Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to develop and validate predictive models using clinical parameters, radiomic features, and a combination of both for invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA) of the lung in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Method: A total of 173 and 391 patients with IMA and non-IMA, respectively, were retrospectively analyzed from January 2017 to September 2022 in our hospital. Propensity Score Matching was used to match the 2 groups of patients. A total of 1037 radiomic features were extracted from contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT). The patients were randomly divided into training and test groups at a ratio of 7:3. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator algorithm was used for radiomic feature selection. Three radiomics prediction models were applied: logistic regression (logistic), support vector machine (SVM), and decision tree. The best-performing model was adopted, and the radiomics score (Radscore) was then computed. A clinical model was developed using logistic regression. Finally, a combined model was established based on a clinical model and a radiomics model. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) and decision curve analysis were used to evaluate the predictive value of the developed models. Results: Both clinical and radiomics models established using the logistic method showed the best performance. The Delong test revealed that the combined model was superior to the clinical and radiomics models (P = .018 and .020, respectively). The ROC-AUC (also decision curve analysis) of the combined model was 0.840 and 0.850 in the training and testing groups, respectively, which showed good predictive performance for IMA. The Brier scores for the combined model were 0.161 and 0.154 in the training and testing groups, respectively. Conclusion: The combined model incorporating radiomic CT features and clinical predictors may have the potential to predict IMA in patients with lung cancer.
Keywords: radiomics, contrast-enhanced CT, predictive model, invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma
Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths and the second most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide. 1 Nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for almost 85% of all primary lung cancers, among which adenocarcinoma is the most common pathological subtype.2,3 Primary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA) is a rare subtype of lung adenocarcinoma. It accounts for only 2% to 10% of lung adenocarcinoma.4,5 Due to its unique pathological, radiological, and prognostic characteristics, it has been separated from other adenocarcinomas and previously classified as nonmucinous bronchoalveolar carcinoma, according to the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification system for lung adenocarcinoma published in 2011. In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) also classified IMA as an invasive adenocarcinoma subtype. 6
Molecular biological differences between IMA and invasive nonmucinous adenocarcinoma affect the prognosis and treatment options of patients.7–9 Previous studies have shown that anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS), and co-occurring oncogenic mutations were observed more commonly in patients with IMA than in those with invasive nonmucinous adenocarcinoma. 10 Previous studies revealed that the frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (72.0% vs 40.0% vs 23.1%, P = .002) and ALK (undetected vs 20.0% vs 26.9%, P = .015) alterations showed a trend of gradual decrease and increase from non-IMA to mixed-IMA to pure-IMA, respectively. 11 Another study showed that KRAS mutations were more common in IMA than in other adenocarcinomas (14%-86% in IMA vs 1.5%-17% in non-IMA).11–16 These driver mutations influenced the choice of clinical drug treatment options. In addition, patients with IMA have significantly different outcomes compared to those with other types of adenocarcinoma. 9 However, nearly 80% of NSCLC patients, including patients with IMA, are diagnosed at an advanced stage and have no opportunity to undergo radical surgical treatment. 17 In these patients, the common methods to obtain these tissue specimens include tissue or liquid biopsy. Sometimes, these specimens cannot represent the entire tumor, as the tumor tissue varies with respect to time and space. Therefore, to evaluate the prognosis of patients accurately and guide precision treatment, it is necessary to find a Supplemental Material to predict IMA.
Computed tomography (CT) is widely used for tumor detection, staging, and therapeutic response monitoring in clinical practice.18,19 However, the noninvasive imaging diagnostic information provided by preoperative CT images is still limited and cannot differentiate IMA from non-IMA. Radiomics proposes a method to extract quantitative and high-throughput data from medical images, which reflect the underlying pathophysiology and reveal information on tumor phenotypes. 20 In the past decade, radiomics, as an alternative to biopsies, achieved a favorable performance in predicting malignancy risk, gene expression pattern, and the tumor microenvironment in lung cancer and in quick diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic.21–24 Based on these former explorations, to better satisfy the need for precise evaluation of pathology, radiomics features were used to develop a model to predict the IMA of the lung.
Materials and Methods
This study was performed following the Helsinki Declaration and approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital. This study was performed following the Helsinki Declaration and approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital (Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University Fourth Affiliated Hospital, reference number: 2022KS017, data 2022.6.27). Ethical approval was obtained from our hospital, and waivers of consent were granted to the study subjects.
Patients’ Selection
We retrospectively analyzed patients diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma between January 2017 and September 2022 in our hospital. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with IMA and non-IMA diagnosed by needle biopsy or surgical pathology, with imaging showing a peripheral lung cancer; (2) patients with complete clinical and pathological data, which can provide analyzable plain and enhanced thin-slice CT image data (1 or 1.25 mm/slice); and (3) availability of CT images taken within 2 weeks before pathological diagnosis. The exclusion criteria for patients were as follows: (1) patients on anti-tumor therapy (including radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, or molecular targeted therapy) prior to CT examination and pathological diagnosis; (2) pathologically mixed mucinous adenocarcinoma (ie, nonmucinous adenocarcinoma component ≥ 10%) or imaging manifestations of pneumonic mucinous adenocarcinoma; (3) too small size of the primary lesion (the largest diameter of the lesion < 0.5 cm) to be segmented; and (4) patients with other types of cancer or with incomplete clinical and imaging data. All patients with IMA matching the inclusion criteria were enrolled from January 2017 to September 2022 at our hospital. In addition, 391 patients with non-IMA matching the inclusion criteria were randomly selected between January 2017 and September 2022 in our hospital. Propensity Score Matching (PSM) was used to match the 2 groups of patients. A previous study revealed no significant difference in age between patients with IMA and non-IMA. 11 However, patients with non-IMA developed metastasis much more easily. To eliminate the confounding factors, the matching factors included age and tumor diameter, and the matching ratio was 1:1.
CT Image Acquisition
For all patients, contrast-enhanced chest CT scans were performed using one of the following multidetector row scanners: Somatom Sensation 64, Definition Flash (Siemens Medical Solutions, Forchheim, Germany), and Discovery CT 750 HD (Revolution; GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA). Before scanning, the patients were trained to breathe and hold their breath at the end of inspiration to scan. The range included the thoracic inlet to the base of the lung. Scanning parameters were as follows: (1) Siemens SOMATOM Definition Flash CT: tube voltage 120 kV, tube current using automatic mAs, a reconstruction layer thickness of 1 mm, matrix 512 × 512, pitch 1.2; (2) GE Revolution CT: tube voltage 120 kV, tube current 200 mAs, a reconstruction layer thickness of 1.25 mm, matrix 512 × 512, and pitch 1.2. The reconstruction algorithm adopted was a lung algorithm. After the plain scan was completed, a bolus dose of (70-90 mL) nonionic contrast agent iohexol or ioversol (300 mg·I/mL) was injected through the cubital vein using a high-pressure syringe at a flow rate of 3 mL/s. Arterial and venous phase dual-phase enhanced scans were performed 30 and 90 s after the contrast agent, respectively. Other parameters were the same as those of the plain scans. After scanning, the raw data were uploaded to a postprocessing workstation for multiplanar reconstruction (MPR).
Image feature analysis was performed by 2 board-certified thoracic radiologists (with 6 and 12 years of experience in chest CT imaging, respectively) who were blinded to clinical and histological findings. All CT image features were independently recorded by 2 radiologists, and any discrepancies in assessments were consistently resolved. The mediastinal window (window width 400 HU; window level 40 HU) and lung window (window width 1200 HU; window level − 600 HU) were set. The CT image features recorded in the image analysis are as follows: (1) primary tumor location (left and right lungs, upper, middle, and lower lobes); (2) adjacent to pleura (the minimum distance between the lesion and the pleura is < 1 cm); (3) tumor size (maximum diameter), type (ground glass density, partially solid, and solid), average CT value (unenhanced scan, arterial phase, and venous phase), ΔCTA value (the difference between the CT value of the arterial phase and the CT value of the plain scan), ΔCTV value (the difference of the CT value of the venous phase and the CT value of the plain scan), shape (round or quasi-round, irregular), and edge (lobular, blur); (4) internal features of the tumor (calcification, necrosis, cyst, air bronchus sign, etc); (5) external features of the tumor (thickening of adjacent bronchovascular bundles, pleural depression, and obstructive changes).
Segmentation, Feature Extraction, and Selection
CT images were imported into an open-source software ITK-SNAP (version 3.6.0, http://www.itksnap.org) and read under lung window (width 1200/−600 HU) and mediastinal window (width 400/40 HU) settings. The primary lesions of patients with adenocarcinomas were selected for tumor segmentation after image acquisition. A radiologist without knowledge of the clinical data manually delineated the regions of interest (ROI) layer by layer. The tumor ROI encompassed the entire lesion as much as possible, including the bronchi, blood vessels, and vacuoles within the nodules, and excluded the normal lung tissue. Tumor segmentation was performed on 50 patients randomly selected from the entire cohort for independent segmentation to assess intraclass agreement one month later. Another radiologist repeated the independent segmentation of the selected 50 patients and evaluated the interclass agreement. Intra- and interclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were used to assess the intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility of feature extraction.
Pyradiomics was used to extract the radiomics features. 25 A total of 1037 features were extracted, including 17 classes of histogram, 14 classes of form factor, 24 classes of Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), 16 classes of Gray Level Run Length Matrix (GLRLM), 16 classes of Gray Level Size Zone Matrix (GLSZM), 5 classes of Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM), and 14 classes of Gray Level Dependence Matrix (GLDM).
To reduce the dimensionality of radiomic features to the number of events, we performed 3 sequential steps for radiomic feature selection. First, we evaluated the interobserver agreement of radiomic features and selected features showing ICC > 0.75. Next, we chose radiomic features that showed statistical significance between the IMA and non-IMA groups. Finally, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression model was used to select the most useful predictive features of radiomics for IMA in the training group. Five-fold cross-validation was performed 100 times to avoid overfitting.
Model Development
Three radiomics prediction models: logistic regression (logistic), support vector machine (SVM), and decision tree were applied. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the performance of the 3-machine-learning model. The best-performing model was adopted, and the radiomics score (Radscore) was then computed.
At the same time, we constructed a model based on clinical and CT features for multivariate logistic regression analysis. The clinical features included sex, age, and smoking status. The CT features have been illustrated above.
Finally, 3 models, namely the clinical model, the radiomics model, and a combination of clinical and radiomics models, were compared statistically to identify the model with higher predictability.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R version 3.6.3 and Python version 3.7. The patients were randomly divided into training and test groups at a ratio of 7:3. All radiomic features were subjected to Z-score normalization. Baseline data were analyzed by univariate analysis using Python statistical model 0.11.1. The chi-square test was used for categorical variables, and the t-test or Mann-Whitney U-test was used for continuous variables. Factors with statistical differences (P < .05) were included in the multivariate logistic regression analysis. Clinical and CT features with statistical differences (P < .05) in the multivariate analysis results were selected to construct the clinical diagnostic model.
The main evaluation indicators were the area under the ROC curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to calculate the clinical impact of the 3 models.
Results
Patient Characteristics
A total of 173 and 391 patients with IMA and non-IMA, respectively, were retrospectively analyzed. Finally, 173 patients with non-IMA were screened and matched with 173 patients with pulmonary IMA. The patients were randomly divided into training and test groups at a ratio of 7:3. The training group included 242 patients (125 and 117 patients with IMA and non-IMA, respectively). The testing group included 104 patients (56 and 48 patients with IMA and non-IMA, respectively). The characteristics of the patients in the training and testing cohorts are shown in detail in Table 1. The average age was 61 years (range was 18-83 years). There were no significant differences in the clinical characteristics (age, smoking, and sex) between the IMA and non-IMA groups (Table 1). Pleural traction, necrosis, and bronchus cutoff signs were more common in patients with non-IMA (P < .05, Table 1). Vascular passage, cystic cavity, early stage, and lower lobe lesion were more common in the IMA group (P < .05, Table 1). The ΔCTV of IMA was significantly lower than that of non-IMA (P < .05, Table 1). A total of 16 patients with IMA underwent preoperative biopsy, of which 7 (43.750%) could not be identified as having mucinous adenocarcinoma and were only diagnosed with adenocarcinoma.
Table 1.
Clinical Characteristics of Patients.
| Training cohort | Testing cohort | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characters | NIMA | IMA | P | NIMA | IMA | P |
| Smoking | ||||||
| No | 64 | 75 | .405 | 38 | 33 | .922 |
| Yes | 53 | 50 | 18 | 15 | ||
| Solid | ||||||
| No | 65 | 81 | .142 | 15 | 10 | .479 |
| Yes | 52 | 44 | 41 | 38 | ||
| Lobul | ||||||
| No | 40 | 33 | .187 | 18 | 11 | .296 |
| Yes | 77 | 92 | 38 | 37 | ||
| Spicul | ||||||
| No | 72 | 74 | .710 | 30 | 31 | .256 |
| Yes | 45 | 51 | 26 | 17 | ||
| Cyst | ||||||
| No | 95 | 64 | <.001 | 43 | 23 | .002 |
| Yes | 22 | 61 | 13 | 25 | ||
| Necrosis | ||||||
| No | 86 | 117 | <.001 | 39 | 43 | .013 |
| Yes | 31 | 8 | 17 | 5 | ||
| Edge | ||||||
| No | 17 | 12 | .238 | 10 | 6 | .450 |
| Yes | 100 | 113 | 46 | 42 | ||
| VS | ||||||
| No | 93 | 83 | .022 | 52 | 29 | <.001 |
| Yes | 24 | 42 | 4 | 19 | ||
| BS | ||||||
| No | 105 | 106 | .250 | 51 | 39 | .143 |
| Yes | 12 | 19 | 5 | 9 | ||
| PLT | ||||||
| No | 45 | 108 | <.001 | 21 | 33 | .001 |
| Yes | 72 | 17 | 35 | 15 | ||
| BCS | ||||||
| No | 73 | 103 | <.001 | 33 | 40 | .007 |
| Yes | 44 | 22 | 23 | 8 | ||
| LL | ||||||
| No | 78 | 47 | <.001 | 36 | 17 | .003 |
| Yes | 39 | 78 | 20 | 31 | ||
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 62 | 62 | .642 | 22 | 16 | .530 |
| Female | 55 | 62 | 34 | 32 | ||
| ΔCTV median [IQR] | 37.000 [10.000, 66.625] | 24.000 [12.000, 76.000] | <.001 | 32.000 [22.000, 51.000] | 25.000 [14.000, 46.000] | .018 |
| Diameter, median [IQR] | 2.300 [1.400, 3.600] | 2.200 [1.500, 3.500] | .795 | 2.400 [1.400, 3.300] | 2.300 [1.300, 3.500] | .855 |
| Age, median [IQR] | 60.000 [53.000, 67.000] | 61.000 [56.000, 67.000] | .697 | 62.000 [56.000, 68.000] | 64.000 [57.000, 67.000] | .802 |
Abbreviations: IMA, invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma; NIMA, noninvasive mucinous adenocarcinoma; Lobul, lobulation; Spicul, spiculation; Cyst, Cyst cavity; VS, vascular passage; BS, bronchus sign; PLT, pleural traction; BCS, bronchus cutoff sign; LL, lesion location in the lower lobe; ΔCTV, venous CT value − plain CT value.
Feature Selection and Clinical Model Construction
Multivariate analysis showed that there were significant differences between mucinous adenocarcinoma and nonmucinous adenocarcinoma in the cystic cavity, vascular passage bronchial truncation, lesion location in the lower lobe, pleural traction, and ΔCTV (venous CT value − plain CT value). A clinical prediction model was established using logistic regression based on 5 features. The AUC values of the clinical models for predicting IMA were 0.780 and 0.770 in the training and testing cohorts, respectively. See Tables 2 and 3 for details.
Table 2.
Multivariate Analysis to Identify Significant Factors for IMA.
| Predictors | P | OR | Lower | Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔCTV | 0.0 | 0.185 | 0.087 | 0.37 |
| Cyst | 0.0 | 2.862 | 1.704 | 4.873 |
| VS | 0.006 | 2.241 | 1.268 | 4.04 |
| PLT | 0.013 | 0.533 | 0.324 | 0.872 |
| LL | 0.0 | 3.553 | 2.171 | 5.9 |
Abbreviations: Cyst, Cyst cavity; VS, vascular passage; PLT, pleural traction; LL, lesion location in the lower lobe; ΔCTV, venous CT value −- plain CT value; OR, odds ratio.
Table 3.
Diagnostic Performance of Prediction Models.
| Model | Training cohort | Testing cohort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | SEN | SPE | AUC | SEN | SPE | |
| RADS | 0.720 | 0.664 | 0.667 | 0.770 | 0.771 | 0.750 |
| Clinical | 0.780 | 0.656 | 0.778 | 0.770 | 0.625 | 0.804 |
| Comb | 0.840 | 0.856 | 0.718 | 0.850 | 0.771 | 0.804 |
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; SEN, sensitivity; SPE, specificity; Radiomics, radiomics model; Clinical, clinical model; Comb, combined model.
Radiomics Feature Selection and Model Construction
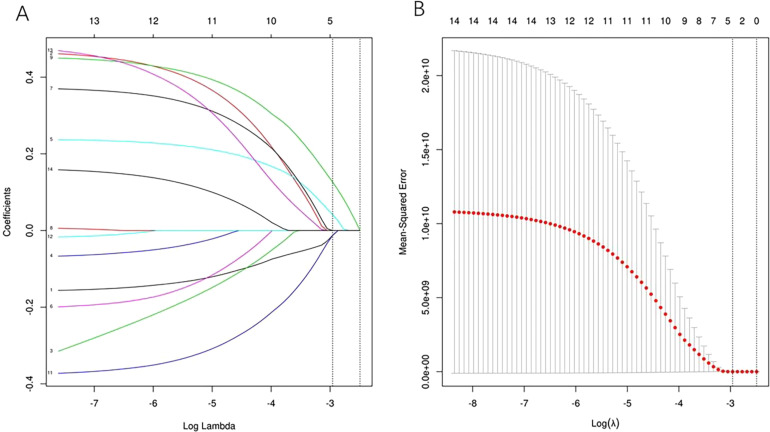
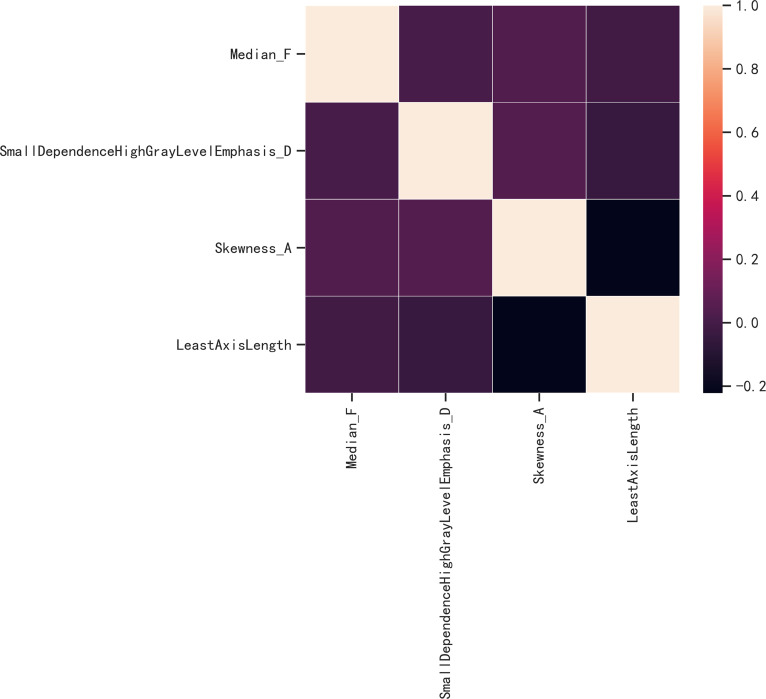
To eliminate redundant features, 612 features that showed no significant difference between IMA and non-IMA and 411 features with ICC values < 0.75 were excluded. After screening out the redundant features by LASSO with the value of λ on the minimum standard and 1-standard error were 0.052 and 0.083, respectively, the 4 most robust radiomics features (Least Axis Length, Small Dependence High Gray Level Emphasis [SDHGLE], median, and skewness) were retained when the value of λ on the minimum standard. The relationship between the 4 radiomic features was significantly weak (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1.
Radiomics feature selection with LASSO. After screening out the redundant features by LASSO, the 4 most robust radiomics features (including Least Axis Length, SDHGLE, median, and Skewness) were retained. The vertical line shows the value of λ, and the dashed lines on the left and right sides indicate the minimum standard and 1-standard error standard (1-SE). The predictive error of the minimum standard is very close to 1-SE. Sometimes, we tend to choose 1-SE to select a much more reduced model.
Abbreviations: LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; SDHGLE, Small Dependence High Gray Level Emphasis.
Figure 2.
The correlation analysis of radiomic features. The correlation coefficient was between −0.222 and 0.041. So there is no significant correlation between any 2 features. The correlation of characters in the model more than 0.6 will influence the stability of the model. Figure 2 shows that the correlation of the characters in the radiomics model was less than 0.6. So it will not influence the stability of our model. A much clear Figure 2 has been provided in the article.
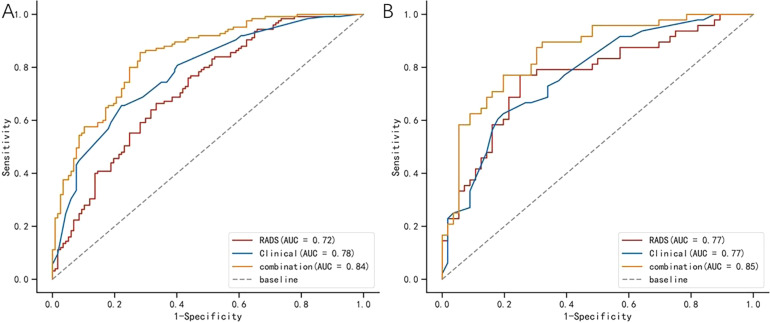
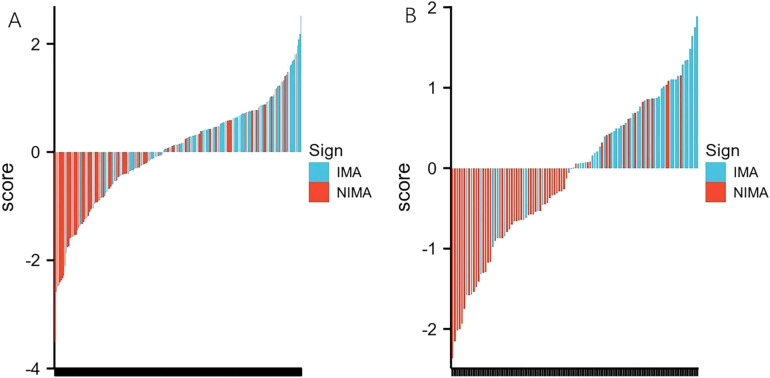
Machine learning models, including logistic regression (logistic), SVM, and decision tree, were developed based on the 4 radiomics features. The model established using the logistic method had the best performance, and the AUC values in the training and testing cohorts were 0.720 and 0.770, respectively (Table 3 and Figure 3). The Radscore for each patient was then calculated using the selected features weighted by their respective coefficients in the logistic model, which can be expressed as follows: Radscore = −0.026 + 0.410*SDHGLE + 0.222*Skewness −0.245*Median −0.223*Least Axis Length. The Radscore for each patient in the training and testing cohorts is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3.
Comparison of ROC curves among the clinical model, radiomics model, and combined model respectively in the training cohorts (A) and testing cohorts (B). The AUC values in the combined model are better than in the clinical model and radiomics model for the prediction of IMA.
Abbreviations: ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; IMA, invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma.
Figure 4.
Bar charts of radscore for each patient in the training cohort (A) and testing cohort (B). The X-axis represents each patient, each bar represents one patient. Red bars indicate the Radscore for patients with NIMA, while blue bars indicate the Radscore for patients with IMA. Red bars above the zero-line or blue bars below the zero-line mean misclassification.
Abbreviations: IMA, invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma; NIMA, noninvasive mucinous adenocarcinoma;.
Combined Model Construction and Validation of Performance
Logistic regression was performed to establish a combined model based on the 5 clinical features and 4 radiomics features. And the nomogram was established (Supplemental Figure 3). The ROC-AUC of the combined model was 0.840 and 0.850 in the training and test groups, respectively (Table 3 and Figure 3). The Delong test revealed that the combined model and radiomics model were superior to the clinical and radiomics models (P = .018 and .020, respectively). The DCA revealed that when the probability of the threshold was over 0%, the net benefits of the combined model for the prediction of IMA were higher than those of the clinical and radiomics models in both the training and testing cohorts. The Brier scores of the combined model were 0.161 and 0.154 in the training and testing groups, respectively, and the calibration plots are shown in the figures (Supplemental Figures 1 and 2).
Discussion
In this study, we developed a model based on clinical and radiomic features to distinguish patients with IMA and non-IMA.
The results of this study revealed that when establishing clinical models, lesion location in the lower lobe, cystic cavity, pleural traction, ΔCTV, and bronchial truncation play significant roles in distinguishing IMA from non-IMA. Similar results indicating that CT features, including lesion location in the lower lobe, cystic cavity, pleural traction, ΔCTV, and bronchial truncation, are significantly related to IMA, have been reported.26–29 This difference may be attributed to the fact that the tumor cells of IMA originate from goblet or columnar epithelial cells. Relatively well-differentiated cancer cells can produce more mucus, which is affected by gravity. Therefore, it is often found in the lower lobe. Cysts appear in IMA because of incomplete obstruction of the bronchioles by mucus, resulting in alveolar hypoventilation. Contrarily, it may also be caused by internal necrosis of the tumor, which is discharged through the bronchus. The difference in the enhanced ΔCTV between IMA and non-IMA may also result from the mucinous component within the mucinous adenocarcinoma. Alternatively, IMA with cancer cells with lower metabolic activity, which are mucin-rich tumor cells, may also result in lower ΔCTV. The mucinous adenocarcinoma tumor cells spread diffuse along the walls of the bronchi and alveoli, secrete mucus, and block parts of the bronchi; nonetheless, mucinous adenocarcinoma tumor cells are less destructive to the bronchi than nonmucinous adenocarcinoma. Generally, nonmucinous adenocarcinomas tend to cause bronchial truncation less frequently than mucinous adenocarcinomas. Based on the clinical features, Cha et al 30 established a model to predict IMAs and the sensitivity and specificity of the model were 54.3% and 89.7%, respectively. Our study also developed a predictive model of IMA based on the characteristics above, and the ROC-AUC, sensitivity, and specificity of the model were 0.780 to 0.770, 65.6% to 62.5%, and 77.8% to 80.4% in the training and testing groups, respectively.
To explore a much more effective method for predicting IMA, we extracted 4 independent radiomic features associated with IMA: Skewness, Median, Small-Dpendence High Gray Level Emphasis, and Least Axis Length. These parameters belong to the GLDM, histogram, and form factor parameters. Small Dependence High Gray Level Emphasis, one of the GLDM parameters, shows that the smaller the difference between the grayscale corresponding pixel and its adjacent pixels, the smaller the spatial change in the image, and the coarser the image texture. The Median, which is a histogram parameter, represents the median pixel value of an image (of the lesion). Another histogram feature was Skewness, which reflects the degree of asymmetry in the histogram distribution. If the predictive value was effective, the absolute values of the skewness would have been higher. The Least Axis Length is a form-factor parameter that is independent of the gray-level intensity distribution in the ROI. All the above features were the conversion of CT images into higher-throughput radiomics feature data. They allow high-throughput mining of quantitative imaging features from general medical images, followed by automated analysis to assist clinical decision-making. A previous study revealed that radiomic features were significantly related to the subtypes (adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, small cell lung cancer, and nonsmall cell lung cancer) of lung cancer. Other studies have also revealed that radiomics features from CT could reflect the map of gene mutations in lung cancer, such as EGFR mutations, KRAS mutations, and PD-L1 expression. In this study, the model based on these radiomic features also demonstrated an effective role in predicting invasive mucinous adenocarcinomas. According to our ROC analyses, the AUC values for the radiomics model were 0.720 and 0.770 for the training and test groups, respectively. The clinical-radiomics combined model (ROC-AUC:0.840-0.850) was comparable for invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma, and it was significantly better than the clinical model. Furthermore, the decision curve analysis demonstrated that the combined model performed significantly better than the clinical and radiomic models in predicting outcomes. Decision curve analysis offers important information beyond the standard performance metrics of discrimination and calibration and could evaluate the clinical impact, indicating that they had a higher chance of success (Figure 5).
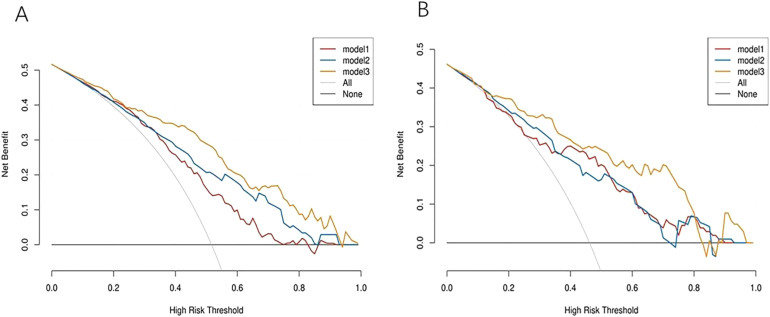
Figure 5.
Decision curve analyses for the radiomics-clinical model compared with the radiomics model and clinical model in training cohort (A) and the testing cohort (B). The decision curve analysis presents that the net benefits of the combined model for the prediction of IMA were higher than the clinical model and radiomics model. Model 1 was the radiomics model, model 2 was the clinical model, and model 3 was the combined model. The decision curve analysis (DCA) showed that the line of the combined model was higher than the clinical model and the radiomics model when the probability ranged from 0 to 1.
Although research bias was minimized through the propensity matching method, this study still has some limitations due to its retrospective nature. First, the sample size was relatively small, and only one institution participated in the study. Second, the CT images used in this study were acquired using different devices and scanning parameters, resulting in a potential bias in the analysis. But previous studies showed that the influences of these factors showed relatively consistent patterns. 31 Third, owing to the short follow-up period after surgery, there was no predictive model for patient survival. To guide clinical practice, the model will be validated in a multicenter prospective manner in the future and will be further optimized.
In conclusion, in the present study, we established a model to predict IMA using clinicopathological, radiomic, and clinical-radiomic features for the first time. The clinical-radiomic model established by us also showed a good predictive value and has potential value in clinical practice. We will also conduct further studies to explore the tumor microenvironment for predicting tumor biological behavior in lung adenocarcinoma in the future to accurately evaluate the prognosis of patients and guide precision treatment.
Supplemental Material
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-tct-10.1177_15330338231174306 for CT Radiomics Combined With Clinicopathological Features to Predict Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinoma by Junjie Zhang, Ligang Hao, Min Li, Qian Xu and Gaofeng Shi in Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment
Acknowledgments
None.
Abbreviations
- AUC
area under the curve
- CT
computed tomography
- DCA
Decision curve analysis
- GLCM
Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix
- GLDM
Gray Level Dependence Matrix
- GLRLM
Gray Level Run Length Matrix
- GLSZM
Gray Level Size Zone Matrix
- ICC
inter-class correlation coefficients
- IMA
invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma
- LASSO
least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- MPR
multiplanar reconstruction
- NGTDM
Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix
- ROC
receiver operating characteristic
- SVM
support vector machine.
Footnotes
Authorship Statement: LG H and JJ Z performed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. M L and GF S delineated regions of interest (ROI) and extract the radiomics features. Q X was responsible for the design of the experiment.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Key development plan of XingTai (ZC20301).
Ethics Statement: This study was performed following the Helsinki Declaration and approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital (Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University Fourth Affiliated Hospital, reference number: 2022KS017, data 2022.6.27). Ethical approval was obtained from our hospital, and waivers of consent were granted to the study subjects.
ORCID iD: Ligang Hao https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2294-8778
Supplemental Material: Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
- 1.Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dong RF, Zhu ML, Liu MM, et al. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: from molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol Res. 2021;167:105583. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105583 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Memmott RM, Wolfe AR, Carbone DP, Williams TM. Predictors of response, progression-free survival, and overall survival in patients with lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16(7):1086-1098. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(2):244-285. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society: international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma: executive summary. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011;8(5):381-385. doi: 10.1513/pats.201107-042ST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, et al. The 2015 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(9):1243-1260. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee MA, Kang J, Lee HY, et al. Spread through air spaces (STAS) in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung: incidence, prognostic impact, and prediction based on clinicoradiologic factors. Thorac Cancer. 2020;11(11):3145-3154. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lin G, Li H, Kuang J, et al. Acinar-predominant pattern correlates with poorer prognosis in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. Am J Clin Pathol. 2018;149(5):373-378. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqx170 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gow CH, Hsieh MS, Liu YN, Lee YH, Shih JY. Clinicopathological features and survival outcomes of primary pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(16):652-662. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shang G, Jin Y, Zheng Q, et al. Histology and oncogenic driver alterations of lung adenocarcinoma in Chinese. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(6):1212-1223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cai L, Wang J, Yan J, et al. Genomic profiling and prognostic value analysis of genetic alterations in Chinese resected lung cancer with invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:603671. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.603671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hu H, Pan Y, Li Y, et al. Oncogenic mutations are associated with histological subtypes but do not have an independent prognostic value in lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7:1423-1437. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S58900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boland JM, Maleszewski JJ, Wampfler JA, et al. Pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma and mixed invasive mucinous/nonmucinous adenocarcinoma—a clinicopathological and molecular genetic study with survival analysis. Hum Pathol. 2018;71:8-19. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ichinokawa H, Ishii G, Nagai K, et al. Distinct clinicopathologic characteristics of lung mucinous adenocarcinoma with KRAS mutation. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(12):2636-2642. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gow CH, Wu SG, Chang YL, Shih JY. Multidriver mutation analysis in pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma in Taiwan: identification of a rare CD74-NRG1 translocation case. Med Oncol. 2014;31(7):34. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0034-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hwang DH, Sholl LM, Rojas-Rudilla V, et al. KRAS and NKX2-1 mutations in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(4):496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5.2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. version 5.2017. 2017;15(4):504-535. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2017.0050. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 18.Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102873 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(6):503-513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RT, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4006. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vicini S, Bortolotto C, Rengo M, et al. A narrative review on current imaging applications of artificial intelligence and radiomics in oncology: focus on the three most common cancers. Radiol Med. 2022;127(8):819-836. doi: 10.1007/s11547-022-01512-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, et al. End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med. 2019;25(6):954-961. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0447-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang K, Liu X, Shen J, et al. Clinically applicable AI system for accurate diagnosis, quantitative measurements, and prognosis of COVID-19 pneumonia using computed tomography. Cell. 2020;182(5):1360. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tian P, He B, Mu W, et al. Assessing PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer and predicting responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors using deep learning on computed tomography images. Theranostics. 2021;11(5):2098-2107. doi: 10.7150/thno.48027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, et al. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017;77(21):e104-e107. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xu L, Li C, Lu H. Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. Transl Cancer Res. 2019;8(8):2924-2932. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.11.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jie B, Yinhua J, Qifeng H, et al. Analysis of MSCT findings in primary pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma with pathology. J Med Imaging. 2020;30(5):871-874. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yuanwei S, Minmin T, Xiaolei W, et al. Clinicopathological features and CT findings of primary pulmonary invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma. J Chin Clin Med Imaging. 2020;31(10):719-722,726. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Qingyi W, Wanhu L, Dexian Z, et al. Imaging findings and pathological features of primary lung invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 2020;27(8):647-652,657. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cha MJ, Lee KS, Kim TJ, et al. Solitary nodular invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung: imaging diagnosis using the morphologic-metabolic dissociation sign. Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(3):513-521. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Peng X, Yang S, Zhou L, et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of computed tomography radiomics for pulmonary nodules: a multicenter phantom study. Invest Radiol. 2022;57(4):242-253. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-tct-10.1177_15330338231174306 for CT Radiomics Combined With Clinicopathological Features to Predict Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinoma by Junjie Zhang, Ligang Hao, Min Li, Qian Xu and Gaofeng Shi in Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment