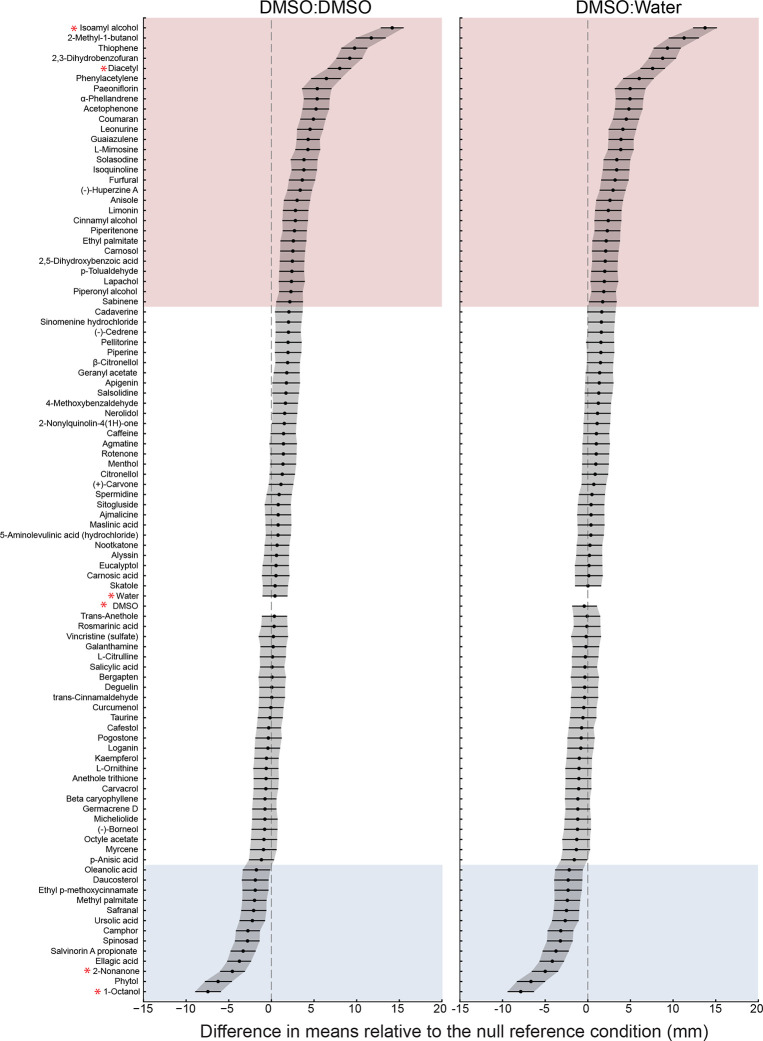
Figure 5: A screen of 96 conditions reveals 37 plant SMs that are chemoactive in wild-type C. elegans, evoking either attraction (pink) or repulsion (blue).
The chemical panel contained 90 plant SMs and 6 reference conditions (red asterisks: isoamyl alcohol, diacetyl, 2-nonanone, 1-octanol, DMSO, and water). Results are sorted (top to bottom) according to the difference in mean position relative to two null reference conditions: symmetric DMSO:DMSO (left) and asymmetric DMSO:water (right). We used a bootstrapping approach [43] to compute differences in mean position. Positive values correspond to attraction or positive chemotaxis and negative values correspond to repulsion or negative chemotaxis. Black points and lines are, respectively, the difference of the mean position in each test condition relative to the reference condition and the 95% confidence intervals of these values. independent biological replicates, at least 150 worms per assay. Table S2 contains the following for all screening conditions: difference of the mean position (in mm) in experimental vs. reference conditions (±95% confidence intervals), and statistical testing against the reference condition (Mann-Whitney U test).