Abstract
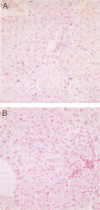
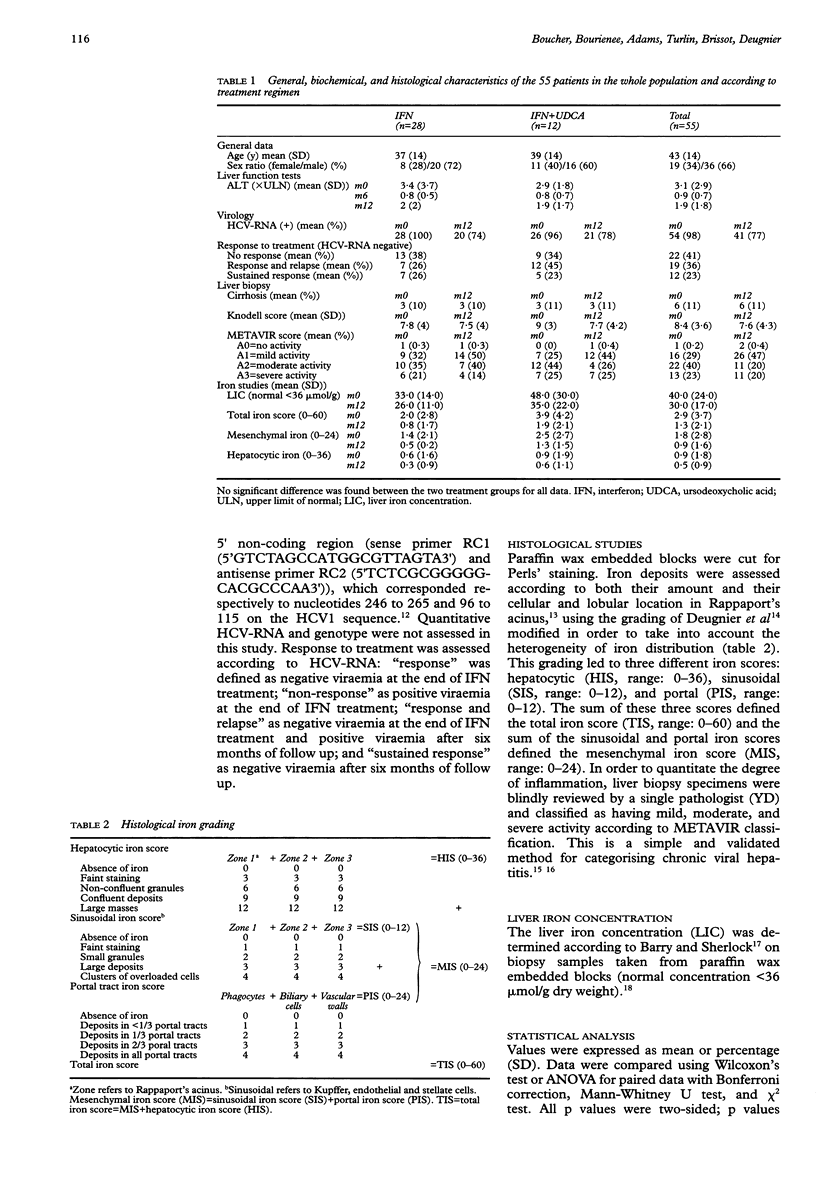
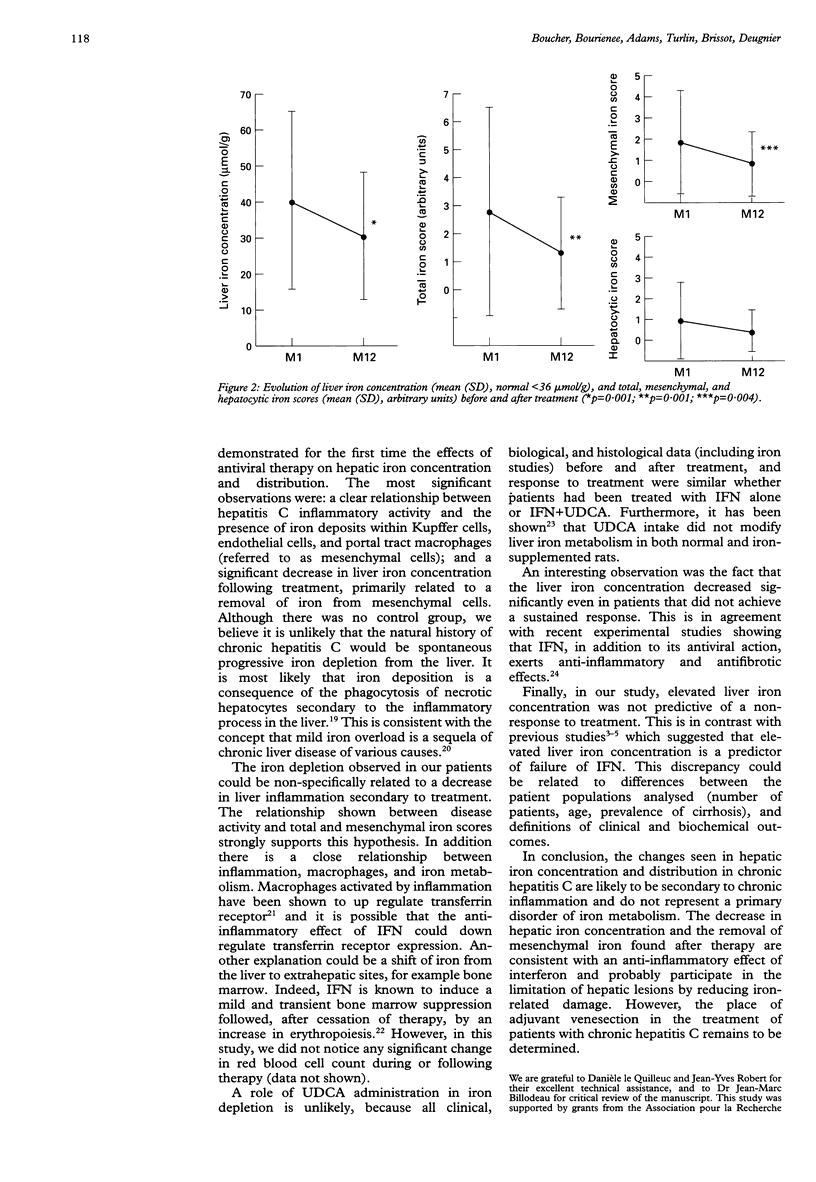
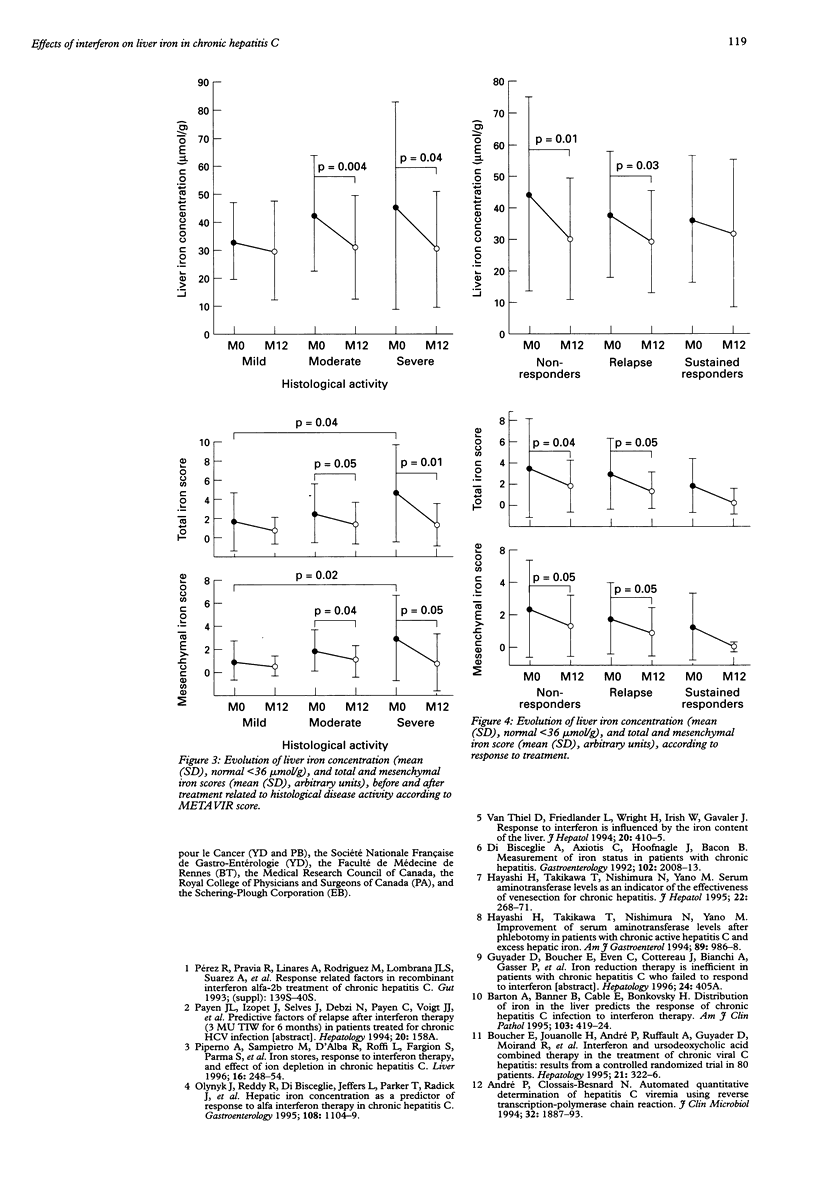
BACKGROUND: Recent studies have suggested that, in patients with chronic hepatitis C, elevated iron stores are predictive of a poor response to interferon. AIMS: To assess liver iron concentration and distribution before and after interferon treatment in patients with hepatitis C in order to evaluate further the role of iron in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C. PATIENTS: Fifty-five patients with hepatitis C treated with alpha interferon for six months. METHODS: Patients were evaluated for liver iron concentration (normal value < 36 mumol/g), and liver iron distribution before and six months after therapy. RESULTS: At entry: liver iron concentration was elevated in 16/55 patients (29%); iron staining (Perls' staining) was found in 31/55 patients (56%) mainly within Kupffer and endothelial cells. Iron load was significantly higher in patients with the most histological inflammatory activity. Following treatment: liver iron concentration decreased significantly (40 (24) to 30 (17) mumol/g, p = 0.001); this was related to iron depletion in mesenchymal cells. Iron depletion occurred regardless of the response to therapy. Elevated liver iron concentration was not found to be a predictive factor of failure of interferon. CONCLUSION: Although liver iron stores were usually normal or only slightly elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis C, biochemical and histological liver iron content decreased following treatment due to the diminution in mesenchymal iron deposits. Iron depletion was interpreted as both a consequence of the anti-inflammatory effect of treatment and a factor of improvement in liver histology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry M., Sherlock S. Measurement of liver-iron concentration in needle-biopsy specimens. Lancet. 1971 Jan 16;1(7690):100–103. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90838-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton A. L., Banner B. F., Cable E. E., Bonkovsky H. L. Distribution of iron in the liver predicts the response of chronic hepatitis C infection to interferon therapy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Apr;103(4):419–424. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedossa P., Poynard T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology. 1996 Aug;24(2):289–293. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besnard N. C., Andre P. M. Automated quantitative determination of hepatitis C virus viremia by reverse transcription-PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Aug;32(8):1887–1893. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.8.1887-1893.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher E., Jouanolle H., Andre P., Ruffault A., Guyader D., Moirand R., Turlin B., Jacquelinet C., Brissot P., Deugnier Y. Interferon and ursodeoxycholic acid combined therapy in the treatment of chronic viral C hepatitis: results from a controlled randomized trial in 80 patients. Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):322–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissot P., Bourel M., Herry D., Verger J. P., Messner M., Beaumont C., Regnouard F., Ferrand B., Simon M. Assessment of liver iron content in 271 patients: a reevaluation of direct and indirect methods. Gastroenterology. 1981 Mar;80(3):557–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deugnier Y. M., Turlin B., Powell L. W., Summers K. M., Moirand R., Fletcher L., Loréal O., Brissot P., Halliday J. W. Differentiation between heterozygotes and homozygotes in genetic hemochromatosis by means of a histological hepatic iron index: a study of 192 cases. Hepatology. 1993 Jan;17(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Takikawa T., Nishimura N., Yano M., Isomura T., Sakamoto N. Improvement of serum aminotransferase levels after phlebotomy in patients with chronic active hepatitis C and excess hepatic iron. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;89(7):986–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Takikawa T., Nishimura N., Yano M. Serum aminotransferase levels as an indicator of the effectiveness of venesection for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1995 Mar;22(3):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loréal O., Chenoufi N., Turlin B., Haziza-Pigeon C., Robert J. Y., Lescoat G., Mathiex-Fortunet H., Deugnier Y., Brissot P. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on liver iron stores and distribution in rats with normal or iron-supplemented diet. Liver. 1997 Feb;17(1):30–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1997.tb00775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olynyk J. K., Reddy K. R., Di Bisceglie A. M., Jeffers L. J., Parker T. I., Radick J. L., Schiff E. R., Bacon B. R. Hepatic iron concentration as a predictor of response to interferon alfa therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 1995 Apr;108(4):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno A., Sampietro M., D'Alba R., Roffi L., Fargion S., Parma S., Nicoli C., Corbetta N., Pozzi M., Arosio V. Iron stores, response to alpha-interferon therapy, and effects of iron depletion in chronic hepatitis C. Liver. 1996 Aug;16(4):248–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1996.tb00737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto J., Barry M., Sherlock S. Serum ferritin in patients with iron overload and with acute and chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):525–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport A. M. Hepatic blood flow: morphologic aspects and physiologic regulation. Int Rev Physiol. 1980;21:1–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault P. F., Hoofnagle J. H. Side effects of alpha interferon. Semin Liver Dis. 1989 Nov;9(4):273–277. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffman M. L., Hofmann C. M., Luketic V. A., Sanyal A. J., Contos M. J., Mills A. S. Improved sustained response following treatment of chronic hepatitis C by gradual reduction in the interferon dose. Hepatology. 1996 Jul;24(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taetle R., Honeysett J. M. Gamma-interferon modulates human monocyte/macrophage transferrin receptor expression. Blood. 1988 Jun;71(6):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Thiel D. H., Friedlander L., Fagiuoli S., Wright H. I., Irish W., Gavaler J. S. Response to interferon alpha therapy is influenced by the iron content of the liver. J Hepatol. 1994 Mar;20(3):410–415. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(94)80017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]