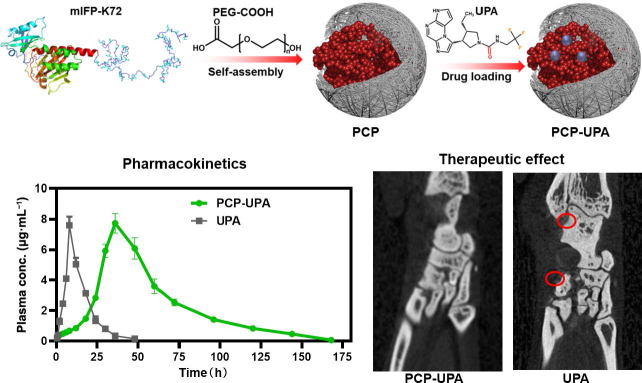
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a relatively common inflammatory disease that affects the synovial tissue, eventually results in joints destruction and even long-term disability. Although Janus kinase inhibitors (Jakinibs) show a rapid efficacy and are becoming the most successful agents in RA therapy, high dosing at frequent interval and severe toxicities cannot be avoided. Here, we developed a new type of fully compatible nanocarriers based on recombinant chimeric proteins with outstanding controlled release of upadacitinib. In addition, the fluorescent protein component of the nanocarriers enabled noninvasive fluorescence imaging of RA lesions, thus allowing real-time detection of RA therapy. Using rat models, the nanotherapeutic is shown to be superior to free upadacitinib, as indicated by extended circulation time and sustained bioefficacy. Strikingly, this nanosystem possesses an ultralong half-life of 45 h and a bioavailability of 4-times higher than pristine upadacitinib, thus extending the dosing interval from one day to 2 weeks. Side effects such as over-immunosuppression and leukocyte levels reduction were significantly mitigated. This smart strategy boosts efficacy, safety and visuality of Jakinibs in RA therapy, and potently enables customized designs of nanoplatforms for other therapeutics.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material (further details of DLS analysis, biocompatibility of PCP-UPA, CIA models construction, etc.) is available in the online version of this article at 10.1007/s12274-023-5838-0.
Keywords: engineered protein, nanocarrier, controlled release, bioefficacy, rheumatoid arthritis
Electronic Supplementary Material
Engineered protein and Jakinib nanoplatform with extraordinary rheumatoid arthritis treatment
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2022YFA0913200, 2021YFF0701800, 2022YFF0710000, and 2020YFA0908900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22107097, 22020102003, 22277064, 82272161, and 22125701), Tsinghua University Spring Breeze Fund grant (No. 2021Z99CFZ005), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS (No. 2021226) All animal experiments were conducted in compliance with the Animal Management Rules of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, and with the approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Animal Experiment Center of Jilin University (No. PZPX20180929070).
Contributor Information
Jian Zhu, Email: jian_jzhu@126.com.
Jingjing Li, Email: jjingli@ciac.ac.cn.
Kai Liu, Email: kailiu@tsinghua.edu.cn.
Huji Xu, Email: huji_xu@tsinghua.edu.cn.
References
- [1].Smolen J S, Aletaha D, McInnes I B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–2038. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Figus F A, Piga M, Azzolin I, McConnell R, Iagnocco A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021;20:102776. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Newsom M, Bashyam A M, Balogh E A, Feldman S R, Strowd L C. New and emerging systemic treatments for atopic dermatitis. Drugs. 2020;80:1041–1052. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01335-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Baker K F, Isaacs J D. Novel therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: What can we learn from their use in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018;77:175–187. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Teng M W L, Bowman E P, McElwee J J, Smyth M J, Casanova J L, Cooper A M, Cua D J. IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines: From discovery to targeted therapies for immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015;27:719–729. doi: 10.1038/nm.3895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Schwartz D M, Kanno Y, Villarino A, Ward M, Gadina M, O’Shea J J. JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017;16:843–862. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Damsky W, Peterson D, Ramseier J, Al-Bawardy B, Chun H, Proctor D, Strand V, Flavell R A, King B. The emerging role of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 0221;177:814–826. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Sandborn W J, Feagan B G, Loftus E V, Jr., Peyrin-Biroulet L, Van Assche G, D’Haens G, Schreiber S, Colombel J F, Lewis J D, Ghosh S, et al. Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib in a randomized trial of patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:2123–2138. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Roskoski R., Jr. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2021 update. Pharmacol. Res. 2021;165:105463. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Serhal L, Edwards C J. Upadacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019;15:13–25. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1544892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Malemud C J. The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2018;10:117–127. doi: 10.1177/1759720X18776224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Burmester G R, Kremer J M, Van Den Bosch F, Kivitz A, Bessette L, Li Y H, Zhou Y J, Othman A A, Pangan A L, Camp H S. Safety and efficacy of upadacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (SELECT-NEXT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2503–2512. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Fang Y, Xue J X, Gao S, Lu A Q, Yang D J, Jiang H, He Y, Shi K. Cleavable PEGylation: A strategy for overcoming the “PEG dilemma” in efficient drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2017;24:22–32. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1388451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Li Y X, Sun J, Li J J, Liu K, Zhang H J. Engineered protein nanodrug as an emerging therapeutic tool. Nano Res. 2022;15:5161–5172. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4103-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Talkington A M, McSweeney M D, Zhang T, Li Z B, Nyborg A C, LaMoreaux B, Livingston E W, Frank J E, Yuan H, Lai S K. High MW polyethylene glycol prolongs circulation of pegloticase in mice with anti-PEG antibodies. J. Control. Release. 2021;338:804–812. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Flintegaard T V, Thygesen P, Rahbek-Nielsen H, Levery S B, Kristensen C, Clausen H, Bolt G. N-glycosylation increases the circulatory half-life of human growth hormone. Endocrinology. 2010;151:5326–5336. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Yousefpour P, Ahn L, Tewksbury J, Saha S, Costa S A, Bellucci J J, Li X H, Chilkoti A. Conjugate of doxorubicin to albumin-binding peptide outperforms aldoxorubicin. Small. 2019;15:1804452. doi: 10.1002/smll.201804452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Metzner H J, Weimer T, Schulte S. Half-life extension by fusion to recombinant albumin. In: Kontermann R, editor. Therapeutic Proteins: Strategies to Modulate Their Plasma Half-Lives. Weinheim: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012. pp. 223–247. [Google Scholar]
- [19].Larsen M T, Kuhlmann M, Hvam M L, Howard K A. Albumin-based drug delivery: Harnessing nature to cure disease. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2016;4:3. doi: 10.1186/s40591-016-0048-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Zhang N, Mei K, Guan P, Hu X L, Zhao Y L. Protein-based artificial nanosystems in cancer therapy. Small. 2020;16:1907256. doi: 10.1002/smll.201907256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Raveendran S, Sen A, Maekawa T, Kumar D S. Three-dimensional visualization of subcellular dynamics of cancer cell destruction on therapeutic nanodrug treatment. Small Struct. 2021;2:2000145. doi: 10.1002/sstr.202000145. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Chang R, Yan X H. Supramolecular immunotherapy of cancer based on the self-assembling peptide design. Small Struct. 2020;1:2000068. doi: 10.1002/sstr.202000068. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Rauf M A, Tasleem M, Bhise K, Tatiparti K, Sau S, Iyer A K. Nano-therapeutic strategies to target coronavirus. View. 2021;2:20200155. doi: 10.1002/VIW.20200155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Wang C Y, Zhang J R, Li B, Zuo J L, Li Y X, Sun Y, Wang F, Liu K, Li J J. High-efficiency treatment for osteoarthritis via self-assembled dual-functionalized nanobiologics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022;8:3320–3328. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Wan S K, Cheng W H, Li J J, Wang F, Xing X W, Sun J, Zhang H J, Liu K. Biological composite fibers with extraordinary mechanical strength and toughness mediated by multiple intermolecular interacting networks. Nano Res. 2022;15:9192–9198. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4595-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Sun J, Chen J S, Liu K, Zeng H B. Mechanically strong proteinaceous fibers: Engineered fabrication by microfluidics. Engineering. 2021;7:615–623. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.02.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Sun J, Li B, Wang F, Feng J, Ma C, Liu K, Zhang H J. Proteinaceous fibers with outstanding mechanical properties manipulated by supramolecular interactions. CCS Chem. 2020;3:1669–1677. doi: 10.31635/ccschem.020.202000231. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Haller J, Hyde D, Deliolanis N, De Kleine R, Niedre M, Ntziachristos V. Visualization of pulmonary inflammation using noninvasive fluorescence molecular imaging. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008;104:795–802. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00959.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Put S, Westhovens R, Lahoutte T, Matthys P. Molecular imaging of rheumatoid arthritis: Emerging markers, tools, and techniques. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014;16:208. doi: 10.1186/ar4542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Lee J H, Jung S Y, Park G K, Bao K, Hyun H, El Fakhri G, Choi H S. Fluorometric imaging for early diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Sci. 2020;7:1902267. doi: 10.1002/advs.201902267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Li J J, Li B, Sun J, Ma C, Wan S K, Li Y X, Göstl R, Herrmann A, Liu K, Zhang H J. Engineered near-infrared fluorescent protein assemblies for robust bioimaging and therapeutic applications. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:2000964. doi: 10.1002/adma.202000964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Ma C, Sun J, Li B, Feng Y, Sun Y, Xiang L, Wu B H, Xiao L L, Liu B M, Petrovskii V S, et al. Ultra-strong bio-glue from genetically engineered polypeptides. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:3613. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23117-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Wang Z L, Gu X Q, Li B, Li J J, Wang F, Sun J, Zhang H J, Liu K, Guo W S. Molecularly engineered protein glues with superior adhesion performance. Adv. Mater. 2022;34:2204590. doi: 10.1002/adma.202204590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Ma C, Li B, Zhang J R, Sun Y, Li J J, Zhou H C, Shen J L, Gu R, Qian J C, Fan C H, et al. Significantly improving the bioefficacy for rheumatoid arthritis with supramolecular nanoformulations. Adv. Mater. 2021;33:2100098. doi: 10.1002/adma.202100098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Li J J, Sun Y, Liang Y X, Ma J, Li B, Ma C, Tanzi R E, Zhang H J, Liu K, Zhang C. Extracellular elastin molecule modulates Alzheimer’s Aβ dynamics in vitro and in vivo by affecting microglial activities. CCS Chem. 2021;3:1830–1837. doi: 10.31635/ccschem.020.202000330. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Wang S D, Li B, Zhang H L, Chen J Y, Sun X, Xu J, Ren T T, Zhang Y Y, Ma C, Guo W, et al. Improving bioavailability of hydrophobic prodrugs through supramolecular nanocarriers based on recombinant proteins for osteosarcoma treatment. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021;60:11252–11256. doi: 10.1002/anie.202101938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Su J J, Lu S, Jiang S J, Li B, Liu B, Sun Q N, Li J J, Wang F, Wei Y. Engineered protein photo-thermal hydrogels for outstanding in situ tongue cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021;33:2100619. doi: 10.1002/adma.202100619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Wu C H, Zhao W W, Zhang X N, Chen X P. Neocryptotanshinone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppression of NF-κB and INOS signaling pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2015;5:323–329. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Xu N L, Wang Y J, Zhao S, Jiao T, Xue H X, Shan F P, Zhang N. Naltrexone (NTX) relieves inflammation in the collagen-induced- arthritis (CIA) rat models through regulating TLR4/NFκB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106056. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Engineered protein and Jakinib nanoplatform with extraordinary rheumatoid arthritis treatment


