Abstract
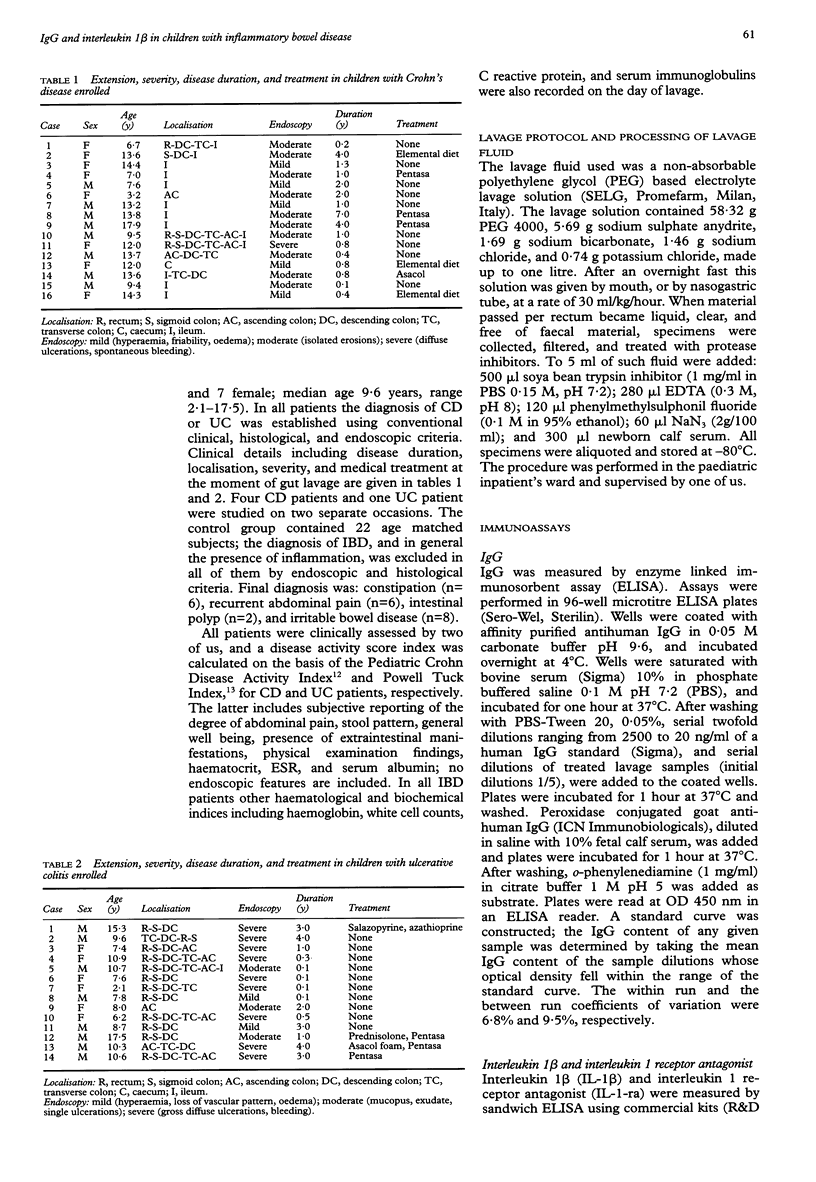
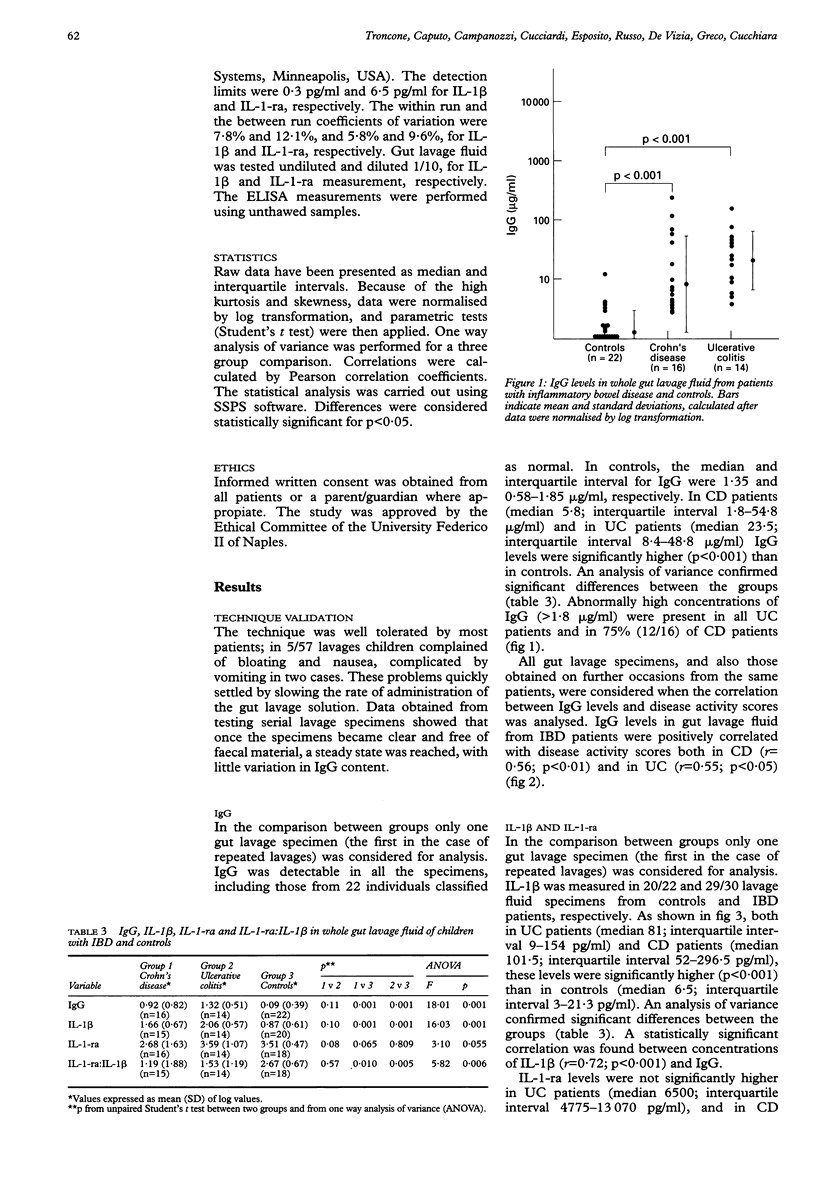
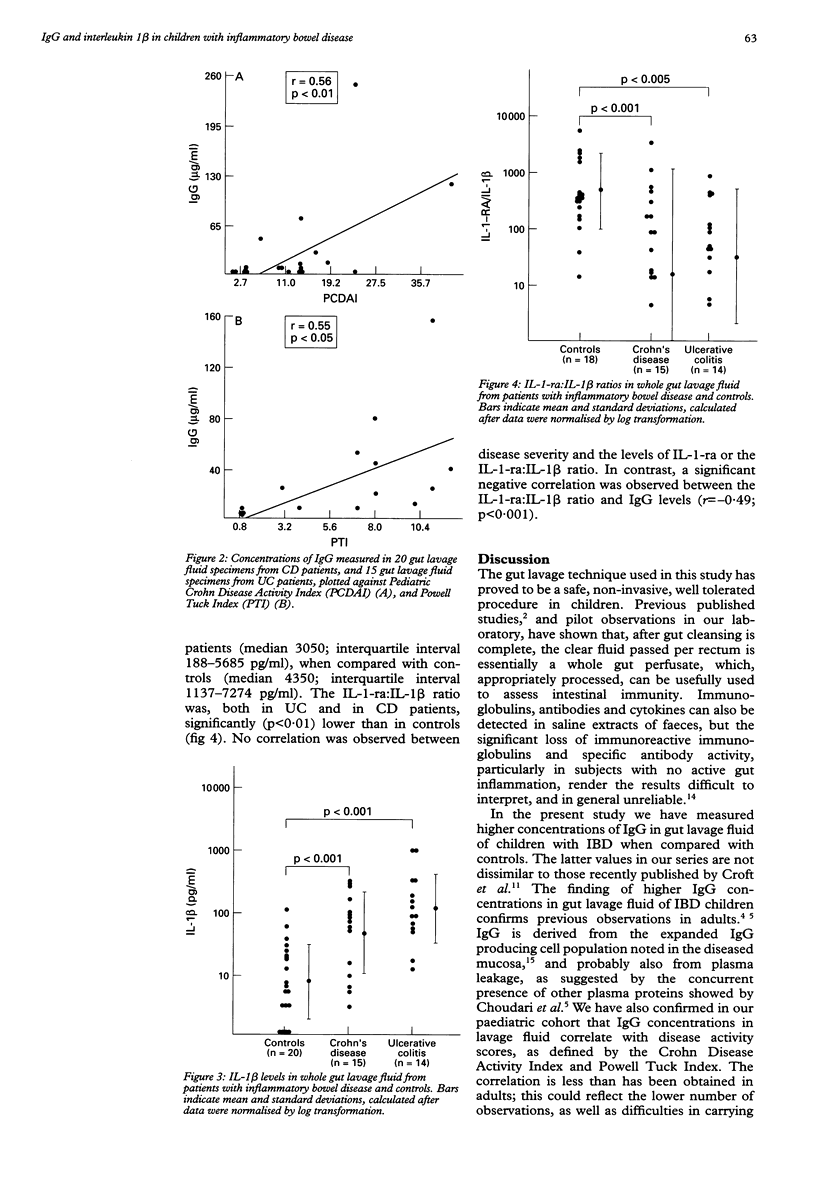
BACKGROUND: Whole gut lavage is currently used as preparation before radiological or endoscopic examination of the large bowel. AIM: To validate the gut lavage technique for the assessment of mucosal inflammation, by measuring intestinal IgG and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta) in the fluid obtained. PATIENTS: Sixteen children with Crohn's disease (CD), 14 with ulcerative colitis (UC), and 22 age matched controls. METHODS: Isotonic, non-absorbable polyethylene glycol based lavage solution was given orally or by nasogastric tube. Clear fluid was collected, filtered, and treated with protease inhibitors. IgG, IL-1 beta and IL-1-receptor antagonist (IL-1-ra) were measured by sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS: In patients with UC and CD, IgG and IL-1 beta levels were significantly (p < 0.001) higher than in controls. A positive correlation (p < 0.05) was found with disease activity scores. IL-1-ra levels were not significantly different in UC and CD, when compared with controls, but the IL-1-ra:IL-1 beta ratio was significantly (p < 0.01) lower in patients with UC and CD, and negatively (p < 0.001) correlated with IgG levels in lavage fluid. CONCLUSIONS: Gut lavage fluid IgG and IL-1 beta levels and IL-1-ra:IL-1 beta ratio may provide objective discrimination between active and inactive disease in children with inflammatory bowel disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Immunohistochemical characterization of local immunoglobulin formation in Crohn's disease of the ileum. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(5):447–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brydon W. G., Ferguson A. Haemoglobin in gut lavage fluid as a measure of gastrointestinal blood loss. Lancet. 1992 Dec 5;340(8832):1381–1382. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92562-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casini-Raggi V., Kam L., Chong Y. J., Fiocchi C., Pizarro T. T., Cominelli F. Mucosal imbalance of IL-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. A novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2434–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choudari C. P., O'Mahony S., Brydon G., Mwantembe O., Ferguson A. Gut lavage fluid protein concentrations: objective measures of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Apr;104(4):1064–1071. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90275-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli F., Nast C. C., Clark B. D., Schindler R., Lierena R., Eysselein V. E., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) gene expression, synthesis, and effect of specific IL-1 receptor blockade in rabbit immune complex colitis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):972–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI114799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft N. M., Marshall T. G., Ferguson A. Gut inflammation in children with cystic fibrosis on high-dose enzyme supplements. Lancet. 1995 Nov 11;346(8985):1265–1267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91864-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Humphreys K. A., Croft N. M. Technical report: results of immunological tests on faecal extracts are likely to be extremely misleading. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Jan;99(1):70–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspari M. M., Brennan P. T., Solomon S. M., Elson C. O. A method of obtaining, processing, and analyzing human intestinal secretions for antibody content. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 25;110(1):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges M., Kingstone K., Brydon W. G., Sallam J., Ferguson A. Use of whole-gut lavage to measure intestinal immunity in healthy Sierra Leonean children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1994 Jul;19(1):65–70. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199407000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S., Fitzgerald J. E., Wyzga N., Muller R., Treem W. R., Justinich C. J., Kreutzer D. L. Relationship of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist to mucosal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 Nov;21(4):419–425. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199511000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebo K. B., Heyman M. B. Polyethylene glycol-electrolyte solution for intestinal clearance in children with refractory encopresis. A safe and effective therapeutic program. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Mar;142(3):340–342. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150030114035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligumsky M., Simon P. L., Karmeli F., Rachmilewitz D. Role of interleukin 1 in inflammatory bowel disease--enhanced production during active disease. Gut. 1990 Jun;31(6):686–689. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.6.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Wu K., Jewell D. P. Enhanced production of interleukin 1-beta by mononuclear cells isolated from mucosa with active ulcerative colitis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):835–838. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield J. C., Holden H., Tarlow J. K., Di Giovine F. S., McDowell T. L., Wilson A. G., Holdsworth C. D., Duff G. W. Novel genetic association between ulcerative colitis and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Gastroenterology. 1994 Mar;106(3):637–642. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony S., Arranz E., Barton J. R., Ferguson A. Dissociation between systemic and mucosal humoral immune responses in coeliac disease. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):29–35. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony S., Barton J. R., Crichton S., Ferguson A. Appraisal of gut lavage in the study of intestinal humoral immunity. Gut. 1990 Dec;31(12):1341–1344. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.12.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony S., Choudari C. P., Barton J. R., Walker S., Ferguson A. Gut lavage fluid proteins as markers of activity of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Sep;26(9):940–944. doi: 10.3109/00365529108996246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Tuck J., Bown R. L., Lennard-Jones J. E. A comparison of oral prednisolone given as single or multiple daily doses for active proctocolitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(7):833–837. doi: 10.3109/00365527809182199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolia V., Fleming S., Dubois R. S. Use of Golytely in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984 Jun;3(3):468–470. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198406000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngman K. R., Simon P. L., West G. A., Cominelli F., Rachmilewitz D., Klein J. S., Fiocchi C. Localization of intestinal interleukin 1 activity and protein and gene expression to lamina propria cells. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91010-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


