Abstract
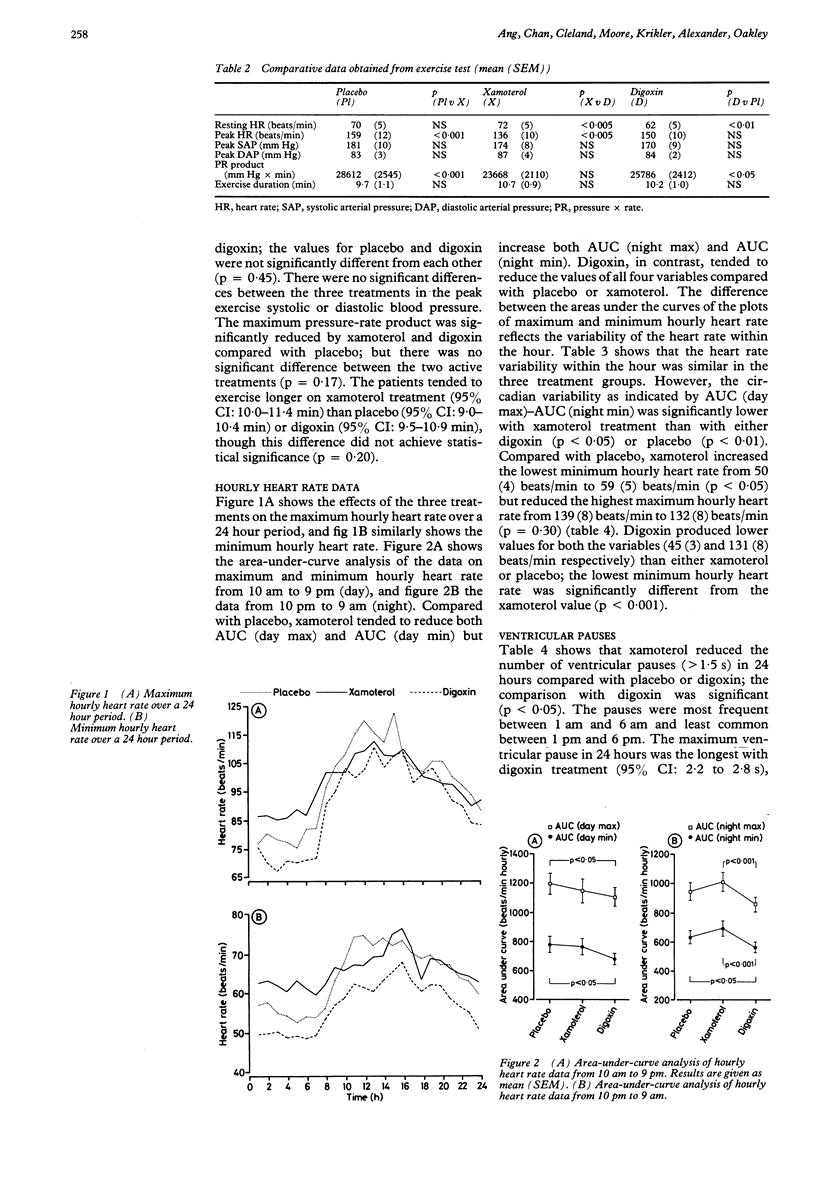
Thirteen patients in chronic atrial fibrillation with a normal resting heart rate but with exercise tachycardia and episodes of bradycardia were randomised to treatment periods of two weeks on xamoterol (200 mg twice daily), low dose digoxin, or placebo, in a blind crossover study. The results (mean SEM) of symptom scores, a treadmill exercise test, and 24 hour ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring were obtained. Xamoterol improved symptom scores and controlled exercise heart rate better than digoxin. Xamoterol was better than digoxin or placebo in reducing the heart rate response to exercise and tended to improve exercise duration. Xamoterol, by reducing the daytime maximum hourly heart rate and increasing the night time minimum hourly heart rate, significantly reduced the difference between the two compared with placebo. In contrast, digoxin tended to reduce both the maximum and minimum hourly heart rates through day and night. Both the frequency and duration of ventricular pauses were reduced by xamoterol but tended to increase with digoxin. Xamoterol reduced both the circadian variation in ventricular response to atrial fibrillation and exercise tachycardia by modulating the heart rate according to the prevailing level of sympathetic activity. These changes were translated into symptomatic benefit for the patients studied.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwood J. E., Sullivan M., Forbes S., Myers J., Pewen W., Olson H. G., Froelicher V. F. Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on exercise performance in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Aug;10(2):314–320. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerregaard P. Mean 24 hour heart rate, minimal heart rate and pauses in healthy subjects 40-79 years of age. Eur Heart J. 1983 Jan;4(1):44–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDAY E., IRVING D. W. Effect of cardiac arrhythmias on the cerebral circulation. Am J Cardiol. 1960 Oct;6:803–808. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(60)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channer K. S., Papouchado M., James M. A., Pitcher D. W., Rees J. R. Towards improved control of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1987 Feb;8(2):141–147. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David D., Segni E. D., Klein H. O., Kaplinsky E. Inefficacy of digitalis in the control of heart rate in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation: beneficial effect of an added beta adrenergic blocking agent. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Dec;44(7):1378–1382. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBianco R., Morganroth J., Freitag J. A., Ronan J. A., Jr, Lindgren K. M., Donohue D. J., Larca L. J., Chadda K. D., Olukotun A. Y. Effects of nadolol on the spontaneous and exercise-provoked heart rate of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation receiving stable dosages of digoxin. Am Heart J. 1984 Oct;108(4 Pt 2):1121–1127. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S., Probst P., Selzer A., Cohn K. Inefficacy of "therapeutic" serum levels of digoxin in controlling the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1975 May;35(5):651–655. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Shiina A., Toyo-Oka T., Hosoda S., Kondo K. The cardiovascular effects of xamoterol, a beta 1-adrenoceptor partial agonist, in healthy volunteers at rest. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;21(3):259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. A., Channer K. S., Papouchado M., Rees J. R. Improved control of atrial fibrillation with combined pindolol and digoxin therapy. Eur Heart J. 1989 Jan;10(1):83–90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Abbott R. D., Savage D. D., McNamara P. M. Epidemiologic features of chronic atrial fibrillation: the Framingham study. N Engl J Med. 1982 Apr 29;306(17):1018–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198204293061703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. O., Kaplinsky E. Verapamil and digoxin: their respective effects on atrial fibrillation and their interaction. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Oct;50(4):894–902. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)91251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., McDevitt D. G. Factors affecting the clinical response to treatment with digoxin and two calcium antagonists in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 May;25(5):603–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molajo A. O., Coupe M. O., Bennett D. H. Effect of Corwin (ICI 118587) on resting and exercise heart rate and exercise tolerance in digitalised patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Br Heart J. 1984 Oct;52(4):392–395. doi: 10.1136/hrt.52.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall A., Snow H. M. The cardiovascular effects of ICI 118,587: A beta 1-adrenoceptor partial agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;77(2):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTRANDER L. D., Jr, BRANDT R. L., KJELSBERG M. O., EPSTEIN F. H. ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS AMONG THE ADULT POPULATION OF A TOTAL NATURAL COMMUNITY, TECUMSEH, MICHIGAN. Circulation. 1965 Jun;31:888–898. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.31.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndahl G., Thulesius O., Hood B. Incidence of persistent atrial fibrillation and conduction defects in coronary heart disease. Am Heart J. 1972 Jul;84(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(72)90314-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch M. C. Lessons from ambulatory electrocardiography. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Sep 7;291(6496):617–618. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6496.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher D., Papouchado M., James M. A., Rees J. R. Twenty four hour ambulatory electrocardiography in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 1;292(6520):594–594. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6520.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebello R., Brownlee W. C. Intermittent ventricular standstill during chronic atrial fibrillation in patients with dizziness or syncope. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1987 Nov;10(6):1271–1276. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1987.tb04963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfors A. Digoxin dosage and ventricular rate at rest and exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation. Acta Med Scand. 1971 Oct;190(4):321–333. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1971.tb07437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth A., Harrison E., Mitani G., Cohen J., Rahimtoola S. H., Elkayam U. Efficacy and safety of medium- and high-dose diltiazem alone and in combination with digoxin for control of heart rate at rest and during exercise in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):316–324. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhadin P., Bran M., De Marneffe M., Denolin H. Management of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;13(Suppl 2):295S–296S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Camm J., Ward D., Washington H., Martin A. Treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation in the elderly, assessed by ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1980 Dec;28(12):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1980.tb00001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


