Abstract
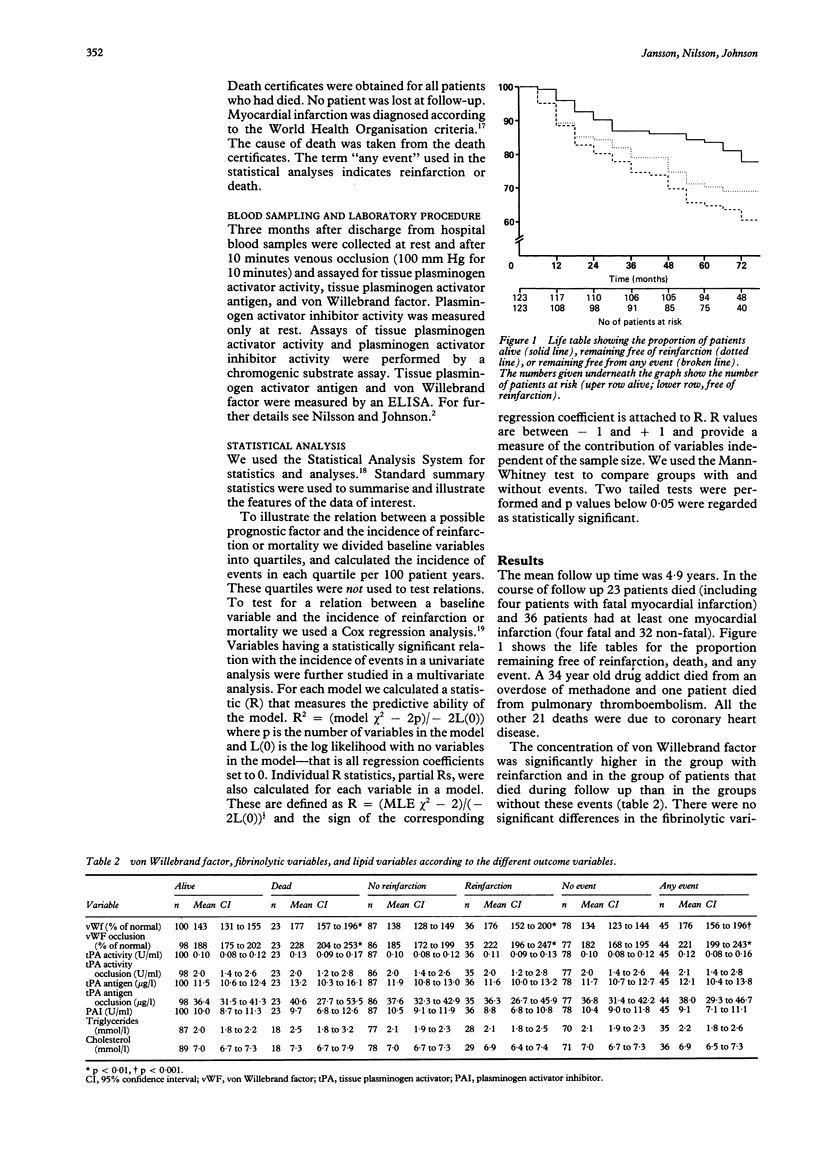
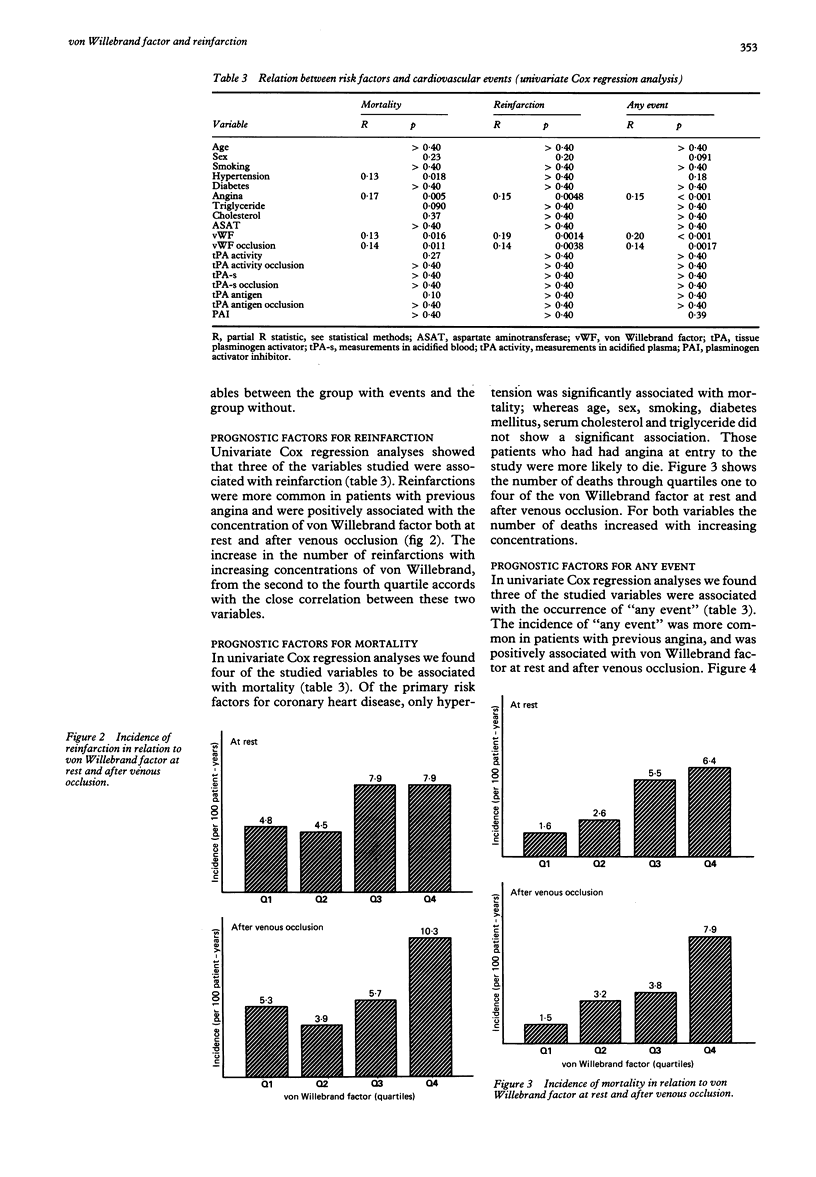
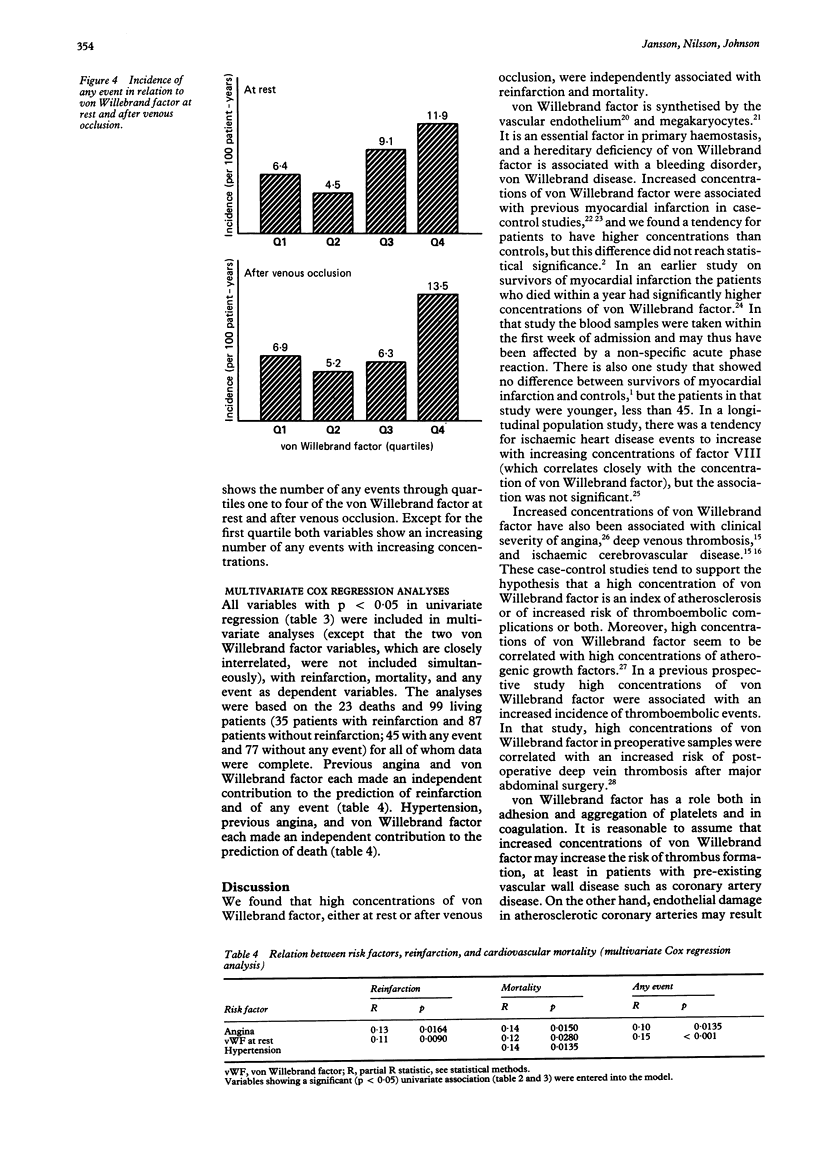
OBJECTIVE--To evaluate as predictors of reinfarction and mortality tissue plasminogen activator antigen and activity before and after venous occlusion, plasminogen activator inhibitor, von Willebrand factor, and established risk factors. DESIGN--Prospective study with a mean observation time of 4.9 years. SETTING--Secondary referral centre, the Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospital of Umeå. PATIENTS--123 consecutive survivors of myocardial infarction under the age of 70 years. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Reinfarction and deaths from all causes. RESULTS--23 patients died and 36 patients had at least one reinfarction. High concentrations of von Willebrand factor were independently associated with both reinfarction and mortality. A history of angina at entry into the study was also independently associated with reinfarction and mortality. Hypertension was independently associated with mortality but not with reinfarction. None of the fibrinolytic or lipid variables was associated with reinfarction or death. CONCLUSION--A high concentration of von Willebrand factor was a novel index of increased risk for reinfarction and mortality in survivors of myocardial infarction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asada Y., Sumiyoshi A., Hayashi T., Suzumiya J., Kaketani K. Immunohistochemistry of vascular lesion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, with special reference to factor VIII related antigen. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 1;38(5):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aznar J., Estellés A., Tormo G., Sapena P., Tormo V., Blanch S., España F. Plasminogen activator inhibitor activity and other fibrinolytic variables in patients with coronary artery disease. Br Heart J. 1988 May;59(5):535–541. doi: 10.1136/hrt.59.5.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrebi A., Talmor M., Vorst E., Resnitzky P., Shtalrid M. IgM lambda globular cytoplasmic inclusions in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia resembling immunocytoma. Scand J Haematol. 1983 Jan;30(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1983.tb00633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boneu B., Abbal M., Plante J., Bierme R. Letter: Factor-VIII complex and endothelial damage. Lancet. 1975 Jun 28;1(7922):1430–1430. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Zwang E., Bronshtein M., Seligsohn U. von Willebrand factor multimer patterns in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):715–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis R. B., Jr, Kawanishi D., Baruch T., Mahrer P., Rahimtoola S., Feinstein D. I. Impaired fibrinolysis in coronary artery disease. Am Heart J. 1988 Apr;115(4):776–780. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(88)90878-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Pickering C., Knight G., Boulton A. J., Ball J., Ward J. D., Preston F. E. Changes in the factor VIII complex in diabetic ketoacidosis: evidence of endothelial cell damage? Diabetologia. 1987 Mar;30(3):160–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00274221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines A. P., Howarth D., North W. R., Goldenberg E., Stirling Y., Meade T. W., Raftery E. B., Millar Craig M. W. Haemostatic variables and the outcome of myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Dec 30;50(4):800–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Blombäck M., Wiman B., Svensson J., Szamosi A., de Faire U., Mettinger L. Haemostatic function in myocardial infarction. Br Heart J. 1986 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1136/hrt.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., Wiman B., de Faire U., Blombäck M. Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1557–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamsten A., de Faire U., Walldius G., Dahlén G., Szamosi A., Landou C., Blombäck M., Wiman B. Plasminogen activator inhibitor in plasma: risk factor for recurrent myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1987 Jul 4;2(8549):3–9. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)93050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of von Willebrand factor by cultured human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1906–1909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. H., Nilsson T. K., Olofsson B. O. Tissue plasminogen activator and other risk factors as predictors of cardiovascular events in patients with severe angina pectoris. Eur Heart J. 1991 Feb;12(2):157–161. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschstein W., Simianer S., Dempfle C. E., Keller H., Stegaru B., Rentrop P., Heene D. L. Impaired fibrinolytic capacity and tissue plasminogen activator release in patients with restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):772–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettinger K. L. A study of hemostasis in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. I. Abnormalities in factor VIII and antithrombin. Thromb Res. 1982 May 1;26(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moiseev S. I. Rol' gemostaza i reologii krovi pri stabil'noi i progressiruiushchei stenokardii napriazheniia. Kardiologiia. 1988 Nov;28(11):67–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J., Elgue G., Wallin M., Hamsten A., Blombck M. Correlation between plasma levels of growth factors and von Willebrand factor. Thromb Res. 1989 Apr 15;54(2):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T. K., Johnson O. The extrinsic fibrinolytic system in survivors of myocardial infarction. Thromb Res. 1987 Dec 15;48(6):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T. K., Löfvenberg E. Decreased fibrinolytic capacity and increased von Willebrand factor levels as indicators of endothelial cell dysfunction in patients with lupus anticoagulant. Clin Rheumatol. 1989 Mar;8(1):58–63. doi: 10.1007/BF02031071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Mellbring G., Hedner U. Relationship between factor XII, von Willebrand factor and postoperative deep vein thrombosis. Acta Chir Scand. 1986 May;152:347–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B. O., Dahlén G., Nilsson T. K. Evidence for increased levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator in plasma of patients with angiographically verified coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 1989 Jan;10(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz-Huebner U., Thompson S. G., Balleisen L., Fechtrup C., Grosse-Heitmeyer W., Kirchhof B., Most E., Müller U. S., Seiffert C., Seiffert D. Lack of association between haemostatic variables and the presence or the extent of coronary atherosclerosis. Br Heart J. 1988 Mar;59(3):287–291. doi: 10.1136/hrt.59.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serological tests for leprosy. Lancet. 1986 Mar 8;1(8480):533–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Chavin S. I., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human megakaryocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1102–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI112064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg T. B., Blombäck M., Overmark I. Blood coagulation studies in 45 patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease and 44 patients with venous thromboembolic disease. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(5):385–390. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb09743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



