Abstract
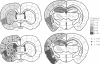
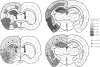
Unilateral cerebral infarcts were produced in the rat by ligation of one common carotid artery and subsequent exposure to carbon monoxide. The incidence and extension of brain infarcts was increased in animals with additional ipsilateral cervical preganglionic sympathectomy. Sympathectomy did not affect markedly the respiration and systemic circulation. The effect of sympathectomy was attributed to a cutaneous vasodilation, leading to an extracranial steal phenomenon.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Shetty G., Chandy J. Preliminary observation on the hemodynamics of the internal carotid artery following bilateral external carotid ligation in the monkey. J Neurosurg. 1971 Aug;35(2):192–196. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.35.2.0192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer L. M., Johansson B. B., Lund S. Reaction of pial arteries and veins to sympathetic stimulation in the cat. Stroke. 1981 Jul-Aug;12(4):528–531. doi: 10.1161/01.str.12.4.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILL A. Effects of cervical sympathetic tone on blood pressure and uveal blood flow after carotid occlusion. Exp Eye Res. 1963 Apr;2:203–209. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(63)80014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw R. J., Peterson L. H. Sympathetic control of the mechanical properties of the canine carotid sinus. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1462–1468. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber B. J., Martin J. S., Rapela C. E. Analysis of the effect of bilateral sympathetic stimulation of cerebral and cephalic blood flow in the dog. Stroke. 1978 Jan-Feb;9(1):29–34. doi: 10.1161/01.str.9.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best M., Masket S., Rabinovitz A. Z. Effect of sympathetic stimulation on ocular hemodynamics. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Apr;11(4):211–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz E. Cerebral blood flow: its measurement and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):595–630. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Cardiac sympathetic adrenergic pathways in which synaptic transmission is blocked by atropine sulfate. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):271–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELANDER O., FOLKOW B. A comparison of the sympathetic vasomotor fibre control of the vessels within the skin and the muscles. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Oct 6;29(2-3):241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUNGCHAROEN D., De BURGH DALY M., NEIL E., SCHWEITZER A. The effect of carotid occlusion upon the intrasinusal pressure with special reference to vascular communications between the carotid and vertebral circulations in the dog, cat and rabbit. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):56–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervos-Navarro J., Matakas F. Electron microscopic evidence for innervation of intracerebral arterioles in the cat. Neurology. 1974 Mar;24(3):282–286. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers J. P., Korner P. I. Effects of arterial hypoxia on the cutaneous circulation of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(3):685–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. Nervous control of the blood vessels. Physiol Rev. 1955 Jul;35(3):629–663. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck B., Mchedlishvili G. I., Owman C. Histochemical demonstration of adrenergic nerves in cortex-pia of rabbit. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1965;23(2):133–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1965.tb03579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. A., Stein B. M., Barrett R. E., Pool J. L. Noradrenergic mediation of experimental cerebrovascular spasm. Stroke. 1970 Sep-Oct;1(5):356–362. doi: 10.1161/01.str.1.5.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H. D., HOWARD W. B., KENAN L. F. Autonomic control of blood flow in hind paw of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1956 Dec;187(3):469–472. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H. D., KEPCHAR J. H. Control of peripheral resistance in major systemic vascular beds. Physiol Rev. 1959 Jul;39(3):617–686. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.3.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEGEDUS S. A., CAHILL M. B., GRANSKY L. R., SHACKELFORD R. T. CERVICAL SYMPATHECTOMY AND CEREBROSPINAL FLUID PRESSURE: THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO BRAIN METABOLISM. Arch Surg. 1965 Mar;90:418–421. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1965.01320090096022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. M., Deshmukh V. D., Rowan J. O., Jennett W. B. The influence of sympathetic nervous activity on cerebral blood flow. Arch Neurol. 1972 Jul;27(1):1–6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490130003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Marcus M. L., Gross P. M. Effects of sympathetic nerves on cerebral vessels in dog, cat, and monkey. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):H544–H552. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.235.5.H544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwayama T., Furness J. B., Burnstock G. Dual adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the cerebral arteries of the rat. An ultrastructural study. Circ Res. 1970 May;26(5):635–646. doi: 10.1161/01.res.26.5.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwayama T. Ultrastructural changes in the nerves innervating the cerebral artery after sympathectomy. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;109(4):465–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00343962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. D., BERNE R. M. INTRINSIC REGULATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE BLOOD FLOW. Circ Res. 1964 Feb;14:126–138. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. M., Millar R. A., Purves M. J. Observations on the extrinsic neural control of cerebral blood flow in the baboon. Circ Res. 1969 Jul;25(1):77–93. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEZDI P. Control by the superior cervical ganglion of the state of contraction and pulsatile expansion of the carotid sinus arterial wall. Circ Res. 1954 Jul;2(4):367–371. doi: 10.1161/01.res.2.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER E. M. CAROTID OCCLUSION IN THE RAT: CIRCULATORY AND RESPIRATORY EFFECTS. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1963;13:350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Scheinberg P., Kishikawa H., Utsunomiya Y., Busto R. Adrenergic control of cerebral blood flow and energy metabolism in the rat. Stroke. 1979 Mar-Apr;10(2):179–184. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laas R., Igloffstein J., Meyerhoff S. Cerebral infarction due to carotid occlusion and carbon monoxide exposure. I. Pathophysiological and neuropathological investigations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Aug;46(8):756–767. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.8.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. W., Smith K. A., Klassen A. C. Sympathetic regulation of cephalic blood flow. Stroke. 1977 Mar-Apr;8(2):197–201. doi: 10.1161/01.str.8.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller S. M., Ertel P. J., Felten D. L., Overhage J. M. Sympathetic nerves protect against blood-brain barrier disruption in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Stroke. 1982 Jan-Feb;13(1):83–88. doi: 10.1161/01.str.13.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musella R. Effects of bilateral external carotid artery ligation on cerebral circulation in the rabbit. 3. Influence on collateral circulation in the brain. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 1965 Jan-Mar;49(1):41–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E., Rennels M. Innervation of intracranial arteries. Brain. 1970;93(3):475–490. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. C., Owman C., Sporrong B. Ultrastructure of the autonomic innervation apparatus in the main pial arteries of rats and cats. Brain Res. 1971 Mar 19;27(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. E., Bevan J. A. Adrenergic innervation of large cerebral blood vessels of the rabbit studied by fluorescence microscopy. Absence of features that might contribute to non-uniform change in cerebral blood flow. Stroke. 1977 Jan-Feb;8(1):82–87. doi: 10.1161/01.str.8.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reivich M. Regulation of the cerebral circulation. Clin Neurosurg. 1969;16:378–418. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/16.cn_suppl_1.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum W. I. Neurogenic control of cerebral circulation. Stroke. 1971 Sep-Oct;2(5):429–439. doi: 10.1161/01.str.2.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson S. R., Mills E. Effects of sympathetic stimulation on discharges of carotid sinus baroreceptors. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1650–1653. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traystman R. J., Fitzgerald R. S. Cerebrovascular response to hypoxia in baroreceptor- and chemoreceptor-denervated dogs. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):H724–H731. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.5.H724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]