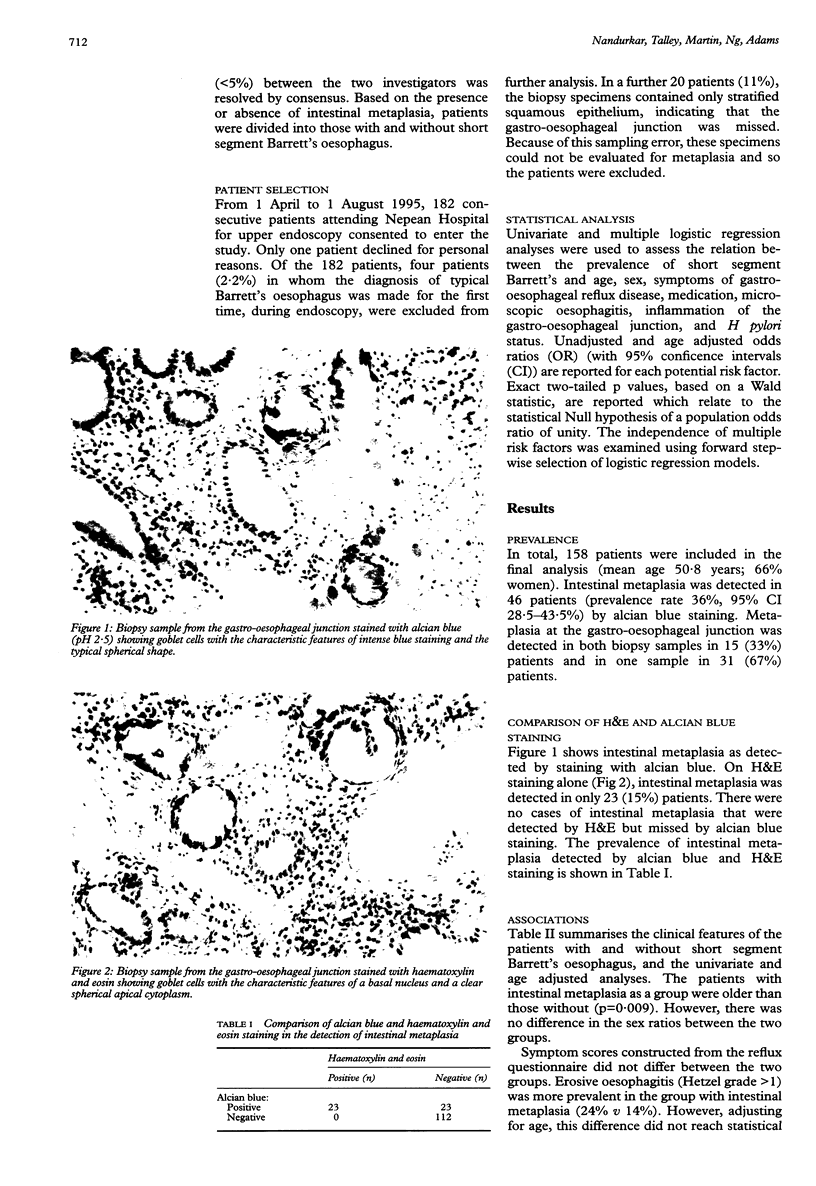
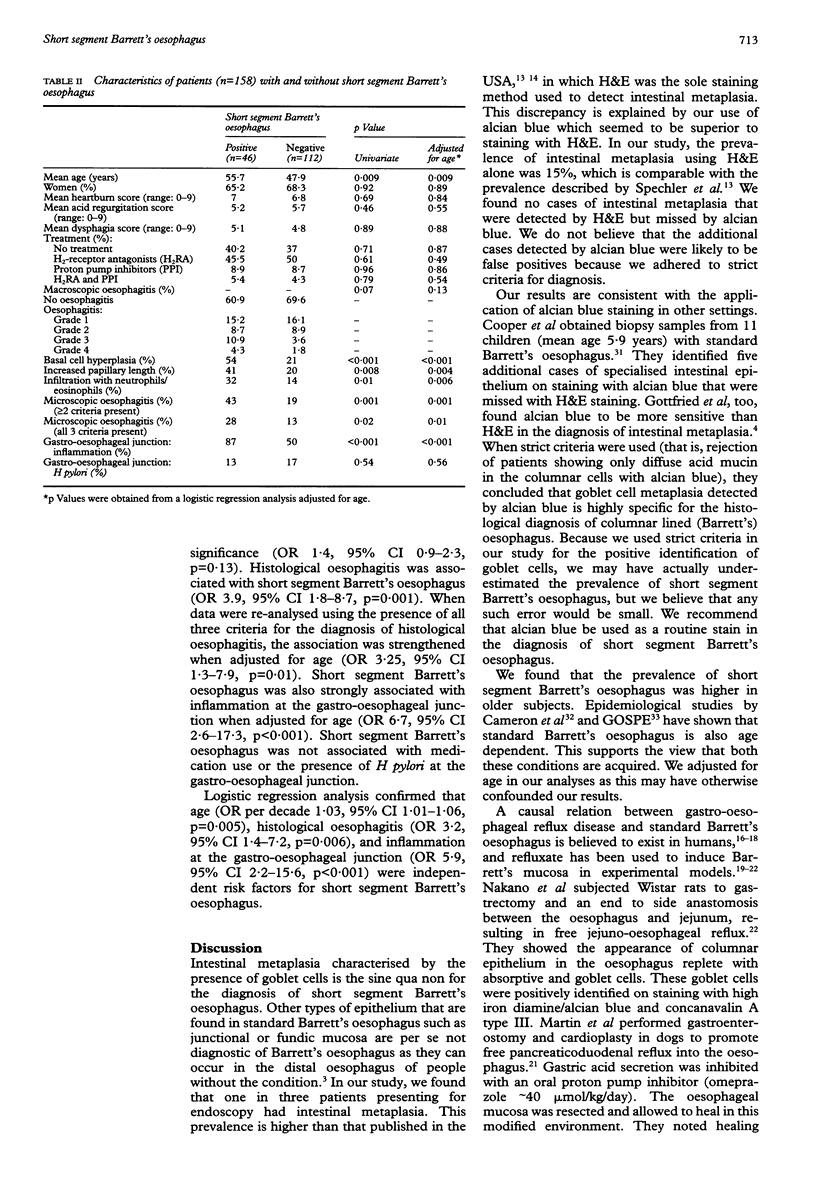
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Prevalence of short segment Barrett's (SSB) oesophagus, defined as the absence of macroscopic Barrett's but histologically identifiable intestinal metaplasia, has been reported to be 18% based on haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. AIMS: To define the prevalence of SSB oesophagus using H&E and alcian blue staining and to determine whether SSB oesophagus is associated with inflammation at the gastro-oesophageal junction (GOJ). SUBJECTS: Consecutive patients (n = 158) presenting for endoscopy completed a structured interview. METHODS: Two biopsy specimens taken from the GOJ were stained with H&E, alcian blue and Giemsa. A third specimen was obtained from the distal oesophagus. Intestinal metaplasia was diagnosed if goblet cells were definitely identified by two independent observers. RESULTS: SSB oesophagus was present in 46 (prevalence 36%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 28.5-43.5) using alcian blue staining. If H&E had been the sole staining method used, 50% cases of intestinal metaplasia would have been overlooked. There were no cases of intestinal metaplasia identified by H&E but missed by alcian blue staining. Logistic regression analysis identified age (odds ratio (OR) per decade 1.03, 95% CI 1.01-1.06), histological oesophagitis (OR 3.2, 95% CI 1.4-7.2) and inflammation at the gastrooesophageal junction (OR 5.9, 95% CI 2.2-15.6) as independent risk factors for SSB oesophagus. CONCLUSION: Unrecognised SSB oesophagus is highly prevalent in patients presenting for diagnostic upper endoscopy if alcian blue staining is applied.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agha F. P., Keren D. F. Barrett's esophagus complicating achalasia after esophagomyotomy. A clinical, radiologic, and pathologic study of 70 patients with achalasia and related motor disorders. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Apr;9(2):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Kneller R. W., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1991 Mar 13;265(10):1287–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozymski E. M., Herlihy K. J., Orlando R. C. Barrett's esophagus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jul;97(1):103–107. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A. J., Lomboy C. T. Barrett's esophagus: age, prevalence, and extent of columnar epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91510-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A. J., Lomboy C. T., Pera M., Carpenter H. A. Adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction and Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1995 Nov;109(5):1541–1546. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. W., Smyrk T. C., Burdiles P., Hoeft S. F., Peters J. H., Kiyabu M., Hinder R. A., Bremner C. G., DeMeester T. R. Is Barrett's metaplasia the source of adenocarcinomas of the cardia? Arch Surg. 1994 Jun;129(6):609–614. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420300051007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. E., Spitz L., Wilkins B. M. Barrett's esophagus in children: a histologic and histochemical study of 11 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1987 Mar;22(3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(87)80324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. E., Spitz L., Wilkins B. M. Barrett's esophagus in children: a histologic and histochemical study of 11 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1987 Mar;22(3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(87)80324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Attwood S. E., Smyrk T. C., Therkildsen D. H., Hinder R. A. Surgical therapy in Barrett's esophagus. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):528–542. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frierson H. F., Jr Histology in the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1990 Sep;19(3):631–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottfried M. R., McClave S. A., Boyce H. W. Incomplete intestinal metaplasia in the diagnosis of columnar lined esophagus (Barrett's esophagus). Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Dec;92(6):741–746. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.6.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggitt R. C. Barrett's esophagus, dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1994 Oct;25(10):982–993. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Smith R. R., Cameron J. L. Prevalence and characteristics of Barrett esophagus in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or esophagogastric junction. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):942–948. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Smith R. R. The relationship between columnar epithelial dysplasia and invasive adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;87(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L. E., Sparén P., Nyrén O. Increasing incidence of carcinoma of the gastric cardia in Sweden from 1970 to 1985. Br J Surg. 1993 Mar;80(3):374–377. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel D. J., Dent J., Reed W. D., Narielvala F. M., Mackinnon M., McCarthy J. H., Mitchell B., Beveridge B. R., Laurence B. H., Gibson G. G. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):903–912. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Horton P. F., Pope C. E., 2nd Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J., Coghill G., Tregaskis B., Hopwood D., Wormsley K. G. Epidermal growth factor in the oesophagus. Gut. 1992 Nov;33(11):1448–1453. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.11.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J., Murphy S., Coghill G., Grant A., Wormsley K. G., Sanders D. S., Kerr M., Hopwood D. Epidermal growth factor receptors in the oesophagus. Gut. 1992 Apr;33(4):439–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiewicz J. J. The Sydney System: a new classification of gastritis. Introduction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):207–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pera M., Cameron A. J., Trastek V. F., Carpenter H. A., Zinsmeister A. R. Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):510–513. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90420-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peuchmaur M., Potet F., Goldfain D. Mucin histochemistry of the columnar epithelium of the oesophagus (Barrett's oesophagus): a prospective biopsy study. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):607–610. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert M. E., Weinstein W. M. Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric pathology. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993 Mar;22(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothery G. A., Patterson J. E., Stoddard C. J., Day D. W. Histological and histochemical changes in the columnar lined (Barrett's) oesophagus. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):1062–1068. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Wiebecke B., Klauser A. G., Voderholzer W. A., Müller-Lissner S. A. Diagnostic value of histology in non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut. 1996 Aug;39(2):151–154. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell T. G., Sontag S. J., Chejfec G. Adenocarcinomas arising in tongues or short segments of Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Jan;37(1):137–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01308357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Walther B. C., Riddell R. H., Schmidt H., Iascone C., DeMeester T. R. Barrett's esophagus. Comparison of benign and malignant cases. Ann Surg. 1983 Oct;198(4):554–565. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198310000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K. Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):362–371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Zeroogian J. M., Antonioli D. A., Wang H. H., Goyal R. K. Prevalence of metaplasia at the gastro-oesophageal junction. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1533–1536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Siewert J. R. Barrett's esophagus: pathogenesis, epidemiology, functional abnormalities, malignant degeneration, and surgical management. Dysphagia. 1993;8(3):276–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01354551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. J., Zinsser K. R., Enterline H. T. Barrett's metaplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jan;14(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C., Jr, Spurling T. J., Chobanian S. J., Curtis D. J., Esposito R. L., Hacker J. F., 3rd, Johnson D. A., Cruess D. F., Cotelingam J. D., Gurney M. S. Barrett's esophagus. A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]