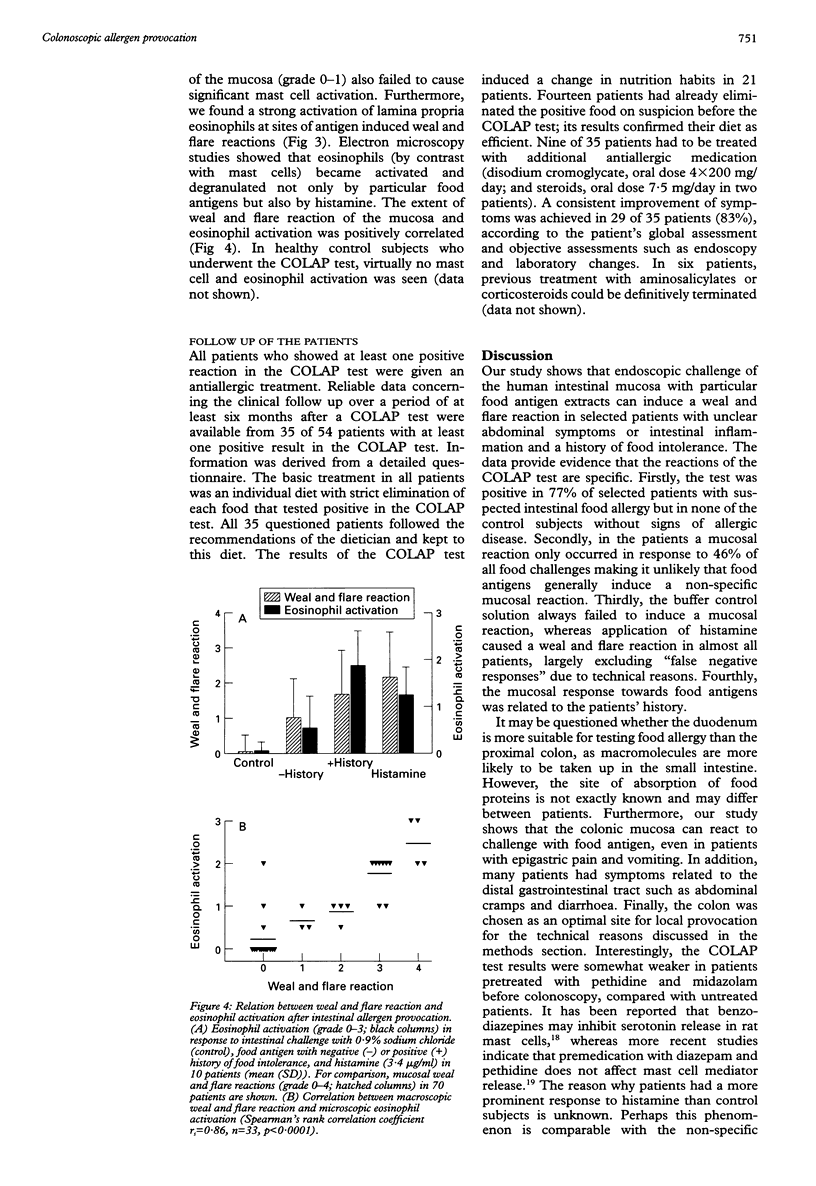
Abstract
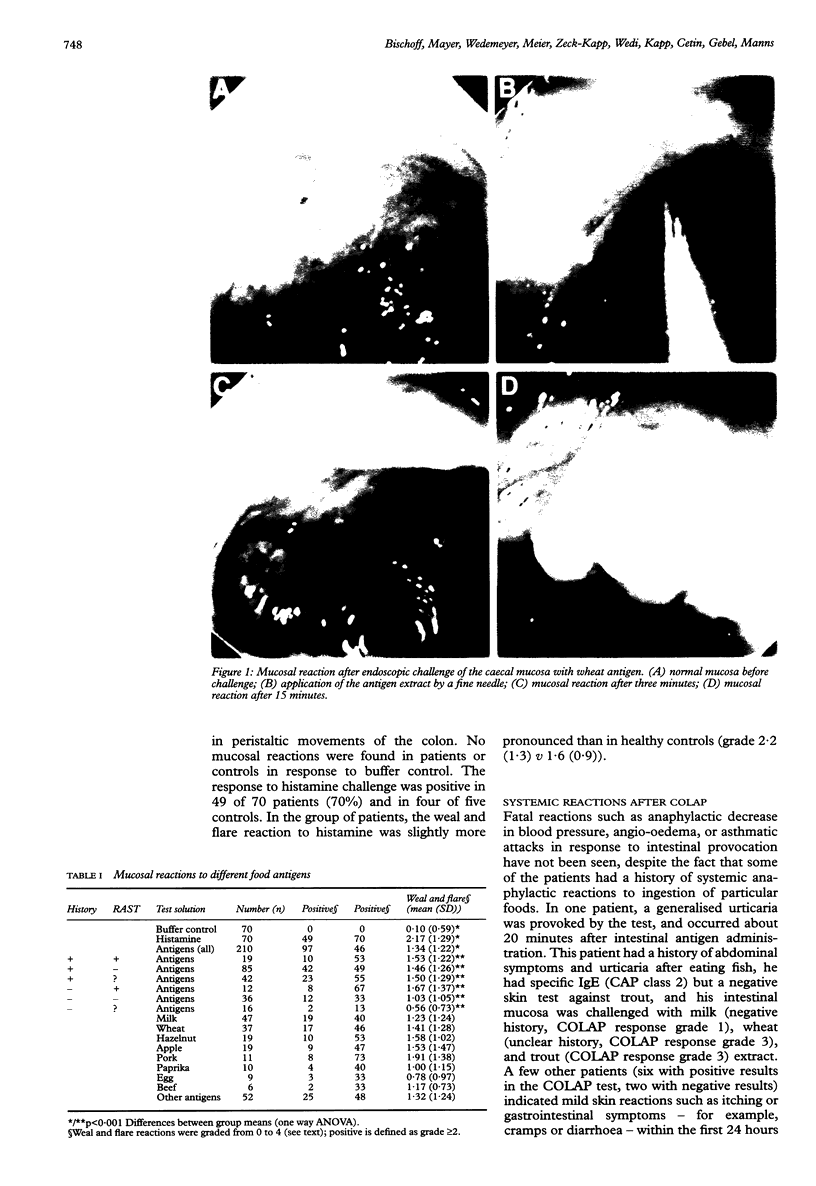
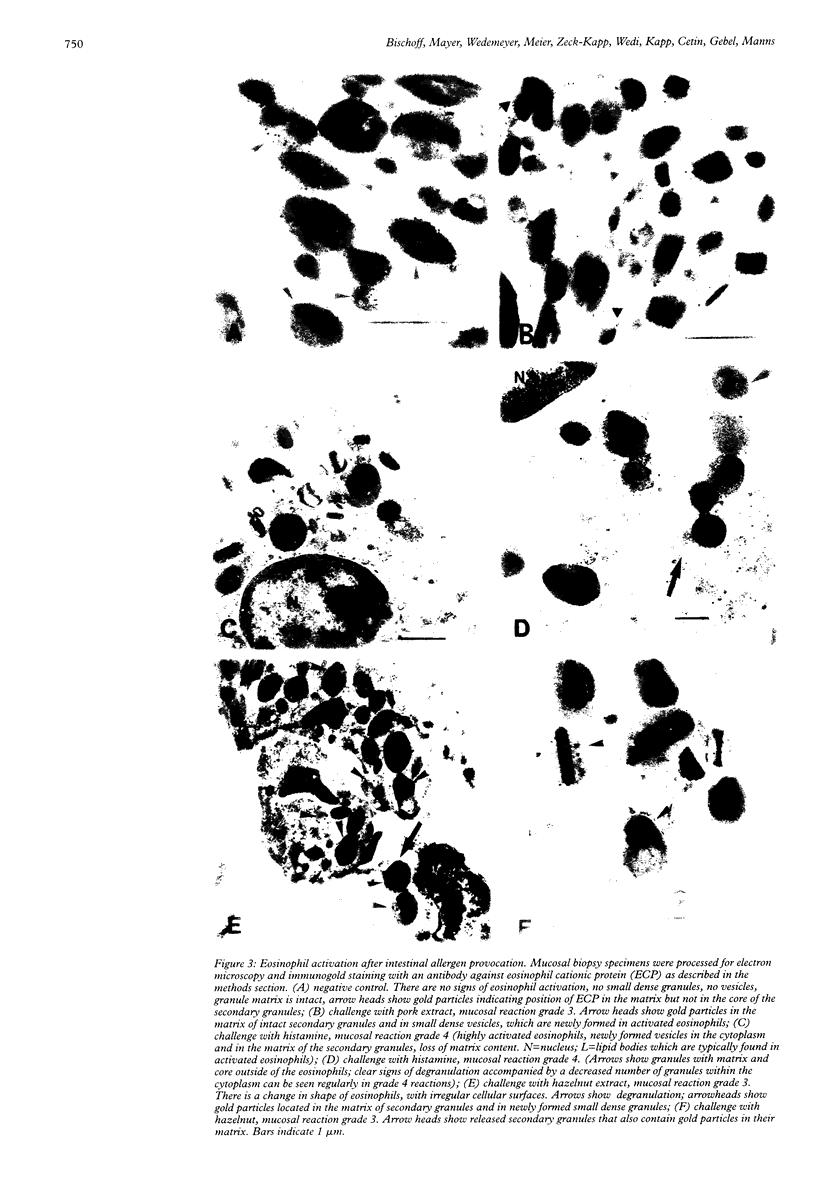
BACKGROUND: The clinical relevance of gastrointestinal food allergy in adults is largely unknown because the mechanisms are poorly understood and the diagnosis is difficult to confirm. AIMS: To improve the diagnostic means for confirming intestinal food allergy on an objective basis, a new colonoscopic allergen provocation (COLAP) test was developed. PATIENTS: The COLAP test was performed in 70 adult patients with abdominal symptoms suspected to be related to food allergy, and in five healthy volunteers. METHODS: During the COLAP test, the caecal mucosa was challenged endoscopically with three food antigen extracts, a buffer control, and a positive control (histamine). The mucosal weal and flare reaction was registered semiquantitatively 20 minutes after challenge, and tissue biopsy specimens were examined for mast cell and eosinophil activation. RESULTS: No severe systemic anaphylactic reactions were found in response to intestinal challenge. The COLAP test was positive to at least one food antigen in 54 of 70 patients (77%), whereas no reaction in response to antigen was found in healthy volunteers. Antigen induced weal and flare reactions were correlated with intestinal mast cell and eosinophil activation, as well as with patients' history of adverse reactions to food, but not with serum concentrations of total or specific IgE or skin test results. CONCLUSION: The COLAP test may be a useful diagnostic measure in patients with suspected intestinal food allergy and may provide a new tool for the study of underlying mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagnato G. F., Di Cesare E., Caruso R. A., Gulli S., Cugliari A., Morabito Lo Prete A., Previti M., Muscarà M., Bottari M. Gastric mucosal mast cells in atopic subjects. Allergy. 1995 Apr;50(4):322–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1995.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Wedemeyer J., Herrmann A., Meier P. N., Trautwein C., Cetin Y., Maschek H., Stolte M., Gebel M., Manns M. P. Quantitative assessment of intestinal eosinophils and mast cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Histopathology. 1996 Jan;28(1):1–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.262309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Barnéon G., Ghavanian N., Enander I., Venge P., Ahlstedt S., Simony-Lafontaine J., Godard P. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1033–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet J., Chanez P., Lacoste J. Y., Barnéon G., Ghavanian N., Enander I., Venge P., Ahlstedt S., Simony-Lafontaine J., Godard P. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1033–1039. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijnzeel-Koomen C., Ortolani C., Aas K., Bindslev-Jensen C., Björkstén B., Moneret-Vautrin D., Wüthrich B. Adverse reactions to food. European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology Subcommittee. Allergy. 1995 Aug;50(8):623–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1995.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijnzeel-Koomen C., Ortolani C., Aas K., Bindslev-Jensen C., Björkstén B., Moneret-Vautrin D., Wüthrich B. Adverse reactions to food. European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology Subcommittee. Allergy. 1995 Aug;50(8):623–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1995.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Grube D. Immunoreactivities for chromogranin A and B, and secretogranin II in the guinea pig entero-endocrine system: cellular distributions and intercellular heterogeneities. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 May;264(2):231–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00313960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth E. N., Hood A. F., Soter N. A., Kagey-Sobotka A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Cutaneous late-phase response to allergen. Mediator release and inflammatory cell infiltration. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1519–1526. doi: 10.1172/JCI114047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe S. E., Perdue M. H. Gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity: basic mechanisms of pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):1075–1095. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural evidence for release of major basic protein-containing crystalline cores of eosinophil granules in vivo: cytotoxic potential in Crohn's disease. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):460–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah D. A., Calder I., Benson L., MacKenzie J. F. Specific food intolerance: its place as a cause of gastrointestinal symptoms. Gut. 1985 Feb;26(2):164–168. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Food sensitivity or self-deception? N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 16;323(7):476–478. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008163230709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounni A. S., Lamkhioued B., Delaporte E., Dubost A., Kinet J. P., Capron A., Capron M. The high-affinity IgE receptor on eosinophils: from allergy to parasites or from parasites to allergy? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Dec;94(6 Pt 2):1214–1216. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounni A. S., Lamkhioued B., Delaporte E., Dubost A., Kinet J. P., Capron A., Capron M. The high-affinity IgE receptor on eosinophils: from allergy to parasites or from parasites to allergy? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Dec;94(6 Pt 2):1214–1216. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern G. M., Scott J. R. Non-IgE antibody mediated mechanisms in food allergy. Ann Allergy. 1987 Jan;58(1):14–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewett D. L., Fein G., Greenberg M. H. A double-blind study of symptom provocation to determine food sensitivity. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 16;323(7):429–433. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008163230701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. A., Dickinson R. J., Workman E., Wilson A. J., Freeman A. H., Hunter J. O. Crohn's disease: maintenance of remission by diet. Lancet. 1985 Jul 27;2(8448):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. A., Dickinson R. J., Workman E., Wilson A. J., Freeman A. H., Hunter J. O. Crohn's disease: maintenance of remission by diet. Lancet. 1985 Jul 27;2(8448):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. A., McLaughlan P., Shorthouse M., Workman E., Hunter J. O. Food intolerance: a major factor in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet. 1982 Nov 20;2(8308):1115–1117. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92782-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Hinde J. Inflammatory component of celiac sprue mucosa. I. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90749-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milici A. J., Porter G. A. Lectin and immunolabeling of microvascular endothelia. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1991 Nov;19(3):305–315. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor A. R. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Scott Med J. 1990 Dec;35(6):163–165. doi: 10.1177/003693309003500601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panula P., Häppölä O., Airaksinen M. S., Auvinen S., Virkamäki A. Carbodiimide as a tissue fixative in histamine immunohistochemistry and its application in developmental neurobiology. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Mar;36(3):259–269. doi: 10.1177/36.3.3343510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raible D. G., Schulman E. S., DiMuzio J., Cardillo R., Post T. J. Mast cell mediators prostaglandin-D2 and histamine activate human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3536–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raithel M., Hochberger J., Hahn E. G. Effect of colonoscopy premedication containing diazepam and pethidine on the release of mast cell mediators in gut mucosal samples. Endoscopy. 1995 Aug;27(6):415–423. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann H. J., Lewin J. Gastric mucosal reactions in patients with food allergy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Nov;83(11):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Broadbent K. R., Bernhisel-Broadbent J. Spontaneous release of histamine from basophils and histamine-releasing factor in patients with atopic dermatitis and food hypersensitivity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 27;321(4):228–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907273210405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki-Nishimura T., Sano T., Uchida M. K. Effects of benzodiazepines on serotonin release from rat mast cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90749-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji S., Bischoff S. C., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. IL-3 and IL-5 prime normal human eosinophils to produce leukotriene C4 in response to soluble agonists. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3855–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talley N. J., Kephart G. M., McGovern T. W., Carpenter H. A., Gleich G. J. Deposition of eosinophil granule major basic protein in eosinophilic gastroenteritis and celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91106-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E., Stoneham M. D., Petruckevitch A., Barton J., Rona R. A population study of food intolerance. Lancet. 1994 May 7;343(8906):1127–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeck-Kapp G., Czech W., Kapp A. TNF alpha-induced activation of eosinophil oxidative metabolism and morphology--comparison with IL-5. Exp Dermatol. 1994 Aug;3(4):176–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1994.tb00275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]