Abstract
Follicular lymphomas (FL) are characterized by BCL2 translocations, often detectable in blood years before FL diagnosis, but also observed in aging healthy individuals suggesting additional lesions are required for lymphomagenesis. We directly characterized early cooperating mutations by ultra-deep sequencing of pre-diagnostic blood and tissue specimens from 48 subjects who ultimately developed FL. Strikingly, CREBBP lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain mutations were the most commonly observed precursor lesions, and largely distinguished patients developing FL (14/48, 29%) from healthy adults with or without detected BCL2 rearrangements (0/13, p=0.03 and 0/20, p=0.007, respectively). CREBBP variants were detectable a median of 5.8 years before FL diagnosis, were clonally selected in FL tumors, and appeared restricted to the committed B-cell lineage. These results suggest that mutations affecting the CREBBP KAT domain are common lesions in FL cancer precursor cells (CPC), with potential for discriminating subjects at risk of developing FL or monitoring residual disease.
Keywords: Follicular lymphoma, common precursors, CREBBP mutations
Introduction
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is the most common indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and is genetically characterized by translocations involving the BCL2 locus. These t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocations are detectable in nearly 90% of tumors driving overexpression of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL2 (1, 2). However, as many as 70% of healthy older adults also carry BCL2-translocated cells in blood and tissues (3, 4, 5). Although the presence of clonally expanded t(14;18) at high frequencies predicts an increased risk, the majority of individuals with detectable BCL2 translocations never develop FL (3, 6, 7). Likewise, while overexpression of BCL2 is seen in potential nodal precursor lesions such as in situ follicular neoplasia (ISFN), fewer than 5% of such patients develop FL (8, 9). BCL2 translocations are therefore critical but not sufficient for FL development. Additional genetic alterations are likely required for lymphomagenesis, as also suggested by murine models (10).
FL samples paired in space (lymph node vs. marrow) or time (diagnosis vs. relapse) often show limited mutational concordance, suggesting that FL evolves and persists from a reservoir of precursor cells bearing early variants (11, 12). The existence of distant circulating FL precursors has been directly confirmed in two studies of clonally related lymphomas in transplant donor-recipient pairs (13, 14). Sequencing studies of FL tumors have identified recurrent and clonally dominant lesions as potential early events(15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20). In addition to the acquisition of novel N-glycosylation sites through somatic mutation of immunoglobulin variable regions (21), an almost ubiquitous feature of FL involves the mutation of chromatin modifying genes (CMGs) including KMT2D, CREBBP, EZH2, and EP300. Potential early lesions have also been identified in ISFN specimens, with alterations in genes recurrently mutated in FL including BCL2, RUNX1, EBF1, and CREBBP (18, 22). Together, these observations suggest that even clones present years before diagnosis may contain committed cancer precursor cells (CPC). However, there has been no direct systematic characterization of FL precursor mutations in pre-diagnostic samples, and little is known about the hierarchy and timing of somatic aberrations preceding FL diagnosis.
Similar precursor cells have been identified in myeloid hematopoiesis, with alterations in genes including DNMT3A, TET2, and ASXL1 associated with clonal expansion(23). As with BCL2 translocations, such mutations are more frequent with age, portend an increased risk for hematological malignancies, and are detectable years prior to clinical diagnosis(24). Identification of precursor lesions in a screening context is therefore a promising strategy for risk stratification in myeloid disease (25, 26). However, while these mutations can be traced to early hematopoietic precursors including stem cells (27), they are less frequently observed in lymphomas, suggesting an alternative genetic repertoire in lymphoid precursors. Detecting such variants presents a technical challenge: a recent large-scale study evaluating myeloid versus lymphoid clonal hematopoiesis uncovered lymphoid mutations primarily in association with subsequent leukemic disease, likely due to the very low concentrations of circulating lymphoma precursors (28).
In this study, we sought to directly and comprehensively profile the genetic hierarchy of precursor lesions contributing to FL. We applied ultra-deep targeted genotyping (29, 30) of 334 commonly mutated lymphoma genes using Cancer Personalized Profiling by deep Sequencing (CAPP-Seq) (31) to four groups of FL subjects based on tissue type. These included (i) t(14;18)-positive pre-diagnostic blood samples from healthy individuals who later developed FL, (ii) pre-diagnostic samples paired with subsequent FL tumors, (iii) paired malignant and non-malignant lymph node biopsies, and (iv) bone marrow specimens from patients diagnosed with FL. We separately profiled blood and splenic samples from healthy adults as controls, including t(14;18)-positive and t(14;18)-undetected subjects. Our findings provide direct evidence for recurrent key FL driver mutations detectable in pre-diagnostic blood and tissues years prior to clinical diagnosis.
Results
Recurrent Mutations in Circulating FL Precursors
To directly profile mutations carried by t(14;18)-translocated CPC years before FL diagnosis, we performed ultra-deep targeted genotyping of 334 FL-associated genes in blood samples from 27 selected subjects from the large, population-based European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study (32) (Fig. 1A). This group was selected from 318 healthy EPIC participants previously found to carry elevated t(14;18) frequencies compatible with the detection sensitivity of error-corrected CAPP-Seq (6, 29). We analyzed 17 patients who developed FL (referred to as pre-diagnostic FL or PDFL patients) at a median time to diagnosis of 6.3 years (range: <1-12 years).
Figure 1). Recurrent CREBBP mutations are observed in screening blood samples years prior to FL diagnosis.
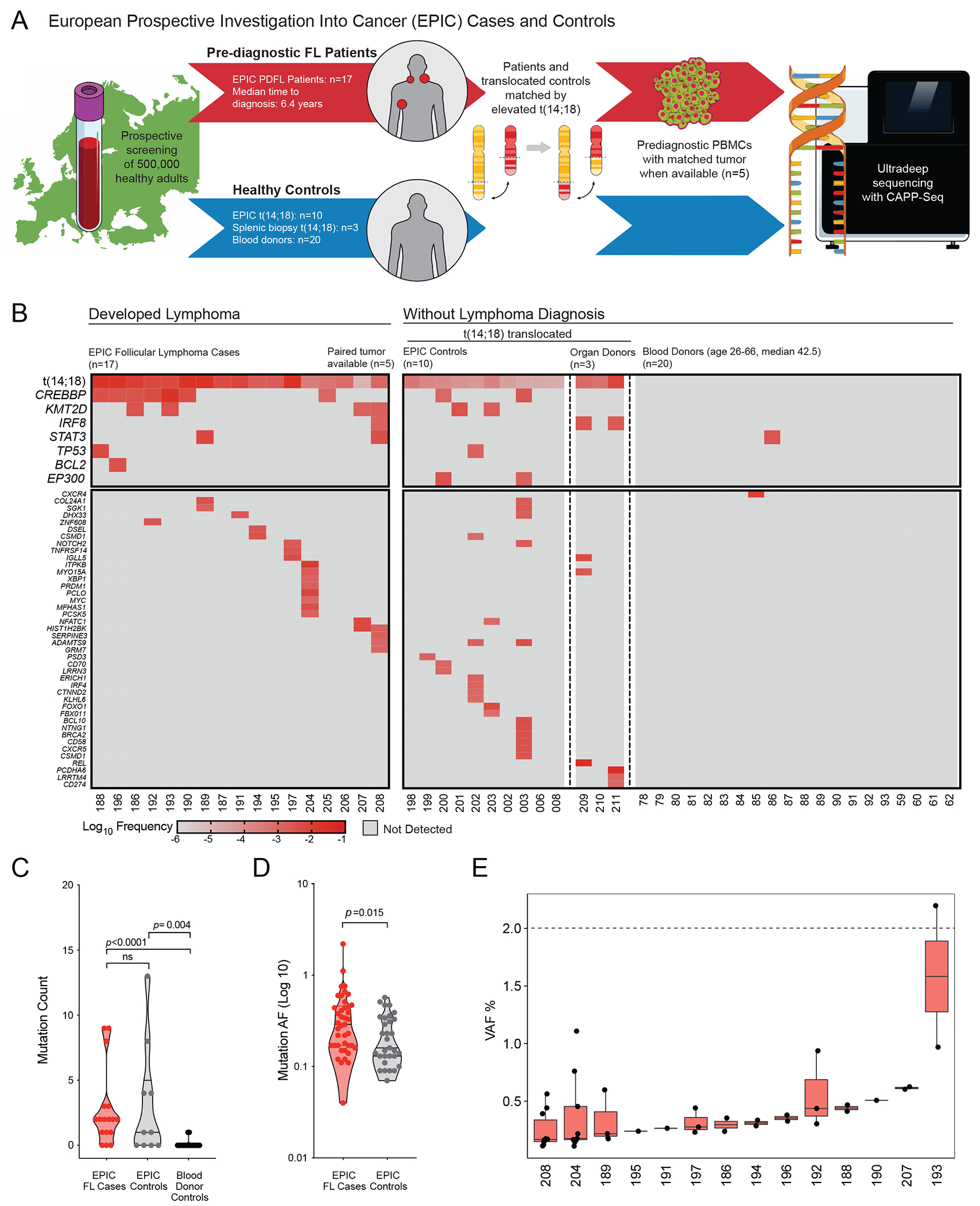
A. Schematic depiction of study design: from a large prospective European screening cohort, 17 patients with a subsequent follicular lymphoma (FL) diagnosis (PDFL patients) were paired with healthy participants with similar elevated circulating t(14;18) but no FL diagnosis at last follow-up. Healthy unrelated subjects (blood donors and normal spleen from organ donors) were included as controls.
B. A heatmap illustrates the observed frequencies of FL-associated lesions in pre-diagnostic samples from EPIC PDFL patients (n=17) and controls (n=33), including recurrent t(14;18) and CREBBP mutations.
C. A violin plot displays enrichment in total mutational burden among individuals bearing t(14;18) translocations as compared to blood donor controls. No significant difference in mutational burden was seen between t(14;18) translocated subjects based on eventual FL status.
D. A violin plot demonstrates increased allelic fraction (AF) of somatic variants among PDFL patients as compared to t(14;18)-bearing controls.
E. Box plots demonstrate the distribution of somatic variant AF in individual PDFL cases in relationship to the clinical CHIP threshold of 2% VAF.
To address the specificity of our findings, 10 EPIC subjects who remained healthy were selected as controls based on comparable t(14;18) frequencies (Fig. 1A, Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Table S1). The median age at screening was 50 years (range 30-64) for PDFL patients and 51 years (range 44-63) for BCL2-translocated controls. We additionally profiled an independent cohort of 20 unselected blood samples from healthy adults (median age 42.5 years) to a similar median sequencing depth (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S2) as well as splenic biopsies from organ donors carrying t(14;18) translocations but without evidence of lymphoma (n=3) (33).
Pre-diagnostic samples from patients later developing FL were significantly enriched in mutations in the CREBBP gene, seen in 7/17 PDFL cases (41% compared to 6.5% in controls, p=0.004) at an average allelic frequency (AF) of 0.41% (range 0.04–2.2%) (Fig 1B; Supplementary Table S3). CREBBP lesions were detected at median 7.8 years and as early as 12 years prior to clinical diagnosis. Additional mutations were detected at a lower prevalence in other genes frequently mutated in FL: KMT2D (4/17), TP53 (2/17), BCL2 (1/17), STAT3 (2/17), and TNFRSF14 (1/17). CREBBP-mutated cases displayed a trend towards higher median t(14;18) frequency (Supplementary Figure S2).
In the t(14;18)-positive control group including 10 blood and 3 splenic samples, coincident CREBBP and EP300 mutations were seen in 2/13 cases (15.4%), with both CREBBP mutations occurring outside characterized functional domains, as well as 2 KMT2D missense mutations. Among 20 healthy blood donors we detected two variants in STAT3 and CXCR4 (Fig. 1B, Supplementary Table S4). Somatic mutations were more frequently detected in PDFL patients than t(14;18)-positive controls (82.3% vs. 60%). Both t(14;18)-positive groups had a higher mutational burden than blood donor controls (Fig. 1C), suggesting an active mutational process in translocation-bearing B-cells(33). Furthermore, PDFL patients bore significantly larger clones relative to t(14;18)-translocated controls (p=0.015) (Fig. 1D). Although cases were selected for detectable t(14;18) by PCR, only one variant exceeded the clinical CHIP threshold of 2% (Fig 1E).
Genotypic Concordance Between Circulating Precursors and FL Tumors
To confirm that precursor variants are persistent and clonally dominant in clinical FL, we identified 34 cases with FL tumor biopsies and paired pre-diagnostic specimens. These included 29 individuals from the population-based American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study II (ACS CPS-II) with screening blood or saliva sample, subsequent FL diagnosis, and available tumor biopsy (Fig. 2A) (34). The median age at screening was 71 years (range 56-83) with a median time to FL diagnosis of 5 years (range <1-12) (Supplementary Table S1). Tumor biopsies were also available for 5 EPIC cases. After identifying mutations in FL tumors, we sequenced matched pre-diagnostic specimens via error-corrected CAPP-Seq to a median 7442x depth (Supplementary Table S2).
Figure 2). Pre-diagnostic CREBBP mutations are concordant in subsequent FL tumor biopsies.
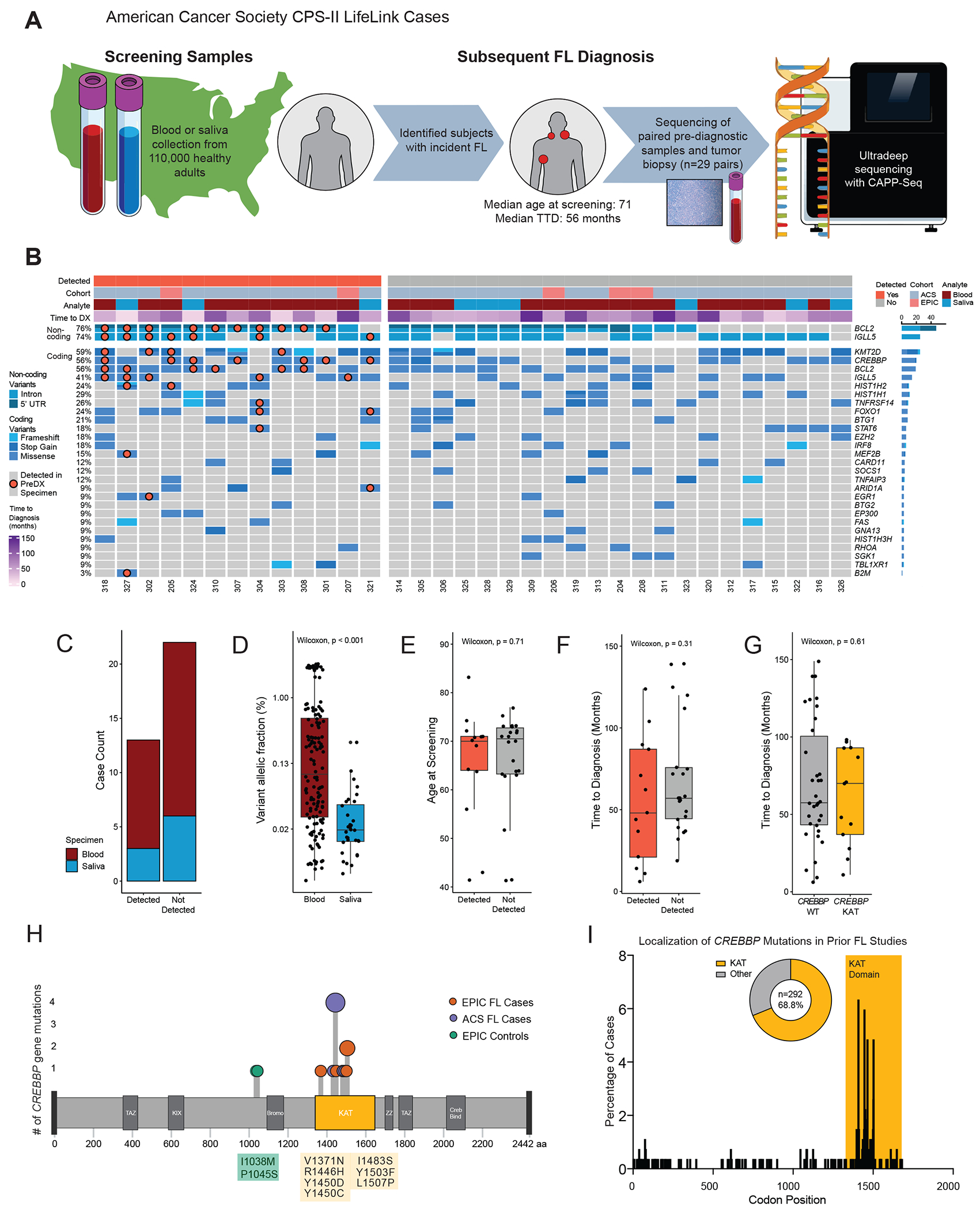
A. Schematic depiction of study design: from a large prospective American screening cohort, 29 individuals were identified with subsequent FL diagnosis and available pre-diagnostic and tumor biopsy specimens. Pre-diagnostic and tumor specimens underwent parallel hybrid capture enrichment and sequencing, with ultra-deep sequencing of pre-diagnostic samples.
B. An oncoprint depicts variants detected in 34 FL tumor biopsies. Cases are grouped by detection of tumor variants in prediagnostic specimens, with detected variants identified by a superimposed marker.
C. A stacked bar graph demonstrates detection status of tumor-derived variants in pre-diagnostic blood (n=25) and saliva (n=9) specimens from FL patients. No difference in detection rate was observed by analyte (Fisher’s exact p=1).
D. A bar plot depicts AF of tumor-confirmed variants depicted in pre-diagnostic specimens by analyte, with significantly lower AF seen in saliva specimens (p<0.001).
E. A bar plot depicts the age at pre-diagnostic sample collection of participants developing FL in the EPIC and ACS CPS-II studies. Cases are grouped by detection status of tumor-confirmed variants, with no significant difference in age between patients with or without detected variants (p=0.71).
F. A bar plot depicts the interval from pre-diagnostic sample collection to FL diagnosis of participants developing FL in the EPIC and ACS CPS-II studies. Cases are grouped by detection status of tumor-confirmed variants, with no significant difference in time to FL diagnosis in patients with or without detected variants (p=0.31)
G. A bar plot depicts the interval from pre-diagnostic sample collection to FL diagnosis of participants developing FL in the EPIC and ACS CPS-II studies. Cases are grouped by detection of CREBBP KAT domain mutations, with no significant difference in time to diagnosis in patients with or without detected variants (p=0.61)
H. A lollipop plot of the CREBBP protein illustrates the localization of observed pre-diagnostic mutations to the lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain. Two mutations in control samples (green) occurred outside of a characterized functional domain.
I. A bar graph depicts the percentage of CREBBP mutations occurring at each codon in a pooled analysis of prior FL genotyping studies (15, 19, 36, 37, 38, 39). Mutations consistently concentrated within the KAT domain, with 68.8% (201/292 cases) occurring between codons 1300 and 1700.
Utilizing a previously described Monte Carlo based statistical test (29), we detected significant tumor-derived variants in 13 of 34 paired pre-diagnostic specimens (38%) at a median 5 years before clinical diagnosis (range 1-9) (Fig. 2B, Supplementary Table S5). Among detected cases, in addition to recurrent non-coding BCL2 mutations adjacent to the t(14;18) breakpoint (10/12 cases, 83%), the most frequent concordant coding lesions occurred in CREBBP (7/9 cases with mutation in tumor, 78%), BCL2 (6/9 cases, 66%), and KMT2D (4/9, 44%) (Supplementary Table S6). One case (#9579) appeared to be an outlier with a median AF of 2.6% at 90 months pre-diagnosis. For the remaining cases, the median AF of other detected variants was 0.068%.
Screening specimens in ACS CPS-II consisted of either blood or saliva specimens, with saliva cell pellets previously noted to contain hematopoietic DNA (35). We detected tumor-confirmed variants in both saliva and blood screening specimens (Fig 2C) although at a significantly lower median AF in saliva (Fig 2D). Individuals with detected variants were not older at screening, suggesting against strictly age-related cumulative acquisition of mutations, nor significantly closer to clinical diagnosis (Fig 2E–F).
The enrichment of CREBBP mutations in pre-diagnostic samples could arise from length-time bias if such cases displayed more indolent disease biology, creating a longer window for detection between mutation acquisition and clinical diagnosis. We compared the time between screening and diagnosis for FL cases in both screening cohorts with or without detected CREBBP mutation and found no significant difference (Fig. 2G).
Considering the localization of precursor CREBBP mutations within functional domains, all confirmed pre-diagnostic variants localized to the lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain (8/8 cases, Fig 2H). This distribution confirms prior studies showing a strong localization of mutations in mature FL tumors to the KAT domain (68.8%, Fig. 2I) (15, 19, 36, 37, 38, 39). By contrast, two CREBBP mutations seen in BCL2-translocated control subjects occurred at I1038M and P1045S, proximal to the bromodomain and outside characterized functional domains. Most importantly, considering all pre-diagnostic and control samples, mutations in the CREBBP KAT domain were significantly enriched in individuals who later developed FL compared to negative controls (14/48 vs 0/33; Fisher’s Exact p<0.0001). This distinction remained significant when considering only control cases with detectable t(14;18) (p=0.03).
These findings demonstrate the patterns of pathogenic CREBBP mutation in PDFL cases compared to controls, suggesting that BCL2 translocations and CREBBP mutations constitute a recurrent model for FL precursor development, with additional events accrued over years likely necessary for overt malignant transformation.
Genotypic Concordance Between Paired Non-Malignant & Malignant Biopsies
To evaluate the persistence of precursor lesions post-treatment and benefit from higher B-cell purity, we identified 8 patients who had multiple excisional biopsies for clinically significant lymphadenopathy before and after FL diagnosis and therapy. For each patient, one cryopreserved biopsy revealed non-malignant histology while another demonstrated overt FL, with a median of 2.27 years (range 0.1-6.8 years) between specimens (Fig. 3A). The non-malignant biopsy either preceded the FL biopsy (n=2, median lead time 2.7 years), was roughly synchronous pre-treatment (n=1, 33 days), or was obtained post-treatment offering an opportunity to assess clonal populations not eradicated by therapy (n=5, median lead time 2.9 years). All patients were without clinical evidence of FL at the time of the non-malignant biopsy, which in post-treatment patients was frequently obtained due to concern for recurrence. Non-malignant histologies included reactive follicular hyperplasia, necrotizing lymphadenitis, and normal lymphoid tissue (Supplementary Table S7). All cases were without evidence of ISFN by blinded hematopathology review including BCL2 immunohistochemistry (Fig 3B).
Figure 3). CREBBP KAT domain mutations are observed as persistent after cancer therapy and in association with histologic precursor lesions.
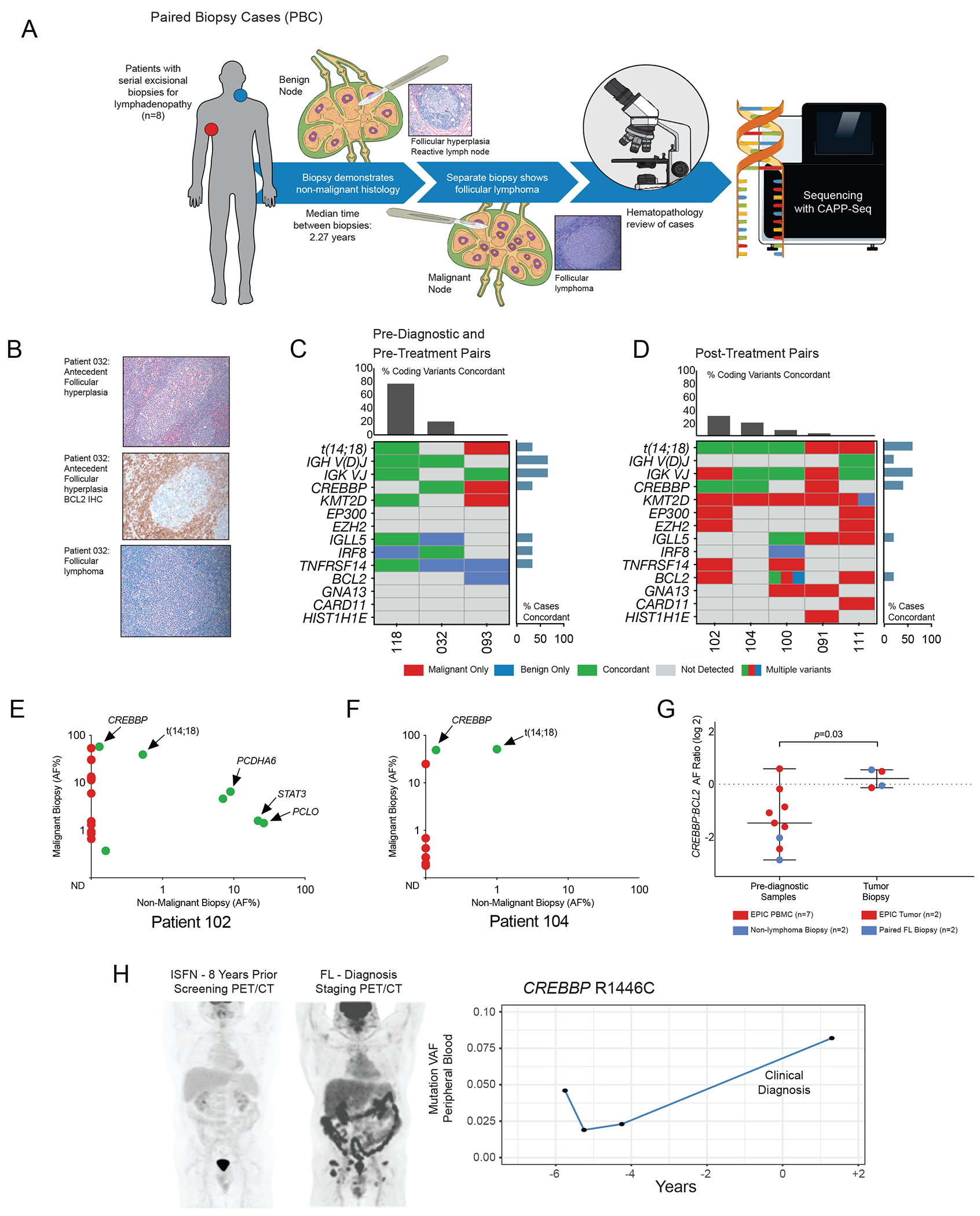
A. Schematic depiction of study design: Chronologically distant paired malignant and benign lymph node biopsies from 8 patients were re-reviewed by a blinded hematopathologist and sequenced in parallel.
B. Representative images from pathology review of paired biopsy cases, including BCL2-negative antecedent follicular hyperplasia.
C. A genotyping map demonstrates genetic concordance (indicated in green) between pre-diagnostic or pre-treatment and paired malignant biopsies. The concordance of selected recurrently mutated genes including chromatin modifying genes (CMGs) is included for comparison, with per-gene concordance displayed as a bar graph on the right and per-case concordance as a bar graph above. One patient (032) was t(14;18) negative by confirmatory PCR.
D. A genotyping map demonstrates genetic concordance (indicated in green) between diagnostic FL biopsy and subsequent post-treatment histologically non-malignant specimens obtained for adenopathy. Annotation is as per the previous panel.
E. A scatter plot demonstrates concordance of coding mutations in paired FL and post-treatment non-malignant biopsies for patient 102. The X-axis indicates log allelic fraction in the non-malignant sample and the Y-axis indicates log AF in the mature FL tumor, demonstrating persistence of t(14;18) and CREBBP KAT domain mutations.
F. A scatter plot as in Fig 3E demonstrates post-treatment concordance of t(14 ;18) and CREBBP KAT domain mutation for patient 104.
G. A scatter plot depicts the increase in CREBBP allelic fraction relative to t(14;18), with red points representing EPIC samples and blue points representing paired biopsies. At time of diagnostic biopsy these lesions were roughly equal (median CREBBP:BCL2 ratio 1.04, range 0.68-1.30), suggesting subclonal mutations in pre-diagnostic specimens proceeding to co-dominance of CREBBP mutations in mature FL tumors.
H. PET/CT imaging of a representative patient at discovery of in-situ follicular neoplasia (ISFN, left) and eight years later at FL diagnosis (right). Serial sequencing of peripheral blood specimens collected during expectant management revealed a tumor-confirmed CREBBP KAT domain mutation (R1446C) detectable at first collected timepoint and increasing in AF to the time of diagnosis.
Genotyping of these paired specimens revealed multiple recurrently mutated genes, most notably CMGs (Fig 3C, Supplementary Table S8) (15, 16, 17). As in the two screening study cohorts, both pre-diagnostic biopsies (patients 118 and 032) carried tumor-confirmed aberrations including clonal IGH rearrangements (Supplementary Table S9) and concordant CREBBP and IRF8 mutations in a case which was t(14;18)-negative by clinical PCR (Patient 032, Supplementary Figure S3).
Among 5 post-treatment biopsies, cases 102, 104, and 100 were found to share clonal t(14;18) (Fig 3D). Both cases carrying CREBBP mutations in tumor (102 and 104) had concordant CREBBP lesions in subsequent hyperplasia (Fig 3E–F). Of note, the CREBBP mutation in case #102 was a stop-gain lesion which may play a similar role to loss of function via KAT domain variants. Other coding mutations (EZH2Y646F, KMT2D, EP300 among others) were only found in tumor, suggesting that subsequent hyperplasias emerged from a residual BCL2-translocated population with a limited set of mutations. While another t(14;18)-concordant patient sharing IGLL5 and BCL2 variants remained disease-free 7 years after initial diagnosis (#100), both patients with detected CREBBP later relapsed, confirming that these mutations were present in a clinically significant CPC population (Supplementary Table S7). While the post-treatment hyperplasias lost multiple tumor mutations, they gained only rare private mutations (Supplementary Table S10). It is unclear whether these events acquired post-chemotherapy reflect selective pressure or incidental passenger mutations.
Three benign biopsies, two post-treatment (091 and 111) and one synchronous (93), did not share t(14;18) with their malignant counterpart, suggesting an unrelated B-cell expansion. None of these patients showed CREBBP in benign biopsies nor had disease progression at last follow-up. Interestingly, while almost all pairs bore KMT2D mutations in the malignant biopsy (7/8, 87.5%), most were nonconcordant irrespective of the order of emergence. Similarly, EZH2 was detected in multiple malignant but not in benign specimens, suggesting these genes may serve as later transforming rather than early CPC lesions. In both EPIC and paired biopsy specimens, the ratio of CREBBP relative to t(14;18) appeared subclonal in pre-diagnostic specimens. This ratio approached equality in the mature FL tumors, consistent with selection and outgrowth of a CREBBP-mutated precursor population (Fig. 3G, median ratio at diagnosis 1.04, range 0.68-1.30, p=0.026 for difference).
Concordant clonal relationships may occur in presumed histologic precursors. In an illustrative independent case with available imaging, a patient undergoing radical prostatectomy was found to have involvement of a single pelvic lymph node with ISFN. Staging PET/CT showed no evidence of FL (Fig. 3H) and he was followed expectantly for several years with no evidence of FL. Eight years after surgery, however, he presented with inguinal swelling and bilateral FDG-avid adenopathy on PET/CT. Excisional biopsy confirmed low grade FL and tumor sequencing revealed a CREBBP KAT domain variant. Retrospective sequencing of serial peripheral blood specimens from his initial surveillance showed detectable CREBBP R1446C at the earliest collected time point (AF range 0.019-0.046%) rising to AF 0.082% after clinical diagnosis.
Collectively, these results reveal the presence of recurrent FL mutations in histologically benign lymph nodes and radiographically occult precursors, and confirm CREBBP lesions and BCL2 translocations as both detectable before FL onset and re-emerging in patients who eventually experience relapse.
Emergence of FL Common Precursor Mutations During Lymphoid Commitment
The initial BCL2 translocation found in FL is thought to occur in pre-B-cell precursors in the bone marrow (18). However, the high prevalence of CREBBP and KMT2D mutations raises the possibility that, analogous to myeloid CHIP mutations, these may occur in common hematopoietic precursors rather than in committed B-cell precursors in the marrow or germinal center (GC). To address this question of mutational hierarchy, we studied blood, bone marrow aspirate, and lymph node samples from 7 patients with CREBBP and/or KMT2D mutations in their FL tumor (Supplementary Table S11). We analyzed flow-sorted purified hematopoietic cell populations by deep sequencing, including hematopoietic progenitor stem cells (HSPCs), mature B-cells, and T-cells or non-B fractions (Supplementary Table S12–13).
Patient FL002, a 45-year-old man with relapsed FL, underwent genotyping of a diagnostic bone marrow biopsy at relapse. Despite the absence of morphologic involvement, a CREBBP mutation concordant with his FL tumor was detected in the bulk bone marrow aspirate. To ascertain the cell population bearing this mutation, we sorted to high purity viable cells from a marrow aspirate by FACS into mature B-cell (CD19+/CD20+/Lambda+), mature T-cell (CD19−/CD20−/CD5+), and precursor lymphoid (CD34+/CD20−) populations (Fig. 4A). While the same CREBBP mutation was observed in the mature FL compartment in BM at an AF of 40.3%, the genetic event was not detectable in other cell populations. (Supplementary Table S14)
Figure 4). Follicular lymphoma CREBBP mutations appear localized to mature B-cells.
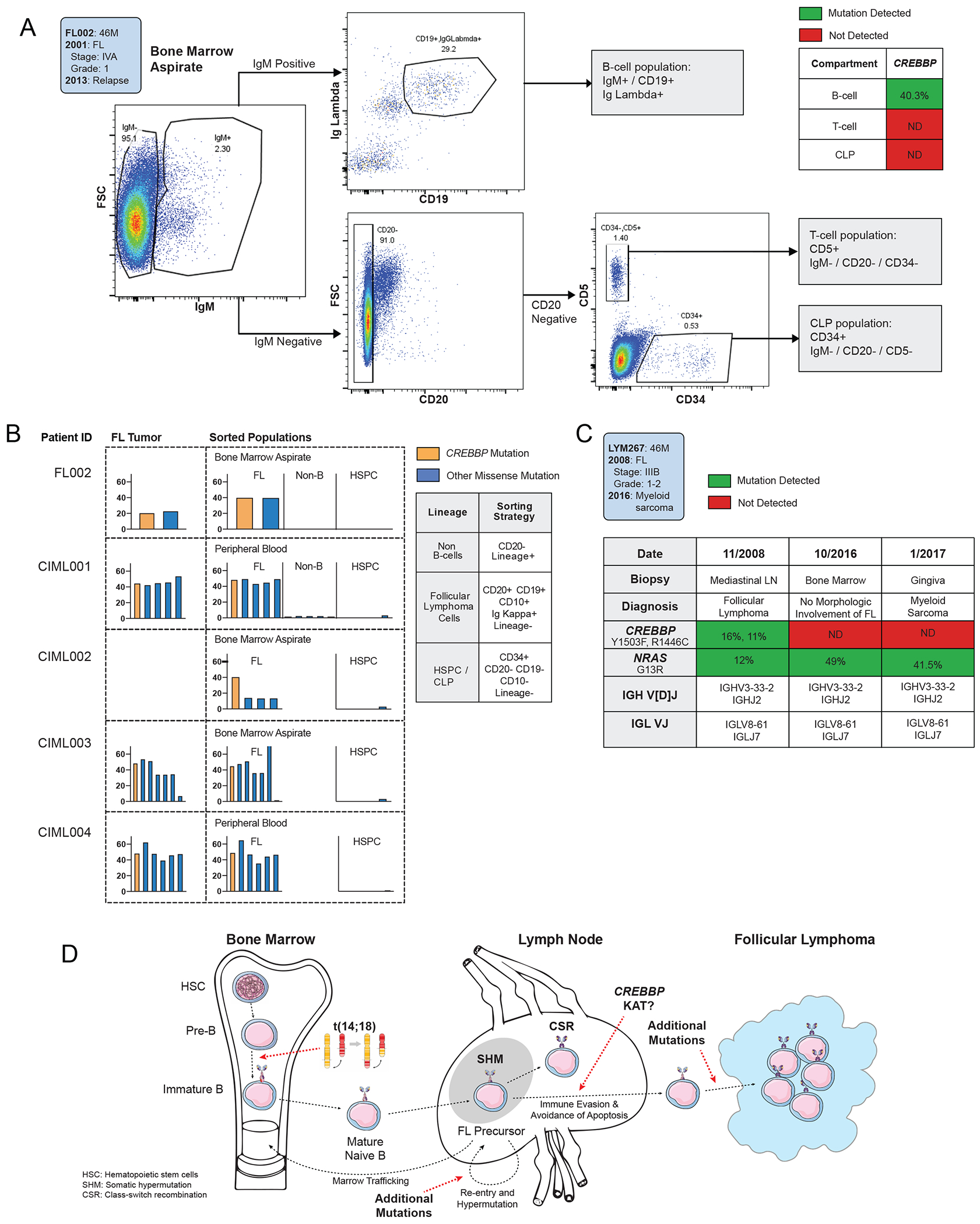
A. Flow cytometry gating strategy for progenitor and mature lymphoid from human bone marrow aspirate of a representative FL patient at diagnosis (FL002).
B. A table of bar graphs demonstrates variant allelic frequency of lymphoma-associated coding mutations in indicated cell subsets from 5 FL patients bearing CREBBP mutations. Each column represents a mutation initially detected in primary tumor or isotype-sorted marrow aspirate.
C. A table demonstrates concordance and discordance of pathogentic mutations and VDJ rearrangements detected in serial biopsies from an FL patient (LYM267) with CREBBP and NRAS mutations who subsequently developed a myeloid neoplasm lacking CREBBP.
D. Schematic figure for a proposed model of early follicular lymphomagenesis. The BCL2 translocation occurring in an early B-cell precursor provides evasion of programmed cell death, while the accrual of CREBBP KAT domain mutations in mature B-cells provides immune evasion and persistence of the GC program.
To validate this finding, a similar sorting strategy was employed on viable bone marrow aspirate or peripheral blood samples from 4 FL patients bearing CREBBP mutations to purify HSPCs, recirculating FL, and non-B-cells. In each case, CREBBP was detected in FL but absent from HSPCs (Fig. 4B, Supplementary Table S14). One patient (CIML004) also carried a characteristic KMT2D stop mutation, which was likewise absent from HSPCs. Although we cannot exclude the possibility of rare CREBBP/KMT2D-bearing HSPCs, our data are consistent with the accrual of CMG mutations later in hematopoiesis.
An atypical case sheds additional light on the timing of CREBBP mutations in FL. Patient 267 was diagnosed at age 46 with Grade 1-2 FL bearing CREBBP and NRAS mutations and achieved a complete response after immunochemotherapy. Eight years into a prolonged remission, he developed cutaneous and gingival myeloid sarcoma with no radiographic or histopathological evidence of FL. While the CREBBP mutation was not detected in bulk marrow sequencing or cutaneous biopsies of myeloid sarcoma, concordant NRAS mutations and clonal VDJ rearrangements were seen in all 3 compartments (Fig. 4C). This unusual case of clonally-related disease favors the occurence of the CREBBP mutation in the commited B-cell lineage after pre-BCR rearrangements, suggesting localization later than the branch point between morphologically distinct lymphoid and myeloid tumors (40) (Supplementary Figure S4).
Together, these results suggest a hierarchy where CREBBP mutations are preceded by BCL2 translocations - evidenced both by relative allelic fractions and by non-detection in all tested HSPC compartments - and localize the likely cellular origin of CREBBP mutations to the committed B-cell lineage (Fig 4D).
Discussion
Our study provides a number of key insights into the lymphomagenesis of human FL. Based on blood and benign tissue samples collected years before diagnosis and after therapy, we had an unique opportunity to map the genomic landscape of FL CPCs and assess the temporal order of mutation acquisition. Prior analyses of concordant gene mutations in sequential tumor biopsies have suggested a stereotyped model for the development and progression of FL (15, 19). These findings have been corroborated in separate studies of anatomically separated FL deposits (11, 12). Collectively these studies, using both space and time to infer hierarchy, have implicated multiple CMGs including CREBBP, KMT2D, EP300, and EZH2 as potential early lesions, with the majority of FL tumors harboring two or more CMG mutations (11, 16, 17, 19).
Our results provide direct pre-diagnostic evidence supporting these inferential studies and demonstrate CREBBP KAT domain mutations as prevailing precursor lesions directly detectable in 29% of pre-diagnostic samples up to 12 years prior to FL diagnosis. Based on three different approaches in blood and tissues, we found that BCL2 and CREBBP are essential features which may also survive immuno-chemotherapy, serving as a reservoir for clonal re-emergence leading to eventual relapse. Our data converge towards an evolutionary history where primary overt FL emerges from a common set of early mutations in the committed B-cell lineage, evolving and widely disseminating over many years in asymptomatic “subclinical” patients.
While CREBBP mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas are observed across the gene, prior genomic studies of FL have noted preferential localization to the KAT domain, which activates gene transcription via acetylation of enhancer regions (15, 19, 36, 37, 38, 39). Evidence from tumor gene expression, cell culture, and animal models associates such lesions with impaired GC exit, decreased MHC class II expression, and aberrant T-cell proliferation(10, 11, 41, 42). Our three pre-diagnostic cohorts confirm the predominance of KAT domain loss-of-function, suggesting a major functional role in early lymphomagenesis potentially via dysfunctional maintenance of the GC phenotype and evasion of immune surveillance (10, 41).
Several other CMGs have been implicated in FL tumorigenesis. The KMT2D (MLL2) gene encodes a histone methyltransferase critical for tumor suppression, GC formation, and immunologic function, and is mutated in most mature FL tumors (43, 44). In our study, we detected KMT2D mutations in the majority of mature tumors but less frequently in paired pre-diagnostic samples. The combination of high prevalence, truncal clonality, and apparent later chronicity is more suggestive of a critical cooperating or transforming event than an early precursor lesion. We speculate that mutations in distinct CMGs might engage unique gene expression programs associated with the germinal center reaction in human FL, with emerging evidence for such specificity emerging in murine lymphoma models (45).
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are believed to be the cell of origin in several lymphoid leukemias, and mouse models have demonstrated lymphoma development with experimentally induced CREBBP lesions in HSCs (20, 46, 47). Cases of lymphomyeloid lineage switch and FL occurring after allogeneic stem cell transplant have also raised the suspicion that FL precursor mutations could occur very early in hematopoietic development (14, 40), and a CREBBP mutation was recently described in a CD34+/CD38+ lymphoid population from the bone marrow of a single FL patient (20). The analysis of early hematopoiesis in FL is also complicated by the frequent trafficking of FL founder cells from secondary lymphoid tissue to marrow-specific niches (48). However, in sorted hematopoietic cell populations from both marrow and peripheral blood, we observed CREBBP mutations in bulk B-cells and isotype-specific FL lineages but not in CD34+/CD20− precursor populations or paired lymphoid/myeloid disease. Our data therefore are not in support of HSPCs as the cell of origin or precursor reservoir in FL.
The clonal selection for CREBBP KAT mutations observed in our cases reinforces the functional importance of CREBBP loss-of-function, but also emphasizes the primacy of BCL2 translocation, which is thought to occur due to errors in D-JH rearrangement after commitment to the pro-B or pre-B lineage in the bone marrow (2). Given that cells harboring the t(14;18) translocation in healthy individuals appear derived from the germinal center (3), recurrent mutations in CREBBP are likely to occur after the pre-B-cell stage and potentially as late as in the germinal center, although this remains to be definitively established.
Limitations of our study include sample size, acknowledging the inherent rarity of paired screening and diagnostic specimens, and lack of comprehensive clinical follow-up data in population-level screening cohorts. The detection of exceedingly rare somatic variants using high throughput sequencing presents an additional technical challenge. For example, as lymphoma precursor cells may be primarily localized in nodal tissue rather than in blood, highly sensitive strategies are required to detect early mutations: a recent study investigating lymphoid clonal hematopoiesis with a CHIP AF cutoff of 2% identified no lymphoid coding mutations in patients developing FL (28). Of note, we detected precursor mutations in the blood of PDFL patients at a median AF of 0.29%, while a similar study of myeloid precursors in the EPIC cohort detected a median AF of 4.3% (25) (Supplementary Figure S5). Nevertheless, additional technical refinements are likely to further enhance early detection of FL precursors.
While CREBBP KAT mutations were frequently detected before FL diagnosis, these lesions were not universal, indicating that other genes likely serve as alternative secondary lesions. Possibilities include the acetyltransferase EP300, homologous to CREBBP and recurrently mutated in mature FL; however, in murine models loss of EP300 is associated with impaired B-cell fitness, and we observed two EP300 KAT domain mutations only in our control cohort(45). It is also unclear if CREBBP KAT domain mutations in conjunction with BCL2 translocation are sufficient for FL development. The long delay to diagnosis in our cohort suggests that additional genetic, epigenetic, or environmental factors are required. While our cohort is focused by design on t(14;18)-translocated disease, a single BCL2-negative case (032) suggests a potential role for CREBBP mutations in this setting as well.
Collectively, our study provides the first direct evidence for the presence of genetic alterations in circulating precursor cells years before overt FL development, dominated by CREBBP mutations within the KAT domain. Larger confirmatory studies are warranted to elucidate the hierarchy of subsequent genetic lesions, and to identify additional cooperating lesions in cases without CREBBP aberrations. Given their prevalence, CREBBP KAT mutations in combination with an elevated frequency of circulating t(14;18)-translocated cells may be of utility in identifying patients at highest risk of developing FL. Such strategies could perhaps allow the early identification of a subset of patients with limited stage FL, where localized therapies can induce exceptionally durable remissions(49). Targeted treatment strategies with agents including histone deacetylase inhibitors are also under investigation for therapy of CREBBP-mutant lymphomas(42). Conversely, in monitoring patients under treatment for FL, it is tempting to speculate whether it might be possible to identify and target residual precursors that serve as a reservoir for relapse after therapy.
Methods
Patient enrollment and sample collection
Precursor mutations in follicular lymphoma were profiled in seven groups of individuals: (i) EPIC FL Cases: Screening blood samples from 17 individuals participating in the EPIC (European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition) study. These patients had confirmed t(14;18) frequencies greater than 7x10−5 in circulating leukocytes at screening and were later diagnosed with FL (6). From 5 of these individuals we also obtained paired diagnostic FL tissue biopsies. (ii) EPIC Controls: Screening blood samples from 10 individuals participating in the EPIC study who had confirmed t(14;18) frequencies greater than 7x10−5 in circulating leukocytes at screening but had not developed lymphoma at a median clinical follow-up of > 15 years(6). (iii) ACS FL Cases: Screening blood or saliva samples with paired FL tumor biopsies from 29 individuals participating in the American Cancer Society (ACS) Cancer Prevention Study II (CPS-II) LifeLink Cohort with subsequent FL diagnosis (34). (iv) Organ Donor Controls: Splenic autopsy samples from 3 adult organ donors who had confirmed tissue t(14;18) frequencies greater than 5x10−4 but no clinical evidence of lymphoid malignancy or reactive hyperplasia (33). (v) Healthy Adult Controls: blood samples from 20 healthy adult blood donors (median age 42.5, range 26–66) from the Stanford Blood Center. (vi) Paired Biopsy Cases (PBC): Lymph node (LN) biopsies from 8 individuals assessed at Stanford University for clinically significant lymphadenopathy. (vii) Bone Marrow Cases: paired bone marrow and tumor biopsies from 7 follicular lymphoma patients, including 1 also included in the Paired Biopsy Cases. Samples from all cohorts were collected with written informed consent and were approved by the corresponding Institutional Review Boards in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The EPIC study was approved by the review board of the International Agency for Research on Cancer and by the local institutes in the participating countries.
Sample processing
EPIC Cases and Controls:
DNA extraction and qPCR were performed as previously described (6). DNA from 5 available FFPE tumor biopsies was extracted using the AllPrep DNA/RNA FFPE Kit (Qiagen).
ACS FL Cases:
Collection and initial processing of the screening specimens was as previously described (34). DNA from blood screening samples was extracted with the QIAmp DNA Micro Kit, while DNA from saliva screening samples was processed via the Qiagen supplementary protocol “Isolation of genomic DNA from saliva (QA19s Jul-10)”. DNA from tumor FFPE samples was extracted using the DNAStorm FFPE kit (Cell Data Sciences).
Organ Donor & Healthy Adult Controls:
Organ donor mononuclear cells were frozen immediately after surgical removal and placed at −80C until DNA extraction. Healthy adult blood specimens were centrifuged at 1800g for 10 minutes and plasma was removed. DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen). Specimens were evaluated for detectable t(14;18) as discussed below in “Identification and Quantification of BCL2 Rearrangements” (6).
Paired Biopsy Cases (PBC):
OCT samples were cut into scrolls with a cryostat, removed from the cryopreservation medium, and rinsed in cold 70% ethanol solution prior to DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was isolated using the AllPrep DNA/RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen).
Bone Marrow and Sorted Cases:
A fraction of the bone marrow aspirate was isolated with the SepMate protocol (STEMCELL) and viably stored in liquid nitrogen for subsequent florescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) experiments. Paired tumor biopsy samples were preserved as FFPE for clinical pathology. All patients had CREBBP mutations identified in their FL tumor.
Pathology Evaluation
All biopsy samples were histologically diagnosed by pathologists according to WHO criteria at time of collection. Histological diagnoses were confirmed by hematopathology review for all Stanford biopsy samples, and additionally reviewed by a blinded hematopathologist (Y.N.).
Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing
Targeted sequencing by the Cancer Personalized Profiling by Deep Sequencing (CAPP-Seq) approach was performed on all blood and tissue samples (29, 31, 50). Samples underwent hybridization capture with customized sequencing panels to enrich for commonly mutated lymphoma genes of interest (Supplementary Table S15). Stereotypical errors and PCR duplicates were removed by using a nucleotide-level background database and specialized computational workflow including deduplication as previously described (29).
Mutational Analysis and Tumor Concordance
For diagnostic tumor samples, SNVs and insertions/deletions were genotyped as previously described (29, 31, 50). Identified genetic aberrations are listed in Supplementary Tables S3–5, S8, S14. The detection of tumor-derived mutations in prediagnostic specimens was assessed for statistical significance using a previously described Monte Carlo based test developed for tumor variant detection at low levels in cell-free DNA (29).
Identification and Quantification of BCL2 Rearrangements
BCL2 translocations in the EPIC cohorts were analyzed 1) by qPCR with breakpoint sequences determined by Sanger sequencing as previously described (6), 2) by calculating the ratio of translocated reads was relative to wild-type IGH and BCL2 regions, and 3) using the Delly2 software package (51).
FACS Experiments
Details of FACS-sorted subpopulations in each patient sample are given in Supplementary Table 12, and details of antibodies are provided in Supplementary Table 13.
Statistical Analyses
To compare continuous data distributions, we used the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Two-sided Fisher’s exact test was used to determine whether mutations were enriched in patient groups. Mutant allele frequencies were expressed as a percentage defined as the number of reads harboring a given variant divided by the total number of reads at a given genomic position. Statistical tests were performed using GraphPad Prism version 7.0d and R version 4.0.3 with P-values <0.05 considered as significant. Comparisons of sets of ratios and fold changes were performed using the BootStRatio resampling method (52).
Data Availability Statement
The human sequence raw data generated in this study are protected per the patient privacy policies of the original population screening studies, but are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author subject to institutional approvals. Data derived from the EPIC study is subject to the EPIC-Europe Data and Biospecimen Access Policy, revised 2/1/2023. Data derived from the ACS CPS-II study is subject to the ACS Department of Population Science Data Access Policies and Procedures, revised 12/8/2020. Variant-level and translocation data generated in this study is available within the article and its supplementary data files. This study does not report original code.
Supplementary Material
Statement of significance.
Our study provides direct evidence for recurrent genetic aberrations preceding FL diagnosis, revealing the combination of BCL2 translocation with CREBBP KAT domain mutations as characteristic committed lesions of FL CPCs. Such pre-diagnostic mutations are detectable years before clinical diagnosis and may help discriminating individuals at risk for lymphoma development.
Acknowledgments:
The authors are grateful to the participants in the EPIC and American Cancer Society CPS-II studies and to the patients at Stanford University and the Hematology Department of Lyon-Sud hospital for their participation. We are grateful for the technical assistance of the EPIC Spain and Italy centers in providing tumor biopsies, and the insightful discussions with the members of the Alizadeh and Diehn laboratories.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest:
FS, JSM, JS, SR, GB, BN: no disclosures or conflict of interest
AAA reports ownership interest in CiberMed, FortySeven Inc., and Foresight Diagnostics, patent filings related to cancer biomarkers, research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and Celgene, and paid consultancy from Genentech, Karyopharm, Roche, Chugai, Gilead, and Celgene.
Grant Support:
National Cancer Institute R01CA233975 (AAA and MD)
US NIH 1U01 CA194389 (AAA)
US NIH Director’s New Innovator Award Program (1-DP2-CA186569 to MD)
Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research (AAA and MD)
Lymphoma Research Foundation FL Pathways Award (AAA)
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (AAA, DK)
American Society of Hematology Scholar Award (AAA)
Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (AAA)
V-Foundation (AAA)
Stanford Cancer Innovation Award (AAA)
ARC foundation (BN)
Institut Carnot CALYM (BN)
Plan Cancer Epigenetique et Cancer (SR)
Canceropole PACA Grant (SR, BN)
Fondation pour la Recherche Medicale (GB)
Philanthropic support:
The Moghadam Family Endowed Professorship (AAA)
The Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research (AAA, MD)
The CRK Faculty Scholar Fund (MD)
German Research Foundation (F.S., SCHE 1870/1–1)
Stanford Cancer Institute (JSM, AAA)
Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (JS, AAA)
Bakewell Foundation (AAA and MD)
SDW/DT and Shanahan Family Foundations (AAA)
The Skeff Family Lymphoma Fund (AAA)
Jewish Communal Fund for Lymphoma Research (AAA)
The Arzang Family Lymphoma Fund (AAA)
The Cane-Nowak Family Foundation (AAA)
The Troper-Wojcicki Family Gift (AAA)
The Marc Benioff Fund (AAA)
The Sara Schottenstein Memorial Fund (AAA)
Anonymous philanthropic donors (AAA)
References
- 1.Yunis JJ, Oken MM, Kaplan ME, Ensrud KM, Howe RR, Theologides A. Distinctive chromosomal abnormalities in histologic subtypes of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. New England Journal of Medicine. 1982;307(20):1231–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tsujimoto Y, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985;228(4706):1440–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Roulland S, Navarro JM, Grenot P, Milili M, Agopian J, Montpellier B, et al. Follicular lymphoma-like B cells in healthy individuals: a novel intermediate step in early lymphomagenesis. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2006;203(11):2425–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Summers KE, Goff LK, Wilson AG, Gupta RK, Lister TA, Fitzgibbon J. Frequency of the Bcl-2/IgH rearrangement in normal individuals: implications for the monitoring of disease in patients with follicular lymphoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2001;19(2):420–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu Y, Hernandez AM, Shibata D, Cortopassi GA. BCL2 translocation frequency rises with age in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1994;91(19):8910–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roulland S, Kelly RS, Morgado E, Sungalee S, Solal-Celigny P, Colombat P, et al. t(14;18) Translocation: A predictive blood biomarker for follicular lymphoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2014;32(13):1347–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hirt C, Camargo MC, Yu KJ, Hewitt SM, Dolken G, Rabkin CS. Risk of follicular lymphoma associated with BCL2 translocations in peripheral blood. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(9):2625–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cong P In situ localization of follicular lymphoma: description and analysis by laser capture microdissection. Blood. 2002;99(9):3376–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jegalian AG, Eberle FC, Pack SD, Mirvis M, Raffeld M, Pittaluga S, et al. Follicular lymphoma in situ: clinical implications and comparisons with partial involvement by follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118(11):2976–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garcia-Ramirez I, Tadros S, Gonzalez-Herrero I, Martin-Lorenzo A, Rodriguez-Hernandez G, Moore D, et al. Crebbp loss cooperates with Bcl2 overexpression to promote lymphoma in mice. Blood. 2017;129(19):2645–56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Green MR, Kihira S, Liu CL, Nair RV, Salari R, Gentles AJ, et al. Mutations in early follicular lymphoma progenitors are associated with suppressed antigen presentation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2015;112(10):E1116–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Araf S, Wang J, Korfi K, Pangault C, Kotsiou E, Rio-Machin A, et al. Genomic profiling reveals spatial intra-tumor heterogeneity in follicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2018;32(5):1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Carlotti E, Wrench D, Matthews J, Iqbal S, Davies A, Norton A, et al. Transformation of follicular lymphoma to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma may occur by divergent evolution from a common progenitor cell or by direct evolution from the follicular lymphoma clone. Blood. 2009;113:3553–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weigert O, Kopp N, Lane AA, Yoda A, Dahlberg SE, Neuberg D, et al. Molecular ontogeny of donor-derived follicular lymphomas occurring after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(1):47–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Green MR, Gentles AJ, Nair RV, Irish JM, Kihira S, Liu CL, et al. Hierarchy in somatic mutations arising during genomic evolution and progression of follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2013;121(9):1604–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Morin RD, Mendez-Lago M, Mungall AJ, Goya R, Mungall KL, Corbett RD, et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature. 2011;476(7360):298–303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pasqualucci L, Dominguez-Sola D, Chiarenza A, Fabbri G, Grunn A, Trifonov V, et al. Inactivating mutations of acetyltransferase genes in B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2011;471(7337):189–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mamessier E, Song JY, Eberle FC, Pack S, Drevet C, Chetaille B, et al. Early lesions of follicular lymphoma: a genetic perspective. Haematologica. 2014;99(3):481–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Okosun J, Bodor C, Wang J, Araf S, Yang CY, Pan C, et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies recurrent mutations and evolution patterns driving the initiation and progression of follicular lymphoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46(2):176–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Horton SJ, Giotopoulos G, Yun H, Vohra S, Sheppard O, Bashford-Rogers R, et al. Early loss of Crebbp confers malignant stem cell properties on lymphoid progenitors. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(9):1093–104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhu D, McCarthy H, Ottensmeier CH, Johnson P, Hamblin TJ, Stevenson FK. Acquisition of potential N-glycosylation sites in the immunoglobulin variable region by somatic mutation is a distinctive feature of follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2002;99(7):2562–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schmidt J, Ramis-Zaldivar JE, Bonzheim I, Steinhilber J, Müller I, Haake A, et al. CREBBP gene mutations are frequently detected in in situ follicular neoplasia. Blood. 2018;132:2687–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, et al. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2014;371(26):2488–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Genovese G, Jaiswal S, Ebert BL, Mccarroll SA. Clonal hematopoiesis and blood-cancer risk. The New England journal of medicine. 2015;372(11):1071–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Abelson S, Collord G, Ng SW, Weissbrod O, Cohen NM, Niemeyer E, et al. Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals. Nature. 2018;559(7714):400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Desai P, Mencia-Trinchant N, Savenkov O, Simon MS, Cheang G, Lee S, et al. Somatic mutations precede acute myeloid leukemia years before diagnosis. Nature medicine. 2018;24(7):1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shlush LI, Zandi S, Mitchell A, Chen WC, Brandwein JM, Gupta V, et al. Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature. 2014;506(7488):328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Niroula A, Sekar A, Murakami MA, Trinder M, Agrawal M, Wong WJ, et al. Distinction of lymphoid and myeloid clonal hematopoiesis. Nature Medicine. 2021;27(11):1921–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Newman AM, Lovejoy AF, Klass DM, Kurtz DM, Chabon JJ, Scherer F, et al. Integrated digital error suppression for improved detection of circulating tumor DNA. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(5):547–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schmitt MW, Fox EJ, Prindle MJ, Reid-Bayliss KS, True LD, Radich JP, et al. Sequencing small genomic targets with high efficiency and extreme accuracy. Nature methods. 2015;12(5):423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Scherer F, Kurtz DM, Newman AM, Stehr H, Craig AF, Esfahani MS, et al. Distinct biological subtypes and patterns of genome evolution in lymphoma revealed by circulating tumor DNA. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(364):364ra155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Riboli E, Hunt K, Slimani N, Ferrari P, Norat T, Fahey M, et al. European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC): study populations and data collection. Public health nutrition. 2002;5(6b):1113–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sungalee S, Mamessier E, Morgado E, Grégoire E, Brohawn PZ, Morehouse CA, et al. Germinal center reentries of BCL2-overexpressing B cells drive follicular lymphoma progression. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2014;124(12):5337–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Jacobs EJ, Almon ML, Chao A, Mccullough ML, et al. The American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition Cohort. Cancer. 2002;94(9):2490–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kaur G, Kumar N, Nandakumar R, Rapthap CC, Sharma G, Neolia S, et al. Utility of saliva and hair follicles in donor selection for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and chimerism monitoring. Chimerism. 2012;3(1):9–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pasqualucci L, Khiabanian H, Fangazio M, Vasishtha M, Messina M, Holmes AB, et al. Genetics of follicular lymphoma transformation. Cell reports. 2014;6(1):130–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Asmann Y, Maurer M, Wang C, Sarangi V, Ansell SM, Feldman AL, et al. Genetic diversity of newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma. Blood cancer journal. 2014;4(10):e256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bouska A, Zhang W, Gong Q, Iqbal J, Scuto A, Vose J, et al. Combined copy number and mutation analysis identifies oncogenic pathways associated with transformation of follicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2017;31(1):83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Krysiak K, Gomez F, White BS, Matlock M, Miller CA, Trani L, et al. Recurrent somatic mutations affecting B-cell receptor signaling pathway genes in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2017;129(4):473–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Feldman AL, Arber DA, Pittaluga S, Martinez A, Burke JS, Raffeld M, et al. Clonally related follicular lymphomas and histiocytic/dendritic cell sarcomas: evidence for transdifferentiation of the follicular lymphoma clone. Blood. 2008;111(12):5433–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jiang Y, Ortega-Molina A, Geng H, Ying HY, Hatzi K, Parsa S, et al. CREBBP Inactivation Promotes the Development of HDAC3-Dependent Lymphomas. Cancer discovery. 2017;7(1):38–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mondello P, Tadros S, Teater M, Fontan L, Chang AY, Jain N, et al. Selective Inhibition of HDAC3 Targets Synthetic Vulnerabilities and Activates Immune Surveillance in Lymphoma. Cancer Discovery. 2020;10(3):440–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang J, Dominguez-Sola D, Hussein S, Lee JE, Holmes AB, Bansal M, et al. Disruption of KMT2D perturbs germinal center B cell development and promotes lymphomagenesis. Nat Med. 2015;21(10):1190–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ortega-Molina A, Boss IW, Canela A, Pan H, Jiang Y, Zhao C, et al. The histone lysine methyltransferase KMT2D sustains a gene expression program that represses B cell lymphoma development. Nature medicine. 2015;21(10):1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Meyer SN, Scuoppo C, Vlasevska S, Bal E, Holmes AB, Holloman M, et al. Unique and shared epigenetic programs of the CREBBP and EP300 acetyltransferases in germinal center B cells reveal targetable dependencies in lymphoma. Immunity. 2019;51(3):535–47.e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chung SS, Kim E, Park JH, Chung YR, Lito P, Teruya-Feldstein J, et al. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Origin of BRAFV600E Mutations in Hairy Cell Leukemia. Science Translational Medicine. 2014;6(238):238ra71–ra71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Damm F, Mylonas E, Cosson A, Yoshida K, Della Valle V, Mouly E, et al. Acquired Initiating Mutations in Early Hematopoietic Cells of CLL Patients. Cancer Discovery. 2014;4:1088–101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bognar A, Csernus B, Bodor C, Reiniger L, Szepesi A, Toth E, et al. Clonal selection in the bone marrow involvement of follicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2005;19(9):1656–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Brady JL, Binkley MS, Hajj C, Chelius M, Chau K, Balogh A, et al. Definitive radiotherapy for localized follicular lymphoma staged by 18F-FDG PET-CT: a collaborative study by ILROG. Blood. 2019;133(3):237–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Newman AM, Bratman SV, To J, Wynne JF, Eclov NC, Modlin LA, et al. An ultrasensitive method for quantitating circulating tumor DNA with broad patient coverage. Nat Med. 2014;20(5):548–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rausch T, Zichner T, Schlattl A, Stütz AM, Benes V, Korbel JO. DELLY: structural variant discovery by integrated paired-end and split-read analysis. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(18):i333–i9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Clèries R, Galvez J, Espino M, Ribes J, Nunes V, de Heredia ML. BootstRatio: a web-based statistical analysis of fold-change in qPCR and RT-qPCR data using resampling methods. Computers in biology and medicine. 2012;42(4):438–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The human sequence raw data generated in this study are protected per the patient privacy policies of the original population screening studies, but are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author subject to institutional approvals. Data derived from the EPIC study is subject to the EPIC-Europe Data and Biospecimen Access Policy, revised 2/1/2023. Data derived from the ACS CPS-II study is subject to the ACS Department of Population Science Data Access Policies and Procedures, revised 12/8/2020. Variant-level and translocation data generated in this study is available within the article and its supplementary data files. This study does not report original code.


