Abstract
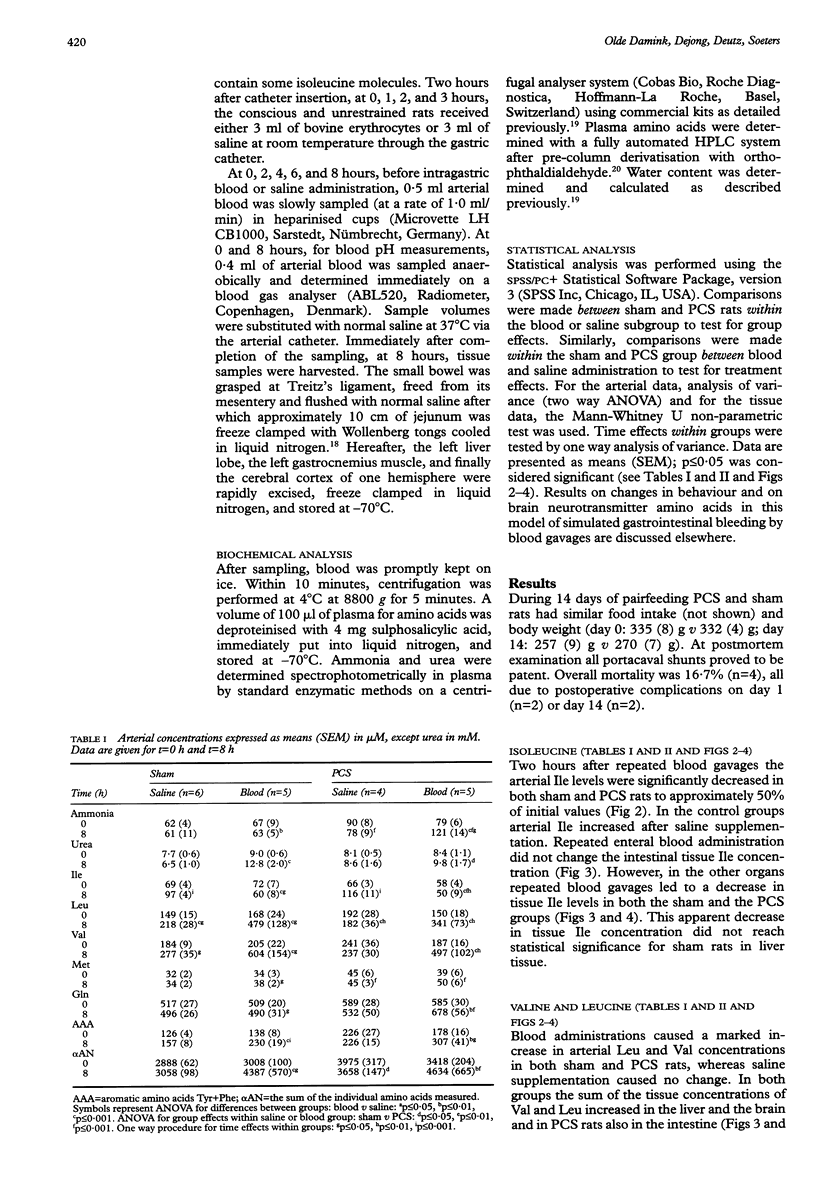
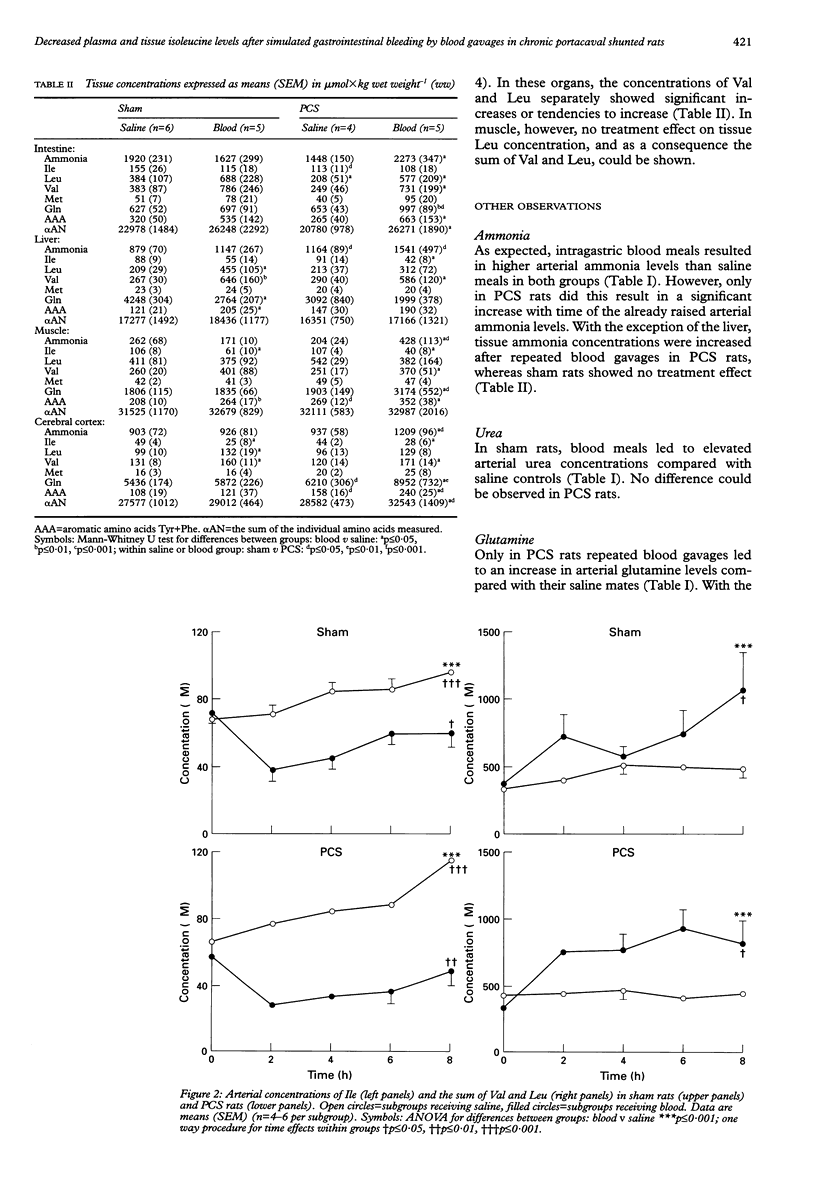
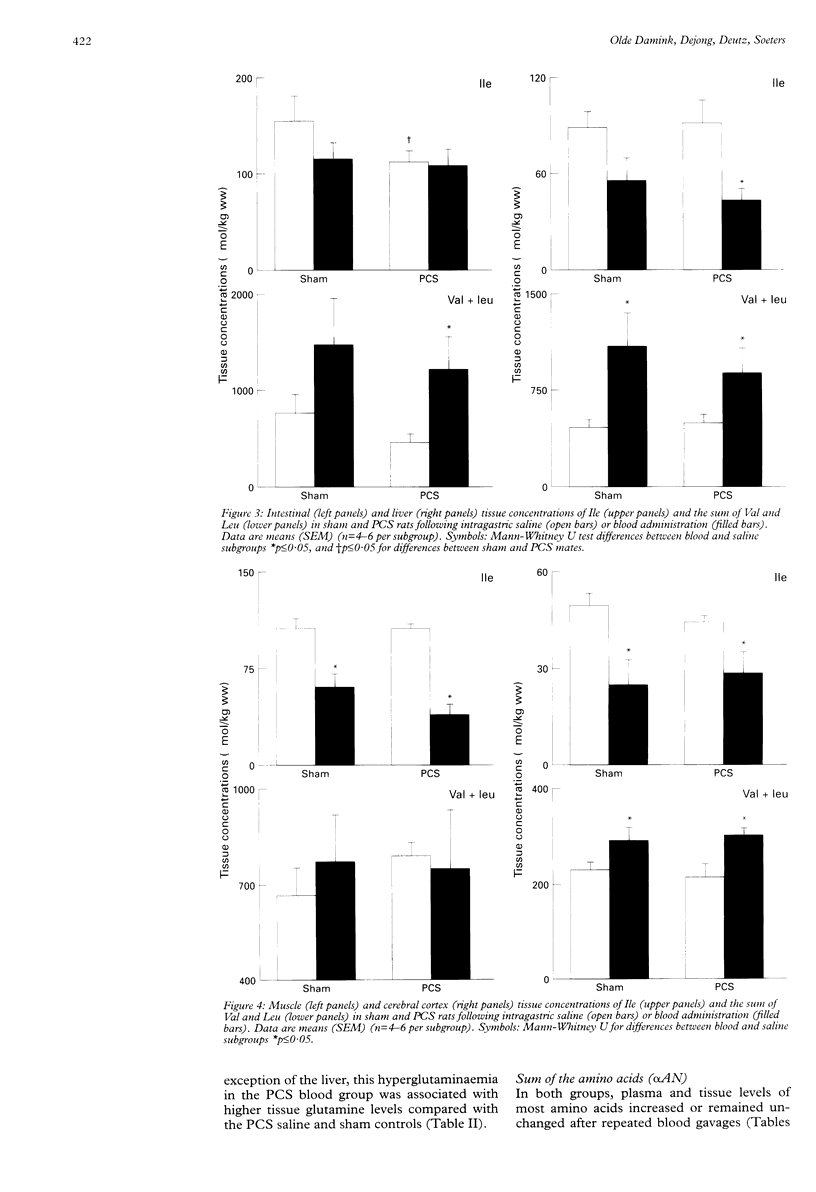
BACKGROUND: Previously, arterial concentrations of the essential branched chain amino acid isoleucine (Ile) were found to have decreased by more than 50% after gastrointestinal haemorrhage in patients and after intragastric blood administration in healthy humans and pigs. Hypothetically, this induced hypoisoleucinaemia could deplete tissue Ile pools. AIMS: To study the effect of repeated blood gavages on arterial and tissue Ile levels during normal and impaired liver function. SUBJECTS: Male Wistar rats. METHODS: 14 days after portacaval shunting or sham surgery, rats received 3 ml bovine erythrocytes or saline at 0, 1, 2, and 3 hours via a gastrostomy catheter in the duodenum. At 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 hours arterial blood and at 8 hours intestine, liver, muscle, and cerebral cortex were sampled for determination of ammonia and amino acid concentrations. RESULTS: In both groups repeated blood administration resulted in a marked decrease in plasma Ile (40-60%). This was accompanied by decreased tissue Ile concentrations in liver (50%), muscle (40-60%), and cerebral cortex (40-50%), but unaltered intestinal Ile levels. In contrast, the arterial and tissue concentrations of ammonia, urea, and of most amino acids increased, most strikingly of the other two branched chain amino acids, valine and leucine. CONCLUSIONS: Simulated gastrointestinal bleeding by blood gavages in rats with and without impaired liver function leads to hypoisoleucinaemia and decreased tissue Ile pools.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSMAN A. N., HAWKINS R. THE RELATIVE EFFECTS OF ENTERICALLY ADMINISTERED PLASMA AND PACKED CELLS ON CIRCULATING BLOOD AMMONIA. Gastroenterology. 1963 Sep;45:368–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSMAN A. N., MIRICK G. S. Blood ammonia levels following the ingestion of casein and whole blood. J Clin Invest. 1958 Jul;37(7):990–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI103695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström J., Fürst P., Norée L. O., Vinnars E. Intracellular free amino acid concentration in human muscle tissue. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jun;36(6):693–697. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.6.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. G., Carrell R. W., Howard B. H. The amino acid sequence of the alpha chain of the major haemoglobin of the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):259–269. doi: 10.1042/bj1490259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F., DePasquale M., Nicholson C., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Rice M. E. Extracellular volume decreases while cell volume is maintained by ion uptake in rat brain during acute hypernatremia. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:277–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Metabolic adaptation of the kidney to hyperammonemia during chronic liver insufficiency in the rat. Hepatology. 1993 Oct;18(4):890–902. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840180422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Kampman M. T., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Altered glutamine metabolism in rat portal drained viscera and hindquarter during hyperammonemia. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):936–948. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Meijerink W. J., van Berlo C. L., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Decreased plasma isoleucine concentrations after upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage in humans. Gut. 1996 Jul;39(1):13–17. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutz N. E., Reijven P. L., Bost M. C., van Berlo C. L., Soeters P. B. Modification of the effects of blood on amino acid metabolism by intravenous isoleucine. Gastroenterology. 1991 Dec;101(6):1613–1620. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90399-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. J., KONIGSBERG W. The structure of human hemoglobin. IV. The chymotryptic digestion of the alpha chain of human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3151–3156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Eriksson S., Wahren J. Influence of leucine on arterial concentrations and regional exchange of amino acids in healthy subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Sep;59(3):173–181. doi: 10.1042/cs0590173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. E., Benevenga N. J., Wohlhueter R. M. Effects of ingestion of disproportionate amounts of amino acids. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jul;50(3):428–558. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. E., Miller R. H., Block K. P. Branched-chain amino acid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1984;4:409–454. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.04.070184.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakesz R., Smith C. A., Aitken S., Huff K., Schuette W., Shackney S., Lippman M. Influence of cell proliferation and cell cycle phase on expression of estrogen receptor in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):619–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn A. Differential effects of isoleucine deprivation on cell motility, membrane transport and DNA synthesis in NIL 8 hamster cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Efstratiadis A., O'Connell C., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of the human beta-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):647–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecavalier L., De Feo P., Haymond M. W. Isolated hypoisoleucinemia impairs whole body but not hepatic protein synthesis in humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 1):E578–E586. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.5.E578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., de Boer P. A., Watford M., Dingemanse M. A., Lamers W. H. Hepatic glutaminase mRNA is confined to part of the urea cycle domain in the adult rodent liver lobule. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 12;356(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooiwa T., Goto H., Tsukamoto Y., Hayakawa T., Sugiyama S., Fujitsuka N., Shimomura Y. Regulation of valine catabolism in canine tissues: tissue distributions of branched-chain aminotransferase and 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complex, methacrylyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Feb 23;1243(2):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)00061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittelkow M. R., Wille J. J., Jr, Scott R. E. Two functionally distinct classes of growth arrest states in human prokeratinocytes that regulate clonogenic potential. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):410–417. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Babin D. R. A comparison of amino acid sequences in the beta-chains of adult bovine hemoglobins A and B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):124–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Babin D. R. Amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of bovine fetal hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Kilberg M. S., Oxender D. L. The regulation of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. D. Hyperammonemia and orotic aciduria in portacaval-shunted rats. J Nutr. 1984 Jan;114(1):210–216. doi: 10.1093/jn/114.1.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A., Ley K. D. Isoleucine-mediated regulation of genome repliction in various mammalian cell lines. Cancer Res. 1971 Jan;31(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLENBERGER A., RISTAU O., SCHOFFA G. [A simple technic for extremely rapid freezing of large pieces of tissue]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;270:399–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve L. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 1987 Sep;2(3):147–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00999607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer J. E., Oostenbroek R. J., van Dongen J. J., Janssen M. A., Soeters P. B. Sequential metabolic characteristics following portacaval shunt in rats. Eur Surg Res. 1986;18(2):96–106. doi: 10.1159/000109126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berlo C. L., van de Bogaard A. E., van der Heijden M. A., van Eijk H. M., Janssen M. A., Bost M. C., Soeters P. B. Is increased ammonia liberation after bleeding in the digestive tract the consequence of complete absence of isoleucine in hemoglobin? A study in pigs. Hepatology. 1989 Sep;10(3):315–323. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eijk H. M., van der Heijden M. A., van Berlo C. L., Soeters P. B. Fully automated liquid-chromatographic determination of amino acids. Clin Chem. 1988 Dec;34(12):2510–2513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


