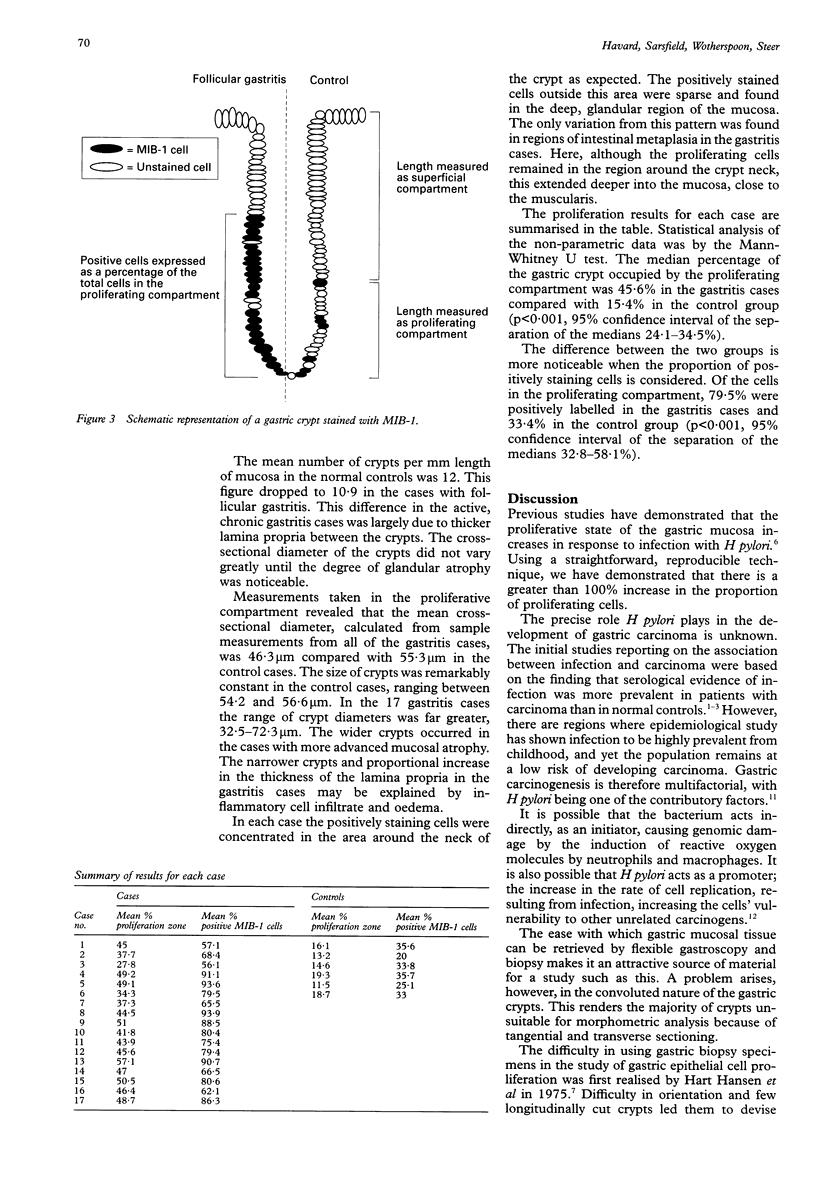
Abstract
AIMS: An increase in the proliferative state of the gastric epithelium has been attributed to infection with Helicobacter pylori. In order to obtain a more precise estimate of the magnitude of this change, the proliferative state of 17 cases of florid H pylori associated follicular gastritis was examined using the antibody MIB-1. METHODS: Comparable results were produced from control and gastritis cases by using a combination of two reproducible measures of the labelled cells. Dividing cells in the gastric mucosa are concentrated within a proliferating compartment, situated at the base of the crypts. This compartment was measured and expressed as a proportion of the total crypt length. The proportion of positively labelled cells within the compartment was also counted. RESULTS: The proliferation compartment in the gastritis cases occupied 45.6% of the gastric crypt compared with 15.4% in the control group. Of the cells in the proliferating compartment, 79.5% were positively labelled in the gastritis cases and 33.4% in the control group. CONCLUSIONS: The convoluted nature of the gastric crypt does not make it a forgiving experimental model. The use of long lengths of mucosa obtained from gastrectomy specimens permitted the production of consistent results, using a morphometric method. The greater than 100% difference in the proportion of proliferating cells between the two groups suggests that further investigation is warranted.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An international association between Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer. The EUROGAST Study Group. Lancet. 1993 May 29;341(8857):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biasco G., Paganelli G. M., Miglioli M., Brillanti S., Di Febo G., Gizzi G., Ponz de Leon M., Campieri M., Barbara L. Rectal cell proliferation and colon cancer risk in ulcerative colitis. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1156–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process--First American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6735–6740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. H., Pedersen T., Larsen J. K. A method to study cell proliferation kinetics in human gastric mucosa. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):23–27. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPKIN M., SHERLOCK P., BELL B. CELL PROLIFERATION KINETICS IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MAN. II. CELL RENEWAL IN STOMACH, ILEUM, COLON, AND RECTUM. Gastroenterology. 1963 Dec;45:721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. A., Clarke A. M., Jackson P., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. Comparison of labelling by bromodeoxyuridine, MIB-1, and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in gastric mucosal biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Feb;47(2):122–125. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.2.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Friedman G. D., Vandersteen D. P., Chang Y., Vogelman J. H., Orentreich N., Sibley R. K. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 17;325(16):1127–1131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S., Rew D. A., Taylor I., Potten C. S., Owen C., Roberts S. A. Study of the proliferation in human gastric mucosa after in vivo bromodeoxyuridine labelling. Gut. 1993 Jul;34(7):893–896. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.7.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney N., Hall P. A. Ki67--structure, function, and new antibodies. J Pathol. 1992 Oct;168(2):161–162. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]