Abstract
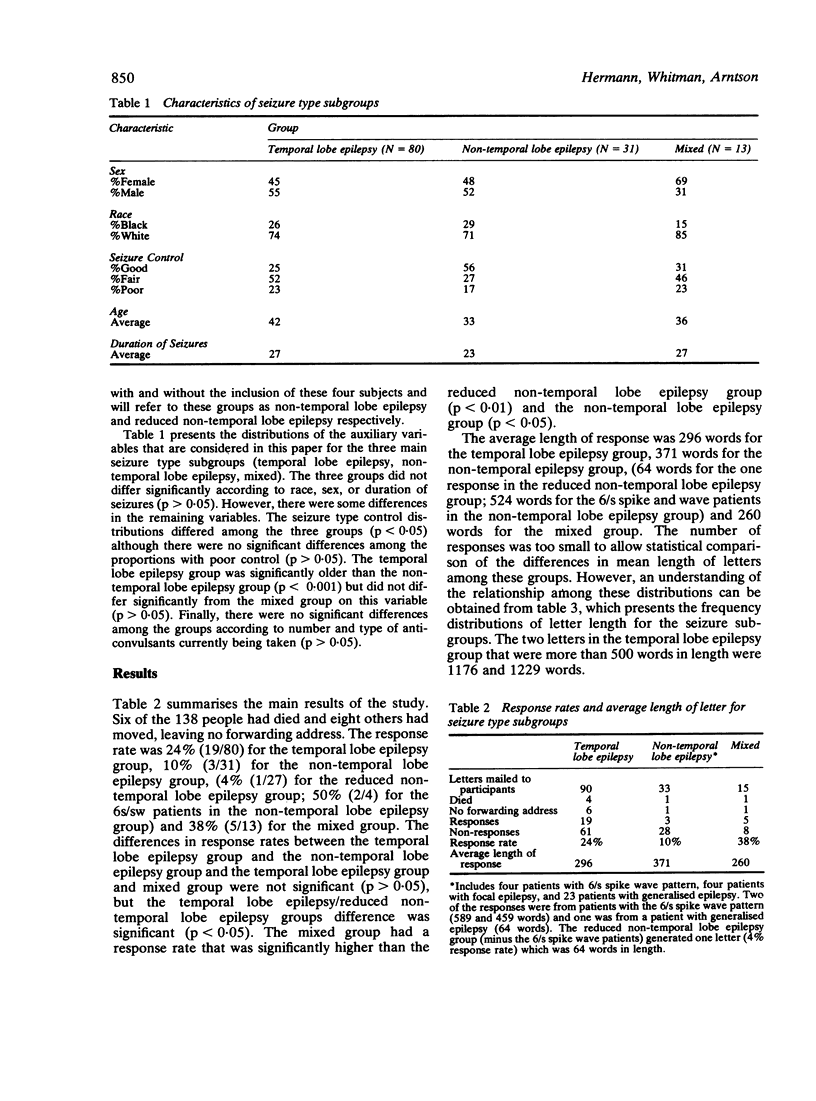
The purpose of this investigation was to determine the specificity of hypergraphia to temporal lobe epilepsy using the paradigm developed by Sachdev and Waxman (1981). One hundred and thirty-eight patients were sent a standard stimulus letter and the response rates were examined for the patient groups with temporal lobe epilepsy (N = 80), and without (N = 31), and mixed seizure types (N = 13). For those patients who responded, additional analyses involved the number of words per response and the presence/absence of any qualitative indices of the postulated interictal behavioural syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. The results were interpreted in the light of the contemporary definitions of hypergraphia and were related to the larger literature concerned with personality and behavioural change in temporal lobe epilepsy.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bear D. M., Fedio P. Quantitative analysis of interictal behavior in temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1977 Aug;34(8):454–467. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500200014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D. M. Temporal lobe epilepsy--a syndrome of sensory-limbic hyperconnection. Cortex. 1979 Sep;15(3):357–384. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(79)80064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D., Levin K., Blumer D., Chetham D., Ryder J. Interictal behaviour in hospitalised temporal lobe epileptics: relationship to idiopathic psychiatric syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;45(6):481–488. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.6.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D., Schenk L., Benson H. Increased autonomic responses to neutral and emotional stimuli in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Psychiatry. 1981 Jun;138(6):843–845. doi: 10.1176/ajp.138.6.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind N. Behavioral change in temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1977 Aug;34(8):453–453. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500200013002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann B. P., Riel P. Interictal personality and behavioral traits in temporal lobe and generalized epilepsy. Cortex. 1981 Apr;17(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(81)80012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. R. Two forms of the 6/sec spike and wave complex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 May;48(5):535–550. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90289-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIER J. M., FRENCH L. A. SOME PERSONALITY CORRELATES OF UNILATERAL AND BILATERAL EEG ABNORMALITIES IN PSYCHOMOTOR EPILEPTICS. J Clin Psychol. 1965 Jan;21:1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mungas D. Interictal behavior abnormality in temporal lobe epilepsy. A specific syndrome or nonspecific psychopathology? Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Jan;39(1):108–111. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290010080014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H., Kristensen O. Personality correlates of sphenoidal EEG-foci in temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1981 Oct;64(4):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1981.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Robertson M. M., Trimble M. R. The lateralising significance of hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Feb;45(2):131–138. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachdev H. S., Waxman S. G. Frequency of hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy: an index of interictal behaviour syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;44(4):358–360. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.4.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Geschwind N. Hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology. 1974 Jul;24(7):629–636. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.7.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Geschwind N. The interictal behavior syndrome of temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1975 Dec;32(12):1580–1586. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1975.01760300118011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


