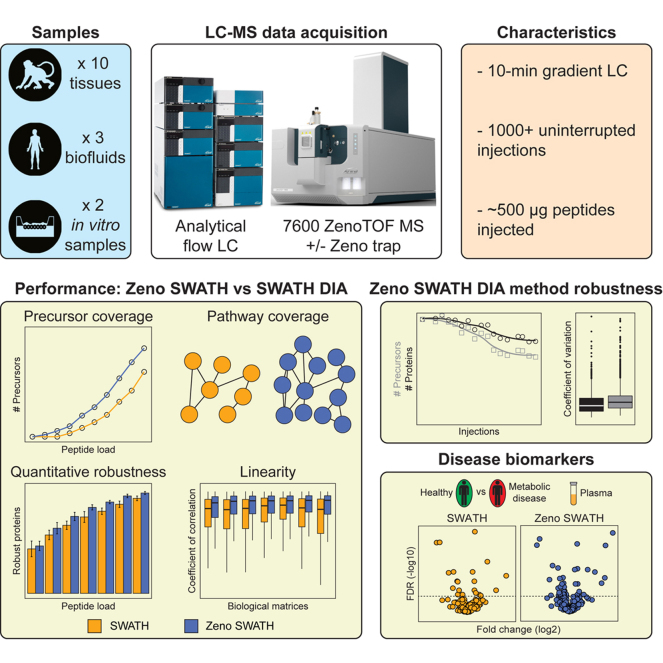
Abstract
Modern mass spectrometers routinely allow deep proteome coverage in a single experiment. These methods are typically operated at nanoflow and microflow regimes, but they often lack throughput and chromatographic robustness, which is critical for large-scale studies. In this context, we have developed, optimized, and benchmarked LC-MS methods combining the robustness and throughput of analytical flow chromatography with the added sensitivity provided by the Zeno trap across a wide range of cynomolgus monkey and human matrices of interest for toxicological studies and clinical biomarker discovery. Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra (SWATH) data-independent acquisition (DIA) experiments with Zeno trap activated (Zeno SWATH DIA) provided a clear advantage over conventional SWATH DIA in all sample types tested with improved sensitivity, quantitative robustness, and signal linearity as well as increased protein coverage by up to 9-fold. Using a 10-min gradient chromatography, up to 3300 proteins were identified in tissues at 2 μg peptide load. Importantly, the performance gains with Zeno SWATH translated into better biological pathway representation and improved the ability to identify dysregulated proteins and pathways associated with two metabolic diseases in human plasma. Finally, we demonstrate that this method is highly stable over time with the acquisition of reliable data over the injection of 1000+ samples (14.2 days of uninterrupted acquisition) without the need for human intervention or normalization. Altogether, Zeno SWATH DIA methodology allows fast, sensitive, and robust proteomic workflows using analytical flow and is amenable to large-scale studies.
Keywords: analytical flow, clinical plasma samples, fast proteomics, Zeno SWATH DIA
Graphical Abstract
Highlights
-
•
Development of a robust and fast proteomics workflow with Zeno SWATH DIA.
-
•
Enhanced sensitivity, data quality, and pathway coverage in 15 biological matrices.
-
•
Reliable and consistent method over 1000+ uninterrupted injections.
-
•
Identification of ∼80% more potential disease biomarkers in clinical plasma samples.
In Brief
In this work, we developed and optimized fast proteomics workflows combining analytical flow LC and Zeno Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra (SWATH) data-independent acquisition (DIA) across a range of biological matrices and assessed the performance gain relative to SWATH DIA. Enabling the Zeno trap systematically improved all the performance metrics examined and identified more potential disease biomarkers in clinical plasma samples. Importantly, the methods developed were extremely robust minimizing the need for human intervention in large-scale studies.
Recent advances in mass spectrometry (MS)–based proteomics, including instrumentation, chromatography, data acquisition strategies, and processing software, allow high-quality deep proteome coverage in a single-run experiment. These advancements are fueling a growing interest in utilizing those technologies in applications requiring high-throughput phenotypic readouts at scale. Notably, MS-based proteomics is emerging as a key player in drug discovery with the promise to accelerate (i) target identification and validation, (ii) lead discovery and optimization as well as (iii) preclinical and clinical assessments of drug safety and efficacy (1). Recently, deep proteome profiling of ∼900 cancer cell lines by MS identified thousands of potential biomarkers of cancer vulnerabilities (2). In addition, proteomics has been widely applied to the field of precision medicine enabling patient stratification (3) and improving patient management (4).
Among discovery-driven acquisition strategies, data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and data-independent acquisition (DIA) methodologies are the most popular. While in DDA, a predefined number of the most abundant peptides from survey scans are selected for fragmentation, all peptides in a sliding m/z window in MS1 scans are selected for fragmentation in DIA. Therefore, DIA demonstrated better quantification robustness, data completeness, and sensitivity than DDA (5). Among DIA methodologies, Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra (SWATH-MS) is a widely used methodology that allows deep proteome coverage with quantitative consistency and accuracy (6). A recent multilaboratory evaluation study demonstrated its reproducibility as well as quantitative and qualitative performances (7).
To date, SWATH-MS methods have been primarily operated at nanoflow (7) and microflow regimes (2) providing excellent proteome depth and data quality. However, these methods often lack throughput and chromatographic robustness necessary for the analysis of large studies. In this context, we developed, optimized, and benchmarked robust and high-throughput analytical flow LC-MS methods with Zeno SWATH DIA approach. Taking advantage of the Zeno trap, Zeno SWATH methods consistently provided higher sensitivity and protein coverage as well as superior data quality across a wide variety of biological matrices in comparison to SWATH. Furthermore, Zeno SWATH DIA improved pathway analysis and enhanced the ability to identify plasma biomarkers for two metabolic diseases in humans, demonstrating the clinical application of this novel method.
Experimental Procedures
Experimental Design and Statistical Rationale
This work was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki ethical principles. The following experiments were performed: (i) triplicate injections of 10-point dilution series from 10 cynomolgus monkey tissues, three human biofluids and two in vitro samples from air-liquid interface cultures, (ii) singlicate injection of clinical plasma samples from 20 healthy individuals and 20 individuals diagnosed with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and 10 individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (T2D), and (iii) repetitive singlicate injection of commercial HeLa cell protein digest along the sequence (n = 17). All experiments were conducted in SWATH DIA mode with and without Zeno trap activated on the same instrument, and HeLa experiments were performed with Zeno trap activated. All data were acquired in a single uninterrupted sequence and are available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD039414. Dilution series were acquired to assess the performance of SWATH DIA experiments with Zeno trap activated (i.e., sensitivity, coverage, signal linearity) and technical replicates were used to evaluate quantitative robustness by calculating coefficients of variation (CVs). Dilution series were run from low to high loads to avoid potential carryover. Clinical plasma samples were run in a random order. Repetitive injections of HeLa extracts were used to evaluate instrument stability over time and method reproducibility. Data processing was performed with DIA-NN (v1.8.1). Additional information on the samples analyzed, data acquisition, and processing procedures can be found below.
Materials and Reagents
Acetonitrile (ACN, LC-MS grade), water (LC-MS grade), methanol (LC-MS grade), 2-chloroacetamide, phosphoric acid solution, and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Bond-Breaker tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) solution, 1M triethylammonium bicarbonate (TEAB), trypsin/Lys-C protease mix (cat# A40009), Pierce protease inhibitor mini tablets (cat# A32953), Pierce HeLa protein digest standard (cat# 88329), and formic acid (LC-MS grade) were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Sample Collection and Origin
Cynomolgus monkey tissue samples including bone marrow, cecum, colon, heart, kidney, liver (left lateral), lung, rectum, spleen, and stomach were collected from healthy cynomolgus monkeys immediately after sacrifice. The procedures involving the care and use of animals were reviewed and approved by Charles River—Nevada Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, and the care and use of animals were conducted following the guidelines of the USA National Research Council. Experiments were conducted using a single tissue piece from a single specimen. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids were collected from 10 healthy individuals using sterile saline. Samples were then filtered with 100 μm filters and centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The resulting supernatants were immediately aliquoted and frozen at −80 °C until further analysis. A pool of all the BAL samples was used in this work. BAL collection was approved by The National Jewish Health institute Ethics committee, and informed consent forms were obtained from all participants. Commercial human EDTA-plasma samples from 20 individuals self-reported as healthy were purchased from BioIVT and EDTA-plasma samples from 20 individuals diagnosed with NASH, and 10 individuals diagnosed with T2D were purchased from ProteoGenex (lot numbers and subject demographics information are available in supplemental Table S4). Commercial samples were obtained following official protocols, with appropriate Institutional Review Board/Independent Ethics Committee approval, which operates in accordance with the current Federal Regulations in addition to ICH, HIPAA, and GCP guidelines pertaining to protection of human subjects. Human subject confidentiality and privacy were ensured by de-identification of all biological samples using a coding system (see respective vendor websites for more details). A pool of all healthy plasma samples was used for the dilution series experiment. Induced human sputum samples from two healthy donors were purchased from BioIVT and pooled for analysis. Mucus and media samples were obtained from in vitro air–liquid interface (ALI) bronchial cell cultures and pooled from experiments performed with primary bronchial cells from three to six human donors. Cryopreserved primary normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells were purchased from Lonza (CC-2540 & CC-2540S) and ATCC (PCS-300–010). NHBE cells were expanded and maintained at an ALI as described previously (8, 9) with minor modifications. Briefly, NHBE cells were expanded in BEGM growth medium (cat# CC-3170, Lonza) before being plated onto Collagen type IV (cat# C7521, Sigma)-coated 0.4-μm pore-size transwells (cat# CLS3470, Corning) and cultured under liquid–liquid interface growth conditions with complete BEGM medium. ALI culture conditions were initiated when cells reached confluence by removal of apical medium and replacement of basolateral growth medium with B-ALI differentiation medium (cat# 193517, Lonza) supplemented with SingleQuots (cat# 193515, Lonza) and retinoic acid (cat# R2625, Sigma). After 4 weeks of airlift culture, the mucus overlaying the epithelium was washed apically using PBS before being collected along with medium samples. All the samples were stored at −80 °C prior to the study.
Sample Preparation
Approximately 25 mg of frozen tissues were transferred to 2 ml Eppendorf Protein Lobind tubes containing one 5 mm stainless steel bead (cat# 69989, Qiagen) and 500 μl of lysis buffer consisting of 5% SDS in 50 mM TEAB with protease inhibitors cocktail (cat# A32953, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Tissue pieces were disrupted with TissueLyser LT (Qiagen) at 50 Hz (1 min ‘on’, 1 min ‘off’ on ice) until fully homogenized. Four microliters of nondepleted plasma was added to 46 μl of lysis buffer, and sputum (200 μl), BAL (300 μl), mucus (300 μl), and media (150 μl) samples were first dried to completion under a stream of nitrogen (TurboVap 96, Biotage) and resolubilized in 50 μl of lysis buffer. Homogenates were sonicated on ice for 5 min at 30% amplitude (1 min ‘on’, 15s ‘off’) with a Qsonica sonicator (Q700MPX) and centrifuged for 10 min at 14,000g at 18 °C. The supernatants were then collected, and protein concentrations were determined using Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (cat# 23225, Thermo Fisher Scientific) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Reduction and alkylation of proteins were performed after incubation of the extracts at 95 °C for 10 min by adding 5 μl of 100 mM TCEP and 5 μl of 400 mM chloroacetamide each followed by an incubation at 95 °C for 5 min.
On-column digestion was performed using S-Trap sample processing technology in 96-well plate format (100–300 μg per well, cat# NC1508276, Protifi LLC) following the manufacturer’s instructions. First, proteins were further denatured by adding 5 μl of phosphoric acid (12%) followed by 300 μl of S-Trap binding buffer (90% MeOH, 100 mM final TEAB, pH 7.1) to protein extracts (15–150 μg of proteins). Proteins were then loaded and captured on the S-Trap columns following centrifugation at 1,500g for 2 min at room temperature. Proteins were then washed three times with 200 μl S-Trap binding buffer (90% MeOH, 100 mM final TEAB, pH 7.1) and centrifuged at 1,500g for 2 min. Protein digestion was performed overnight at 37 °C with trypsin/Lys-C protease mix (cat# A40009, Thermo Fisher Scientific) in 125 μl 50 mM TEAB (1:30 enzyme:protein ratio). Stepwise elution of peptides was performed with 80 μl of 50 mM TEAB, 80 μl of 0.2% formic acid in water, and 80 μl of 0.2% formic acid in 50% ACN each followed by centrifugation at 1,500g for 2 min. Flowthroughs were then pooled and dried under a stream of nitrogen (TurboVap 96, Biotage), and peptides were resuspended in 100 μl of 0.1% (v/v) formic acid in 5% (v/v) ACN. Peptide concentrations were determined using Pierce Quantitative Colorimetric Peptide Assay (cat# 23275, Thermo Fisher Scientific), and samples were frozen at −80 °C until LC-MS data acquisition.
Untargeted Proteomics by LC-MS
Peptide extracts were analyzed using an Exion LC system coupled with a 7600 ZenoTOF mass spectrometer (SCIEX). Peptides were separated on an Acquity BEH C18 column 2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 μm (cat# 186003687, Waters), and mobile phase solvents consisted in 0.1% formic acid in water (A) and 0.1% formic acid in ACN (B). Peptides were eluted from the column using a 10-min linear gradient (5–40% B) at a flow rate of 0.2 ml/min, and the oven temperature was set at 40 °C. Autosampler temperature was set at 10 °C. The 7600 ZenoTOF was equipped with an OptiFlow Turbo V ion source and operated in SWATH mode with or without Zeno trap activated. The source conditions were as follows: ionization voltage: 5500 V, positive polarity, temperature: 500 °C, ion source gas 1: 60 psi, ion source gas 2: 80 psi, curtain gas: 40 psi. The acquisition settings were as follows: number of Q1 windows: 50, MS1 accumulation time: 100 ms, MS1 m/z range: 400 to 900 Da, MS2 accumulation time: 18 ms (plasma and media) or 15 ms (rest of the samples), MS2 m/z range: 100 to 900 Da. Q1 window widths were determined for each sample type from DDA runs using SWATH Variable Window Calculator_V1.2 provided by SCIEX. All tissues were run with the same method optimized on liver sample. External calibration was performed every three to eight runs using the automatic calibration function and ESI positive calibration solution for SCIEX X500B system (cat# 5049910, SCIEX). Ten-point dilution series (3.9 ng – 2000 ng) were prepared the day prior to the experiment, stored at 4 °C overnight, and injected from low to high concentrations in triplicates in both SWATH DIA and Zeno SWATH DIA modes. Healthy and diseased plasma samples were injected in singlicate in a random order in SWATH mode first followed by Zeno SWATH. All samples were injected no more than 1.7 days after being loaded in the autosampler. Signal stability over time and method robustness were monitored by repetitive injection of 800 ng of HeLa protein digest (cat# 88329, Thermo Fisher Scientific) in Zeno SWATH mode. HeLa protein digest sample was left in the autosampler, and the detector parameters were left unchanged during the whole duration of the study.
Data Processing
All raw data were processed with DIA-NN (v1.8.1) with a fragment ion m/z range of 200 to 1800, precursor false-discovery rate (FDR) threshold of 1%, automatic settings of mass accuracy at the MS2 and MS1 level and scan window, protein inference of ‘Genes’ and quantification strategy of “robust LC (high precision)". For dilution series, triplicate samples from each dilution level and acquisition mode were processed separately with cross-run normalization disabled and analyzed with match-between-runs enabled. Clinical plasma samples from each case study and each acquisition mode were processed separately with cross-run normalization enabled (‘RT-dependent’) and analyzed with match-between-runs enabled. All database searches were performed using in silico predicted libraries from Homo sapiens UniProt canonical sequence database (UP000005640 containing 29,376 protein groups) for human biofluids and in vitro samples and Macaca fascicularis UniProt canonical sequence database (UP000233100 containing 32,943 protein groups) for cynomolgus monkey tissues. Predicted libraries were generated using the following parameters: Trypsin/P, one missed cleavage allowed, N-term M excision, fixed modification: C carbamidomethylation, variable modification: none, peptide length range: 7 to 30 amino acids, precursor charge range: 1 to 4. Mass tolerance for precursor and fragment ions was determined automatically in DIA-NN based on the first run in the experiment. Details on library of decoy precursors generation and data matching to spectral libraries can be found in the original DIA-NN article (10). HeLa digests were processed using an experimental library generated from HeLa and K562 cell extracts provided by SCIEX. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (11) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD039414.
Data Analysis and Visualization
Unless otherwise mentioned, analyses were performed in R (v4.1.3) and RStudio (v1.4.1103). For all analyses pertaining to dilution series, global FDR thresholds of 1% and 5% were used for precursors and protein groups, respectively (Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3 and S1–S3). Analysis of clinical plasma samples was performed using global FDR thresholds of 1% for precursors and protein groups (Figs. 4 and S4).
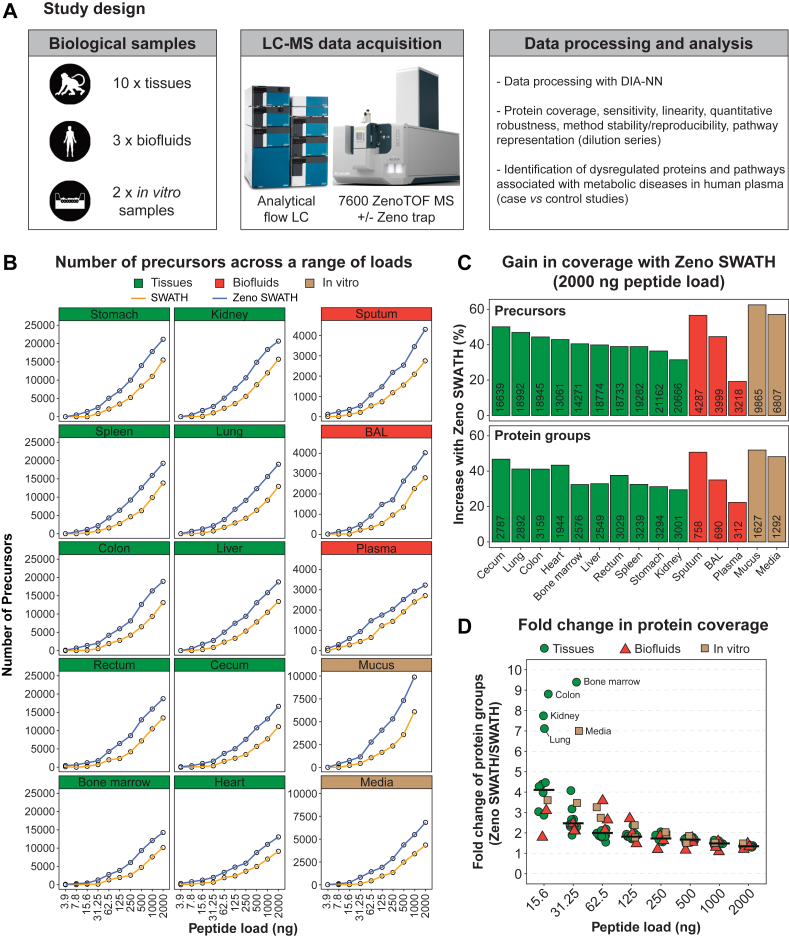
Fig. 1.
Study design, assay sensitivity and proteome coverage.A, overview of the study design including cynomolgus monkey and human matrices analyzed with an analytical flow SWATH DIA workflow with and without Zeno trap activated and analysis plan. B, number of precursors identified across technical triplicates in various biological matrices at different peptide loads in SWATH and Zeno SWATH DIA modes. Peptide loads range from 3.9 ng to 2000 ng for all sample types except for mucus that ranges from 3.9 ng to 1000 ng. C, gain in precursors and protein groups with Zeno SWATH in comparison to SWATH at the highest peptide load (2000 ng). The number of precursors and protein groups detected with Zeno trap activated is indicated in bars. D, fold change in protein groups identified in Zeno SWATH mode across peptide loads. The horizontal bars represent the median. See also supplemental Fig. S1. DIA, data-independent acquisition; SWATH, Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra.
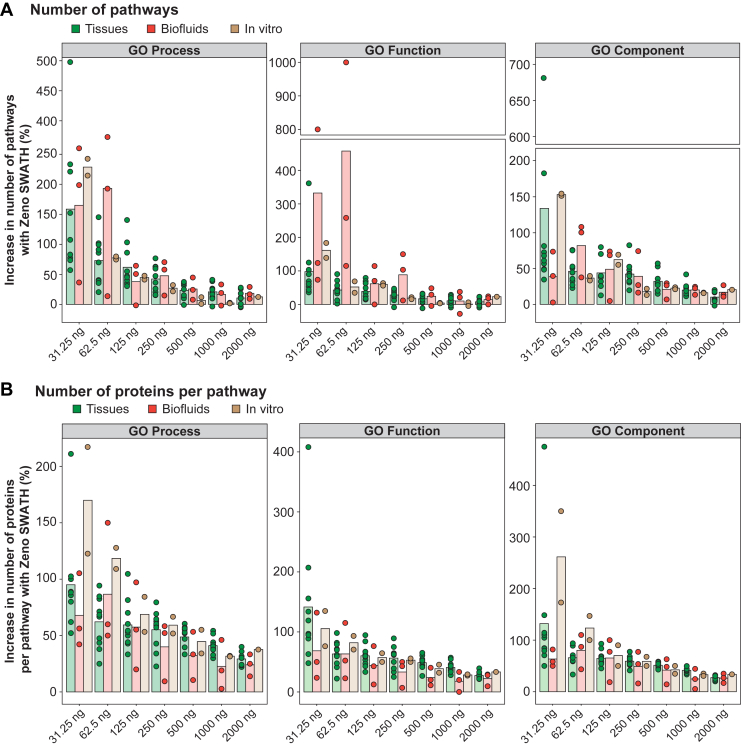
Fig. 2.
Pathway representation with and without Zeno trap activated.A, gain in pathway coverage using proteins identified in Zeno SWATH DIA mode in comparison to SWATH DIA. Pathway enrichment was performed using Gene Ontology database. B, gain in number of proteins per pathway in Zeno SWATH DIA mode in comparison to SWATH DIA. Pathways covered in both modes were used in this analysis. Bars represent the mean across samples belonging to each matrix type (tissues [n = 10], biofluids [n = 3], in vitro samples [n = 2]). See also supplemental Fig. S2. DIA, data-independent acquisition; SWATH, Sequential Windowed Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra.
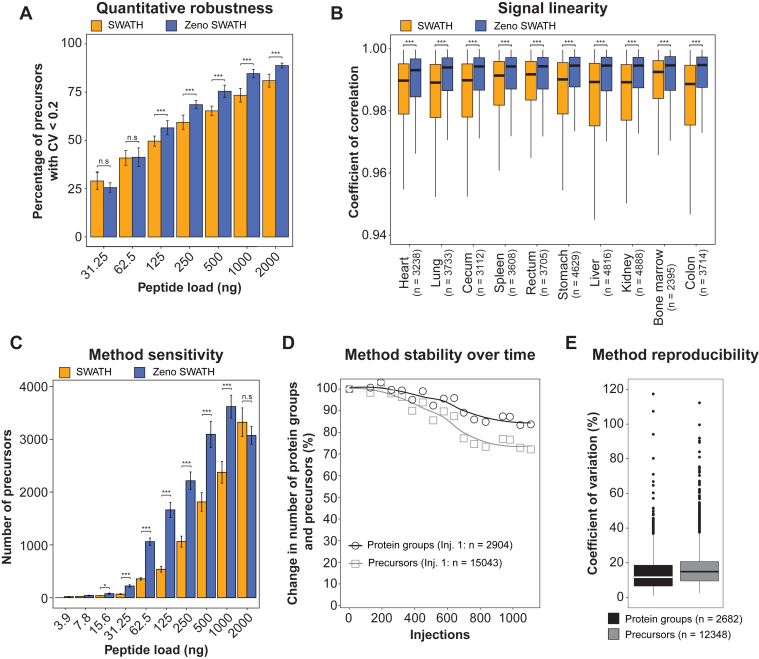
Fig. 3.
Evaluations of quantitative robustness, signal linearity, and method stability over time.A, proportion of precursors with a coefficient of variation (CV) below 0.2 calculated across technical triplicates at different loads in SWATH and Zeno SWATH DIA modes. Only precursors detected in 100% of the triplicates were considered, and only conditions with more than 50 proteins identified were plotted. Bars represent the mean across 10 cynomolgus monkey tissues, and the error bars represent the standard deviation. A two-sided Welch’s t test was used for differential analysis. n.s: not significant, ∗: p-value <0.05, ∗∗∗ p-value <0.001. Proportion of proteins with a CV below 0.2 in tissues, biofluids and in vitro samples are available in supplemental Fig. S3A. B, boxplot showing the distribution of Pearson coefficients of correlation of precursor abundances against peptide loads in cynomolgus monkey tissues. Only precursors detected in at least three levels in both SWATH and Zeno SWATH DIA modes were considered in the analysis. The number of precursors is indicated in parenthesis. The box illustrates the first and third quartile, the whiskers are 1.5 times the interquartile range, and the horizontal bar depicts the median of the distribution. A two-sided Mann–Whitney U test was used for differential analysis. ∗∗∗ p-value <0.001. Boxplot showing the distribution of Pearson coefficients of correlation of precursor abundances against peptide loads in biofluids and in vitro samples are available in supplemental Fig. S3B. C, ability of Zeno SWATH and SWATH methods to robustly quantify precursors across loads in cynomolgus monkey tissues. Bars represent the mean across 10 cynomolgus monkey tissues and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean. A two-sided Welch’s t test was used for differential analysis. n.s: not significant, ∗: p-value <0.05, ∗∗∗ p-value <0.001. The results obtained from biofluids and in vitro samples are available in supplemental Fig. S3C. D, number of protein groups and precursors detected in quality control HeLa protein digest samples (n = 17) in Zeno SWATH DIA mode along the study. The curves represent a LOESS (locally estimated scatterplot smoothing) fit. The numbers of protein groups and precursors detected in the first injection of HeLa digest are indicated in parenthesis. E, coefficient of variation of protein groups and precursors detected in at least half of the HeLa samples. The number of protein groups and precursors considered for the analysis are indicated in parenthesis. The box illustrates the first and third quartile, the whiskers are 1.5 times the interquartile range, and the horizontal bar depicts the median of the distribution. See also supplemental Fig. S3. DIA, data-independent acquisition; SWATH, Sequential Windowed Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra.
Fig. 4.
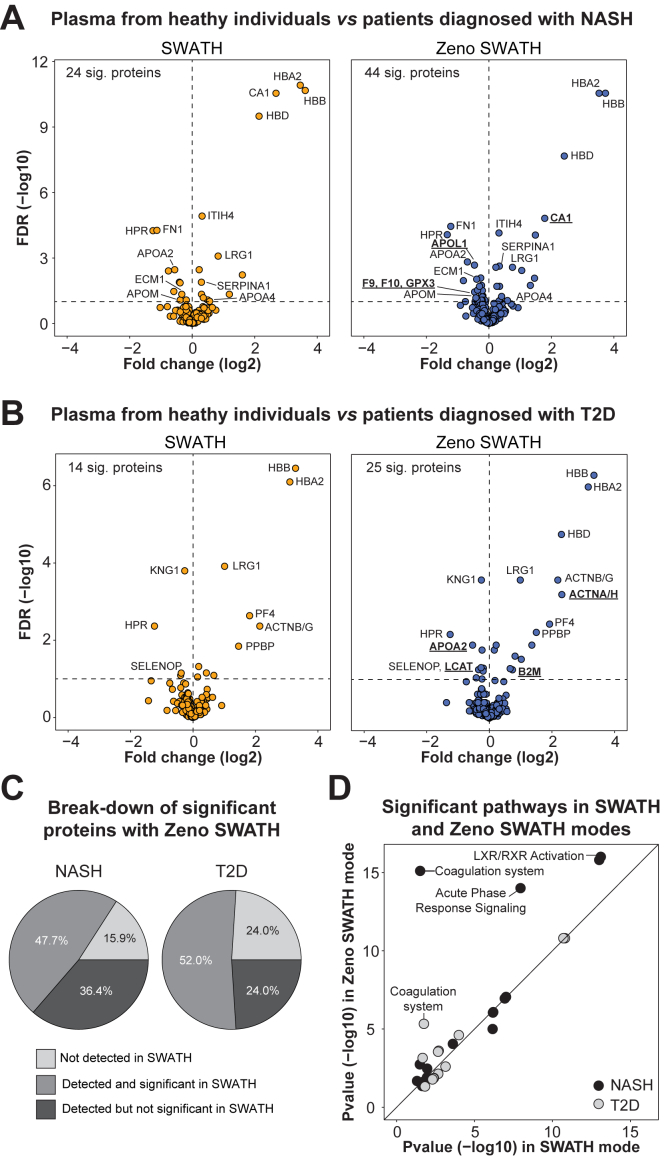
Clinical proteomics biomarker discovery.A and B, volcano plots representing differential proteins in individuals diagnosed with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, n = 20) (A) and type 2 diabetes (T2D, n = 10) (B) in comparison to healthy individuals (n = 20). A two-sided Welch’s t test was used for differential analysis and proteins with FDR < 0.1 were considered significant. Proteins underlined and in bold are uniquely significant in Zeno SWATH mode. C, pie charts representing the proportion of significant proteins (FDR <0.1) in Zeno SWATH DIA mode that were (i) not detected, (ii) detected and significant, and (iii) detected but not significant in SWATH DIA mode. D, comparison of pathway significance using significant proteins identified in SWATH and Zeno SWATH DIA modes in NASH and T2D studies. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis was used for enrichment analysis, and pathways with p-values <0.05 were considered significant. See also supplemental Fig. S4. B2M, beta-2 microglobulin; DIA, data-independent acquisition; ECM1, extracellular matrix protein 1; FDR, false-discovery rate; GPX3, glutathione peroxidase 3; ITIH4, inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4; LCAT, lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase; LRG1, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1; PF4/CXCL4, platelet factor 4; PPBP, pro-platelet basic protein; SELENOP, selenoprotein P; SERPINA1, alpha-1 antitrypsin; SWATH, Sequential Windowed Acquisition of All Theoretical Fragment Ion Mass Spectra.
Protein content similarity in tissue samples was assessed by calculating pairwise Pearson correlations of median expression levels across triplicates using protein groups present in at least 50% of the tissue samples (supplemental Fig. S2). The heatmap was plotted using pheatmap package (v1.0.12) in R, and the clustering distance used was ‘maximum’. Pathway analysis in tissues was performed using STRINGdb package (v2.6.5) in R, and database version 11.5 for species 9541 (M. fascicularis) was used for the analysis. Enrichment analyses were performed using the detected proteins in each condition, and all the proteins in the database were used as background. Pathways with FDR <0.05 were considered significant (Fig. 2). The number of protein groups per pathway was calculated in pathways covered with and without Zeno trap activated (Fig. 2B). CVs were calculated across triplicate injections, and the proportions of precursors and protein groups with a CV < 0.2 were determined relative to proteins detected in 100% of the triplicates (Figs. 3A and S3A). Differential analysis was performed using a two-sided Welch’s t test. Pearson coefficients of correlation of precursor abundances against peptide loads were calculated in all matrices (Figs. 3B and S3B). Only precursors detected in at least three levels in both SWATH and Zeno SWATH modes were considered in the analysis. A two-sided Mann–Whitney U test was used for differential analysis. The ability to robustly quantify precursors across loads was determined on precursors with a CV below 0.2 across triplicate injections (Figs. 3C and S3C). Differential analysis was performed using a two-sided Welch’s t test. Coefficients of variation in HeLa protein digests were calculated using protein groups and precursors detected in at least half of the samples (Fig. 3E). Analysis of plasma samples from healthy and diseased individuals was performed as follows: (i) discard protein groups present in less than 50% of the plasma samples within each study, (ii) minimum value imputation, and (iii) statistical analysis using a two-sided Welch’s t test (Fig. 4). The p-values were adjusted using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure, and proteins with FDR <0.1 were considered significant. Pathway analysis was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (v81348237, Qiagen), and pathways with p-value <0.05 were considered significant (Fig. 4D).
Results
Zeno Trap Enhances Sensitivity and Proteome Coverage
The Zeno trap featured on SCIEX 7600 ZenoTOF instrument is a linear ion trap located after the collision cell that reportedly improves detectability of fragments by up to 20-fold (12, 13, 14). This increased sensitivity can mitigate the main drawback of analytical flow methods (i.e. limited sensitivity) in comparison to more conventional microflow or nanoflow set-ups. To assess the gain in information obtained with Zeno trap activated, we prepared protein extracts from a variety of biological matrices including 10 cynomolgus monkey tissues (stomach, kidney, spleen, lung, colon, liver, rectum, cecum, bone marrow, and heart), three human biofluids (sputum, BAL fluid, and nondepleted plasma), and two in vitro samples from air–liquid interface cultures (mucus and media) (Fig. 1A).
Peptide separation was performed at an analytical flow regime with a 10-min gradient chromatography to ensure throughput and robustness, and LC-MS parameters were optimized to identify the most protein groups and precursors in each biological matrix. The parameters evaluated included flow rate, source parameters, MS1 and MS2 accumulation time as well as SWATH window number and window width (Methods and supplemental Tables S1 and S2). Notably, the optimal parameters selected were slightly different for each sample type reflecting variable protein compositions and expression levels.
Sensitivity and protein coverage were determined on 10-point dilution series across all biological matrices (3.9 ng to 2000 ng) using optimized LC-MS methods with and without Zeno trap activated and raw data were processed using in silico predicted libraries in DIA-NN (Methods) (10). Zeno SWATH DIA methods systematically detected more precursors and protein groups at all peptide loads across all sample types in comparison to conventional SWATH DIA methods run on the same instrument (Figs. 1B and S1A). At maximum load (2000 ng), enabling Zeno trap increased the number of detected precursors by 20 to 60% and protein groups by 20 to 50% (Fig. 1C). Among the various sample types, nondepleted plasma benefited the least from the boost in sensitivity, while sputum, mucus, and media benefited the most. At 2000 ng load, Zeno SWATH methods detected 13,100 to 21,200, 3200 to 4300, and 6800 to 9900 precursors in tissues, biofluids, and in vitro samples, respectively, corresponding to 1950 to 3300, 300 to 750, and 1300 to 1600 protein groups.
While Zeno trap improved protein coverage at high loads, the gain in sensitivity was the most remarkable at low peptide loads (15.6 ng and 31.25 ng) with increases in protein and precursor coverage by 2- to 4-fold across the various matrices and up to 9-fold for bone marrow and colon (Figs. 1D and S1B). Tissues and in particular bone marrow, colon, kidney, and lung benefited the most from the increase in sensitivity due to their distribution in protein abundances where (1) a relatively small number of proteins were detected with SWATH DIA and (2) the boost in sensitivity provided by the Zeno trap enabled identification of many additional proteins. Finally, while SWATH methods were unable to detect any precursor at very low peptide loads (3.9 ng and 7.8 ng), Zeno SWATH methods typically enabled detection of precursors and protein groups at these loads, demonstrating the utility of this technology when sample input is limited (Figs. 1B and S1A).
Zeno Trap Improves Pathway Coverage
First, we investigated global protein expression profiles of cynomolgus monkey tissues using hierarchical clustering to assess data quality. As expected, samples from the gastrointestinal tract (cecum, rectum, colon, and stomach) and hematopoietic tissues (bone marrow and spleen) clustered together indicating similarities in protein expression (supplemental Table S2). These results confirm previous observations made in human tissues (15).
Next, we asked whether the gain in protein coverage with Zeno trap activated could improve pathway representation. Pathway enrichment analysis was performed using Gene Ontology (GO) database (16, 17) and revealed a systematic increase in pathway coverage across GO categories and peptide loads with larger gains at lower loads (Fig. 2A and supplemental Table S3). We observed an average increase in GO Process, Function, and Component pathways by 159%, 98%, and 133%, respectively at 31.25 ng peptide load in tissues. Similarly, pathway coverage increased by 179% and 181% on average across GO databases in biofluids and in vitro samples, respectively, at 31.25 ng peptide load. While the gain in pathway coverage was mostly comparable among tissues and in vitro samples, results from biofluid specimens were more variable. In particular, pathway coverage increase in nondepleted plasma was modest in comparison to other biofluids (54% on average across GO databases at 31.25 ng peptide load), reflecting the limited improvement in the number of proteins detected.
In addition, the number of proteins detected per pathway was assessed in pathways captured in both SWATH and Zeno SWATH modes. We observed a substantial increase in the number of proteins identified per pathway with +123%, +67%, and +179% proteins on average across GO databases in tissues, biofluids, and in vitro samples, respectively, at 31.25 ng peptide load (Fig. 2B and supplemental Table S3).
Altogether, Zeno SWATH DIA provided more biologically meaningful information by covering more pathways and improving pathway level data quality.
Zeno Trap Enhances Quantitative Robustness, Signal Linearity and Method Performance Is Stable Over Time
In addition to proteome coverage and sensitivity, the quantitative quality of the data generated in Zeno SWATH mode was assessed leveraging dilution series and technical triplicates at each level. Quantitative robustness—as calculated by the proportion of precursors robustly quantified with a CV below 0.2 across triplicate injections—was significantly improved in tissues at all peptide loads above 62.5 ng (Fig. 3A). For instance, 88.8% ± 1.3% and 81.0% ± 3.3% of precursors were detected with a CV < 0.2 in Zeno SWATH and SWATH modes, respectively, at 2000 ng peptide load. At protein groups level, 91.3% ± 1.3% and 86.5% ± 2.1% of proteins were detected with a CV < 0.2 in Zeno SWATH and SWATH modes, respectively, at 2000 ng peptide load (supplemental Fig. S3A). Similar observations were made in biofluids and in vitro samples (supplemental Fig. S3A). Signal linearity was assessed by calculating Pearson coefficients of correlation of precursor intensities against peptide loads. While high coefficients of correlation were observed in both modes (r > 0.98 in average), Zeno SWATH significantly improved linearity in all matrices (p-value <1.3E-04, Figs. 3B and S3B). We also investigated the ability of Zeno SWATH and SWATH methods to robustly quantify precursors across loads by categorizing precursors based on the smallest load that allowed robust quantification of each precursor (CV < 0.2 across triplicate injections). As expected, a clear increase in the number of reliable precursors was observed at lower loads with Zeno SWATH DIA confirming the gain in sensitivity (Figs. 3C and S3C).
We demonstrated that the combination of analytical flow chromatography with a 10-min gradient and Zeno SWATH DIA enhanced sensitivity, expanded protein coverage, and generated higher quality data. However, for this method to be well suited to large-scale studies, method stability over time remained to be shown. To evaluate method stability, HeLa digests (n = 17) were injected repetitively along the study which consisted in uninterrupted injections of 1000+ samples (equivalent to ∼500 μg peptides injected in total) that lasted 14.2 days. We observed a modest decrease in the number of precursors (27.8%) and protein groups detected (16.6%) demonstrating method robustness (Fig. 3D). In addition, signal intensity remained stable without the need for normalization with median coefficients of variation across all HeLa digest injections of 14.9% and 11.7% for precursors and protein groups, respectively (Fig. 3E).
Altogether, we have demonstrated robust and consistent performance of our high-throughput LC-MS method over the injection of 1000+ samples without the need for human intervention (e.g., instrument maintenance, tuning, or cleaning) and data normalization.
Zeno Trap Identifies More Potential Disease Biomarkers in Plasma Samples
Finally, we assessed the ability of Zeno SWATH to identify biomarkers and inform our understanding of disease mechanisms. In this context, we profiled protein content in plasma from patients diagnosed with NASH and T2D with and without Zeno trap activated. Subject demographics information can be found in supplemental Table S4.
Differential analysis of samples from NASH patients versus healthy individuals identified 24 and 44 significantly dysregulated proteins in SWATH and Zeno SWATH modes, respectively (FDR <0.1, Fig. 4A and supplemental Table S5). As expected, most significant proteins in SWATH mode (87.5%) were also significant with Zeno SWATH and included proteins that have been associated with NASH onset (leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 [LRG1] (18)), progression (inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 [ITIH4] (19)), and severity (alpha-1 antitrypsin [SERPINA1] (20)) as well as fibrosis (extracellular matrix protein 1 [ECM1] (21)). Zeno SWATH identified additional dysregulated proteins among which 36.4% were not significant, and 15.9% were not detected in SWATH mode (Fig. 4C). Further investigation of the proteins that were ‘detected but not significant in SWATH mode’ shows that Zeno SWATH data were less variable within each patient group with systematically smaller CVs (supplemental Fig. S4) which translated into smaller p-values (supplemental Table S5). Some of these proteins were previously described in the context of NASH and included oxidative stress marker glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) (22) and coagulation factors F9 and F10 (23). Pathway enrichment analysis identified expected pathways associated with metabolism and liver inflammation such as ‘liver X receptors and farnesoid X receptor activation’ (24) and ‘acute phase response signaling’ (25) as well as coagulation (23) (i.e., ‘coagulation system’) (supplemental Table S6). While these pathways were significant in both SWATH and Zeno SWATH modes, their significance was enhanced with Zeno trap activated (Fig. 4D). In particular, the significance of ‘coagulation system’ improved dramatically (p-value = 3.1E-02 in SWATH mode and p-value = 7.9E-16 in Zeno SWATH mode) indicating that additional significant proteins in Zeno SWATH mode belong to this pathway.
Similarly, 14 and 25 differential proteins were identified in plasma from patients with T2D versus healthy individuals in SWATH and Zeno SWATH modes, respectively (FDR <0.1, Fig. 4B and supplemental Table S5). Among overlapping proteins, pro-platelet basic protein (PPBP) has been associated with diabetic nephropathy podocyte injury (26), selenoprotein P (SELENOP) is a hepatokine that causes insulin resistance in T2D (27), and platelet factor 4 (PF4/CXCL4) reflects platelet function (28). Zeno SWATH identified additional relevant proteins involved in the pathophysiology of T2D such as beta-2 microglobulin (B2M)—a potential biomarker of diabetic nephropathy (29) and lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT)—a marker of metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus (30). Among significant proteins with Zeno SWATH, 24.0% were not significant, and 24.0% were not detected in SWATH mode (Figs. 4C and S4). At the pathway level, results were similar with and without Zeno trap activated except pathway significance improved for a subset of them including ‘coagulation system’ (p-value = 1.8E-02 in SWATH mode and p-value = 4.7E-6 in Zeno SWATH mode) (Fig. 4D and supplemental Table S6) (31).
Altogether, Zeno trap resulted in the identification of ∼80% more differential proteins in plasma from patients diagnosed with metabolic diseases and these proteins and associated pathways were relevant to each disease condition.
Discussion
In this work, we developed and optimized analytical flow LC-MS methods with Zeno SWATH DIA across a range of biological matrices and assessed the performance gain relative to SWATH DIA methods. Enabling the Zeno trap systematically improved all the performance metrics examined encompassing coverage in proteins and pathways, data quality, and ability to identify plasma biomarkers in clinical samples.
MS-based proteomics is rapidly evolving owing to incremental hardware and software improvements (6, 10, 32, 33, 34, 35). As instruments and acquisition methods are becoming more sensitive and processing software more elaborated, the proteomics community is moving toward shorter gradients and higher flow rates to enable wider application of the methodology to studies requiring large sample size. One example uses a 5-min gradient method at 800 μl/min to profile plasma proteins (36). While such a method is beneficial for plasma analysis due to its unique distribution in protein abundance, protein coverage in other sample types remains limited due to decreased sensitivity. The gain in sensitivity provided by the Zeno trap improved protein and precursor coverage by up to 50% at 2 μg peptide load with a 10-min gradient analytical flow chromatography. These methods detected up to 3300 proteins from tissues which is close to performances obtained at microflow using slightly longer gradients (37). The gain in protein coverage was the most notable at low peptide loads with up to 9-fold increase highlighting the utility of the technology when sample input is limited.
With omics technologies becoming more mature, they are being increasingly used in epidemiological studies generating high content quality datasets for disease risk prediction and prevention as well as disease mechanism investigation. Focusing on circulating blood markers, metabolomics, and proteomics are the two most popular approaches and successfully generated predictive models for a wide range of disorders, including metabolic, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases (38, 39, 40, 41). Even though proteomics has been successful in capturing important aspects of human disease pathophysiology, adding information from complementary omics layers has improved sensitivity and specificity of predictive models in studies of complex diseases (i.e., type 2 diabetes) (42) and physiological processes (i.e., acute exercise and pregnancy) (43, 44). In addition, proteomics has the potential to benefit interventional studies with the discovery of safety and efficacy biomarkers as well as the investigation of mechanisms of drug toxicity and drug action. For instance, large-scale plasma proteomics revealed mechanisms by which torcetrapib—a cholesterol ester transfer protein inhibitor that was being developed to treat hypercholesterolemia and prevent cardiovascular disease—may exert harmful effects (45). The authors were also able to identify a 9-protein signature that could predict an increase in derived risk from torcetrapib within just 3 months of treatment.
In order to further democratize the use of proteomics technologies in clinical trials, there is a clear need to develop high throughput and robust methods that can capture the proteome in-depth while minimizing the need for instrument maintenance. Analytical flow regime provides chromatographic robustness and signal stability over time as demonstrated by the modest decrease in sensitivity after the uninterrupted injection of 1000+ samples and high reproducibility of quality control samples injected throughout the study. Even though postacquisition methods have been developed to improve instrument reproducibility over time, they are typically computationally intensive and imperfect in deconvoluting unwanted variation (46, 47).
In conclusion, our comparative study reveals that SWATH DIA with Zeno trap enabled improves sensitivity, quantitative robustness, and signal linearity and expands protein coverage in all sample types tested. The gain in protein coverage translated into better biological pathway representation and enabled identification of potential disease biomarkers and dysregulated pathways in a cross-sectional setting. In addition, the methods developed using analytical flow chromatography were extremely robust minimizing the need for human intervention in large-scale studies. Thus, Zeno SWATH DIA technology is well suited for applications that require a phenotypic readout at scale and will likely benefit drug development, toxicological, mechanistic, and clinical biomarker discovery studies.
Data Availability
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (11) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD039414. All other data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Supplemental data
This article contains supplemental data.
Conflict of interest
W. S., Y. H., J. C., S. T., A. I. R., and K. C. are employees of AstraZeneca and may have stock and/or options in the company. Y. L. was a paid intern for AstraZeneca.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jose Castro-Perez, Elliott Jones, Ihor Batruch, Patrick Pribil and Zoe Zhang from SCIEX for providing technical expertise and valuable comments on the manuscript and Vadim Demichev (Institute of Biochemistry - Charité) for guidance with DIA-NN. We are grateful to Kristina Kovacina, Kate Liu and Hui Yin Tan from AstraZeneca for sharing BAL and commercial plasma and sputum samples.
Author contributions
K. C., W. S., Y. L., Y. H., and A. I. R. conceptualization; W. S., Y. L., and K. C. methodology; Y. L. and W. S. investigation; Y. L., W. S., and K. C. validation; W. S. and K. C. data curation; K. C., W. S., and Y. L. formal analysis; K. C., W. S., and Y. L. visualization; K. C. software; Y. H., J. C., and S. T. resources; K. C. and A. I. R. supervision; K. C., W. S., and A. I. R. project administration; K. C., W. S., and A. I. R. writing—original draft; K. C., W. S., A. I. R., Y. L., Y. H., J. C., and S. T. writing—review & editing.
Contributor Information
Anton I. Rosenbaum, Email: anton.rosenbaum@astrazeneca.com.
Kévin Contrepois, Email: kevin.contrepois@astrazeneca.com.
Supplemental Data
References
- 1.Meissner F., Geddes-McAlister J., Mann M., Bantscheff M. The emerging role of mass spectrometry-based proteomics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022;21:637–654. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goncalves E., Poulos R.C., Cai Z., Barthorpe S., Manda S.S., Lucas N., et al. Pan-cancer proteomic map of 949 human cell lines. Cancer Cell. 2022;40:835–849.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Messner C.B., Demichev V., Wendisch D., Michalick L., White M., Freiwald A., et al. Ultra-high-throughput clinical proteomics reveals classifiers of COVID-19 infection. Cell Syst. 2020;11:11–24.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2020.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Demichev V., Tober-Lau P., Lemke O., Nazarenko T., Thibeault C., Whitwell H., et al. A time-resolved proteomic and prognostic map of COVID-19. Cell Syst. 2021;12:780–794.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2021.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barkovits K., Pacharra S., Pfeiffer K., Steinbach S., Eisenacher M., Marcus K., et al. Reproducibility, specificity and accuracy of relative quantification using spectral library-based data-independent acquisition. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2020;19:181–197. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ludwig C., Gillet L., Rosenberger G., Amon S., Collins B.C., Aebersold R. Data-independent acquisition-based SWATH-MS for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018;14 doi: 10.15252/msb.20178126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Collins B.C., Hunter C.L., Liu Y., Schilling B., Rosenberger G., Bader S.L., et al. Multi-laboratory assessment of reproducibility, qualitative and quantitative performance of SWATH-mass spectrometry. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:291. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00249-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zaidman N.A., Panoskaltsis-Mortari A., O'Grady S.M. Differentiation of human bronchial epithelial cells: Role of hydrocortisone in development of ion transport pathways involved in mucociliary clearance. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016;311:C225–C236. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00073.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rayner R.E., Makena P., Prasad G.L., Cormet-Boyaka E. Optimization of normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cell 3D cultures for in vitro lung model studies. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36735-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Demichev V., Messner C.B., Vernardis S.I., Lilley K.S., Ralser M. DIA-NN: neural networks and interference correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat. Met. 2020;17:41–44. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0638-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Perez-Riverol Y., Csordas A., Bai J., Bernal-Llinares M., Hewapathirana S., Kundu D.J., et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucl. Acids Res. 2019;47:D442–D450. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Loboda A.V., Chernushevich I.V. A novel ion trap that enables high duty cycle and wide m/z range on an orthogonal injection TOF mass spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009;20:1342–1348. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2009.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Baba T., Ryumin P., Duchoslav E., Chen K., Chelur A., Loyd B., et al. Dissociation of biomolecules by an intense low-energy electron beam in a high sensitivity time-of-flight mass spectrometer. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021;32:1964–1975. doi: 10.1021/jasms.0c00425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang Z., Mulleder M., Batruch I., Chelur A., Textoris-Taube K., Schwecke T., et al. High-throughput proteomics of nanogram-scale samples with Zeno SWATH MS. Elife. 2022;11 doi: 10.7554/eLife.83947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Uhlen M., Fagerberg L., Hallstrom B.M., Lindskog C., Oksvold P., Mardinoglu A., et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347 doi: 10.1126/science.1260419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ashburner M., Ball C.A., Blake J.A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J.M., et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gene C. Ontology, the Gene ontology resource: enriching a GOld mine. Nucl. Acids Res. 2021;49:D325–D334. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.He S., Ryu J., Liu J., Luo H., Lv Y., Langlais P.R., et al. LRG1 is an adipokine that mediates obesity-induced hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 2021;131 doi: 10.1172/JCI148545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nakamura N., Hatano E., Iguchi K., Sato M., Kawaguchi H., Ohtsu I., et al. Elevated levels of circulating ITIH4 are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from pig model to human study. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:621. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5825-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Semmler G., Balcar L., Oberkofler H., Zandanell S., Strasser M., Niederseer D., et al. PNPLA3 and SERPINA1 variants are associated with severity of fatty liver disease at first referral to a tertiary center. J. Per. Med. 2021;11:165. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fan W., Liu T., Chen W., Hammad S., Longerich T., Hausser I., et al. ECM1 prevents activation of transforming growth factor beta, hepatic stellate cells, and fibrogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:1352–1367.e13. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gentric G., Maillet V., Paradis V., Couton D., L'Hermitte A., Panasyuk G., et al. Oxidative stress promotes pathologic polyploidization in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2015;125:981–992. doi: 10.1172/JCI73957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ogresta D., Mrzljak A., Cigrovski Berkovic M., Bilic-Curcic I., Stojsavljevic-Shapeski S., Virovic-Jukic L. Coagulation and endothelial dysfunction associated with NAFLD: current status and therapeutic implications. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022;10:339–355. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jiao Y., Lu Y., Li X.Y. Farnesoid X receptor: a master regulator of hepatic triglyceride and glucose homeostasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015;36:44–50. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tilg H., Moschen A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology. 2010;52:1836–1846. doi: 10.1002/hep.24001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang F., Jiang N., Gao Y., Fan Z., Li Q., Ke G., et al. PPBP as a marker of diabetic nephropathy podocyte injury via Bioinformatics Analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021;577:165–172. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.08.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saito Y. Selenoprotein P as an in vivo redox regulator: disorders related to its deficiency and excess. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020;66:1–7. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.19-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Davi G., Gresele P., Violi F., Basili S., Catalano M., Giammarresi C., et al. Diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension but not vascular disease per se are associated with persistent platelet activation in vivo. Evidence derived from the study of peripheral arterial disease. Circulation. 1997;96:69–75. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ekrikpo U.E., Effa E.E., Akpan E.E., Obot A.S., Kadiri S. Clinical utility of urinary beta2-microglobulin in detection of early nephropathy in african diabetes mellitus patients. Int. J. Nephrol. 2017;2017 doi: 10.1155/2017/4093171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tanaka S.I., Fujioka Y., Tsujino T., Ishida T., Hirata K.I. Impact of serum cholesterol esterification rates on the development of diabetes mellitus in a general population. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17:180. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0822-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sobczak A.I.S., Stewart A.J. Coagulatory defects in type-1 and type-2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:6345. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meier F., Geyer P.E., Virreira Winter S., Cox J., Mann M. BoxCar acquisition method enables single-shot proteomics at a depth of 10,000 proteins in 100 minutes. Nat. Met. 2018;15:440–448. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Meier F., Brunner A.D., Frank M., Ha A., Bludau I., Voytik E., et al. diaPASEF: parallel accumulation-serial fragmentation combined with data-independent acquisition. Nat. Met. 2020;17:1229–1236. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-00998-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Meier F., Park M.A., Mann M. Trapped ion mobility spectrometry and parallel accumulation-serial fragmentation in proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2021;20 doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2021.100138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Frohlich K., Brombacher E., Fahrner M., Vogele D., Kook L., Pinter N., et al. Benchmarking of analysis strategies for data-independent acquisition proteomics using a large-scale dataset comprising inter-patient heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:2622. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30094-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Messner C.B., Demichev V., Bloomfield N., Yu J.S.L., White M., Kreidl M., et al. Ultra-fast proteomics with scanning SWATH. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021;39:846–854. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00860-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sun R., Hunter C., Chen C., Ge W., Morrice N., Liang S., et al. Accelerated protein biomarker discovery from FFPE tissue samples using single-shot, short gradient microflow SWATH MS. J. Proteome Res. 2020;19:2732–2741. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Buergel T., Steinfeldt J., Ruyoga G., Pietzner M., Bizzarri D., Vojinovic D., et al. Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Nat. Med. 2022;28:2309–2320. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01980-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bragg F., Trichia E., Aguilar-Ramirez D., Besevic J., Lewington S., Emberson J. Predictive value of circulating NMR metabolic biomarkers for type 2 diabetes risk in the UK Biobank study. BMC Med. 2022;20:159. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02354-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang Z., Zhu C., Nambi V., Morrison A.C., Folsom A.R., Ballantyne C.M., et al. Metabolomic pattern predicts incident coronary heart disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019;39:1475–1482. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Williams S.A., Ostroff R., Hinterberg M.A., Coresh J., Ballantyne C.M., Matsushita K., et al. A proteomic surrogate for cardiovascular outcomes that is sensitive to multiple mechanisms of change in risk. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022;14 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj9625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schussler-Fiorenza Rose S.M., Contrepois K., Moneghetti K.J., Zhou W., Mishra T., Mataraso S., et al. A longitudinal big data approach for precision health. Nat. Med. 2019;25:792–804. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0414-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Contrepois K., Wu S., Moneghetti K.J., Hornburg D., Ahadi S., Tsai M.S., et al. Molecular choreography of acute exercise. Cell. 2020;181:1112–1130.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stelzer I.A., Ghaemi M.S., Han X., Ando K., Hedou J.J., Feyaerts D., et al. Integrated trajectories of the maternal metabolome, proteome, and immunome predict labor onset. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021;13 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd9898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Williams S.A., Murthy A.C., DeLisle R.K., Hyde C., Malarstig A., Ostroff R., et al. Improving assessment of drug safety through proteomics: early detection and mechanistic characterization of the unforeseen harmful effects of torcetrapib. Circulation. 2018;137:999–1010. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Poulos R.C., Hains P.G., Shah R., Lucas N., Xavier D., Manda S.S., et al. Strategies to enable large-scale proteomics for reproducible research. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:3793. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17641-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cuklina J., Lee C.H., Williams E.G., Sajic T., Collins B.C., Rodriguez Martinez M., et al. Diagnostics and correction of batch effects in large-scale proteomic studies: a tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021;17 doi: 10.15252/msb.202110240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (11) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD039414. All other data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.