Abstract
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR) represents a model promoter system and the identification and characterisation of cellular proteins that interact with this region has provided a basic understanding about both general eukaryotic and HIV-1 proviral transcriptional regulation. To date a large number of sequence-specific DNA–protein interactions have been described for the HIV-1 LTR. The aim of this report is to provide a comprehensive, updated listing of these HIV-1 LTR interactions. It is intended as a reference point to facilitate on-going studies characterising the identity of cellular proteins interacting with the HIV-1 LTR and the functional role(s) of specific regions of the LTR for HIV-1 replication.
INTRODUCTION
The regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) proviral gene expression is tightly regulated by the binding of cellular host proteins to a variety of cis-acting DNA sequences located within the long terminal repeat (LTR) region of the viral genome (1). The HIV-1 LTR is divided into three regions: U3, R and U5 (Fig. 1). These contain four functional regions related to the regulation of HIV-1 transcription: the transactivation response (TAR) element found within R (nt +1 to +60), the basal or core promoter (nt –78 to –1), a core enhancer (nt –105 to –79) and a modulatory region (nt –454 to –104) (1). The last three are found within U3. The modulatory region has also been proposed to contain a negative regulatory element (NRE) between nt –340 and –184 because deletions within this region increased HIV-1 LTR-directed transcription and viral replication (2,3).
Figure 1.
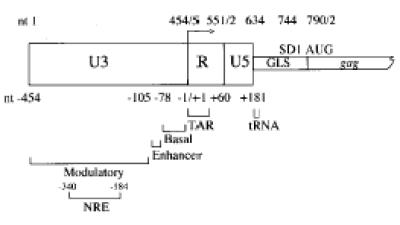
Structure of the HIV-1 5′-LTR and gag leader sequence (GLS). The U3 region contains basal, enhancer and modulatory promoter elements, including the negative regulatory element (NRE). The sequence of the transactivating region (TAR) is found in the repeat (R) region. The tRNA primer binding (tRNA) and major splice donor (SD) sites are within the GLS. The initiation codon of the gag gene is depicted by AUG. Numbering above the boxed regions starts from the first nucleotide of the proviral DNA sequence (here using the HIV-1HXB2 sequence; accession no. K03455), numbering below the boxed regions is relative to the transcription start site nucleotide +1.
Early reports showed the three Sp1 core promoter binding sites and two NF-κB core enhancer motifs to be key elements involved in the regulation of HIV-1 transcription (1). Several cellular proteins including c-Myb, NF-AT, USF and COUP have also been proposed to interact with the modulatory region and contribute to HIV-1 LTR promoter activity (1,4–7). Subsequent studies have revealed a wealth of additional U3 and TAR DNA–protein interactions that significantly influence levels of HIV-1 LTR transcription. More recently, important motifs within the U5 region and gag leader sequence (GLS) have been described (8–11). Furthermore, we have identified a fourth Sp1 binding site at the 5′-end of the U3 region and, in addition to the U3 USF and NF-κB sites, found it to be essential for negative sense transcription from the HIV-1 LTR (12,13). Together these various binding sites and their relative orientations mediate combinatorial DNA–protein and protein–protein interactions that form a complex regulatory network through which HIV-1 regulates its levels of positive and negative sense gene expression in a diverse range of target host cells under a variety of extracellular stimuli.
DESCRIPTION OF THE COMPILATION
The present report provides an updated listing covering previously published HIV-1 LTR DNA–protein interactions (Tables 1–5). Interactions are tabulated according to the functional regions of the LTR (R/U5 junction, U5, GLS, TAR, basal/core promoter, core enhancer and modulatory region). The identity and site of interaction are listed in the first and second columns, respectively. Within each table interactions are listed in an order that is relative to the transcription start site +1. While most interactions are highly conserved across strains of HIV-1, not all sites are found in all strains and the exact position of an interacting site may differ slightly. Therefore, sites are recorded according to the numbering of the HIV-1 strain used in the original description. The source cell type and stimulatory conditions under which the interaction was observed are listed in the third column. In some instances interactions have been defined using only proteins in either a recombinant or purified form. For each interaction, the effect on levels of HIV-1 LTR transcription is provided in the fourth column. For more specific details of transcription factor interactions with the HIV-1 LTR and their proposed effect(s) on levels of transcription readers are referred to publications cited in the fifth column.
Table 1. Cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR R/U5 junction, U5 region and GLS (nt +78 to +296).
| Factor | Region (nt) | Cell type/source | Effect on transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp1 | +271 to +289 | Recombinant Sp1, ACH-2, U1 | + | 8, 11 |
| IRF-1 and IRF-2 | +204 to +223 | Jurkat (IFN-induced), Raji, U937, HeLa, SupT1 | + | 8, 11 |
| AP-3 (NFAT) | +169 to +181 | A3.01 (TPA + ionomycin treated), Raji, U937, HeLa, SupT1 | + | 8, 11 |
| AP-1, ATF-1, ATF-2, CREB-1 | +160 to +167 | Jurkat (TPA treated), SW480, SW620, HT29 | + | 8–11,14 |
| AP-1 | +122 to –129 | Recombinant AP-1, Jurkat (TPA treated) | + | 8,11 |
| AP-1, ATF-1, ATF-2, CREB-1 | +92 to +102 | Jurkat (TPA treated), SW480, SW620, HT29 | + | 8,9,11,14 |
+, activator of HIV-1 LTR transcription; Recombinant, E.coli synthesised factor, in vitro transcribed/translated or artificially expressed in a cell line.
Table 5. Cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR modulatory region (nt –454 to –104).
| Factor | Region (nt) | Cell type/source | Effect on transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nuclear matrix factor | –117 to –220 | HIV-1 infected HUT-78 | – | 65 |
| RBF-2 | –121 to –131 | Jurkat | + | 32,33 |
| LEF-1 | –122 to –142 | Recombinant, Jurkat | + | 20,66 |
| Ets-1 | –140 to –160 | Recombinant | + | 66 |
| cEts-1 | –141 to –149 | Recombinant, T cell | Unclear | 67 |
| RBF-1 | –142 to –151 | Jurkat | + | 32,33 |
| HIV-TF1 | –159 to –173 | BALL-1 | + | 68 |
| NF-IL6 | –157 to –177 | Recombinant, PMA-stimulated U937, THP-1 | +/– | 62,64,69 |
| Unclear | –150 to –170 | H9IIIB | Unclear | 35 |
| USF, TFE3, TFEB | –166 to –161 | HeLa | – | 6 |
| LPS-inducible factor | –171 to –163 | Human monocytes, THP-1 | Unclear | 70 |
| ILF | –206 to –220 | Recombinant | Unclear | 71 |
| Unclear | –215 to –280 | H9IIIB, U1 | Unclear | 35 |
| NF-IL6 | –238 to –258 | Recombinant | + | 64 |
| AP-1 | –247 to –222 | U373-MG, TC620, HeLa | + | 72 |
| NFAT | –254 to –216 | Activated T cells | Unclear | 7 |
| Glucorticoid receptor | –259 to –264 | Recombinant | Unclear | 73 |
| Unclear | –255 to –238 | RA or HMBA-stimulated NTERA-2 | + | 74 |
| Unclear | –260 to –290 | HeLa | – | 75 |
| Unclear | –260 to –275 | H9IIIB, U1 | Unclear | 35,36 |
| ILF | –262 to –276 | Recombinant | Unclear | 71 |
| Unclear | –273 to –255 | SK23 T cell | – | 76 |
| GATA-2, GATA-3, GATA-4 | –293 to –290 | Recombinant, MT-2 | – | 77 |
| NRT-1 | –295 to –320 | H9IIIB, H9, Jurkat, MOLT4, HeLa | – | 78 |
| HTF4, E2A, ITF-1 | –299 to –304 | Recombinant, MT-2, Jurkat | Unclear | 34,79 Pereira,L.A. et al., J. Biol. Chem., submitted for publication |
| c-Myb | –299 to –304 | Recombinant | + | 5,79 |
| Novel factor | –306 to –285 | U373-MG, SK-N-MC, TC620, Jurkat, HeLa | Unclear | 72 |
| Factor A1 | –317 to –288 | Jurkat and clone 2F6 T cell | Unclear | 80 |
| RARα, ARP-1, EAR-2, EAR-3, HNF-4, NGFI-B, PPAR | –320 to –356 | U373-MG, SK-N-MC, TC620, Cos-1 and recombinant | +/– | 40,81 |
| Factor R | –322 to –298 | Jurkat and clone 2F6 T cell | Unclear | 80 |
| COUP-TF | –324 to –357 | Jurkat T cell, HeLa | Unclear | 4 |
| Unclear | –324 to –357 | U937 | + | 82 |
| NRT-2 | –325 to –338 | H9IIIB, H9, Jurkat, MOLT4 | – | 78 |
| Novel steroid/hormone receptor (not COUP) | –327 to –350 | Jurkat T cell, HeLa and PBL | – | 83,84 |
| GATA-2, 3 | –338 to –343 | BAF3 B cell, Recombinant | + | 78,85 |
| Unclear | –361 to –379 | Jurkat | Unclear | 84 |
| NFI family (not YB-1), CREB/ATF family | –370 to –377 | Jurkat T cell, HeLa | +/– | 86 |
| GATA-3 | –373 to –377 | Recombinant | + | 77 |
| GATA-2 | –401 to –405 | BAF3 | + | 85 |
| GATA-2 | –409 to –413 | BAF3 | + | 85 |
| GATA-3 | –433 to –441 | Recombinant | + | 77 |
| Sp1 | –421 to –454 | Recombinant, Jurkat | *+ | 12,13 |
+, activator of HIV-1 LTR transcription; *+, essential for negative sense HIV-1 LTR transcription; –, repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; +/–, shown to be both an activator and repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; Recombinant, E.coli synthesised factor, in vitro transcribed/translated or artificially expressed in a cell line; Unclear, identity of transcription factor and/or effect on HIV-1 LTR transcription not determined.
Table 2. Cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR TAR DNA region (nt +1 to +60), initiator element (Inr; nt –7 to +30) and the inducer of short transcripts (IST, nt –5 to +82).
| Factor | Region (nt) | Cell type/source | Effect on transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF-κB | +31 to +40 | MC3 treated with mitomycin C, Jurkat and 293 treated with or without TNFα recombinant p50, p52 and p65 | + | 15 |
| CTF | +41 to +46 | HeLa | Unclear | 16 |
| USF | +35 to +60 | Recombinant | + | 17 |
| UPF-2 | +28 to +36 | HeLa | Unclear | 18 |
| PRDII-BF1 | +27 to +52 | Recombinant | + | 19 |
| LEF-1 | +17 to +32 | Jurkat | + | 20 |
| Glucocorticoid receptor | +15 to +20 | Recombinant | – | 21 |
| IST, FBI-1 | +1 to +8 and +49 to +78 | HeLa | Required for the establishment of abortive transcription complexes | 22,23 |
| Glucocorticoid receptor | –1 to –6 | Recombinant | No effect | 21 |
| Oct-1 and Oct-2 | –7 to –14 | HeLa | – | 24 |
| USF | –3 to +20 | Recombinant | + | 17 |
| NF-κB | –1 to +9 | Jurkat and 293 treated with or without TNFα, recombinant p50, p52 | + | 25 |
| LBP-1 (UP-1, CP-2) | –16 to +27 | Recombinant | +/– | 26–28 |
| YY1 | –17 to +25 | HeLa | – | 29 |
| TDP-43 | –18 to +28 | HeLa, recombinant | – | 30,88 |
| HIP-116 | –25 to +2 | HeLa, recombinant | Unclear | 31 |
+, activator of HIV-1 LTR transcription; –, repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; +/–, shown to be both an activator and repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; Recombinant, E.coli synthesised factor, in vitro transcribed/translated or artificially expressed in a cell line; Unclear, identity of transcription factor and/or effect on HIV-1 LTR transcription not determined; No effect, mutation of binding site shown to have no effect on levels of HIV-1 LTR transcription compared to the wild-type LTR.
Table 3. Cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR basal/core promoter (nt –78 to –1).
| Factor | Region (nt) | Cell type/source | Effect on transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBF-2 | –5 to –26 | Jurkat | + | 32,33 |
| LBP-1 (UP-1, CP-2) | –16 to –38 | Recombinant | +/– | 26–28 |
| E47, AP-4, HTF4 | –17 to –22 | Recombinant | – | 30,34 |
| Unclear | –20 to –102 | H9IIIB, U1 | Unclear | 35,36 |
| IE2-86 | –20 to –120 | Recombinant | + | 37 |
| TATA binding protein | –23 to –27 | Ubiquitous | Essential | 38 |
| LEF-1 | –37 to –51 | Jurkat | + | 20 |
| HMBP | –39 to –81 | Hut 78, HeLa | Unclear | 39 |
| YB-1 | –40 to –83 | U-87MG, SK-N-MC, Jurkat | + | 40,89 |
| T3Rα | –45 to –76 | HeLa | + | 41,42 |
| Sp1 | –46 to –78 (three sites) | Ubiquitous | + | 43 |
| Sp3 | –46 to –78 | HeLa, Jurkat | – | 44 |
| Sp4 | –46 to –78 | Unclear | + | 44 |
| GBF | –46 to –78 | Human Peripheral Blood Leukocyte cDNA Library | Unclear | 45 |
| BTEB | –46 to –78 | Recombinant | + | 46 |
| AAV Rep78 | –54 to –34 | Recombinant | – | 47 |
| T3Rα | –59 to –64 | Mononuclear cells and leukaemic cell lines | + | 48 |
| p53 | –64 to –75 | Jurkat | + | 49 |
| PEBP2 | –67 to –73 | NIH 3T3 | Unclear | 50 |
+, activator of HIV-1 LTR transcription; –, repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; +/–, shown to be both an activator and repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; Recombinant, E.coli synthesised factor, in vitro transcribed/translated or artificially expressed in a cell line; Unclear, identity of transcription factor and/or effect on HIV-1 LTR transcription not determined.
Table 4. Cellular transcription factors interacting with the HIV-1 LTR core enhancer region (nt –105 to –79).
| Factor | Region (nt) | Cell type/source | Effect on transcription | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/EBP family members | –79 to –109 | Recombinant, Jurkat, HeLa, U138MG, C1.7W2 | +/– | 51–53 |
| T3R | –80 to –104 | HeLa | + | 41,42 |
| EBP-1 | –80 to –105 | Jurkat | + | 54 |
| NF-κB/Rel family | –81 to –91 and –95 to –104 | Jurkat, H9, myeloid | + | 55–57 |
| GABP-α and -β | –81 to –91 and –95 to –104 | Recombinant, TPA-stimulated Jurkat | + | 58 |
| Prototypic NF-κB | –81 to –91 and –95 to –104 | CNS cells | + | 59 |
| RBF-1 | –80 to –104 | Jurkat | + | 32,33 |
| PRDII-BF1 | –83 to –108 | Recombinant | + | 19 |
| E2F-1 | –93 to –99 | Recombinant | – | 60 |
| Ets-2, PU.1 | –95 to –104 | Recombinant | + | 61 |
| NF-IL6 | –97 to –132 | Recombinant | + | 62–64 |
+, activator of HIV-1 LTR transcription; –, repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; +/–, shown to be both an activator and repressor of HIV-1 LTR transcription; Recombinant, E.coli synthesised factor, in vitro transcribed/translated or artificially expressed in a cell line.
Acknowledgments
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to members of the AIDS Molecular Biology Unit, in particular Paul F. Lambert and Mandy Ludford-Menting, for helpful discussions and assistance. We thank Prof. John Mills for critical review of the manuscript. L.A.P. was in receipt of a Commonwealth AIDS Research Grant PhD Scholarship. Work in the AIDS Molecular Biology Unit is supported by an Australian Commonwealth AIDS Research Grant as a Laboratory of the National Centre in HIV Virology Research and the Research Fund of the Macfarlane Burnet Centre for Medical Research.
REFERENCES
- 1.Gaynor R. (1992) AIDS, 6, 347–363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rosen C.A., Sodroski,J.G. and Haseltine,W.A. (1985) Cell, 41, 813–823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siekevitz M., Josephs,S.F., Dukovich,M., Peffer,N., Wong-Staal,F. and Greene,W.C. (1987) Science, 238, 1575–1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cooney A.J., Tsai,S.Y., O’Malley,B.W. and Tsai,M. (1991) J. Virol., 65, 2853–2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dasgupta P., Saikumar,P., Reddy,D. and Reddy,E.P. (1990) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 8090–8094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Giacca M., Gutierrez,M.I., Menzo,S., Di Fagagna,F.D. and Falaschi,A. (1992) Virology, 186, 133–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shaw J., Utz,P.J., Durand,D.B., Toole,J.J., Emmel,E.A. and Crabtree,G.R. (1988) Science, 241, 202–205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.El Kharroubi A.E. and Verdin,E. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 19916–19924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rabbi M.F., Saifuddin,M., Gu,D.S., Kagnoff,M.F. and Roebuck,K.A. (1997) Virology, 233, 235–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roebuck K.A., Gu,D.S. and Kagnoff,M.F. (1996) AIDS, 10, 819–826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Van Lint C., Amella,C.A., Emiliani,S., John,M., Jie,T. and Verdin,E. (1997) J. Virol., 71, 6113–6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peeters A. (1997) PhD thesis, Department of Microbiology, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia.
- 13.Peeters A., Lambert,P.F. and Deacon,N.J. (1996) J. Virol., 70, 6665–6672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Roebuck K.A., Brenner,D.A. and Kagnoff,M.F. (1993) J. Clin. Invest., 92, 1336–1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mallardo M., Dragonetti,E., Baldassarre,F., Ambrosino,C., Scala,G. and Quinto,I. (1996) J. Biol. Chem., 271, 20820–20827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jones K.A., Luciw,P.A. and Duchange,N. (1988) Genes Dev., 2, 1101–1114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Du H., Roy,A.L. and Roeder,R.G. (1993) EMBO J., 12, 501–511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Garcia J.A., Harrich,D., Soultanakis,E., Wu,F., Mitsuyasu,R. and Gaynor,R.B. (1989) EMBO J., 8, 765–778 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Seeler J.-S., Muchardt,C., Suessle,A. and Gaynor,R. (1994) J. Virol., 68, 1002–1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Waterman M.L. and Jones,K.A. (1990) New Biol., 2, 621–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mitra D., Sikder,S.K. and Laurence,J. (1996) Virology, 214, 512–521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pessler F., Pendergrast,P.S. and Hernandez,N. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 3786–3798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sheldon M., Ratnasabathy,R. and Hernandez,N. (1993) Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 1251–1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu Y.-Z. and Latchman,D.S. (1997) Biochem. J., 322, 155–158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Montano M.A., Kripke,K., Norina,C.D., Achacoso,P., Herzenberg,L.A., Roy,A.L. and Nolan,G.P. (1996) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 12376–12381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kato H., Horikoshi,M. and Roeder,R.G. (1991) Science, 251, 1476–1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yoon J.B., Li,G. and Roeder,R.G. (1994) Mol. Cell. Biol., 14, 1776–1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhong F., Swendeman,S.L., Popik,W., Pitha,P.M. and Sheffery,M. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 21269–21276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Margolis D.M., Somasundaran,M. and Green,M.R. (1994) J. Virol., 68, 905–910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ou S.-H.I., García-Martínez,L.F., Paulssen,E.J. and Gaynor,R.B. (1994) J. Virol., 68, 7188–7199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sheridan P.L., Schorpp,M., Voz,M.L. and Jones,K.A. (1995) J. Biol. Chem., 270, 4575–4587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bell B. and Sadowski,I. (1996) Oncogene, 13, 2687–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Estable M.C., Bell,B., Hirst,M. and Sadowski,I. (1998) J. Virol., 72, 6465–6474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang Y., Doyle,K. and Bina,M. (1992) J. Virol., 66, 5631–5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Demarchi F., D’Agaro,P., Falaschi,A. and Giacca,M. (1992) J. Virol., 66, 2514–2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Demarchi F., D’Agaro,P., Falaschi,A. and Giacca,M. (1993) J. Virol., 67, 7450–7460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yurochko A.D., Huong,S.M. and Huang,E.S. (1999) J. Hum. Virol., 2, 81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jones K.A. and Peterlin,B.M. (1994) Annu. Rev. Biochem., 63, 717–743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Joel P., Shao,W. and Pratt,K. (1993) Nucleic Acids Res., 21, 5786–5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sawaya B.E., Rohr,O., Aunis,D. and Schaeffer,E. (1996) J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23572–23576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Desai-Yajnik V. and Samuels,H.H. (1993) Mol. Cell. Biol., 13, 5057–5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Desai-Yajnik V., Hadzic,E., Modlinger,P., Malhotra,S., Gechlik,G. and Samuels,H.H. (1995) J. Virol., 69, 5103–5112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jones K.A., Kadonaga,J.T., Luciw,P.A. and Tjian,R. (1986) Science, 232, 755–759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Majello B., De Luca,P., Hagen,G., Suske,G. and Lania,L. (1994) Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 4914–4921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suzuki T., Yamamoto,T., Kurabayashi,M., Nagai,R., Yazaki,Y. and Horikoshi,M. (1998) J. Biochem., 124, 389–395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Imataka H., Mizuno,A., Fujii-Kuriyama,Y. and Hayami,M. (1993) AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, 9, 825–831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kokorina N.A., Santin,A.D., Li,C. and Hermonat,P.L. (1998) J. Hum. Virol., 1, 441–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rahman A., Esmaili,A. and Saatcioglu,F. (1995) J. Biol. Chem., 52, 31059–31064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gualberto A. and A.S. Baldwin,J. (1995) J. Biol. Chem., 270, 19680–19683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shigesada K. personal communication.
- 51.Kinoshita S., Su,L., Amano,M., Timmerman,L.A., Kaneshima,H. and Nolan,G.P. (1997) Immunity, 6, 235–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Macian F. and Rao,A. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 3645–3653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mondal D., Alam,J. and Prakash,O. (1994) J. Mol. Neurosci., 5, 241–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Clark L., Matthews,J.R. and Hay,R.T. (1990) J. Virol., 64, 1335–1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nabel G. and Baltimore,D. (1987) Nature, 326, 711–713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Phares W., Franza,B.R.,Jr and Herr,W. (1992) J. Virol., 66, 7490–7498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Roulston A., Lin,R., Beauparlant,P., Wainberg,M.A. and Hiscott,J. (1995) Microbiol. Rev., 59, 481–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Flory E., Hoffmeyer,A., Smola,U., Rapp,U.R. and Bruder,J.T. (1996) J. Virol., 70, 2260–2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Taylor J.P., Pomerantz,R.J., Oakes,J.W., Khalili,K. and Amini,S. (1995) Oncogene, 10, 395–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kunda M., Guermah,M., Roeder,R.G., Amini,S. and Khalili,K. (1997) J. Biol. Chem., 272, 29468–29474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sweet M.J., Stacey,K.J., Ross,I.L., Ostrowski. M.C. and Hume,D.A. (1998) J. Inflamm., 48, 67–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Henderson A.J., Zou,X. and Calame,K.L. (1995) J. Virol., 69, 5337–5344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ruocco M.R., Chen,X., Ambrosino,C., Dragonetti,E., Liu,W., Mallardo,M., Falco,G.D., Palmieri,C., Franzoso,G., Quinto,I., Venuta,S. and Scala,G. (1996) J. Biol. Chem., 271, 22479–22486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tesmer V.M., Rajadhyaksha,A., Babin,J. and Bina,M. (1993) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 7298–7302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hoover T., Mikovits,J., Court,D., Liu,Y.-I., Kung,H.-f. and Raziuddin. (1996) Nucleic Acids Res., 24, 1895–1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sheridan P.L., Sheline,C.T., Cannon,K., Voz,M.L., Pazin,M.J., Kadonaga,J.T. and Jones,K.A. (1995) Genes Dev., 9, 2090–2104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Holzmeister J., Ludewig,B., Pauli,G. and Simon,D. (1993) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 197, 1229–1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Maekawa T., Sudo,T., Kurimoto,M. and Ishii,S. (1991) Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 4689–4694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Honda Y., Rogers,L., Nakata,K., Zhao,B.Y., Pine,R., Nakai,Y., Kurosu,K., Rom,W.M. and Weiden,M. (1998) J. Exp. Med., 188, 1255–1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Musso T., Bosco,M.C., Longo,D.L., Espinoza-Delgado,I., Sica,A., Cox,G.W., Gusella,G.L., Forni,G. and Varesio,L. (1994) J. Leukoc. Biol., 56, 21–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Li C., Lai,C., Sigman,D.S. and Gaynor,R.B. (1991) Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 88, 7739–7743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Cannone-Hergaux F., Aunis,D. and Schaeffer,E. (1995) J. Virol., 69, 6634–6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ghosh D. (1992) J. Virol., 66, 586–590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zeichner S.L., Hirka,G., Andrews,P.W. and Alwine,J.C. (1992) J. Virol., 66, 2268–2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.West M., Mikovits,J., Princler,G., Liu,Y.L., Ruscetti,F.W., Kung,H.F. and Raziuddin. (1992) J. Biol. Chem., 267, 24948–24952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sikder S.K., Mitra,D. and Laurence,J. (1994) Arch. Virol., 137, 139–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Yang Z. and Engel,J.D. (1993) Nucleic Acids Res., 21, 2831–2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Yamamoto K., Mori,S., Okamoto,T., Shimotohno,K. and Kyogoku,Y. (1991) Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 6107–6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Churchill M.J. (1993) PhD thesis. University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia.
- 80.Guy B., Acres,R.B., Kieny,M.P. and Lecocq,J.-P. (1990) J. AIDS, 3, 797–809. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ladias J.A.A. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 5944–5951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Feng C., Kulka,M. and Aurelian,L. (1993) J. Gen. Virol., 74, 715–723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Orchard K., Lang,G., Collins,M. and Latchman,D. (1992) Nucleic Acids Res., 20, 5429–5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Orchard K., Perkins,N., Chapman,C., Harris,J., Emery,V., Goodwin,G., Latchman,D. and Collins,M. (1990) J. Virol., 64, 3234–3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Towatari M., Kanei,Y., Saito,H. and Hamaguchi,M. (1997) J. AIDS, 12, 253–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Schwartz C., Cannone-Hergaux,F., Aunis,D. and Schaeffer,E. (1997) Nucleic Acids Res., 25, 1177–1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ou S.-H., Wu,F., Harrich,D., Garcia-Martinez,L.F. and Gaynor,R.B. (1995) J. Virol., 69, 3584–3596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sawaya B.E., Khalili,K. and Amini,S. (1998) J. Gen. Virol., 79, 239–246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


