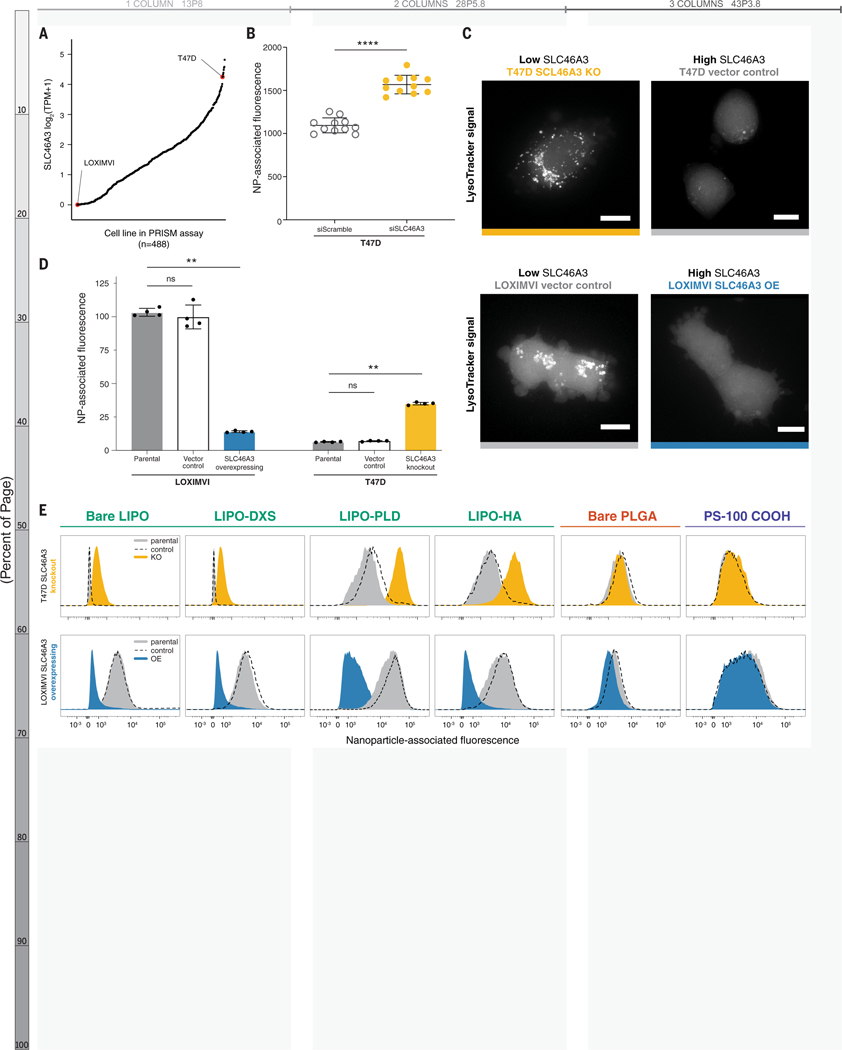
Figure 4. Modulating SLC46A3 expression in cancer cell lines is sufficient to negatively regulate interaction with liposome NP formulations.
(A) T47D and LOXIMVI cells have high and low SLC46A3 expression, respectively, among the cells in the nanoPRISM cell line pool. (B) T47D cells treated with siRNA to knock down SLC46A3 have higher uptake of Lipo-PLD compared to T47D cells treated with a scrambled siRNA control (**** p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (C) Representative micrographs of Lysotracker signal in engineered cell lines showed endolysosomal compartments. Scale bars = 10 μm. (D) Using lentivirus to overexpress SLC46A3 in LOXIMVI cells and CRISPR/Cas9 to knock out SLC46A3 in T47D cells, we showed that modulation results in significantly changed liposome association, as determined by flow cytometry (** p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). NP-associated fluorescence is defined as median fluorescence intensity normalized to untreated cells. Data are represented as the mean and standard deviation of four biological replicates. (E) Shifts in NP association were consistently observed across all tested liposomes, independent of surface modification. No shifts were observed with PLGA or PS formulations.