Abstract
BACKGROUND: Patients with severe acute pancreatitis die of complications closely related to the systemic activation of protease cascades. AIM: To examine the effects of human C1 esterase inhibitor (C1 INH) and antithrombin III (AT III) on two experimental models of acute pancreatitis. METHODS: Oedematous pancreatitis was induced by continuous intravenous infusion of caerulein and haemorrhagic pancreatitis by retrograde injection of sodium taurocholate into the biliopancreatic duct. C1 INH and AT III were given intravenously, either before or after the induction of pancreatitis. Treatment with C1 INH and AT III had no beneficial effect on oedematous pancreatitis. On the other hand, combined C1 INH and AT III therapy improved the survival in haemorrhagic pancreatitis compared with treatment with human serum albumin. This reduction in mortality was found regardless of whether the treatment was given prophylactically or therapeutically. CONCLUSIONS: Treatment with C1 INH and AT III represents a promising therapeutic concept for patients with severe haemorrhagic pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler G., Hupp T., Kern H. F. Course and spontaneous regression of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1979 May 14;382(1):31–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01102739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleeker W. K., Agterberg J., Rigter G., Hack C. E., Gool J. V. Protective effect of antithrombin III in acute experimental pancreatitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Feb;37(2):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01308184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickneite G., Pâques E. P. Reduction of mortality with antithrombin III in septicemic rats: a study of Klebsiella pneumoniae induced sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Feb 1;69(2):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson T. E., Jr, Fournel M. A., Leach W. J., Redens T. B. Protection against disseminated intravascular coagulation and death by antithrombin-III in the Escherichia coli endotoxemic rat. Circ Shock. 1987;21(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Ogilvie A. C., Eisele B., Eerenberg A. J., Wagstaff J., Thijs L. G. C1-inhibitor substitution therapy in septic shock and in the vascular leak syndrome induced by high doses of interleukin-2. Intensive Care Med. 1993;19 (Suppl 1):S19–S28. doi: 10.1007/BF01738946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knot E. A., de Jong E., ten Cate J. W., Gie L. K., van Royen E. A. Antithrombin III: biodistribution in healthy volunteers. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Dec 18;58(4):1008–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch M. M., Saluja A. K., Rünzi M., Dawra R., Saluja M., Steer M. L. Pancreatic duct obstruction triggers acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the opossum. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):853–861. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91022-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch M. M., Weidenbach H., Gress T. M., Adler G. Effect of kinin inhibition in experimental acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol. 1995 Oct;269(4 Pt 1):G490–G499. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.4.G490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., Regoli D., Giroud J. P. Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(2):209–229. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederau C., Brinsa R., Niederau M., Lüthen R., Strohmeyer G., Ferrell L. D. Effects of C1-esterase inhibitor in three models of acute pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1995 Apr;17(2):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02788538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuijens J. H., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Huijbregts C. C., Schreuder W. O., Felt-Bersma R. J., Abbink J. J., Thijs L. G., Hack C. E. Proteolytic inactivation of plasma C1- inhibitor in sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):443–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI114185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orfan N. A., Kolski G. B. Angioedema and C1 inhibitor deficiency. Ann Allergy. 1992 Sep;69(3):167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley R. A., Schapira M., Colman R. W. The regulation of human factor XIIa by plasma proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1723–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruud T. E., Aasen A. O., Pillgram-Larsen J., Stadaas J. O. Effects on peritoneal proteolysis and hemodynamics of prophylactic infusion with C1 inhibitor in experimental acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Oct;21(8):1018–1024. doi: 10.3109/00365528608996414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
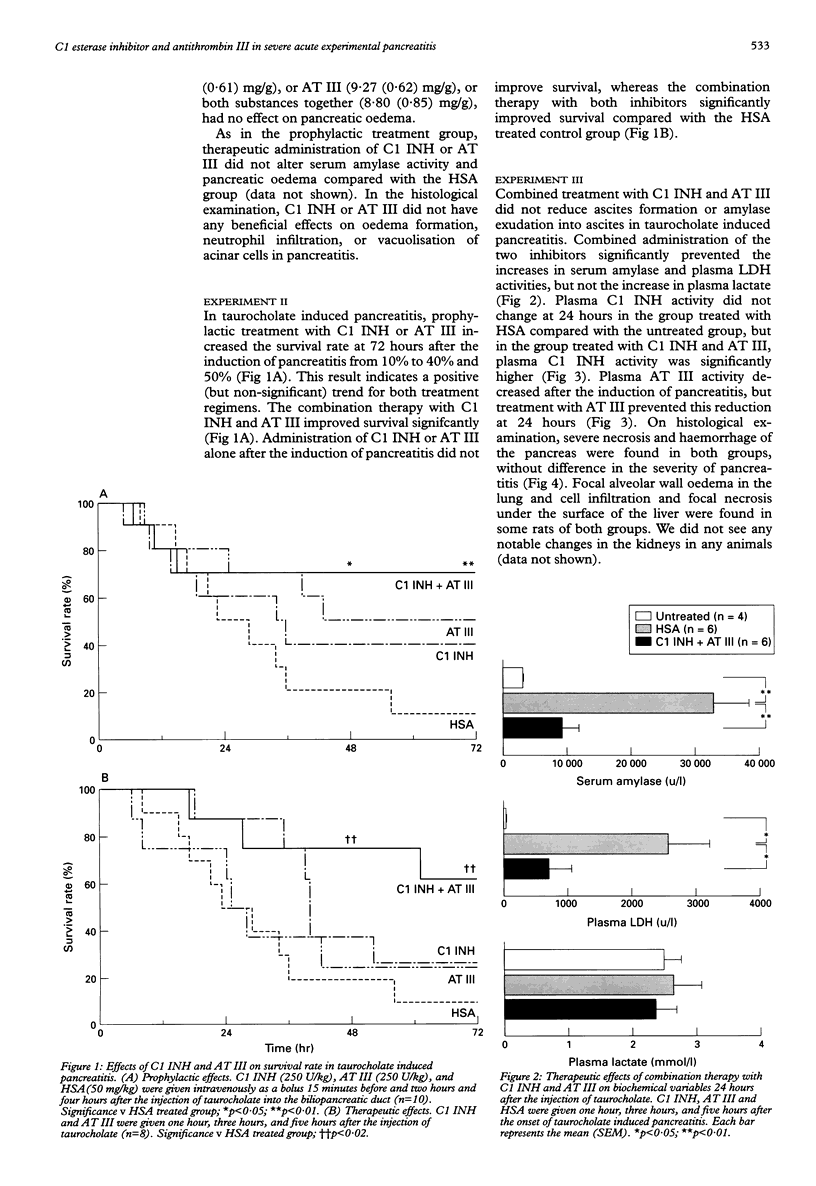
- Satake K., Koh I., Nishiwaki H., Umeyama K. Toxic products in hemorrhagic ascitic fluid generated during experimental acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis in dogs and a treatment which reduces their effect. Digestion. 1985;32(2):99–105. doi: 10.1159/000199225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seung W. P., Feldman B. F. Early phase components of the kallikrein kinin system in hemorrhagic ascitic fluid and plasma in the rat with induced acute pancreatitis. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Sep;46(9):1961–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Interaction of 125I-labelled complement subcomponents C-1r and C-1s with protease inhibitors in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllopoulos D. C. Effects of human antithrombin III on mortality and blood coagulation induced in rabbits by endotoxin. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Apr 30;51(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesentini S., Benetti L., Bassi C., Bonora A., Campedelli A., Zamboni G., Castelli P., Pederzoli P. Effects of choline-esterase inhibitor in experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Preliminary results. Int J Pancreatol. 1993 Jun;13(3):217–220. doi: 10.1007/BF02924443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidenbach H., Lerch M. M., Gress T. M., Pfaff D., Turi S., Adler G. Vasoactive mediators and the progression from oedematous to necrotising experimental acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1995 Sep;37(3):434–440. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.3.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Kimura T., Nawata H. Does stress play a role in the development of severe pancreatitis in rats? Gastroenterology. 1990 Jun;98(6):1682–1688. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91107-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smet B. J., de Boer J. P., Agterberg J., Rigter G., Bleeker W. K., Hack C. E. Clearance of human native, proteinase-complexed, and proteolytically inactivated C1-inhibitor in rats. Blood. 1993 Jan 1;81(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Graaf F., Koedam J. A., Bouma B. N. Inactivation of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]