Abstract
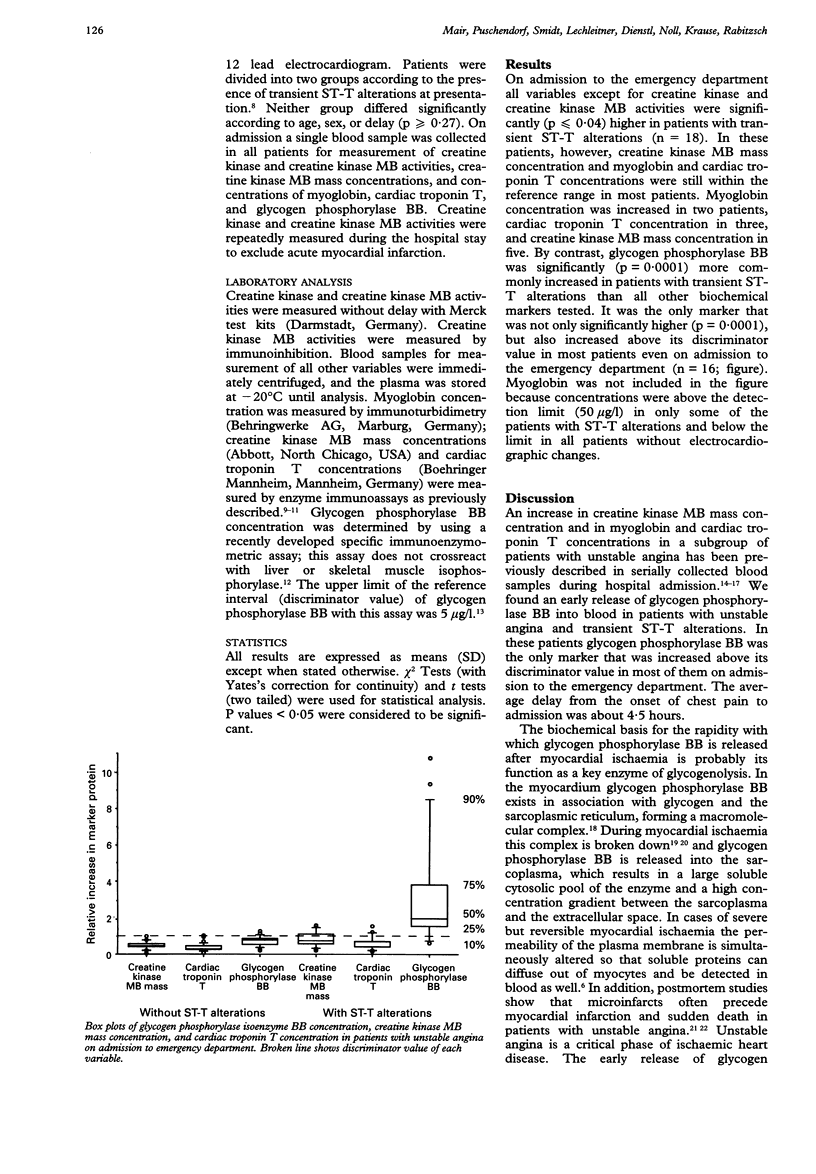
OBJECTIVE--To determine whether transient ST-T alterations in patients with unstable angina are associated with an increase in plasma glycogen phosphorylase BB concentrations on admission to hospital. DESIGN--Prospective screening of patients with unstable angina for markers of myocardial cell damage. SETTING--Accident and emergency department of university hospital. PATIENTS--48 consecutive patients admitted for angina pectoris (18 with transient ST-T alterations). None of the patients had acute myocardial infarction according to standard criteria. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Creatine kinase and creatine kinase MB activities, creatine kinase MB mass concentration, and myoglobin, cardiac troponin T, and glycogen phosphorylase BB concentrations on admission. RESULTS--All variables except for creatine kinase and creatine kinase MB activities were significantly higher on admission in patients with unstable angina and transient ST-T alterations than in patients without. However, glycogen phosphorylase BB concentration was the only marker that was significantly (p = 0.0001) increased above its discriminator value in most patients (16). In the 18 patients with transient ST-T alterations creatine kinase MB mass concentration and troponin T and myoglobin concentrations were significantly (p = 0.0001) less commonly increased on admission (in five, three, and two patients, respectively). CONCLUSIONS--The early release of glycogen phosphorylase BB may help to identify high risk patients with unstable angina even on admission to an emergency department. Glycogen phosphorylase BB concentrations could help to guide decisions about patient management.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt D. R., Gates R. C., Eng K. K., Forsythe C. M., Korom G. K., Nitro A. S., Koffler P. A., Ogunro E. A. Quantifying the MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase with the Abbott "IMx" immunoassay analyzer. Clin Chem. 1990 Feb;36(2):375–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bøtker H. E., Ravkilde J., Søgaard P., Jørgensen P. J., Hørder M., Thygesen K. Gradation of unstable angina based on a sensitive immunoassay for serum creatine kinase MB. Br Heart J. 1991 Feb;65(2):72–76. doi: 10.1136/hrt.65.2.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. C., Knapman P. A., Hangartner J. R. Intramyocardial platelet aggregation in patients with unstable angina suffering sudden ischemic cardiac death. Circulation. 1986 Mar;73(3):418–427. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entam M. L., Kanike K., Goldstein M. A., Nelson T. E., Bornet E. P., Futch T. W., Schwartz A. Association of gylcogenolysis with cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3140–3146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entman M. L., Bornet E. P., Van Winkle W. B., Goldstein M. A., Schwartz A. Association of glycogenolysis with cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum: II. Effect of glycogen depletion, deoxycholate solubilization and cardiac ischemia: evidence for a phorphorylase kinase membrane complex. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1977 Jul;9(7):515–528. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(77)80367-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk E. Unstable angina with fatal outcome: dynamic coronary thrombosis leading to infarction and/or sudden death. Autopsy evidence of recurrent mural thrombosis with peripheral embolization culminating in total vascular occlusion. Circulation. 1985 Apr;71(4):699–708. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.71.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt W., Katus H., Ravkilde J., Hamm C., Jørgensen P. J., Peheim E., Ljungdahl L., Löfdahl P. S-troponin T in suspected ischemic myocardial injury compared with mass and catalytic concentrations of S-creatine kinase isoenzyme MB. Clin Chem. 1991 Aug;37(8):1405–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm C. W., Ravkilde J., Gerhardt W., Jørgensen P., Peheim E., Ljungdahl L., Goldmann B., Katus H. A. The prognostic value of serum troponin T in unstable angina. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 16;327(3):146–150. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207163270302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoberg E., Katus H. A., Diederich K. W., Kübler W. Myoglobin, creatine kinase-B isoenzyme, and myosin light chain release in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Eur Heart J. 1987 Sep;8(9):989–994. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann U., Rabitzsch G., Löster K., Handschack W., Noll F., Krause E. G. Immunenzymometric assay for the heart specific glycogen phosphorylase BB in human serum using monoclonal antibodies. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1989;48(2-3):S132–S136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Shimizu A., Kurobe N., Takashi M., Koshikawa T. Human brain-type glycogen phosphorylase: quantitative localization in human tissues determined with an immunoassay system. J Neurochem. 1989 May;52(5):1425–1432. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katus H. A., Looser S., Hallermayer K., Remppis A., Scheffold T., Borgya A., Essig U., Geuss U. Development and in vitro characterization of a new immunoassay of cardiac troponin T. Clin Chem. 1992 Mar;38(3):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer A., Freeman M. R., Armstrong P. W. ST segment shift in unstable angina: pathophysiology and association with coronary anatomy and hospital outcome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Jun;13(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mair J., Artner-Dworzak E., Lechleitner P., Morass B., Smidt J., Wagner I., Dienstl F., Puschendorf B. Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction by a newly developed rapid immunoturbidimetric assay for myoglobin. Br Heart J. 1992 Nov;68(5):462–468. doi: 10.1136/hrt.68.11.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael L. H., Hunt J. R., Weilbaecher D., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Lewis R. M., Entman M. L. Creatine kinase and phosphorylase in cardiac lymph: coronary occlusion and reperfusion. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 2):H350–H359. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.3.H350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Hwang P. K., Fletterick R. J. The family of glycogen phosphorylases: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24(1):69–99. doi: 10.3109/10409238909082552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Littman D. R., van Genderen C., Smith M., Fletterick R. J. Human brain glycogen phosphorylase. Cloning, sequence analysis, chromosomal mapping, tissue expression, and comparison with the human liver and muscle isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3850–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper H. M., Schwartz P., Spahr R., Hütter J. F., Spieckermann P. G. Early enzyme release from myocardial cells is not due to irreversible cell damage. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1984 Apr;16(4):385–388. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(84)80609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabitzsch G., Mair J., Lechleitner P., Noll F., Hofmann V., Krause E. G., Dienstl F., Puschendorf B. Isoenzyme BB of glycogen phosphorylase b and myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1993 Apr 17;341(8851):1032–1033. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91129-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabitzsch G., Noll F., Hofmann U., Krause E. G., Armbruster F. P. Basal concentration of the isoenzyme BB of the glycogen phosphorylase b in human blood. Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Jan 31;214(1):109–111. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(93)90309-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze W., Krause E. G., Wollenberger A. On the fate of glycogen phosphorylase in the ischemic and infarcting myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1971 Aug;2(3):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(71)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


