Abstract
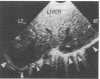
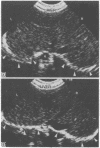
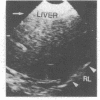
Phrenic nerve palsy is a recognised complication of operation for congenital heart disease in children. The accuracy of ultrasound in assessing diaphragmatic motion was prospectively compared with fluoroscopy in 16 patients in whom phrenic nerve palsy was suspected. Ultrasound successfully identified the five patients with phrenic nerve palsy; there were no false positive or false negative diagnoses. Ultrasound was as effective as fluoroscopy in the diagnosis of abnormalities of diaphragmatic motion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affatato A., Villagra F., De Leon J. P., Gomez R., Checa S. L., Vellibre D., Sanchez P., Diez Balda J. I., Brito J. M. Phrenic nerve paralysis following pediatric cardiac surgery. Role of diaphragmatic plication. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1988 Sep-Oct;29(5):606–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich T. K., Herman J. H., Rochester D. F. Bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1980 Dec;97(6):988–991. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diament M. J., Boechat M. I., Kangarloo H. Real-time sector ultrasound in the evaluation of suspected abnormalities of diaphragmatic motion. J Clin Ultrasound. 1985 Oct;13(8):539–543. doi: 10.1002/1097-0096(199010)13:8<539::aid-jcu1870130805>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber K., Asher M., Freimanis A. K. Echographic evaluation of diaphragmatic motion in intra-abdominal diseases. Radiology. 1975 Jan;114(1):141–144. doi: 10.1148/114.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller J. O., Schneider M., Kassner E. G., Friedman A. P., Waldroup L. D. Sonographic evaluation of the chest in infants and children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980 May;134(5):1019–1027. doi: 10.2214/ajr.134.5.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. S., Giovannetti M., Kim B. K. Normal ventilatory movement of the right hemidiaphragm studied by ultrasonography and pneumotachography. Radiology. 1983 Jan;146(1):141–144. doi: 10.1148/radiology.146.1.6849035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangarloo H., Sukov R., Sample W. F., Lipson M., Smith L. Ultrasonographic evaluation of juxtadiaphragmatic masses in children. Radiology. 1977 Dec;125(3):785–787. doi: 10.1148/125.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing I. A., Teele R. L., Stark A. R. Diaphragmatic movement in newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1988 Apr;112(4):638–643. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Trusler G. A., Williams W. G., Edmonds J. F., Coles J. G., Hosokawa Y. Phrenic nerve paralysis after pediatric cardiac surgery. Retrospective study of 125 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1987 Sep;94(3):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]