Abstract
Provided herein are 2,5-diazabicyclo[4.2.0]octanes as GLP-1 receptor modulators, pharmaceutical compositions, use of such compounds in treating type 2 diabetes, and processes for preparing such compounds.
Important Compound Classes
Title
Certain 2,5-Diazabicyclo[4.2.0]octanes as GLP-1 Receptor Modulators
Patent Publication Number
WO 2023/057427 A1
Publication Date
April 13, 2023
Priority Application
US 63/262,105 and US 63/264,441
Priority Date
October 5, 2021 and November 23, 2021
Inventors
Polla, M.; Bergman, J.; Sundell, J.; Brånalt, J.; Ratkova, E.; Kajanus, J.; Johansson, M.
Assignee Company
AstraZeneca AB, Sweden
Disease Area
Type 2 diabetes
Biological Target
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R)
Summary
Obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) are major and growing health problems worldwide. The two diseases are strongly associated with each other, with obesity proceeding development of insulin resistance and T2D. Incretin hormones including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are gut peptides that are secreted after nutrient intake and stimulate insulin secretion.
GLP-1 is secreted from L-cells in the lower gut in response to food intake. GLP-1 stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreatic cells in a glucose-dependent manner. GLP-1 also inhibits glucagon secretion, reduces appetite and shows down gastric emptying. The GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) is also present in the heart, kidneys and immune system, and its activation has been shown to reduce blood pressure, increase nutrients and decrease inflammation. Pharmacological stimulation of GLP-1 receptors has been shown to significantly reduce HbA1c levels, provide long-term weight loss and reduce blood pressure.
The present application describes a series of novel 2,5-diazabicyclo[4.2.0]octanes as GLP-1 receptor modulators for the treatment of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases, in particular, type 2 diabetes. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, and pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
X1 = N or C;
X2 = N or C, provided that no more than two atoms in the aromatic ring A are N;
Z1 = N or CR3;
Z2 and Z3 = N or CR4, provided that when Z1 or Z3 is N, Z2 is CR4;
R1 = 0, 1, 2, or 3 substituents selected from F, Cl, Br, CN, OCH3, OCFH2, OCF2H, OCF3, CH3, CFH2, CF2H and CF3;
R2 = F, Cl or CN;
R5 = H, CH3, CFH2, CF2H and CF3;
R6 = selected from (4- to 6-membered)heterocycloalkyl, (5- to 6-membered)heteroaryl, CN, C1–4alkyl, O(C1–4alkyl), S(C1–4alkyl), cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, O(cyclopropyl), S(cyclopropyl), wherein (4- to 6-membered)heterocycloalkyl and (5- to 6-membered)heteroaryl is substituted by 0 or 1 substituent selected from C1–4alkyl and wherein said C1–4alkyl is substituted by 0 or 1 substituent selected from CN or OCH3 and 0, 1, 2, or 3 F;
R7 = F, C1–2alkyl and OC1–2alkyl, wherein said C1–2alkyl is substituted by 0, 1, 2, or 3 F;
m = 1, 2 or 3; n = 0 or 1; p = 1, 2 or 3; and q = 0, 1 or 2.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The CHOK1 GLP-1R cAMP assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit GLP-1R. The GLP-1R EC50 values (nM) are shown in the table below.
Biological Data
The following table shows representative
compounds that were tested for GLP-1R inhibition and the biological
data obtained from testing representative examples.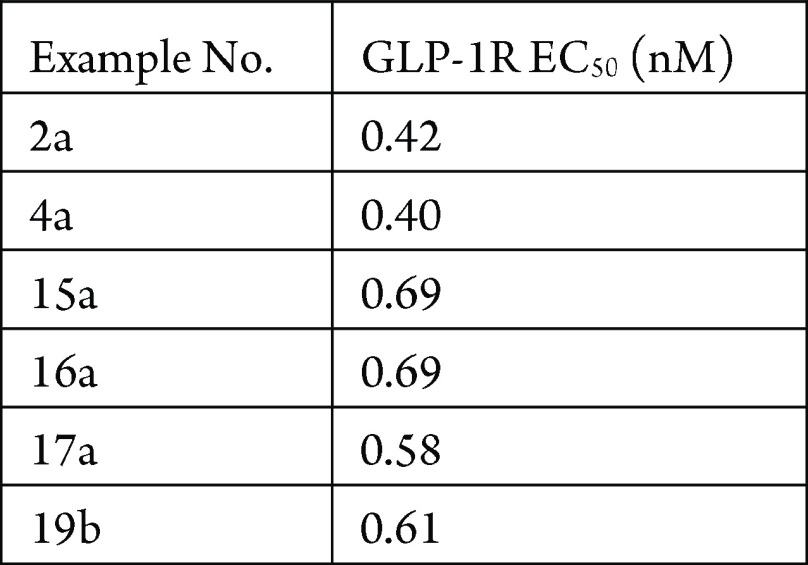
Claims
Total claims: 14
Compound claims: 10
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 2
Use of compound claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Thomas M. C.; Coughlan M. T.; Cooper M. E. The postprandial actions of GLP-1 receptor agonists: The missing link for cardiovascular and kidney protection in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 253–273. 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer G. A.; Hay D. L.; Tups A. Obesity pharmacotherapy: incretin action in the central nervous system. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 50–63. 10.1016/j.tips.2022.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso I.; Marrano N.; Biondi G.; Genchi V. A.; D'Oria R.; Sorice G. P.; Perrini S.; Cignarelli A.; Natalicchio A.; Laviola L.; Giorgino F. Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe?. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, 39, e3609. 10.1002/dmrr.3609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg S. S.; Kushwaha K.; Dubey R.; Gupta J. Association between obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights into signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 200, 110691. 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabnis R. W. Novel 6-Methoxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline Compounds for Treating Diabetes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 891–892. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng W.; Li L.; Li H. Phytochemicals modulate pancreatic islet β cell function through glucagon-like peptide-1-related mechanisms. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 197, 114817. 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





