Abstract
The clinical and electrophysiological features of a case of hemimasticatory spasm are presented. The findings are in many respects similar to those described in hemifacial spasm. A peripheral cranial neuropathy as proposed in hemifacial spasm also may be responsible for hemimasticatory spasm.
Full text
PDF
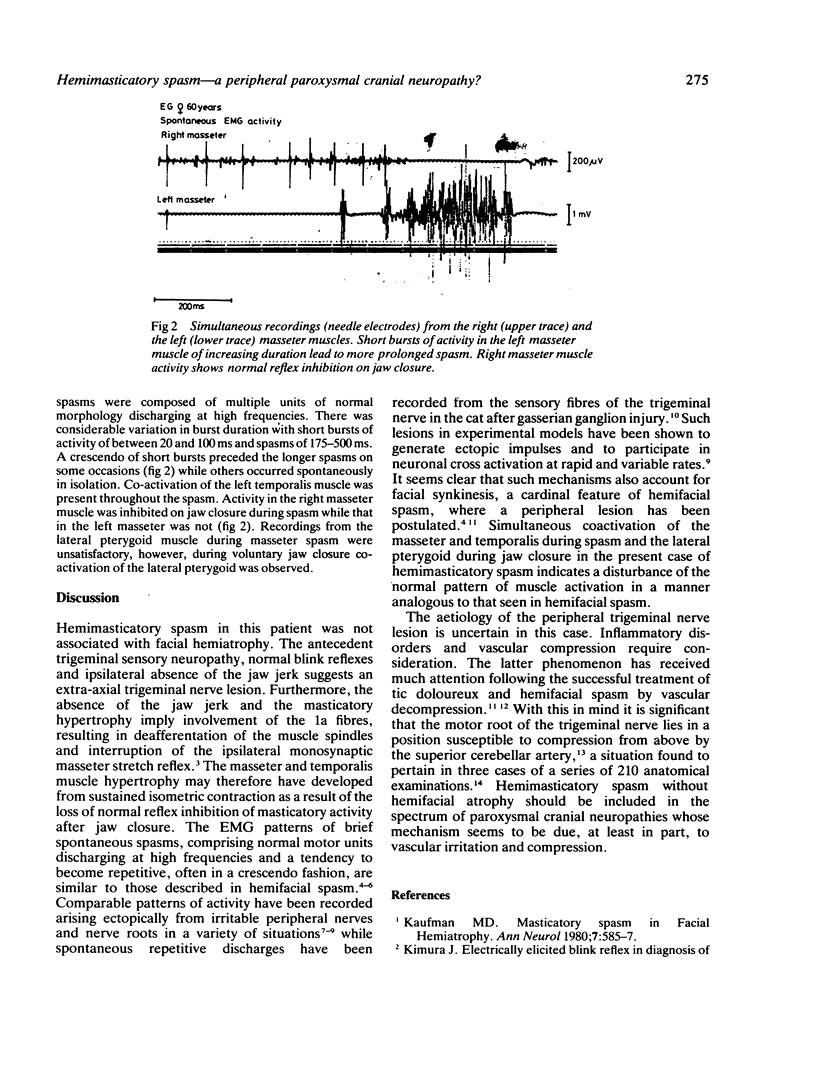

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger R. G. Hemifacial spasm: clinical and electrophysiologic observations. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1261–1272. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger R. G., Piepgras D. G., Laws E. R., Jr, Miller R. H. Microvascular decompression of the facial nerve for hemifacial spasm: clinical and electrophysiologic observations. Neurology. 1981 Mar;31(3):346–350. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchiel K. J. Ectopic impulse generation in demyelinated axons: effects of PaCO2, pH, and disodium edetate. Ann Neurol. 1981 Apr;9(4):378–383. doi: 10.1002/ana.410090411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson K., Rhoton A. L., Jr, Rushton J. G. Detailed anatomy of the intracranial portion of the trigeminal nerve. J Neurosurg. 1971 Nov;35(5):592–600. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.35.5.0592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth R. J., Willison R. G. The electromyogram in facial myokymia and hemifacial spasm. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannetta P. J. Observations on the etiology of trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, acoustic nerve dysfunction and glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Definitive microsurgical treatment and results in 117 patients. Neurochirurgia (Stuttg) 1977 Sep;20(5):145–154. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1090369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman M. D. Masticatory spasm in facial hemiatrophy. Ann Neurol. 1980 Jun;7(6):585–587. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. Electrically elicited blink reflex in diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Review of 260 patients over a seven-year period. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):413–426. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Rodnitzky R. L., Van Allen M. W. Electrodiagnostic study of trigeminal nerve. Orbicularis oculi reflex and masseter reflex in trigeminal neuralgia, paratrigeminal syndrome, and other lesions of the trigeminal nerve. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):574–583. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance J. W., Burke D., Pollard J. Hyperexcitability of motor and sensory neurons in neuromyotonia. Ann Neurol. 1979 Jun;5(6):523–532. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa J. L., Torebjörk H. E. Paraesthesiae from ectopic impulse generation in human sensory nerves. Brain. 1980 Dec;103(4):835–853. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasminsky M. Ectopic generation of impulses and cross-talk in spinal nerve roots of "dystrophic" mice. Ann Neurol. 1978 Apr;3(4):351–357. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]