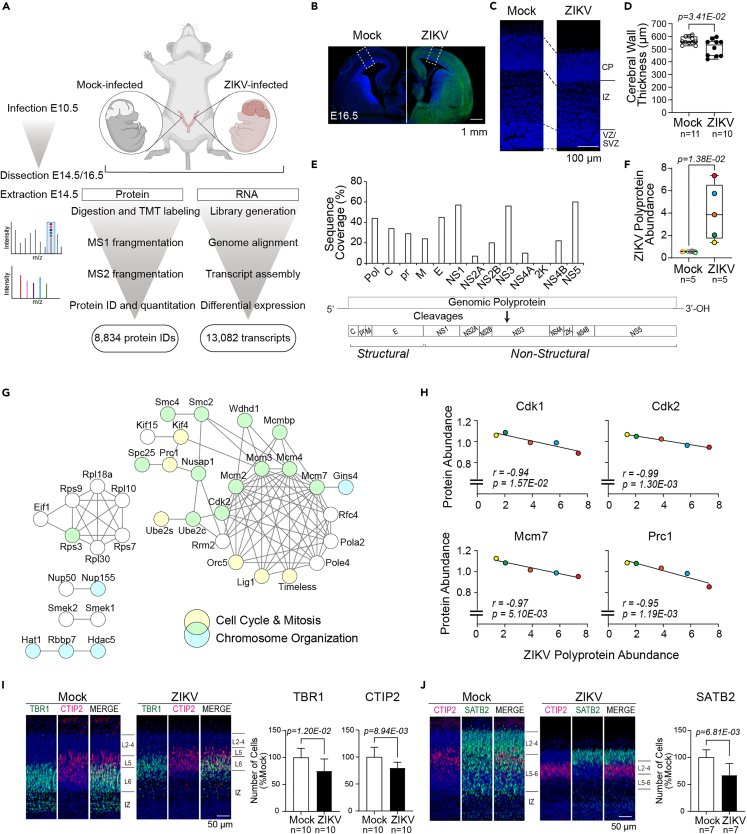
Figure 1.
Embryonic ZIKV infection recapitulates human microcephaly and shows viral load-dependent dysregulation of cell cycle-associated proteins
(A) Multiplexed proteomic and RNA-sequencing (RNA-Seq) analysis workflow for Mock (PBS) or Zika virus (ZIKV)-infected brains (n = 5 for proteomics and n = 3 for RNA-Seq per condition). Each placenta of the embryos received ZIKV or Mock injection at embryonic day 10.5 (E10.5). Brains were collected at E14.5 for quantitative tandem mass tag (TMT) mass spectrometry analysis and RNA-Seq, resulting in 8,834 protein IDs and 13,082 transcripts identified. Structural analysis was conducted at E16.5.
(B) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of brains at E16.5, following Mock or ZIKV infection at E10.5; ZIKV Env (green), Hoechst (nuclei, blue), scale bar = 1 mm. Dotted square corresponds to the primary somatosensory area of the cerebral cortex.
(C) IHC staining of the primary somatosensory area at E16.5 showing the ventricular zone (VZ)/subventricular zone (SVZ), intermediate zone (IZ), and cortical plate (CP); Hoechst (nuclei, blue), Scale bar = 100 μm.
(D) The total thickness of the cerebral wall at E16.5. Boxplot shows the median, interquartile range, and maximum/minimum values.
(E) ZIKV polyprotein and potential processed polyprotein constituent sequence coverages for structural (C-capsid, prM-premembrane, M-membrane, E-envelope) and non-structural (NS1-5) proteins, identified by proteomics.
(F) Mean normalized abundance of ZIKV polyprotein in Mock- or ZIKV-infected brain at E14.5. Color-coding shows the embryos deriving from the same litter.
(G) Interaction network of proteins with strong negative correlation (Pearson correlation r < −0.95) with ZIKV polyprotein abundance. Node color indicates functional classification (blue, chromosome organization; yellow, cell cycle and mitosis; green, both functions); edges represent the highest confidence interactions (confidence score = 0.90) between proteins in the network based on protein-protein interaction information curated by the STRING database. Connected nodes are shown.
(H) Sum-normalized protein abundance of selected cell cycle-associated proteins, Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1 (Cdk1), Cdk2, Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Component 7 (Mcm7), and Protein Regulator of Cytokinesis 1 (Prc1), plotted against ZIKV polyprotein abundance across five ZIKV-infected brains. Color coding follows 1F. Note the negative correlation between the abundances of ZIKV polyprotein and cell cycle-inducing proteins.
(I) IHC staining of CP layers 2–6 (L2-6) and IZ from Mock- or ZIVK-infected embryonic brains, T-box Brain Protein 1 (TBR1) (green), B Cell CLL/Lymphoma 11b (CTIP2) (red) and Hoechst (nucleus, 8 blue), scale bar = 50 μm; Quantification of TBR1-positive (ZIKV-infected embryos, n = 10 from 8 litters, Mock-infected embryos, n = 10 from 6 litters) and CTIP2-positive (ZIKV-infected embryos, n = 10 from 8 litters, Mock-infected embryos, n = 10 from 6 litters) post-mitotic neurons.
(J) IHC staining of L2-6 and IZ from Mock- or ZIKV-infected embryonic brains, CTIP2 (red), Special AT-Rich Sequence-Binding Protein 2 (SATB2) (green), and Hoechst (nucleus, blue), scale bar = 50 μm; Quantification of SATB2-positive post-mitotic neurons (ZIKV-infected embryos, n = 7 from 6 litters, Mock-infected embryos, n = 7 from 5 litters). Error bars indicate standard deviation.