Abbreviations
- ABC
activated B‐cell‐like
- CI
confidence interval
- CNS
central nervous system
- COO
cell‐of‐origin
- DLBCL
diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma
- EPOCH‐R
etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab
- IPI
International Prognostic Index
- MTX
methotrexate
- OS
overall survival
- PFS
progression‐free survival
- PS
performance status
Dear Editor,
CD5‐positive (CD5+) DLBCL is characterized by aggressive clinical characteristics and frequent CNS relapse. 1 In 2020, we reported the results of the primary analysis of a phase 2 study of dose‐adjusted (DA)‐EPOCH‐R combined with high‐dose (HD)‐MTX (DA‐EPOCH‐R/HD‐MTX) (PEARL5 study) with a median follow‐up of 3.1 years. 2 In this letter, we report the results of our preplanned 5‐year follow‐up of this study.
At a median follow‐up time of 6.0 (range, 5.0–7.7) years, the 5‐year PFS and OS of 47 eligible patients were 72% (90% CI, 57–83; 95% CI, 57–83) and 79% (90% CI, 67–87; 95% CI, 64–88), respectively (Figure 1A,B). One patient experienced a relapse in the cervical lymph nodes, Waldeyer's ring, and nasal cavity after the primary analysis. The 5‐year PFS and OS of patients with CD5+ ABC DLBCL (n = 39) were 72% and 74%, respectively (Figure 2A,B).
FIGURE 1.
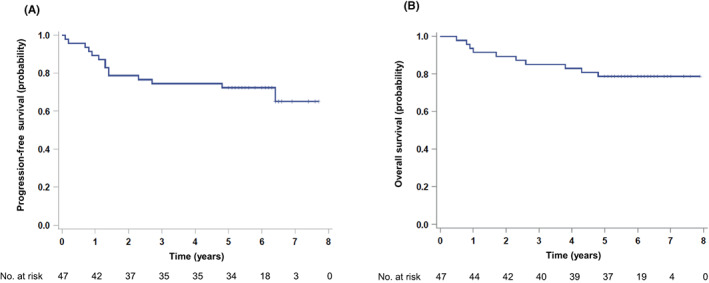
Survival curves for patients with CD5‐positive (CD5+) DLBCL with a median follow‐up of 6.0 years. (A) PFS and (B) OS for all patients (n = 47).
FIGURE 2.
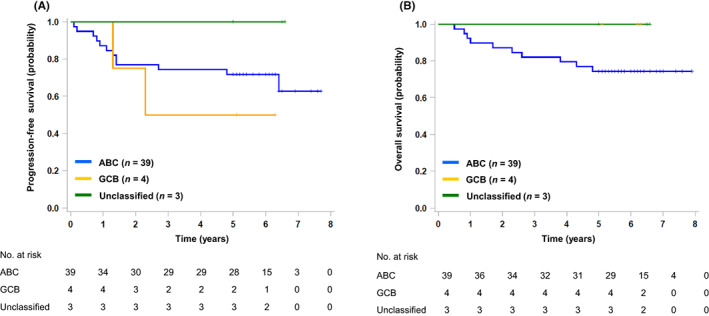
Survival according to COO categories. (A) PFS and (B) OS according to COO categories (n = 46).
The 5‐year CNS relapse rate was 9% (95% CI, 3–22) (Figure 3A). There were no CNS relapse events after the primary analysis. There was no significant difference in the CNS relapse rate among the CNS‐IPI categories (data not shown). In our previous retrospective study of CD5+ DLBCL, CNS events occurred in 13% of the patients at the median follow‐up of 6.8 years, and half of them were documented after 2 years of diagnosis. 3 Given that no CNS events were observed in the present phase 2 study, the treatment protocol may have contributed to the prevention of late CNS relapse.
FIGURE 3.
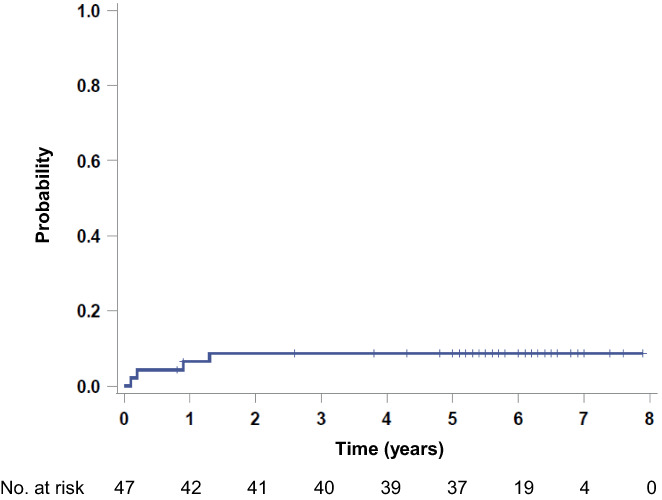
Probability of CNS relapse in CD5+ DLBCL patients (n = 47).
No patients experienced grade 3 or higher late toxicity. There was no cardiovascular event and leukoencephalopathy during this follow‐up. Second malignancies were reported in six patients (6%) and all were above 60 years of age (Table S1). Among them, two patients who had colon cancers were successfully treated with endoscopic resection. Among two patients who died during this follow‐up, one died of a second malignancy.
Our updated analysis confirmed that both excellent efficacy and safety of DA‐EPOCH‐R/HD‐MTX were maintained for more than 5 years, indicating that DA‐EPOCH‐R/HD‐MTX is one of the most reasonable first‐line treatments for stage II–IV CD5+ DLBCL (UMIN000008507; jRCTs041180159).
FUNDING INFORMATION
This study was supported by grants‐in‐aid from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, AMED (JP15Ack0106157, JP16ck0106157, JP17ck0106157, JP18ck0106439), the Ministry of Labour, Health, and Welfare of Japan (201438142A), the director of Mie University Hospital (2012, 2013), and the National Cancer Center Research and Development Fund (26‐A‐4, 29‐A‐3).
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
KMiyazaki reports research funding (Kyowa Kirin, Zenyaku). RSakai reports honoraria (Chugai, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol Myers Squibb); research funding (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin). KS reports honoraria (Bristol Myers Squibb); research funding (Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin). IY reports honoraria (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Takeda); research funding (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin); NT reports honoraria (Takeda); research funding (Bristol Myers Squibb, Kyowa Kirin). YS reports honoraria (Chugai, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer); research funding (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin). NF reports honoraria (Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Takeda, Zenyaku); research funding (Chugai). AA reports research funding (Chugai). YM reports research funding (Kyowa Kirin, Asahi Kasei, Takeda, Chugai). AY reports honoraria (Kyowa Kirin, Chugai, Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb); research funding (Kyowa Kirin). KMiyawaki reports honoraria (Chugai). KI reports research funding (Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Kyowa Kirin, Chugai). RSuzuki reports honoraria (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda); research funding (Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Shionogi). KK reports honoraria (Kyowa Kirin, Chugai); research funding (Chugai, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol Myers Squibb). NK reports research funding (Kyowa Kirin). MY reports research funding (Kyowa Kirin, Chugai). The other authors have nothing to disclose. Tomohiro Kinoshita, Koichi Ohshima, and Ritsuro Suzuki are editorial board members of Cancer Science.
ETHICS STATEMENT
Approval of the research protocol by an Institutional Review Board: The study was approved by the protocol review committee of the study and the institutional review board of each institution in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent: Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients.
Registry and the registration no. of the study/trial: UMIN000008507; jRCTs041180159.
Animal studies: N/A.
Supporting information
Table S1
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We wish to thank Takuya Matsunaga (Hokuou Hospital), Noriko Usui (The Jikei University School of Medicine), and Akiko Kada (Nagoya Medical Center) as members of the Data and Safety Monitoring Board.
REFERENCES
- 1. Miyazaki K, Yamaguchi M, Suzuki R, et al. CD5‐positive diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma: a retrospective study in 337 patients treated by chemotherapy with or without rituximab. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1601‐1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Miyazaki K, Asano N, Yamada T, et al. DA‐EPOCH‐R combined with high‐dose methotrexate in patients with newly diagnosed stage II‐IV CD5‐positive diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma: a single‐arm, open‐label, phase II study. Haematologica. 2020;105:2308‐2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Yamaguchi M, Nakamura N, Suzuki R, et al. De novo CD5+ diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma: results of a detailed clinicopathological review in 120 patients. Haematologica. 2008;93:1195‐1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1


