Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To document regional plasma concentrations of brain natriuretic factor (BNF) and their relations to concurrent concentrations of atrial natriuretic factor, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, and haemodynamic state. DESIGN--Regional blood sampling from a systemic artery and vein, renal vein, and coronary sinus together with concurrent haemodynamic indices in patients coming forward for left and right cardiac catheterisation. SETTING--Tertiary referral centre. PATIENTS--22 consecutive unselected patients coming forward for left and right cardiac catheterisation or electrophysiological studies in the course of standard diagnosis for a range of cardiac disorders. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Significant arteriovenous gradients for plasma BNF concentration were found across the lower limb, the kidney, and the heart. These were less than concurrent arteriovenous gradients in plasma atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). Arterial concentrations of plasma BNF were positively related to concurrent concentrations of ANF (r = 0.72, p < 0.01) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (r = 0.52, p < 0.05). Arterial plasma concentrations of BNF showed a significant positive correlation with right atrial pressure and pulmonary artery wedge pressure and an inverse relation to cardiac output. CONCLUSIONS--Regional plasma concentrations of BNF indicate cardiac secretion of this peptide and clearance in a number of tissues. Renal clearance is proportionally greater than that found across the limb. Absolute and proportional arteriovenous gradients of this peptide are considerably less than for concomitant concentrations of ANF suggesting slower metabolic clearance of BNF. Plasma BNF concentrations rise with increasing cardiac impairment and are related to indices of cardiac function. These findings are consistent with a role for BNF in the neurohumoral response to cardiac impairment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates E. R., Shenker Y., Grekin R. J. The relationship between plasma levels of immunoreactive atrial natriuretic hormone and hemodynamic function in man. Circulation. 1986 Jun;73(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.6.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Kaminsky N. I., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Kinetic parameters and renal clearances of plasma adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2222–2236. doi: 10.1172/JCI106441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. J., Espiner E. A., Richards A. M., Yandle T. G., Frampton C. Renal, endocrine, and hemodynamic effects of human brain natriuretic peptide in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jan;76(1):91–96. doi: 10.1210/jcem.76.1.8380606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
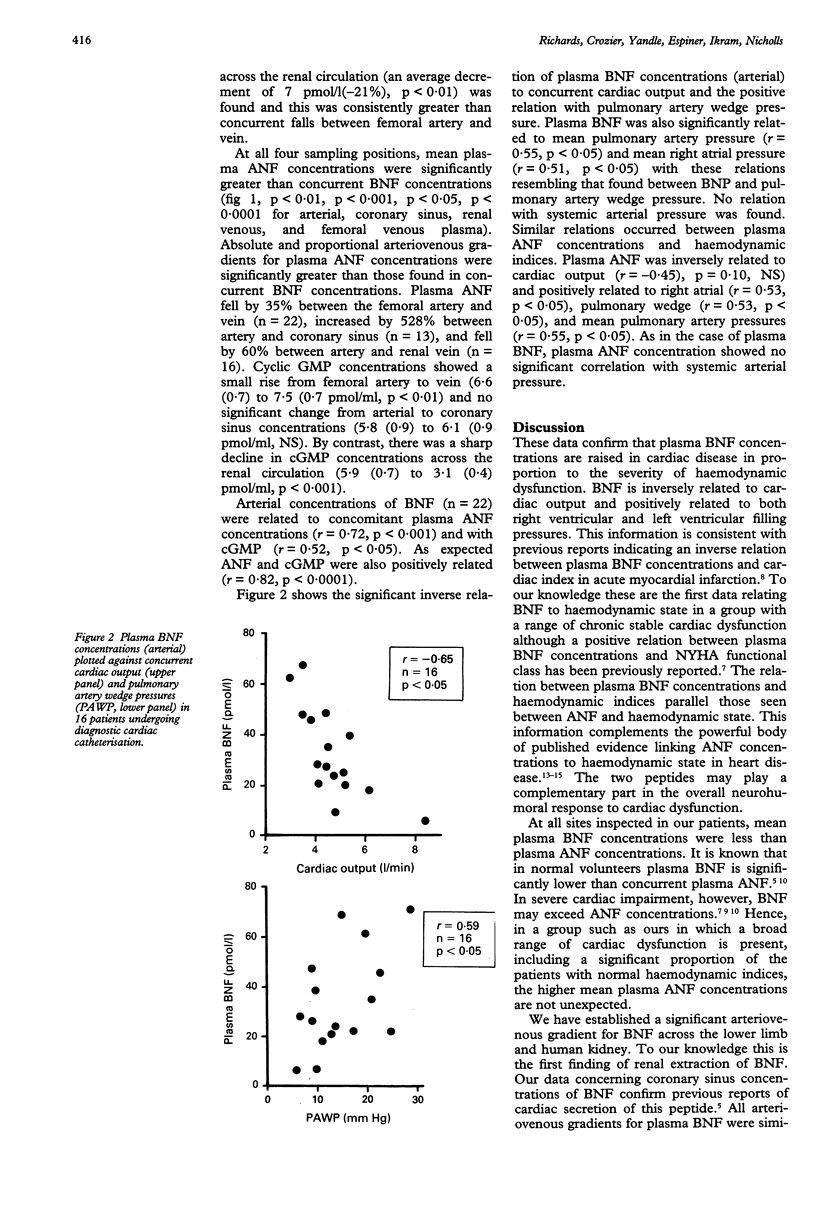
- Itoh H., Nakao K., Saito Y., Yamada T., Shirakami G., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Hosoda K., Suga S., Minamino N. Radioimmunoassay for brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection of BNP in canine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Lowe D. G., Bennett G. L., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Goeddel D. V. Selective activation of the B natriuretic peptide receptor by C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):120–123. doi: 10.1126/science.1672777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Isolation and identification of a high molecular weight brain natriuretic peptide in porcine cardiac atrium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):402–409. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukoyama M., Nakao K., Hosoda K., Suga S., Saito Y., Ogawa Y., Shirakami G., Jougasaki M., Obata K., Yasue H. Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1402–1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI115146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukoyama M., Nakao K., Saito Y., Ogawa Y., Hosoda K., Suga S., Shirakami G., Jougasaki M., Imura H. Increased human brain natriuretic peptide in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 13;323(11):757–758. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009133231114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine A. E., Erne P., Bürgisser E., Müller F. B., Bolli P., Burkart F., Bühler F. R. Atrial natriuretic peptide and atrial pressure in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):533–537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine A. E., Erne P., Bürgisser E., Müller F. B., Bolli P., Burkart F., Bühler F. R. Atrial natriuretic peptide and atrial pressure in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):533–537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. M., Cleland J. G., Tonolo G., McIntyre G. D., Leckie B. J., Dargie H. J., Ball S. G., Robertson J. I. Plasma alpha natriuretic peptide in cardiac impairment. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 16;293(6544):409–412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6544.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Itoh H., Yamada T., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Hosoda K., Shirakami G., Suga S., Minamino N. Brain natriuretic peptide is a novel cardiac hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):360–368. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H. A new natriuretic peptide in porcine brain. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):78–81. doi: 10.1038/332078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandle T. G., Espiner E. A., Nicholls M. G., Duff H. Radioimmunoassay and characterization of atrial natriuretic peptide in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):72–79. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandle T. G., Espiner E. A., Nicholls M. G., Duff H. Radioimmunoassay and characterization of atrial natriuretic peptide in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):72–79. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Yasue H., Morita E., Sakaino N., Jougasaki M., Kurose M., Mukoyama M., Saito Y., Nakao K., Imura H. Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal responses to brain natriuretic peptide infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1991 Oct;84(4):1581–1588. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.4.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


