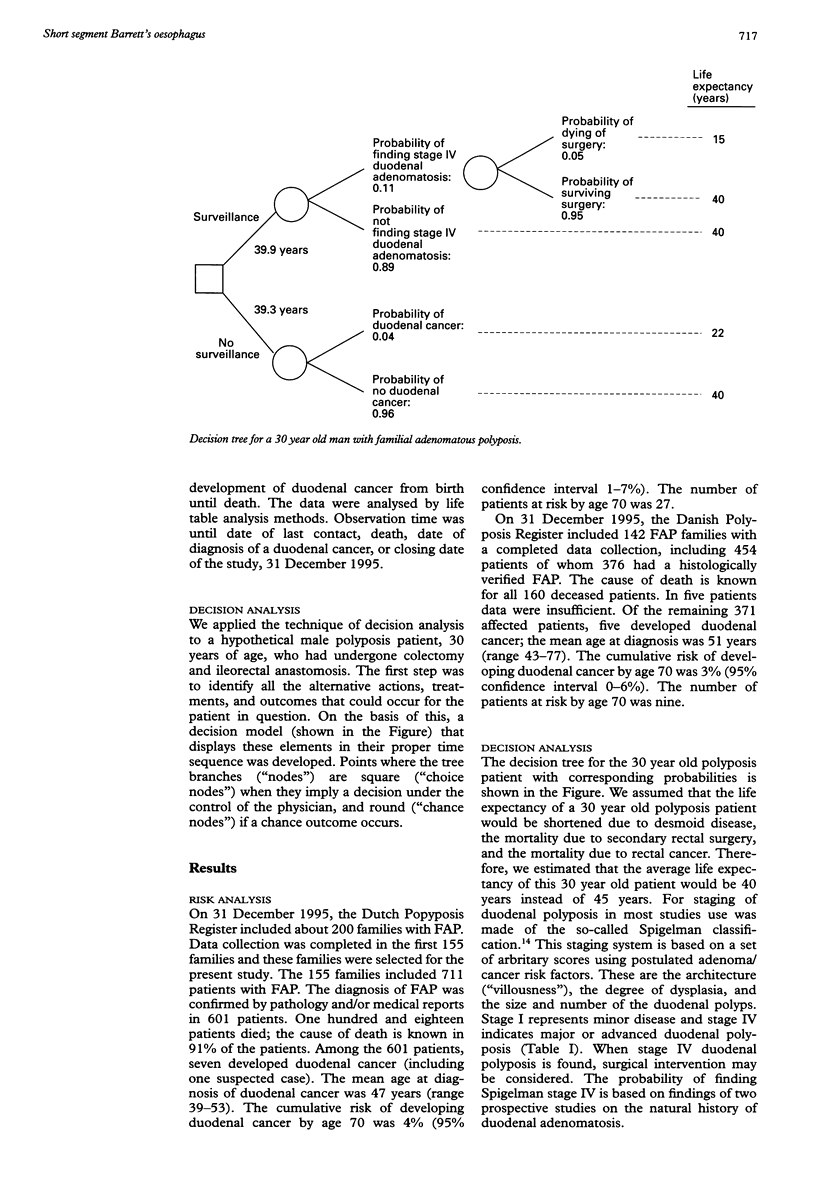
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Patients with familial adenomatous polyposis are not only at high risk of developing adenomas in the colorectum but a substantial number of patients also develop polyps in the duodenum. Because treatment of duodenal polyps is extremely difficult and it is unknown how many patients ultimately develop duodenal cancer, the value of surveillance of the upper digestive tract is uncertain. AIMS: (1) To assess the cumulative risk of duodenal cancer in a large series of polyposis patients. (2) To develop a decision model to establish whether surveillance would lead to increased life expectancy. METHODS: Risk analysis was performed in 155 Dutch polyposis families including 601 polyposis patients, and 142 Danish families including 376 patients. Observation time was from birth until date of last contact, death, diagnosis of duodenal cancer, or closing date of the study. RESULTS: Seven Dutch and five Danish patients developed duodenal cancer. The lifetime risk of developing this cancer by the age of 70 was 4% (95% confidence interval 1-7%) in the Dutch series and 3% (95% confidence interval 0-6%) in the Danish series. Decision analysis showed that surveillance led to an increase in life expectancy by seven months. CONCLUSIONS: Surveillance of the upper digestive tract led to a moderate gain in life expectancy. Future studies should evaluate whether this increase in life expectancy outweighs the morbidity of endoscopic examination and proximal pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt R. W., Berenson M. M., Lee R. G., Tolman K. G., Freston J. W., Gardner E. J. Upper gastrointestinal polyps in Gardner's syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S., Burn J., Neale K., Northover J., Vasen H. The establishment of a polyposis register. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1993 Mar;8(1):34–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00341274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S., Lauritsen K. B., Johansen A., Svendsen L. B., Søndergaard J. O. Gastroduodenal polyps in familial polyposis coli. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985 Feb;28(2):90–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02552651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church J. M., McGannon E., Hull-Boiner S., Sivak M. V., Van Stolk R., Jagelman D. G., Fazio V. W., Oakley J. R., Lavery I. C., Milsom J. W. Gastroduodenal polyps in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Dec;35(12):1170–1173. doi: 10.1007/BF02251971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J. Follow-up study of a family group exhibiting dominant inheritance for a syndrome including intestinal polyps, osteomas, fibromas and epidermal cysts. Am J Hum Genet. 1962 Dec;14:376–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G., DeCosse J. J., Bussey H. J. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1988 May 21;1(8595):1149–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91962-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Nance F. C. Periampullary malignancy in Gardner's syndrome. Ann Surg. 1977 May;185(5):565–573. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197705000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J., Sipponen P. Gastroduodenal polyps in familial adenomatous and juvenile polyposis. Endoscopy. 1986 Nov;18(6):230–234. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz R. C., Sternberg S. S., Miller H. H., Decosse J. J. Upper gastrointestinal neoplasia in familial polyposis. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 May;32(5):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF01296027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. P., Spigelman A. D., Williams C. B., Talbot I. C., Phillips R. K. Surveillance of duodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: progress report. J R Soc Med. 1994 Nov;87(11):704–706. doi: 10.1177/014107689408701123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offerhaus G. J., Giardiello F. M., Krush A. J., Booker S. V., Tersmette A. C., Kelley N. C., Hamilton S. R. The risk of upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1980–1982. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90322-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penna C., Phillips R. K., Tiret E., Spigelman A. D. Surgical polypectomy of duodenal adenomas in familial adenomatous polyposis: experience of two European centres. Br J Surg. 1993 Aug;80(8):1027–1029. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarre R. G., Frost A. G., Jagelman D. G., Petras R. E., Sivak M. V., McGannon E. Gastric and duodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective study of the nature and prevalence of upper gastrointestinal polyps. Gut. 1987 Mar;28(3):306–314. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.3.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur P. L., David E., Brown P. W., Jr, Beahrs O. H., ReMine W. H., Harrison E. G., Jr Adenocarcinoma of the duodenum and the Gardner syndrome. JAMA. 1973 Mar 12;223(11):1229–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigelman A. D., Williams C. B., Talbot I. C., Domizio P., Phillips R. K. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):783–785. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugihara K., Muto T., Kamiya J., Konishi F., Sawada T., Morioka Y. Gardner's syndrome associated with periampullary carcinoma, duodenal and gastric adenomatosis. Report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 1982 Nov-Dec;25(8):766–771. doi: 10.1007/BF02553308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboulsi E. I., Krush A. J., Gardner E. J., Booker S. V., Offerhaus G. J., Yardley J. H., Hamilton S. R., Luk G. D., Giardiello F. M., Welsh S. B. Prevalence and importance of pigmented ocular fundus lesions in Gardner's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 12;316(11):661–667. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703123161104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



