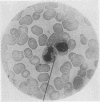
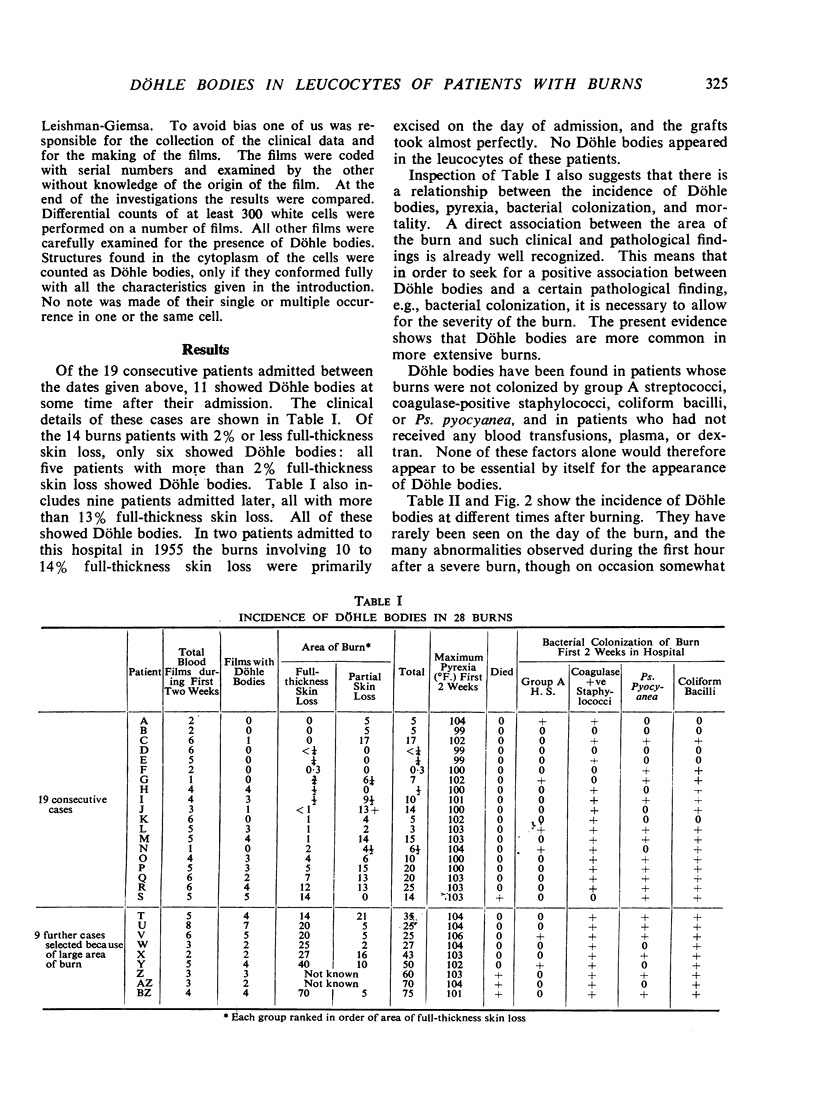
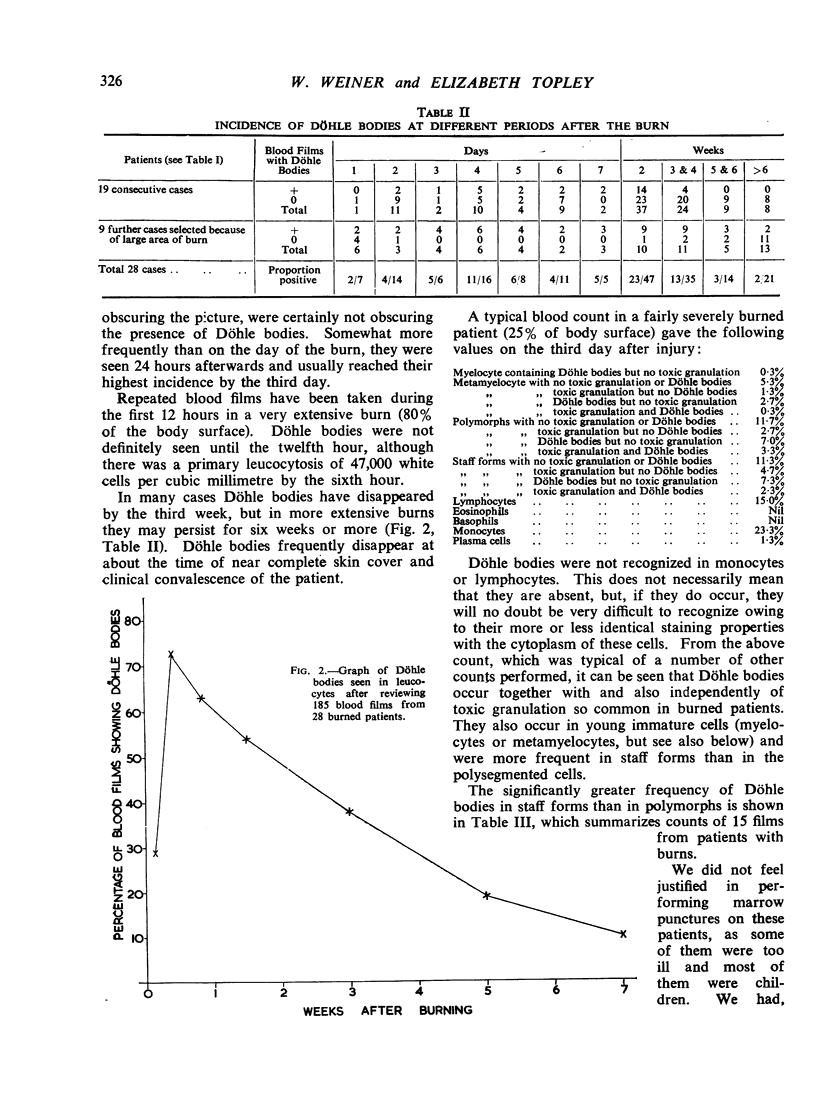
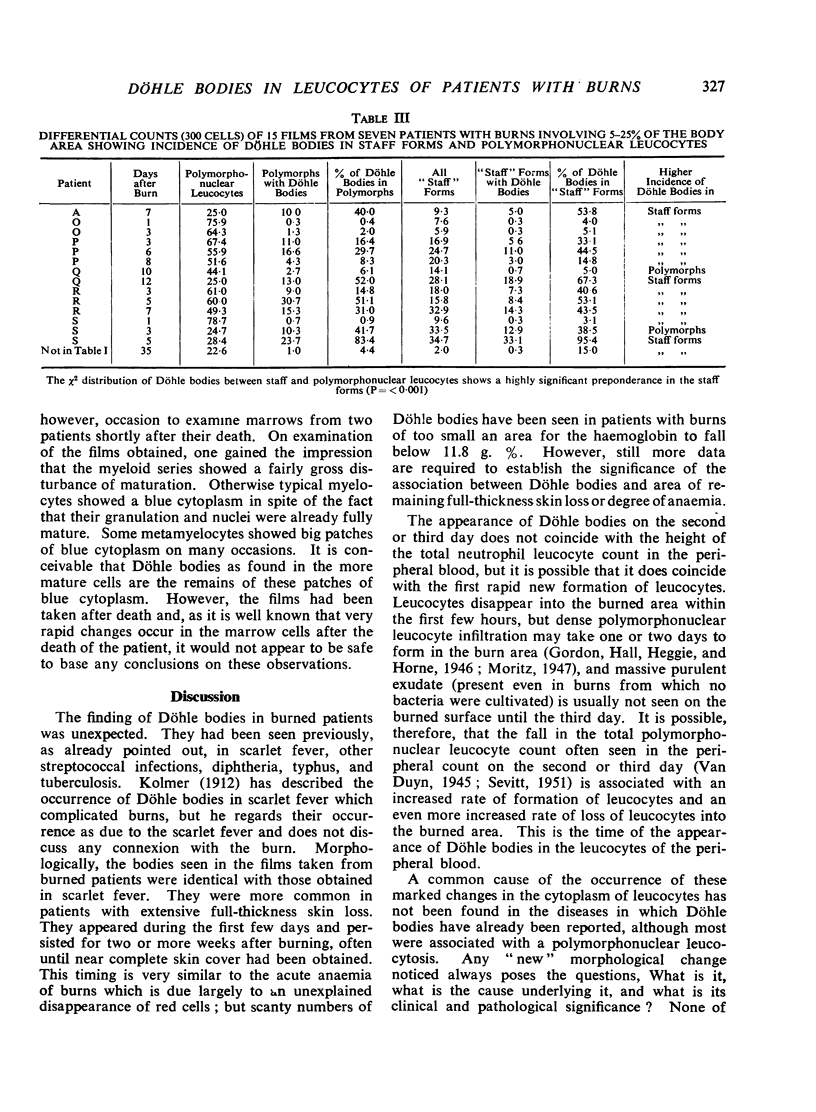
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Moritz A. R. Studies of Thermal Injury: III. The Pathology and Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Burns. An Experimental Study. Am J Pathol. 1947 Nov;23(6):915–941. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S. Eosinophil and other leucocyte changes in burned patients, with special reference to adreno-cortical activity. Br Med J. 1951 May 5;1(4713):976–983. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4713.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]